What Is Blood Glucose
Blood glucose comes from food. When an individual eats, the food is broken down into sugar and sent to the blood. The insulin is what helps the sugar go into the cells. Once this happens, the sugar that has moved from the blood into the cells is used for energy or is stored.
Glucose is known as the bodys main energy source. Too much glucose in the blood, or if it is not absorbed properly, can create health issues both long and short term. To keep a healthy blood sugar level, it is important to:
- Eat healthily
- Check blood glucose levels
- Keep in contact with your healthcare provider
It is important to keep in contact with a healthcare professional, eat properly, check your blood glucose, and exercise regularly to keep a healthy blood sugar level.
What Are Normal Blood Sugar Levels
They’re less than 100 mg/dL after not eating for at least 8 hours. And they’re less than 140 mg/dL 2 hours after eating.
During the day, levels tend to be at their lowest just before meals. For most people without diabetes, blood sugar levels before meals hover around 70 to 80 mg/dL. For some people, 60 is normal for others, 90.
What’s a low sugar level? It varies widely, too. Many people’s glucose won’t ever fall below 60, even with prolonged fasting. When you diet or fast, the liver keeps your levels normal by turning fat and muscle into sugar. A few people’s levels may fall somewhat lower.
Diabetes Is Diagnosed By Any One Of The Following:
Sometimes you may have symptoms of fatigue, excessive urination or thirst, or unplanned weight loss. However, often people have no symptoms of high blood glucose and find a diabetes diagnosis surprising.
Also Check: Fruits For Type 1 Diabetes
Prevent Type 2 Diabetes
If your test results show you have prediabetes, ask your doctor or nurse if there is a lifestyle change program offered through the CDC-led National Diabetes Prevention Program in your community. You can also search for an online or in-person program. Having prediabetes puts you at greater risk for developing type 2 diabetes, but participating in the program can lower your risk by as much as 58% .
What Is The Normal Blood Sugar Level For Adults
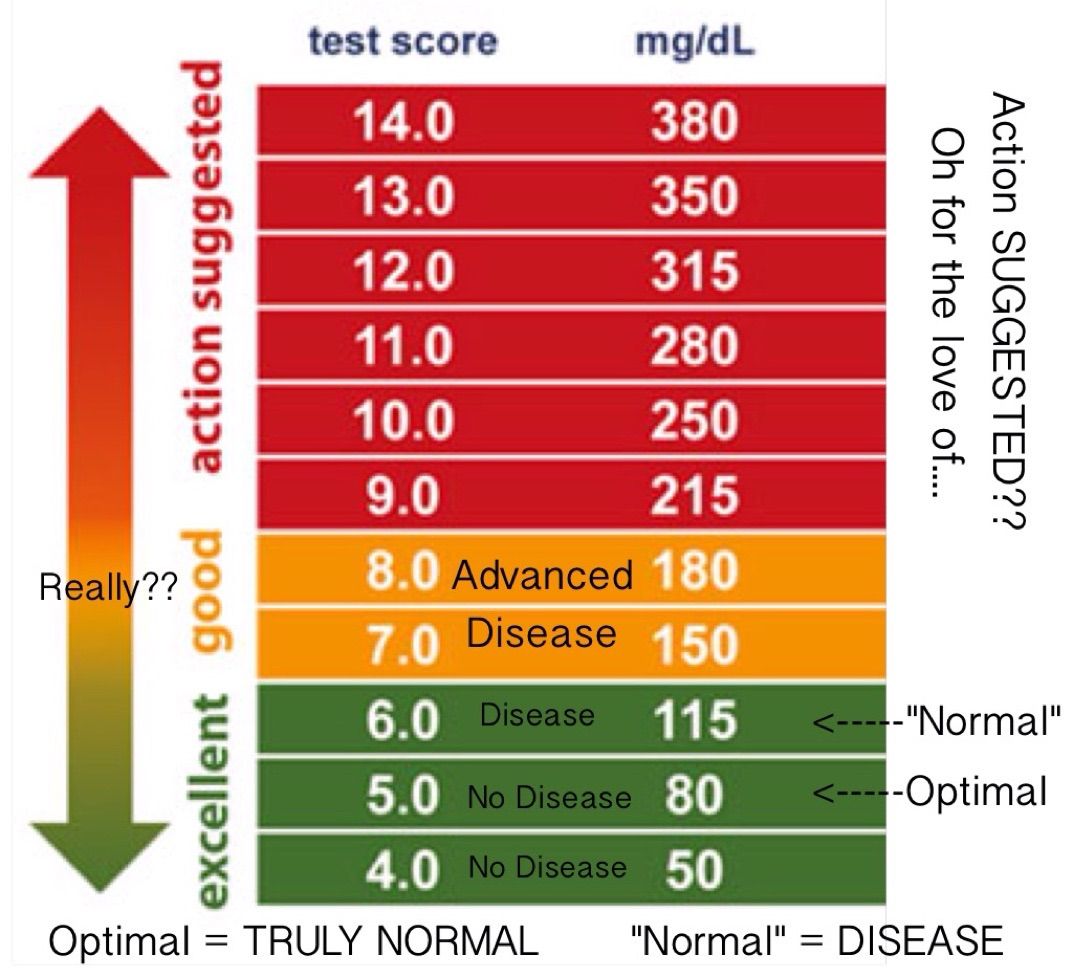
As we age, our bodies become less able to regulate blood sugar levels as well as they used to. Thatâs why the ADA recommends that older adults aim for a fasting blood sugar level of less than 100 mg/dL. After eating, itâs ideal that your blood sugar level is below 180 mg/dL.
The ADA recommends that most adults with diabetes aim for the following blood sugar goals:
- Fasting: Less than 100 mg/dL
- Preprandial : 70-130 mg/dL
- Postprandial : Less than 180 mg/dL
- Bedtime: 100-140 mg/dL
If you experience high blood sugar levels or low blood glucose levels compared to this range you should speak to your doctor.
Don’t Miss: Natural Remedies For Type 2 Diabetes
Consequences Of Blood Sugar Levels
Whilst most symptoms of low and high blood sugar levels are mild, they can worsen if left untreated and sometimes have long term consequences and/or complications. Overtime, a high blood sugar level is what can cause consequences. Lack of treatment can cause severe damage to the blood vessels and lead to complications such as:
- Heart attack
What Is The Test To Check Blood Sugar Levels For Type 2 Diabetes
You can check your blood sugar levels several times a day at home with a blood glucose monitor, which uses a drop of blood from your finger. A better measure of how well your diabetes is being managed, however, is a blood test called the A1C.
The A1C test involves a blood test that measures the percentage of hemoglobin proteins in your blood that are bound to sugar. In a more practical sense, these tests show how well your blood sugar levels have been managed in the last two to three months.
Instead of relying on occasional blood glucose tests that can spike or drop for many reasons, A1C tests provide a more accurate picture of how well your diabetes has been managed on average across the preceding three months.
Some people are diagnosed with diabetes using the A1C test, and doctors often recommend that those with prediabetes should get a yearly A1C test. Those with diabetes who don’t use insulin may only need two of these tests per year. People who use insulin, or struggle to keep blood sugar levels within their target range, may get four A1C tests per year.
A1C tests don’t require any preparation for fasting beforehand, so you can have this blood test any time of the day, even after eating and drinking normally.
Read Also: How Do People Get Type 1 Diabetes
Diabetes By The Numbers
Staying healthy with type 2 diabetes is a numbers game. Get the scoop on the health indicators you should be measuring and why.
Thinkstock
When you have type 2 diabetes, youve got to know your numbers. Its not just about blood sugar. To successfully manage diabetes, there are several measurements that you should take, or have taken, on a regular basis. Keeping track of the following numbers can help you live well with type 2 diabetes and lower your risk of complications.
Blood sugar levels. This is probably the type 2 diabetes measure youre most familiar with. Testing your blood sugar regularly allows you to see how certain foods, exercise, and other activities affect your blood sugar levels on a day-to-day basis. Many people with type 2 diabetes need to test once or twice a day to make sure blood sugar levels are in target range. If your blood sugar is very well controlled, you may only need to check a few times a week, according to the National Institutes of Health.
The American Diabetes Association recommends aiming for a blood sugar level between 70 to 130 mg/dl before meals and less than 180 mg/dl one to two hours after a meal. To keep your blood sugar within this range, follow a healthy, well-rounded diet and eat meals and snacks on a consistent schedule. If your blood sugar is not well controlled, talk to your doctor about adjusting your diabetes management plan.
Recommended Reading: Sugar Tablets Side Effects
Symptoms Of Blood Blood Sugar Levels
Symptoms of blood sugar levels differ depending on if it is high or low. To determine which way the blood sugar have moved, the symptoms for each are typically:
| High Blood Sugar Symptoms | |
| Slow healing wounds | Turning pale |
If symptoms are left untreated, more extreme circumstances can happen such as fainting, weakness, disorientation, vomiting and dehydration. When you notice symptoms, usually more than one at one time, it is advised to see a doctor right away.
It is important to get the right treatment so that you can return to a healthy normal blood sugar level and inhibit it from occurring again.
Treatment methods vary from the severity of the blood sugar level, whether it is high or low and if the patient has existing medical conditions, such as diabetes. Here are ways in which blood sugar levels can be treated:
Don’t Miss: Ginger For Diabetes Type 2
What Is High Blood Glucose
People who do not have diabetes typically have fasting plasma blood glucose levels that run under 100 mg/dl.
Your physician will define for you what your target blood glucose should be identifying a blood glucose target that is as close to normal as possible that you can safely achieve given your overall medical health. In general, high blood glucose, also called ‘hyperglycemia’, is considered “high” when it is 160 mg/dl or above your individual blood glucose target. Be sure to ask your healthcare provider what he or she thinks is a safe target for you for blood glucose before and after meals.
If your blood glucose runs high for long periods of time, this can pose significant problems for your long-term increased risk of complications, such as eye disease, kidney disease, heart attacks and strokes and more. High blood glucose can pose health problems in the short-term as well. Your treatment plan may need adjustment if the blood glucose stays over 180 mg/dl for 3 days in a row. It is important to aim to keep your blood glucose under control and treat hyperglycemia when it occurs.
- Increased thirst
- Slow healing cuts and sores
- Unexplained weight loss
- Too much food
- Too little exercise or physical activity
- Skipped or not enough diabetes pills or insulin
- Insulin that has spoiled after being exposed to extreme heat or freezing cold
- Stress, illness, infection, injury or surgery
- A blood glucose meter that is not reading accurately
For Those Diagnosed With Diabetes You Can Reduce The Risk Of Complications:
- Monitor blood glucose levels with appropriate testing and an A1C blood test every three months to measure the average amount of sugar in your blood
- If you smoke, it’s never too late to quit
- Be physically active
- Examine feet and skin every day
- Have an eye exam at least once a year
- Have a kidney function test at least once a year
- Visit your healthcare provider regularly
Read Also: Blood Sugar Levels After Meals For Diabetics
Normal Hba1c For Person Without Diabetes
For someone who does not have diabetes, a normal HbA1C level is below 5.7%. An A1C between 5.7% to 6.4% is indicative of prediabetes.
Its recommended that adults over the age of 45 or adults under 45 who are overweight and have one or more risk factors for diabetes have a baseline A1C checked. If the result is normal, the A1C should be checked every 3 years. If the result indicates prediabetes, the A1C should be checked every 1 to 2 years.
When Should I Go To The Hospital For Blood Sugar
Certain symptoms of blood sugar levels signal when you should seek medical help. Typically, if you feel extremely fatigued, notice increased thirst and urination, or weight loss, you should seek help right away. These symptoms can signify an abnormal blood sugar level and/or other health conditions.
A routine health check is also advised, even if you do not show any symptoms.
You May Like: Weight Loss Supplements For Diabetics
What Are Considered Normal Blood Sugar Levels
You might not have diabetes now, but do you know the risk factors?
In 2015, 22% of Canadian adults were pre-diabetic and the number of Canadians suffering from diabetes has increased by 44% in the last 10 years. As the leading cause of blindness, kidney problems, and non-trauma amputations, it is important to protect ourselves against diabetes.
But its not all bad news, diabetes is often a preventable disease. Knowing whether you have normal blood sugar levels is one of the best indicators of risk. If your blood sugar levels are high, mindful eating and lifestyle changes can reduce your risk of developing diabetes.
Read on for all the hottest tips on how to manage your blood sugar levels and prevent diabetes.
What Is Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Continuous glucose monitoring is another way to check your glucose levels. Most CGM systems use a tiny sensor that you insert under your skin. The sensor measures glucose levels in the fluids between your bodys cells every few minutes and can show changes in your glucose level throughout the day and night. If the CGM system shows that your glucose is too high or too low, you should check your glucose with a blood glucose meter before making any changes to your eating plan, physical activity, or medicines. A CGM system is especially useful for people who use insulin and have problems with low blood glucose.
Don’t Miss: How Much Does Diabetes Insulin Cost
Type 2 Diabetes And Blood Sugar Levels
Type 2 diabetes prevents glucose sugar from entering your body’s cells to properly use for energy. Insulin is a hormone released by your pancreas , which helps glucose get into your cells to carry out body functions.
However, in those with type 2 diabetes, the cells become resistant to insulin. This makes it more difficult for the glucose in your bloodstream to get into the cells to provide your body with the energy it needs for many of its functions. This can lead to high levels of sugar in your blood that can’t get into your cells, which over time may result in dangerous health consequences.
Controlling Blood Glucose Levels
Uncontrolled blood sugar can result in regular episodes of hyperglycemia . This can cause a variety of symptoms including:
- Dry mouth
- Nausea
- Fatigue
These symptoms are uncomfortable to experience but there are things you can do at home to reduce your blood sugar. In terms of drinks, water is the best as it will help to maintain hydration and dilute excess sugar in the blood. Also, try to add more fiber to your diet to reduce your blood sugar apples, bananas, oranges, and strawberries are all fibrous fruits.
However, uncontrolled blood sugar levels can also lead to more severe, long term disease. Poorly managed diabetes leads to vision loss, kidney problems, nerve damage, heart attack, and stroke. Therefore, if your blood sugar level reaches 16.7mmol/L, this could be dangerous and you need to seek immediate medical attention.
Recommended Reading: Dialysis And Diabetes Diet Plan
Recommended Blood Sugar Targets
For people with type 1 diabetes, the American Diabetes Association recommends that blood sugar targets be based on a person’s needs and goals. Talk to your doctor and diabetes educator about these goals. A general guideline is:
Before meals, your blood sugar should be:
- From 90 to 130 mg/dL for adults
- From 90 to 130 mg/dL for children, 13 to 19 years old
- From 90 to 180 mg/dL for children, 6 to 12 years old
- From 100 to 180 mg/dL for children under 6 years old
After meals , your blood sugar should be:
- Less than 180 mg/dL for adults
At bedtime, your blood sugar should be:
- From 90 to 150 mg/dL for adults
- From 90 to 150 mg/dL for children, 13 to 19 years old
- From 100 to 180 mg/dL for children, 6 to 12 years old
- From 110 to 200 mg/dL for children under 6 years old
For people with type 2 diabetes, the American Diabetes Association also recommends that blood sugar targets be individualized. Talk to your doctor and diabetes educator about your goals.
In general, before meals, your blood sugar should be:
- From 70 to 130 mg/dL for adults
After meals , your blood sugar should be:
- Less than 180 mg/dL for adults
How Can You Find Out If You Have Normal Blood Sugar Levels
There are a few different ways that you can test or keep track of your average blood sugar level. Some popular glucose monitoring methods include a continuous glucose monitor , an A1C test, a glucose meter, doing a fasting blood glucose test, or an oral glucose tolerance test. You can also get your ketones tested, which usually appear in the urine of Type 1 diabetes patients.
Your healthcare provider will analyze your test results, and let you know the best course of action if theyâre not in the normal range. This may include diabetes medications like metformin or lifestyle changes.
Read Also: How To Control High Sugar Level Immediately
Also Check: What Is Considered Uncontrolled Diabetes
Symptoms Of Low Sugar Level
Low blood sugar condition or Hypoglycemia occurs when blood glucose levels fall below 70 mg/DL.
Fluctuation in blood sugar levels may be due to the following factors:
It is possible to eliminate these symptoms with the right guidance from certified diabetes reversal coaches who understand your routine and current lifestyle and help you with diet and lifestyle changes that can be easily done by you. These small changes lead to a drastic impact on your blood sugar levels and help you reverse your diabetes.
How Much Is Ozempic Without Insurance
Is Ozempic covered by insurance | How much does Ozempic cost without insurance? | How to get Ozempic without insurance
Ozempic is a brand-nameprescription drug that lowers blood sugar levels in people diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes. It is also prescribed to reduce the risk of cardiovascular problems such as heart attack in people diagnosed with both Type 2 diabetes and heart disease. Ozempic is not used to treat Type 1 diabetes. Belonging to a family of drugs called GLP-1agonists, semaglutide reduces blood sugar by enhancing insulin release in the body and decreasing the bodys production of glucose.
Ozempic is administered once per week as a subcutaneous injection. Doses will start low and could rise to as high as 1 mg per week. Common side effects include constipation, diabetic retinopathy, and injection site or allergic reactions. Rarely, it may cause low blood sugar or hypoglycemia. There is no generic version of Ozempic yet available, so uninsured patients may need to pay the full retail price for the drug.
Recommended Reading: Safest Sugar Substitute For Diabetics
At What Number Range Are You Considered Diabetic
Question Originally asked by Community Member teresa At What Number Range Are You Considered Diabetic what numbers must you have to be consider borderline and what number range to be considered to be diabetic such as type 2 diabectic and type 1 Answer Hello teresa, Diagnosis of diabetes is based on blood sugar measurements. The difference between type 1 and type 2 is not based on blood sugar levels, but in the mechanisms that raise blood sugar. Fasting glucose levels above 140 mg/dl on at least two occations are diagnosic for diabetes. Anything above 110mg/dl but less than 140mg/dl after fasting is considered impaired impaired glocose tolerence. There is a formal test, called a glucose tolerance test, that involves ingesting a specified amount of glucose and lthen measuring how the blood sugar levels increase and fall. Likely, anybody with a blood sugar level about 200 mg/dl on at least 2 occasions without fasting is likely diabetic and needs to be treated. To your health, Neil MD You should know Answers to your question are meant to provide general health information but should not replace medical advice you receive from a doctor. No answers should be viewed as a diagnosis or recommended treatment for a condition. Answered By: Neil MDContinue reading > >