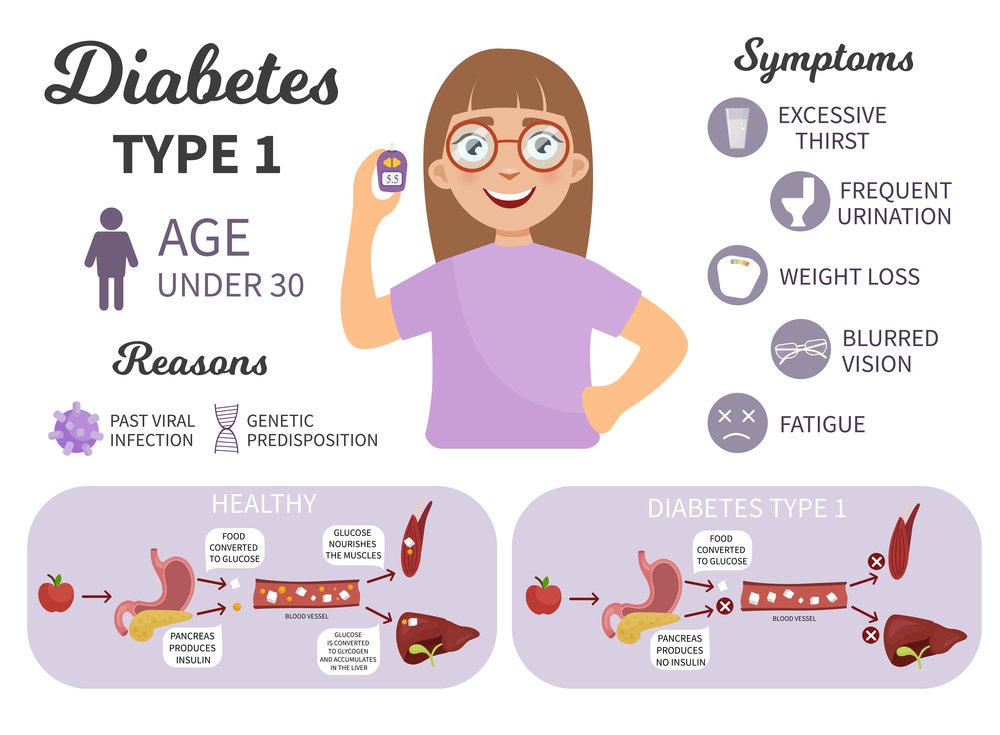
What Causes Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is thought to be caused by an autoimmune reaction that destroys the cells in the pancreas that make insulin, called beta cells. This process can go on for months or years before any symptoms appear.
Some people have certain genes that make them more likely to develop type 1 diabetes, though many wont go on to have type 1 diabetes even if they have the genes. Being exposed to a trigger in the environment, such as a virus, is also thought to play a part in developing type 1 diabetes. Diet and lifestyle habits dont cause type 1 diabetes.
Further Information And Support
For further information and support contact your doctor, practice nurse, or: Diabetes New Zealand Freephone: 0800 DIABETES Email: admin@diabetes.org.nz Website: www.diabetes.org.nz Diabetes New Zealand provides education and support resources specifically for young New Zealanders with type 1 diabetes and many of its branches around the country host Type 1 youth support groups.
Kids Health Website: www.kidsheatlh.org.nz
How Is Diabetes Diagnosed
In most cases the diagnosis of diabetes is simple. A blood test is used to diagnose diabetes. Sometimes your doctor may do a urine test to look for sugar or ketones in your urine. This is a simple test and the results are available immediately but a urine test is not accurate enough to be used to diagnose or rule out diabetes all the time.
Read Also: What Foods Help Produce Insulin
Prevention Of Type 1 Diabetes
Doctors arent aware of a way to prevent type 1 diabetes, but researchers are exploring ways to do so or at least slow its progression, says the NIDDK.
For instance, the monoclonal antibody drug teplizumab is in phase 3 clinical trials after an article published in August 2019 in the New England Journal of Medicine found it delayed the onset of type 1 diabetes by an average of two years in people who had relatives with the disease.
How Else Can I Manage Type 1 Diabetes
Along with insulin and any other medicines you use, you can manage your diabetes by taking care of yourself each day. Following your diabetes meal plan, being physically active, and checking your blood glucose often are some of the ways you can take care of yourself. Work with your health care team to come up with a diabetes care plan that works for you. If you are planning a pregnancy with diabetes, try to get your blood glucose levels in your target range before you get pregnant.
You May Like: Diet For Insulin Resistance To Lose Weight
Treating T1d: Beyond Insulin
Pramlintide, brand name Symlin, is an injectable hormone that works along with insulin. It has been found that when insulin is not made, neither is amylin. This product was designed to fill that gap. Its main use is to help with post-meal blood sugars. Symlin was approved by the FDA in 2005 and is designed to be taken as an injection at all meals and snacks to reduce insulin doses, reduce stomach emptying and reduce the rise in post-meal blood sugars.
It cannot be mixed with insulinNote it must be taken separately. It is currently available by injectable pen only. Research results indicate that use of Symlin in type 1 diabetes, in conjunction with insulin, can reduce the amount of insulin needed by 0.8-7.1 units per day.
In addition, pramlintide has been shown to achieve a beneficial reduction in A1c of -0.24-0.58% and may support weight loss of 1.8-3.5 pounds. While these benefits may be very appealing, you’ll need to decide if you are up to consistently taking an additional 3-5 injections a day. Another factor is health insurance reimbursement, which will vary and should be checked before deciding whether to add this treatment or not.
Whats The Difference Between Ketosis And Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Its important to seek immediate medical attention for DKA, and it may involve a hospital trip. A blood or urine test for ketones can detect DKA. Treatment involves insulin injections and fluid replacement.
Frequently, a bout of DKA is what leads to a diagnosis of type 1 diabetes, particularly in young people. Dr. Dutta says this can happen to anyone with type 1 diabetes at any age, but if a person develops the disease in their middle or later years, the progression is typically more gradual and they are therefore more likely to already be under a doctors care for high blood sugar.
You May Like: What Is An Average Blood Sugar Level For Diabetics
Initiation Of Insulin Therapy
The initial daily insulin dose is calculated on the basis of the patients weight. This dose is usually divided so that one half is administered before breakfast, one fourth before dinner, and one fourth at bedtime. After selecting the initial dose, adjust the amounts, types, and timing according to the plasma glucose levels. Adjust the dose to maintain preprandial plasma glucose at 80-150 mg/dL .
The insulin dose is often adjusted in increments of 10% at a time, and the effects are assessed over about 3 days before any further changes are made. More frequent adjustments of regular insulin can be made if a risk of hypoglycemia is present.
Carbohydrate counting may be used to determine the meal-time insulin dose. Because patients may experience hyperglycemic episodes despite strict adherence to carbohydrate counting, particularly after meals that are high in protein or fat, Australian researchers developed an algorithm for estimating the mealtime insulin dose on the basis of measurements of physiologic insulin demand evoked by foods in healthy adults. The researchers showed that use of this algorithm improved glycemic control.
Initiation of insulin therapy in children
Multiple daily injections
Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion
Changes in altitude may affect delivery from insulin pumps. During the flight of a commercial airliner , excess insulin delivery of 0.623% of cartridge volume was demonstrated as a result of bubble formation and expansion of preexisting bubbles.
Causes And Risk Factors Of Type 1 Diabetes
It’s unknown exactly what causes type 1 diabetes, but experts think it could be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. For instance, MedlinePlus states that the risk of type 1 diabetes in increased if you have certain variants of genes in the human leukocyte antigen complex. These genes are involved in making proteins that play a critical role in immune response.
Coxsackieviruses have been studied as possible triggers for type 1 diabetes, and prolonged viral infection may increase a childs risk for developing the disease, according to a June 2019 study in Nature Medicine.
Other possible risk factors for type 1 diabetes include:
- Being male. The risk of being diagnosed with type 1 diabetes is approximately 1.5 times higher for males than for females, says Thomas.
- Having autoantibodies that are associated with higher risk
- Being of European descent , per the CDC. Most white people with the disease have gene variants HLA-DR3 or HLA-DR4, according to the ADA.
- Having a close family relative who has type 1 diabetes.
In fact, the odds that a man with type 1 diabetes has a child who develops it are 1 in 17. For a woman who bears a child before age 25, that risk is 1 in 25, but it drops to 1 in 100 if the child is born after she is 25.
Yet 80 percent of people with type 1 diabetes have no family history of the disease, according to the JDRF.
More on Diabetes Causes
Don’t Miss: What Is The Average Cost Of An Insulin Pump
How Do Health Care Professionals Diagnose Type 1 Diabetes
Health care professionals usually test people for type 1 diabetes if they have clear-cut diabetes symptoms. Health care professionals most often use the random plasma glucose test to diagnose type 1 diabetes. This blood test measures your blood glucose level at a single point in time. Sometimes health professionals also use the A1C blood test to find out how long someone has had high blood glucose.
Even though these tests can confirm that you have diabetes, they cant identify what type you have. Treatment depends on the type of diabetes, so knowing whether you have type 1 or type 2 is important.
To find out if your diabetes is type 1, your health care professional may test your blood for certain autoantibodies. Autoantibodies are antibodies that attack your healthy tissues and cells by mistake. The presence of certain types of autoantibodies is common in type 1 but not in type 2 diabetes.
Testing For Type 1 Diabetes
A simple blood test will let you know if you have diabetes. If youve gotten your blood sugar tested at a health fair or pharmacy, follow up at a clinic or doctors office to make sure the results are accurate.
If your doctor thinks you have type 1 diabetes, your blood may also be tested for autoantibodies that are often present with type 1 diabetes but not with type 2. You may have your urine tested for ketones , which also indicate type 1 diabetes instead of type 2.
Recommended Reading: What Can People With Type 2 Diabetes Eat
Alternatives To Injecting Insulin
There has been plenty of research done in recent years to develop ways to administer insulin other than by injection. These have included insulin nasal and oral sprays, patches, tablets and inhalers. After many years of work, some of the methods being researched are showing a degree of success. However, it will be some time before any of these devices will be available to people with diabetes in the UK.
Very High Blood Glucose Level
If you are not treated, or use too little insulin, a very high blood sugar level can develop quite quickly – over several days. If left untreated this causes lack of fluid in the body , drowsiness, and serious illness which can be life-threatening. A very high blood glucose level sometimes develops if you have other illnesses such as any infections. In these situations you may need to adjust the dose of insulin to keep your blood glucose level normal.
Also Check: What Is The Most Common Form Of Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes And Transplantation
Another form of treating type 1 diabetes is to have an injection of insulin producing cells. This procedure, known as islet cell transplantation, allows the transplanted insulin producing islet cells to produce insulin inside your body.
Islet cell transplantation can help to reduce the amount of insulin you need to take and can make managing your diabetes easier but it is an expensive procedure and has drawbacks as well. For these reasons, islet cell transplants are only given to a small number of people each year.
Preference is given to people that experience severe hypoglycemia on a regular basis.
Keep Your Blood Pressure Down
It is very important to have your blood pressure checked regularly. The combination of high blood pressure and diabetes is a particularly high risk factor for complications. Even mildly raised blood pressure should be treated if you have diabetes. Medication, often with two or even three different medicines, may be needed to keep your blood pressure down. See the separate leaflet called Diabetes and High Blood Pressure.
Recommended Reading: Advanced Diabetes Supply Freestyle Libre
Favorite Orgs For Essential Diabetes Info
JDRF
This nonprofit is among the most prominent in the United States focused specifically on type 1 diabetes research and advocacy. Its offerings are vast, with chapters nationwide, and they include a wealth of resources in English and Spanish to help you navigate life with the disease. You can also get matched with outreach volunteers who have a close personal connection to type 1 diabetes, and they can help you cope. They can also help you learn how to use their clinical trials matching tool. And because insulin therapy can be so expensive, they also provide a guide to navigating health insurance, and information on other ways to afford your medication.
American Diabetes Association
The largest organization in the United States focusing on all types of diabetes, it is a treasure trove of information about the disease, in part because of its prominent role in the research world through a professional society that hosts yearly conferences its highly respected, peer-reviewed journals and a key role setting standards of diabetes care in the United States. They advocate for legislation to make insulin more affordable, and host InsulinHelp.org, a guide to information about drug manufacturers patient assistance programs.
Lifestyle And Home Remedies
Careful management of type 1 diabetes is important to reduce the risk of acute and long-term serious complications. The following tips will help:
- Wear a tag or bracelet that says you have diabetes, in case of emergency
- Get yearly physical check-ups and regular eye checks to look for diabetes-related complications
- Get annual influenza vaccinations as high blood glucose levels can weaken the immune system
- Wash and moisturise your feet daily and check them for blisters, cuts, and sores
- Control blood pressure and cholesterol levels to help minimise the risk of complications
- Dont smoke. Smoking increases the risk of complications
- Drink alcohol responsibly. Alcohol can cause high or low blood glucose levels
- Minimise stress. Stress hormones may prevent insulin from working properly.
Also Check: Smoking And Type 2 Diabetes
There Are A Number Of Treatments Available To Help You Manage And Treat Your Diabetes Everyone Is Different So Treatment Will Vary Depending On Your Own Individual Needs
If you have type 1 diabetes, youll need to use insulin to treat your diabetes. You take the insulin by injection or by using a pump.
If you have Type 2 diabetes, you may have to use insulin or tablets, though you might initially be able to treat your diabetes by eating well and moving more.
If you have another type of diabetes, your treatment options may be different. Speak to your healthcare professional, or call our helpline if youre not sure.
Your GP or a healthcare professional can help you find the right diabetes treatment plan to suit you and your lifestyle.
People with diabetes are entitled to free prescriptions.
How Well Is Your Type 2 Diabetes Treatment Plan Working
Living with type 2 diabetes requires ongoing management: being mindful of what you eat, regularly exercising, monitoring your blood sugar, and, for most, taking medication as directed. But even when youre doing everything right, diabetes can change over time.
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic, lifelong condition. Diabetes is caused by two core defects: the pancreas not making an appropriate amount of insulin and the bodys cells not taking in glucose as they should. That tends to get worse over time, says Laurie Kane, MD, an endocrinologist at Providence Saint John’s Health Center in Santa Monica, California. Due to these changes, your diabetes treatment plan may require adjustments through the years to help keep things under control.
Knowing when and if you need to make changes to your treatment plan can be tricky. While some symptoms losing weight despite eating more, blurry vision may be more noticeable, others fatigue, dry eyes are harder to recognize as a sign that you may benefit from a treatment change. Diabetes can be a silent disease, explains Dr. Kane. Thats why its important to work with your primary care provider or endocrinologist to monitor it closely. We really want your numbers at the levels that have been proven in research studies to prevent complications, she adds.
Is your type 2 diabetes treatment working as well as it should to keep these measurements within healthy ranges? Take the assessment to find out.
Also Check: Is Propel Water Good For Diabetics
Try To Lose Weight If You Are Overweight Or Obese
Excess weight is also a risk factor for heart and blood vessel disease. Getting to a perfect weight is often unrealistic. However, if you are overweight, losing some weight will help.
Some of these lifestyle issues may not seem to be relevant at first to young children who are diagnosed as having diabetes. However, as children grow, a healthy lifestyle should be greatly encouraged for the long-term benefits. See the separate leaflet called Cardiovascular Disease .
Animal Models In Dm Type 1 Research
Animal models are used in autoimmune diabetes research to understand the pathogenesis and etiology of this disease, and to find and test predictive biomarkers and therapeutic interventions. Currently available models of T1D can be divided into spontaneously autoimmune, chemically induced, virus induced and genetically induced.
Spontaneous autoimmune
- Non-obese diabetic mouse
The NOD mouse is the best known and most widely used animal model for type 1 DM research. It is an inbred, genetically well characterized mouse strain that spontaneously develops T1D. The onset of insulitis occurs at 3â4 weeks of age. The islets of Langerhans are infiltrated by CD4+, CD8+ T lymphocytes, NK cells, B lymphocytes, dendritic cells, macrophages and neutrophils, similar to the disease process in humans. Insulitis leads to destruction of β-cells, resulting in the apparent occurrence of T1D, which varies by sex. The incidence is about 60-80% in females and 10-30% in males. In addition to sex, breeding conditions, gut microbiome composition or diet also influence the onset of T1D. NOD Mice are used to understand the pathogenesis and etiology of the disease, to identify novel autoantigens and biomarkers or to test new intervention strategies.
- BioBreeding Diabetes-Prone rat
- LEW -1AR1 / -iddm rat
Chemically induced
Genetically induced
Virally induced
Also Check: Free Stuff For Type 1 Diabetes
How Is Type 1 Diabetes Treated
People with Type 1 diabetes need to replenish their insulin each day. There are different types of insulin. Some insulin starts acting as soon as you take the medicine other insulins take several hours to work. The various types of insulin also last in your body for different lengths of time. Some are more expensive than others. Work with your doctor to find the right type of insulin for your needs.