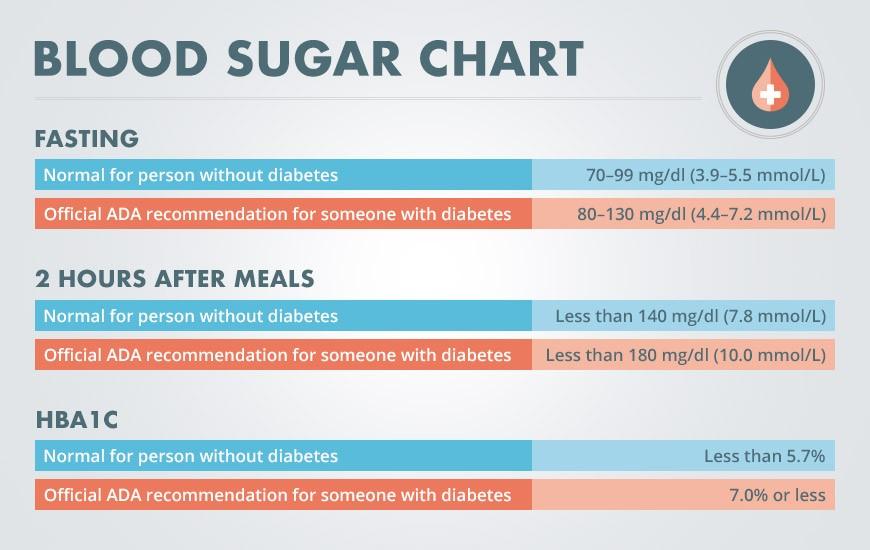
What Are The Recommended Targets For Blood Glucose Levels
Many people with diabetes aim to keep their blood glucose at these normal levels:
- Before a meal: 80 to 130 mg/dL
- About 2 hours after a meal starts: less than 180 mg/dL
Talk with your health care team about the best target range for you. Be sure to tell your health care professional if your glucose levels often go above or below your target range.
Why Is It Important To Reduce The Size And Duration Of These Spikes
Reducing these spikes may help you to increase the amount of time you spend in your target blood sugar range , which will have a positive impact on your future health. You should consult your healthcare team to understand the best target range for you, as this will differ from person to person. However, the International Society for Paediatric and Adolescent Diabetes recommends a target of 5.0-10.0 mmol/L .
Symptoms of a high blood sugar level also vary in individuals, but they may cause you to feel thirsty, tired, stressed and need to go to the toilet a lot. In the short term, by avoiding prolonged high blood sugar readings after eating, you should also reduce the occurrence of these symptoms and improve your energy, cognitive and athletic ability and overall mood.
What Is Blood Glucose
Blood glucose is the main sugar content in your blood. It comes from the food you eat, and it’s your body’s main source of energy. Blood glucose levels are a measure of how much sugar is in your blood. Blood sugar levels can fluctuate during the day and night because of various reasons. What we eat, how active we are, and even stress can all affect our blood sugar levels.
Recommended Reading: Diabetes And Metabolism Impact Factor
What Is The Normal Blood Sugar Level For Teens
Teenagers are recommended to have a blood sugar range between 70-150 mg/dL. It’s not easy for a teenager to maintain a tight range, therefore it’s important to aim for these numbers to give them a bit more flexibility.
- Fasting: 70-150 mg/dL
- Preprandial : 90-130 mg/dL
- Postprandial : Less than 140 mg/dL
- Bedtime: 90-150 mg/dL
How To Use A Blood Glucose Meter:
- After washing your hands, insert a test strip into your meter.
- Use your lancing device on the side of your fingertip to get a drop of blood.
- Touch and hold the edge of the test strip to the drop of blood and wait for the result.
- Your blood glucose level will appear on the meter’s display.
Note: All meters are slightly different, so always refer to your user’s manual for specific instructions.
Read Also: Body Wash For Diabetic Skin
Why Your Blood Sugar Level May Be High
Based on the ADA guidelines above, if your blood sugar is above 180 mg/dL two hours after a meal, it is considered above the normal range. What might cause your glucose or blood sugar to rise? Consider the following factors:
- Consuming more carbohydrates or a larger meal than usual
- Not taking enough insulin or oral diabetes medication based on carbohydrates or activity levels
- Reduced physical activity
- Side effects from medications like steroids or antipsychotics
Blood Sugar Levels After Meals For Diabetics
Low Blood Sugar, Blood Sugar Levels After Meals For Diabetics, When To Test Blood Sugar Levels, Blood Sugar Level.
Metabolic actions of insulin like development factor I in normal physiology and diabetes A two hour oral glucose tolerance take a look at with any value over 200 mg dl clinches the prognosis An RBS can be safely carried out in the home setting by the affected person utilizing a simple package which features a finger prick system and a glucometer.
Once sufficient alcohol has been eradicated, your liver will regain the ability to release sugar It can occur throughout a date, throughout a enterprise assembly, and even while driving, which is the most harmful situation if there s confusion or loss of consciousness while behind the wheel It s important to use your blood glucose meter to examine your blood sugar before you drive to keep yourself and others protected.
Add notes about something which may have made the reading out of your target range, similar to food, exercise, and so forth Squeezing from the base of the finger, gently place a small amount of blood onto the test strip Please share this article to help as many patients as you presumably can If the result s between 56 mmol L to 7zero mmol L, the affected person is considered prediabetic Blood sugar is alleged to be high whether it is over one hundred thirty mg dL Blood Sugar Levels After Meals For Diabetics earlier than a meal of a hundred and eighty mg dL within two hours of a meal.
Don’t Miss: What’s The Best Diet For Type 2 Diabetes
Blood Sugar Levels In Children With Diabetes:
Summary
Diabetes & Ketones: Everything You Need To Know
These days, understanding what ketones are can be confusing, because even mainstream society and non-diabetics are talking about ketones.
What has always been something people with diabetes feared, has now become something that low-carb and ketogenic dieters strive for: ketosis.
In this article, well talk about the crucial differences between diabetic ketones , starvation ketones, and nutritional ketosis. Well also cover what to do if youve developed diabetic ketones and how to manage ketones and diabetes during an illness.
Don’t Miss: Diabetic Meals Delivered To Home
Normal Blood Sugar Ranges In Healthy Non
For a person without any type of diabetes, blood sugar levels are generally between 70 to 130 mg/dL depending on the time of day and the last time they ate a meal. Newer theories about non-diabetic blood sugar levels have included post-meal blood sugar levels as high as 140 mg/dL.
Here are the normal blood sugar ranges for a person without diabetes according to the American Diabetes Association:
- Fasting blood sugar : under 100 mg/dL
- 1 hour after a meal: 90 to 130 mg/dL
- 2 hours after a meal: 90 to 110 mg/dL
- 5 or more hours after eating: 70 to 90 mg/dL
Is Blood Sugar Of 135 High
A blood sugar level of 135 is not considered high. However, it is still important to take steps to lower your blood sugar levels if they are above your target range. You can do this by making changes to your diet and exercise routine. You should also talk to your doctor about ways to lower your blood sugar levels.
Read Also: Best App To Track Diabetes
Blood Sugar Levels Chart
The above chart and the one below are exactly the same, in different formats.
| Category | |
| More than 11.1 mmol/l |
These are the diagnostic ranges. As you can see, the normal range for fasting glucose is under 100 mg/dl or 6 mmol/l. Though just to note, there is some debate about the normal range in mmol/l, ranging from 5.5 to 6 mmol/l. So depending what chart you look at, you may see either of those numbers.
After a meal, the maximum reading you ideally want to see is 140 or 7.8.
If youre getting readings above this, you would be diagnosed with prediabetes or type 2 diabetes, as shown in the charts above.
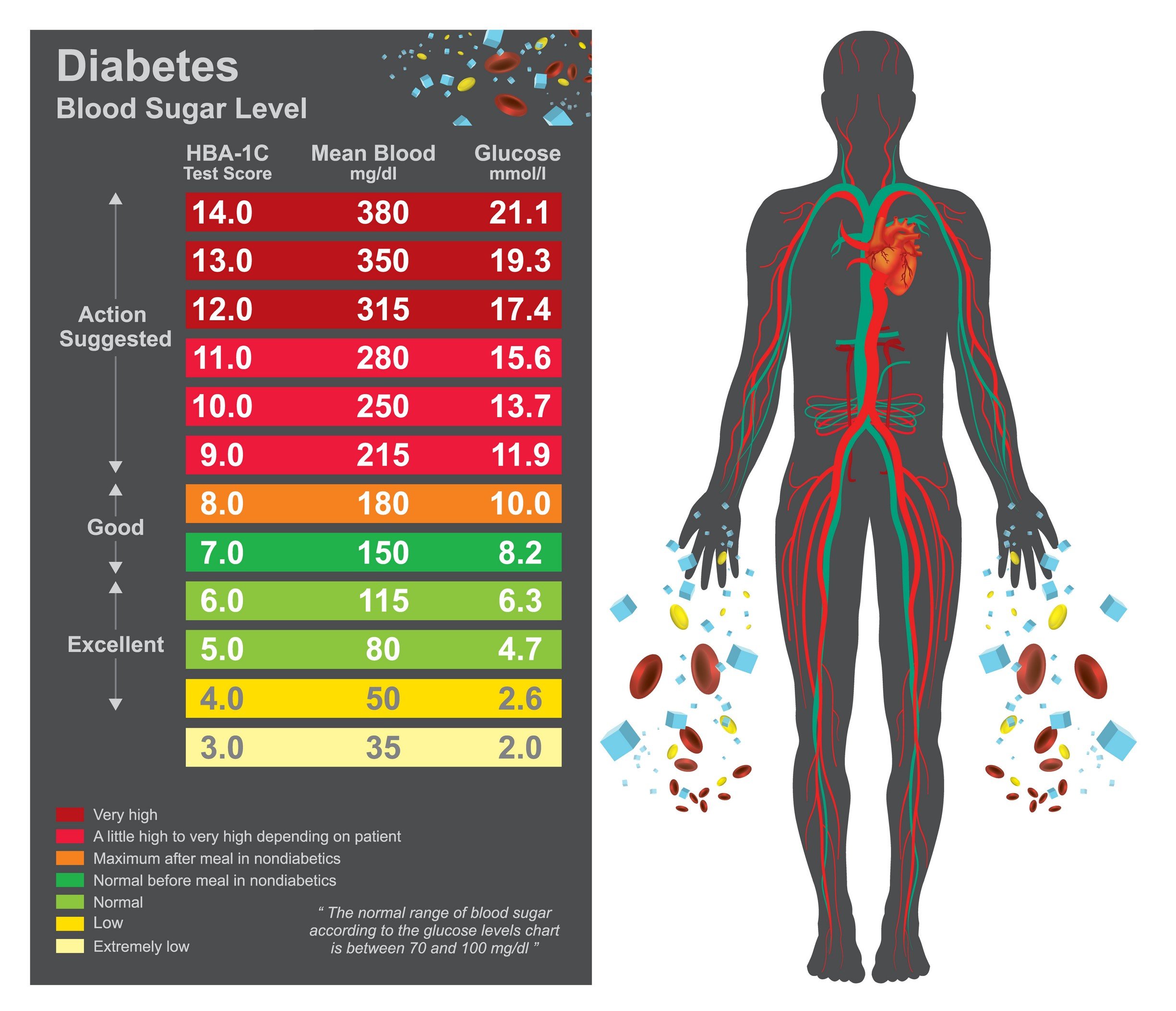
A1c Goals Should Be Individualized

A1c goals should be individualized based on the individual capabilities, risks, and prior experiences, explains Gary Scheiner, MS, CDE, founder of Integrated Diabetes, and author of Think Like a Pancreas.
For example, we generally aim for very tight A1c levels during pregnancy and more conservative targets in young children and the elderly.
However, Scheiner highlights important factors that could justify aiming for a higher A1c, like hypoglycemia unawareness, which is described as when a person with diabetes no longer feels the oncoming warning signs of low blood sugar. This can put you at significant risk for severe low blood sugars resulting seizures or death. To reduce that risk, you would aim for higher target blood sugar ranges.
Someone with significant hypoglycemia unawareness and a history of severe lows should target higher blood glucose levels than someone who can detect and manage their lows more effectively, adds Scheiner. And certainly, someone who has been running A1cs in double digits for quite some time should not be targeting an A1c of 6% better to set modest, realistic, achievable goals.
Learn how to lower your A1c in DiabetesStrongsA1C Guide.
Read Also: What Is The Earliest Sign Of Diabetes Nephropathy
What Causes Low Blood Sugar
Low blood sugar has many causes, including missing a meal, taking too much insulin, taking other diabetes medicines, exercising more than normal, and drinking alcohol. Blood sugar below 70 mg/dL is considered low.
Signs of low blood sugar are different for everyone. Common symptoms include:
- Shaking.
- Dizziness.
- Hunger.
Know what your individual symptoms are so you can catch low blood sugar early and treat it. If you think you may have low blood sugar, check it even if you dont have symptoms. Low blood sugar can be dangerous and should be treated as soon as possible.
How To Lower Your A1c: The Complete Guide
We are always told that having a low A1c is an important goal in our diabetes management, but do you know why? Do you know what a good A1c target is, how to lower your A1c, and how quickly you can lower your A1c safely?
These are the questions I will answer in this comprehensive guide on what A1c is, how to lower your A1c, and why achieving a low A1c isnt the only goal when it comes to diabetes management.
Read Also: Diabetic Recipes For Picky Eaters
When Should I Check My Blood Sugar
How often you check your blood sugar depends on the type of diabetes you have and if you take any diabetes medicines.
Typical times to check your blood sugar include:
- When you first wake up, before you eat or drink anything.
- Before a meal.
- Two hours after a meal.
- At bedtime.
If you have type 1 diabetes, have type 2 diabetes and take insulin, or often have low blood sugar, your doctor may want you to check your blood sugar more often, such as before and after youre physically active.
What Is A Normal Blood Sugar Level For Diabetics
A normal blood sugar level for diabetics is more difficult to define because it can vary greatly from person to person and is measured differently per age.
What’s important is that you work with your doctor to set goals that are achievable for you and that you maintain good blood sugar control as much as possible.
Recommended Reading: How To Prevent Type 2 Diabetes
How To Monitor Your Blood Sugar Levels
1. Set a Desirable Goal
If you are aiming at an A1c level of 7% or less, which translates to an average blood sugar level of 154mg/dl, the doctor will give you an A1c test every 3 to 6 months. The goals you are aiming at and when you should test will depend on:
- Existing health problems
- How long you have had diabetes
- Medication you are on
- If you have complications like neuropathy or retinopathy
- If you have low blood sugar without warning symptoms
2. Monitor Regularly
Once you and your doctor determine your blood sugar targets, you should get tested on a regular basis. Monitoring is important, more so if you are taking insulin or medication that can result in hypoglycemia. In addition, it will help you compare your blood sugar levels after eating and before meals. This will give you a better understanding of your glucose patterns and how you can improve them.
- A fasting blood glucose level should be taken first thing in the morning before drinking or eating anything.
- You can also take another test right before going to bed.
- For the other times, a test 1-2 hours after breakfast or before lunch should be able to give you a clear picture of your blood sugar levels, according to CDC. According to the American Diabetes Committee, a test immediately after eating will give your doctor good information in case your pre-meal blood sugar levels are fine but have not achieved your A1c goal.
3. Keep a Record
Know how to control you blood sugar with diet from the video blow:
Ways To Better Control Blood Sugar After Eating
Do you find it difficult to stabilize your blood sugar levels after eating? Follow these mealtime tips to help keep your blood sugar in range.
When you have type 2 diabetes, life can often feel like a juggling act: You have to balance how much you eat, and when you eat it, with the right amount of exercise all while taking your medications consistently. Strike a good balance and your blood glucose can remain stable. If you don’t make it work, your risk of diabetes complications rises.
Food makes your blood sugar levels rise soon after eating. The particular food you eat, how much you eat, and the timing of your medication around the time you eat make a difference in your levels, too.
Damage to your body from high blood sugar can happen pretty quickly, and the higher the level, the greater your risk of complications, according to a 2015 review in the Diabetes & Metabolism Journal. The higher the blood sugar levels reach, the more likelihood for damage to vessels and other parts of the body.
And problems can develop when the numbers stay high for just a few days, according to the Joslin Diabetes Center in Boston. The specialty medical center advises making changes to your treatment plan if blood glucose levels stay over 180 mg/dl for three days in a row.
Additional reporting by Andrea Peirce
Don’t Miss: How To Count Carbs For Type 1 Diabetes
What Are Ketones
Simply put: ketones are what your body produces when your body cant adequately burn glucose in your bloodstream or produced from your diet for fuel. Instead, it will burn body fat for fuel which results in different acids, including ketone acids.
While this may seem like a great thing body fat being burned for fat it is actually not always a good thing, especially if you have diabetes.
You cant fully answer the question of what are ketones in one sentence because there are several types of ketosis and the several ways ketones can develop in the human body some are safe, some are very dangerous.
The four types of ketones and states of being in ketosis are:
- Diabetic ketoacidosis
How Do I Check
People with diabetes check their blood sugar levels by poking their fingertips and using a blood glucose meter or a continuous glucose monitor to measure the blood glucose level at that moment. Read on to find out how to use a blood glucose meter. To find out more about CGMs, start by talking to your doctor.
You May Like: Diabetes Kidney Failure Life Expectancy
Ways To Lower Your Glucose
As you learn more about the way food, combinations of foods, amounts of food, sleep, stress, meal timing, exercise, and more impact your glucose, youâll inevitably experience glucose spikes. Again, it can be completely normal to have high glucose spikes! But as you start to see what foods make your glucose go high, youâll start to see patterns in how your body reacts to food and drinks.
Some ways to keep your glucose in range:
- Limit carbohydrate intake, particularly from added sugars and processed, refined carbs from foods like white bread, pasta, and chips.
- Increase water intake to maintain hydration.
- Engage in physical activity, such as a post-meal walk, to burn excess blood sugar. Exercise encourages the release of glucagon from the pancreas to allow stored glucose back into the bloodstream to fuel your workout. This flood of glucose into the blood doesn’t require insulin, so it’s a healthy way to burn through glucose stores.
- Eat meals with more fiber, protein, and fat: A small study showed that meals with higher fiber, protein, and fat resulted in a smaller increase in glucose with post-meal glucose peaks ranging from 99â122 mg/dL or 5.5â6.8 mmol/L.
- Strive to eat minimally processed whole foods. Check out our one-week low-glycemic meal plan to get some kitchen inspo.
- Reduce stress through meditation, deep breathing, reframing negative thoughts.
References