What Is Normal Blood Sugar After Meals
Normal blood sugar 2 hours after meals for non diabetics is under 140 mg/dL or 7.8 mmol/L.
This is considered normal and therefore, a maximum of 140 mg/dL or 7.8 mmol/L is the ideal blood sugar after meals for people with type 2 diabetes or prediabetes as well.
Both the American Association of Clinical Endocrinology and the International Diabetes Federation agree that working toward a maximum of 140 or 7.8 is ideal, if you can achieve it.
So lets consider why this is so important
Genes And Family History
As in type 1 diabetes, certain genes may make you more likely to develop type 2 diabetes. The disease tends to run in families and occurs more often in these racial/ethnic groups:
- African Americans
- Native Hawaiians
- Pacific Islanders
Genes also can increase the risk of type 2 diabetes by increasing a persons tendency to become overweight or have obesity.
How Can I Treat Low Blood Sugar
If youve had low blood sugar without feeling or noticing symptoms , you may need to check your blood sugar more often to see if its low and treat it. Driving with low blood sugar can be dangerous, so be sure to check your blood sugar before you get behind the wheel.
Carry supplies for treating low blood sugar with you. If you feel shaky, sweaty, or very hungry or have other symptoms, check your blood sugar. Even if you dont have symptoms but think you may have low blood sugar, check it. If your blood sugar is lower than 70 mg/dL, do one of the following immediately:
- Take four glucose tablets.
- Drink four ounces of fruit juice.
- Drink four ounces of regular soda, not diet soda.
- Eat four pieces of hard candy.
Wait for 15 minutes and then check your blood sugar again. Do one of the above treatments again until your blood sugar is 70 mg/dL or above and eat a snack if your next meal is an hour or more away. If you have problems with low blood sugar, ask your doctor if your treatment plan needs to be changed.
You May Like: What Does It Mean If You Have High Glucose
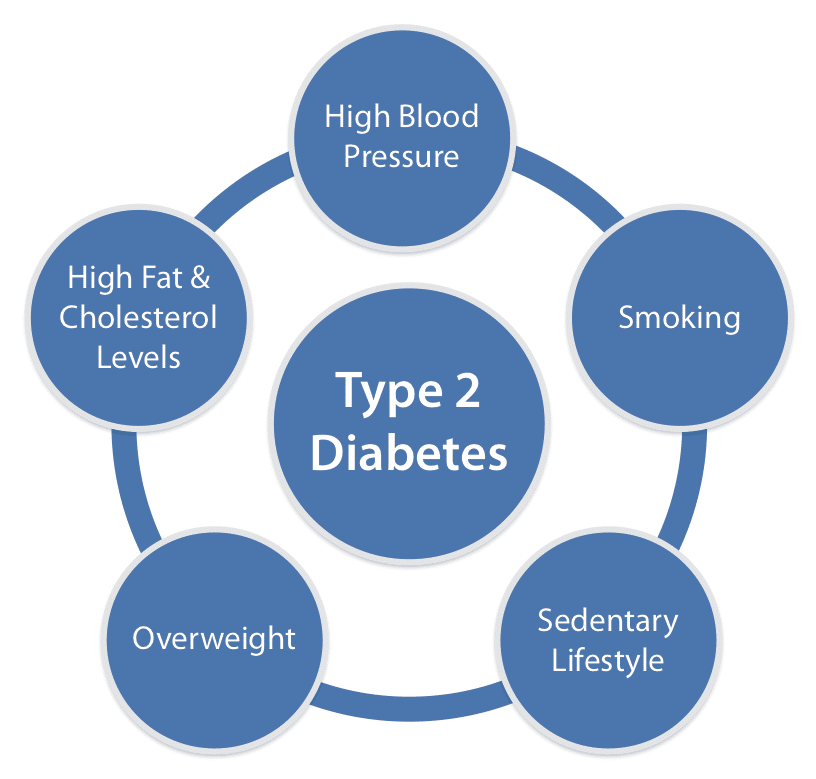
Being Overweight Or Obese
You’re more likely to develop type 2 diabetes if you’re overweight or obese with a body mass index of 30 or more.
Fat around your tummy particularly increases your risk. This is because it releases chemicals that can upset the body’s cardiovascular and metabolic systems.
This increases your risk of developing a number of serious conditions, including coronary heart disease, stroke and some types of cancer.
Measuring your waist is a quick way of assessing your diabetes risk. This is a measure of abdominal obesity, which is a particularly high-risk form of obesity.
Women have a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes if their waist measures 80cm or more.
Asian men with a waist size of 89cm or more have a higher risk, as do white or black men with a waist size of 94cm or more.
Exercising regularly and reducing your body weight by about 5% could reduce your risk of getting diabetes by more than 50%.
Read about measuring your waist size
Do Not Inject Insulin
If a person with diabetes is having symptoms so severe that they cannot treat themselves, such as losing consciousness, others should not inject them with insulin, as this will lower their blood glucose further.
Additionally, they should not give them food or fluids, as the person may choke.
People taking diabetes medication should work with their healthcare team to develop a management plan to prevent hypoglycemia.
Additionally, the following strategies may help avoid low blood sugar:
- checking blood glucose levels
- eating regular meals or snacks
- engaging in physical activity safely
Regularly monitoring blood glucose levels may also lower a personâs risk of developing complications from hypoglycemia.
Read Also: How To Heal Diabetic Ulcers
What’s It Like For Teens With Type 2 Diabetes
Sometimes people who have diabetes feel different from their friends because they need to think about how they eat and how to control their blood sugar levels every day.
Some teens with diabetes want to deny that they even have it. They might hope that if they ignore diabetes, it will just go away. They may feel angry, depressed, or helpless, or think that their parents are constantly worrying about their diabetes management.
If you’ve been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, it’s normal to feel like your world has been turned upside down. Your diabetes care team is there to provide answers and support. Don’t hesitate to ask your doctors, dietitian, and other treatment professionals for advice and tips. It also can help to find support groups where you can talk about your feelings and find out how other teens cope.
Diabetes brings challenges, but teens who have it play sports, travel, date, go to school, and work just like their friends.
High Blood Sugar: Hydration
Managing high blood sugar may also help treat dehydration. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day can help the body stay well-hydrated. For more severe cases of dehydration, people may need to replenish their electrolytes.
It is best to avoid sugary drinks or fruit juices, as these could increase blood sugar levels.
Recommended Reading: Natural Medicine For Diabetes Type 2
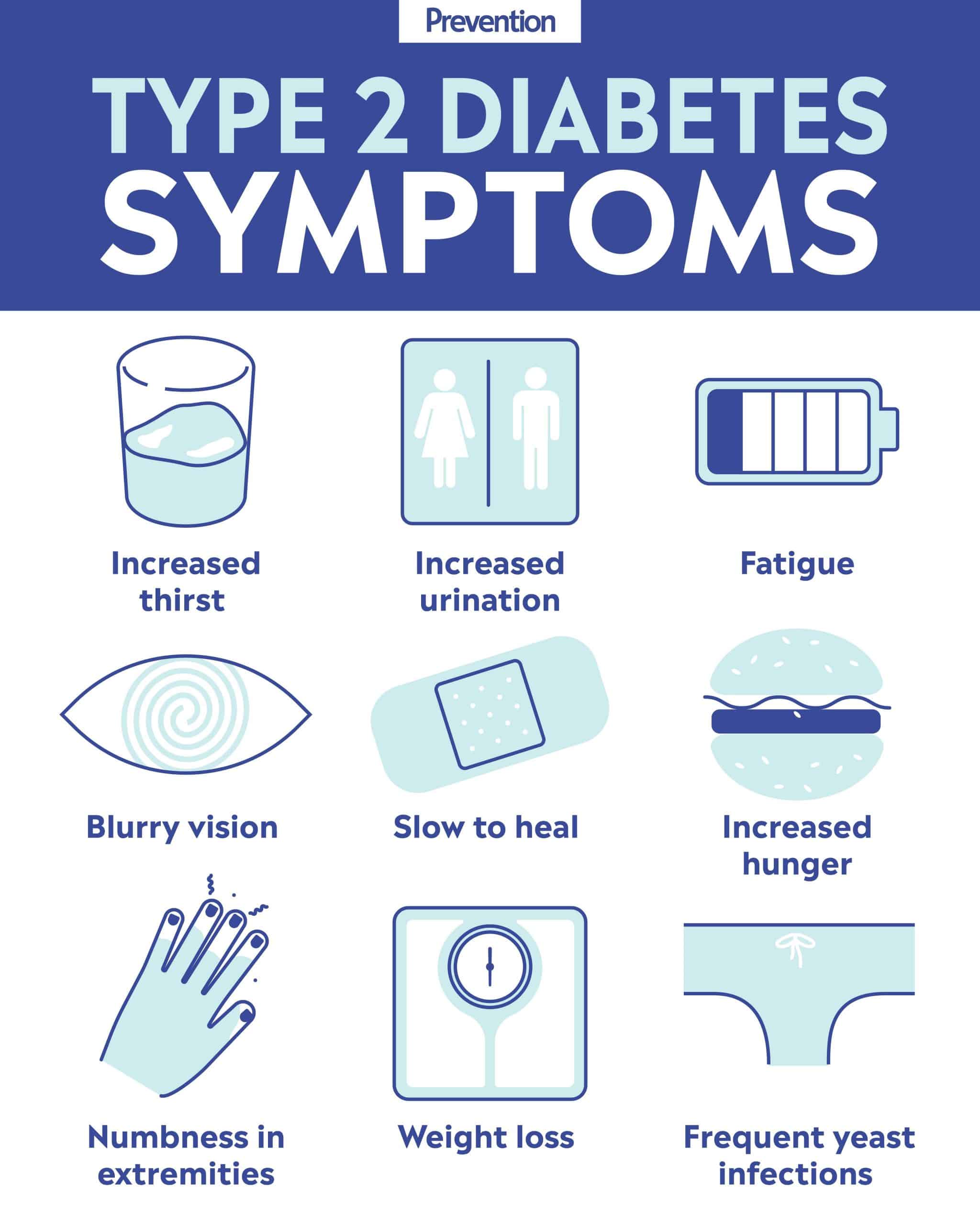
What Are The Symptoms Of Diabetes
Symptoms of diabetes include
- numbness or tingling in the feet or hands
- sores that do not heal
- unexplained weight loss
Symptoms of type 1 diabetes can start quickly, in a matter of weeks. Symptoms of type 2 diabetes often develop slowlyover the course of several yearsand can be so mild that you might not even notice them. Many people with type 2 diabetes have no symptoms. Some people do not find out they have the disease until they have diabetes-related health problems, such as blurred vision or heart trouble.
What Causes Type 2 Diabetes
You can prevent or delay type 2 diabetes with proven, achievable lifestyle changessuch as losing a small amount of weight and being more physically activeeven if youre at high risk.
Theres more to why people get type 2 diabetes than you may know. Although lifestyle is a big part, so are family history, age, and race. Learn about what causes type 2 diabetes and how you can help lower your risk.
Youve probably heard the expression, you cant judge a book by its cover. In the same way we cant tell whats inside a book without reading it, we cant look at a person and know if theyre at risk of type 2 diabetes.
Its true that being overweight is a risk factor for developing type 2 diabetes, but your family history, age, and race are risk factors too.
Learn about what causes type 2 diabetes, and how you can help lower your risk.
Don’t Miss: Ways To Manage Type 2 Diabetes
Is Type 2 Diabetes Increasing
Type 2 diabetes is increasing at an epidemic rate, and is being diagnosed at younger and younger ages. The most likely reason for this increase is that individuals with a genetic susceptibility to type 2 diabetes are developing the disease due to lifestyle changes namely less physical activity, weight gain, and longer life span.
The good news is that scientific research confirms that by eating healthy foods, exercising regularly and maintaining an ideal body weight, you can delay or prevent the onset of type 2 diabetes.
If You’ve Been Newly Diagnosed Make Sure To Take Some Space For Rest And Relaxation So You Can Embark On A New Conversation With Your Body With Confidence And Courage
When we think of fat, we think of the visible kind, the fat that exists under the skin. What we donât think of is the fat around our organs. People with type 2 diabetes tend to have more fat stored inside their liver and pancreas, and it’s this internal fat that impacts the organsâ ability to produce insulin and regulate blood sugar.
Why and how this fat builds up inside the liver and pancreas can be due to a number of factors that arenât necessarily directly linked to weight, such as genetics. Some researchers even talk about a âpersonal fat thresholdâ, which is the amount of fat a person can gain before it starts to cause a problem in the organs. Some thinner people may not be able to put down fat under their skin as well as others, so instead their bodies lay down fat inside of their organsâincluding the pancreas and liver. So while you might not know by looking at them, their fat stores could still be causing damage. Itâs a popular idea that is still in discussion, but it would help explain why people develop type 2 diabetes at all body weights.
You May Like: Signs Your Kid Has Diabetes
The Nhs And Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is already one of the most common long term health conditions and the prevalence of type 2 diabetes in the UK is growing year on year.
The cost of treating a growing number of people with type 2 diabetes, and the health complications associated with the condition, is estimated to cost the NHS around £12 billion a year on direct and indirect care.
Your Diabetes Healthcare Team
A lifelong condition like diabetes is best managed with the support of a diabetes healthcare team. You are the most important member of your diabetes team. Other members are:
Depending on your needs, the team may also include:
- an endocrinologist and other medical specialists such as a kidney specialist
Don’t Miss: When Was Type 2 Diabetes Discovered
Managing Type 2 Diabetes
Many people with type 2 diabetes can manage their blood glucose levels with diet and exercise alone. Others may need diabetes pills or insulin injections, along with medicines to manage other conditions like high blood pressure and high cholesterol. Over time, a person with diabetes may need both lifestyle changes and medication.
Once youve been told you have diabetes, a health care team will work with you to create a diabetes management plan. Your plan will be based on your lifestyle, preferences, health goals, and other health conditions you have.
As part of your plan, your doctor may prescribe one or more medications. Other health care professionals may also be involved. For example, a diabetes educator may help you understand diabetes and provide support as you make lifestyle changes to manage your diabetes. A dietitian may help with meal planning. An exercise coach may help you become more physically active.
Treating Type 2 Diabetes
Treatment for diabetes aims to keep your blood glucose levels as normal as possible and to control your symptoms. This is to prevent health problems developing later in life.
If you’ve been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, your GP will be able to explain your condition in detail to help you understand your treatment.
You will be given advice on diet and exercise to improve control of your blood glucose.
For some people this will be enough to control the blood glucose others may need to start on medication .
They’ll also closely monitor your condition to identify any health problems that may occur. If there are any problems, you may be referred to a hospital-based diabetes care team.
As type 2 diabetes controlled by diet and exercise usually gets worse you may eventually need medication. This is usually tablets to keep your blood glucose at normal levels. Some patients with more severe type 2 diabetes may need insulin injections.
You May Like: What Type Of Diabetes Produces Too Much Insulin
Can Diabetes Be Prevented
Type 1 diabetes cant be prevented.
You may be able to reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes by managing your weight, staying active, and following a healthy diet. However, genetics and other risk factors may increase your risk despite your best efforts.
If you have any risk factors for diabetes, its important to get regular checkups with your doctor or healthcare professional. This will help prevent diabetes from progressing and causing other serious health complications.
Type 2 Diabetes Treatment
First line treatment for type 2 diabetes typically includes a combination of diet modification with regular and appropriate exercise.
The NICE guidelines state that treatment for type 2 diabetes should take into account an individuals needs and preferences into account. People with diabetes should be given the opportunity to make informed decisions about their care and work together with healthcare professionals.
The NICE guidelines encourage having high-fibre, low-glycemic-index carbohydrate in the diet. This allows a good amount of flexibility and it is possible to follow a range of diets, including lower-carb and low-calorie, whilst ensuring you get a good source of low-GI foods such as vegetables, beans and pulses.
Your health team should help you with setting recommendations for carbohydrate and alcohol intake that work for you.
You May Like: Diabetes Blood Sugar Level Tester
Diagnosing Type 2 Diabetes
NYU Langone doctors are experts at identifying people with type 2 diabetes, a condition in which a person has chronically high levels of blood sugar. It occurs when the body lacks or is resistant to insulin, a hormone that helps the body use glucose, or sugar. As a result, the body is unable to convert glucose into energy.
Schedule an Appointment
In prediabetes, a person has higher-than-normal levels of blood sugar, which increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. To help the body use some of the excess blood sugar levels, the pancreas produces more insulin. Over time, prediabetes may progress into type 2 diabetes.
In most people, insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes develop gradually. If you have prediabetes and take steps to prevent type 2 diabetes, you may be able to avoid it altogether.
What Is Normal Blood Glucose
There is no one blood glucose level that defines a person as normal. The table of blood glucose levels below gives the appropriate values at different times and in different states, according to the American Diabetes Association. For example, insulin-dependent diabetics often use an upper limit of 7 mmol/L or 140 mg/dL, while non-insulin-dependent diabetics may aim for less than 6 mmol/L or 108 mg/DL.
The blood glucose levels range between less than 100-180 mg/dL for adults from 20 years or older. Depending on your age this may vary.
- Fasting: Less than 5.6 mmol/L or 100 mg/DL
- Before meal: 3.9-7.2 mmol/L or 70-130 mg/DL
- 1-2 hours after eating: Less than 10 mmol/L or 180 mg/DL
- Bedtime: 5.6-7.8 mmol/L or 100-140 mg/DL
Be aware that the above numbers might be different for everyone depending on your doctors recommendations.
Don’t Miss: Ice Pack For Insulin Pen
Eat The Right Carbohydrates
The two main kinds of carbohydrates simple and complex affect blood sugar levels differently.
Simple carbohydrates are mainly made up of one kind of sugar. They are found in foods, such as white bread, pasta, and candy. The body breaks these carbohydrates down into sugar very quickly, which causes blood sugar levels to rise rapidly.
Complex carbohydrates are made up of three or more sugars that are linked together. Because the chemical makeup of these kinds of carbohydrates is complicated, it takes the body longer to break them down.
As a result, sugar is released into the body more gradually, meaning that blood sugar levels do not rapidly rise after eating them. Examples of complex carbohydrates include whole grain oats and sweet potatoes.
Recommended Reading: What Glucose Meter Does Medicare Cover
Type 2 Diabetes And Covid
The CDC points out that having type 2 diabetes can make it more likely that you will experience complications from COVID-19, the disease caused by the novel coronavirus. Nonetheless, proper blood sugar management can help lessen this risk.
Everyday Health editors attend the ADCES annual meeting to connect with certified diabetes care and education specialists, registered dietitian nutritionists, and people like you, who are looking for ways to better manage blood sugar, diet, medication, and more. Check out information on the next meeting here.
The ADA is considered the leading nonprofit for type 1 and type 2 diabetes education. The ADA’s free yearlong program Living With Diabetes offers top-of-the-line resources for anyone new to living with diabetes. Youll get access to their newsletter, expert Q& A session, and online support system, among other perks.
One of our favorite features from the AHA is a go-to resource for preventing heart disease: Know Diabetes by Heart. The ADA-supported initiative lays out a step-by-step guide for keeping your heart healthy while living with diabetes.
You May Like: What Is The First Sign Of Type 1 Diabetes
Medications For Type 2 Diabetes
In some cases, lifestyle changes are enough to keep type 2 diabetes under control. If not, there are several medications that may help. Some of these medications include:
- Metformin.This can lower your blood glucose levels and improve how your body responds to insulin. Its the first-line treatment for most people with type 2 diabetes.
- Sulfonylureas. These are oral medications that help your body make more insulin.
- Meglitinides. These are fast-acting, short-duration medications that stimulate your pancreas to release more insulin.
- Thiazolidinediones. These make your body more sensitive to insulin.
- Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors. These are milder medications that help reduce blood glucose levels.
- Glucagon-like peptide-1 agonists. These slow digestion and improve blood glucose levels.
- Sodium-glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors. These help your kidneys remove sugar in your body through urine.
Each type of medication listed above can cause side effects. It may take some time for you and your doctor to find the best medication or combination of medications to treat your diabetes.
If your blood pressure or cholesterol levels are also not ideal, you may need medications to address those needs as well.
If your body is unable to make enough insulin, you may need insulin therapy. You may only need a long-acting injection you can take at night, or you may need to take insulin several times per day.