Causes Of Type 2 Diabetes
People with type 2 diabetes have insulin resistance. The body still produces insulin, but its unable to use it effectively.
Researchers arent sure why some people become insulin resistant and others dont, but several lifestyle factors may contribute, including being inactive and carrying excess weight.
Other genetic and environmental factors may also play a role. When you develop type 2 diabetes, your pancreas will try to compensate by producing more insulin. Because your body is unable to effectively use insulin, glucose will accumulate in your bloodstream.
Type 2 diabetes is much more common than type 1.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Preventions , 34.2 million people in the United States were living with diagnosed or undiagnosed diabetes in 2018. Thats a little over 1 in 10 people. Ninety to 95 percent of people with diabetes have type 2.
The percentage of people with diabetes increases with age.
About 10.5 percent of the general population has diabetes. Among those 65 years old and older, the rate reaches 26.8 percent. Only 25 out of every 10,000 Americans under 20 years old had been diagnosed with diabetes in 2018.
Men and women get diabetes at roughly the same rate. However, prevalence rates are higher among certain races and ethnicities.
Prevalence rates are higher for Hispanic Americans of Mexican or Puerto Rican descent than they are for those of Central and South American or Cuban descent.
Diabetes Sick Day Rules
If you need to take insulin to control your diabetes, you should have received instructions about looking after yourself when you’re ill known as your “sick day rules”.
Contact your diabetes care team or GP for advice if you haven’t received these.
The advice you’re given will be specific to you, but some general measures that your sick day rules may include could be to:
- keep taking your insulin it’s very important not to stop treatment when you’re ill your treatment plan may state whether you need to temporarily increase your dose
- test your blood glucose level more often than usual most people are advised to check the level at least four times a day
- keep yourself well hydrated make sure you drink plenty of sugar-free drinks
- keep eating eat solid food if you feel well enough to, or liquid carbohydrates such as milk, soup and yoghurt if this is easier
- check your ketone levels if your blood glucose level is high
Seek advice from your diabetes care team or GP if your blood glucose or ketone level remains high after taking insulin, if:
- you’re not sure whether to make any changes to your treatment
- you develop symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis
- you have any other concerns
Read more about sick day rules
Treatments For Type 1 Diabetes
Although there is currently no known cure for type 1 diabetes, several effective treatments are available, helping people to manage the disease and live a full life. Your doctor can help you manage Type 1 diabetes so you can assume life normally. You may need an insulin shot every day to manage blood levels and provide the energy the body needs.
Your doctor may also recommend checking your blood sugar levels regularly. This helps ensure that youre keeping it as close to the target level as possible to avoid complications.
Managing diabetes is similar to managing any healthy lifestyle by eating healthy foods, getting adequate physical activity, and controlling both cholesterol and blood pressure.
Recommended Reading: How Many Carbs Should A Pre Diabetic Eat Per Day
What Is The Treatment For Type 1 Diabetes In Children
Treatment for type 1 diabetes is lifelong and requires daily insulin injections or use of an insulin pump. The pump holds a reservoir filled with insulin. Tubing connects the reservoir to the cannula, or tube, which is inserted just under the skin. The pump is worn outside the body on a belt or pocket. These treatments help to control blood glucose levels.
Symptoms Of Type 1 Diabetes In Adults May Occur Suddenly
Its important to realize that early signs of type 1 diabetes in adults often develop quickly and may sometimes be brushed offor mistaken for illness. Heres what you should look out for:
Frequent UrinationIf youre constantly running to the bathroom, your kidneys may be trying to rid your blood of excess sugar, resulting in an increased need to urinate.
Extreme thirstIncreased urination can then result in dehydration, which will leave you feeling more thirsty than normal.
Increased appetiteIf youre suddenly hungry all the time it may be because your body isnt able to get proper energy from the food you eat.
Unexpected weight lossAlong the same lines, if your body is losing sugar in your urine instead of absorbing it, you may lose weight without trying.
You May Like: Protein Shake For Diabetic Patients
What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Type 1 Diabetes
People can have diabetes without knowing it because the symptoms aren’t always obvious and they can take a long time to develop. Type 1 diabetes may come on gradually or suddenly.
When a person first has type 1 diabetes, they may:
- pee a lot because the body tries to get rid of the extra blood sugar by passing it out of the body in the urine
- drink a lot to make up for all that peeing
- eat a lot because the body is hungry for the energy it can’t get from sugar
- lose weight because the body starts to use fat and muscle for fuel
- feel tired a lot
If these early symptoms of diabetes aren’t recognized and treatment isn’t started, chemicals can build up in the blood and cause stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, breathing problems, and even loss of consciousness. Doctors call this diabetic ketoacidosis, or DKA.
There’s good news, though getting treatment can control or stop these diabetes symptoms from happening and reduce the risk of long-term problems.
Regulator Of Endocannabinoid Metabolism
Insulin is a major regulator of and insulin treatment has been shown to reduce ECs, the and , which correspond with insulin-sensitive expression changes in enzymes of EC metabolism. In insulin-resistant , patterns of insulin-induced enzyme expression is disturbed in a manner consistent with elevated EC and reduced EC degradation. Findings suggest that adipocytes fail to regulate EC metabolism and decrease intracellular EC levels in response to insulin stimulation, whereby insulin-resistant individuals exhibit increased concentrations of ECs. This dysregulation contributes to excessive accumulation and reduced release from abdominal adipose tissue, and further to the onset of several cardiometabolic risk factors that are associated with obesity and .
, also known as “low blood sugar”, is when decreases to below normal levels. This may result in a variety of including clumsiness, trouble talking, confusion, , or death. A feeling of hunger, sweating, shakiness and weakness may also be present. Symptoms typically come on quickly.
The most common cause of hypoglycemia is used to treat such as insulin and . Risk is greater in diabetics who have eaten less than usual, exercised more than usual or have drunk . Other causes of hypoglycemia include , certain , such as , , , , , , and a number of drugs including alcohol. Low blood sugar may occur in otherwise healthy babies who have not eaten for a few hours.
Recommended Reading: How Many People In The Us Have Type 1 Diabetes
What Is Diabetic Coma
Diabetic coma is a situation in which the patient suffers from unconsciousness due to very high or very low blood sugar and glucose levels. Diabetic coma is a dangerous condition as it might even lead to the death of the patient concerned. It is therefore important to understand the causes behind the same.
Causes of Diabetic Coma
Following are the causes of diabetic coma:
Hypoglycemia:
You can suffer from hypoglycemia or low blood sugar if you have too much of insulin in your body or due to lack of food.
Diabetic Hyperosmolar Syndrome:
This is the condition when the blood glucose levels are too high. The excess sugar makes its way to the urine through the blood and this process drains away a lot of useful fluids from the blood. This condition might lead to diabetic coma by causing excessive dehydration. This condition is most common in middle-aged people who usually suffer from type 2 diabetes.
Diabetes Ketoacidosis:
This is a condition when ketones get accumulated in the body. This happens when there is a lack of energy in the muscle cells of the body and the stored fat of the body may then be utilized.
This condition is most common in those who suffer from type 1 diabetes condition.
Structural Analysis And Synthesis
Purified animal-sourced insulin was initially the only type of insulin available for experiments and diabetics. was the first to produce the crystallised form in 1926. Evidence of the protein nature was first given by , , and Philip A. Shaffer in 1924. It was fully proven when Hans Jensen and Earl A. Evans Jr. isolated the amino acids phenylalanine and proline in 1935.
The amino acid structure of insulin was first characterized in 1951 by , and the first synthetic insulin was produced simultaneously in the labs of at the and at in the mid-1960s. was achieved by Chinese researchers in 1965. The complete 3-dimensional structure of insulin was determined by in ‘s laboratory in 1969.
The first genetically engineered, synthetic “human” insulin was produced using in 1978 by and at the of the in collaboration with at . Genentech, founded by Swanson, Boyer and , went on in 1982 to sell the first commercially available biosynthetic human insulin under the brand name . The vast majority of insulin used worldwide is biosynthetic recombinant “human” insulin or its analogues. Recently, another approach has been used by a pioneering group of Canadian researchers, using an easily grown plant, for the production of much cheaper insulin.
Two other Nobel Prizes have been awarded for work on insulin. British molecular biologist , who determined the of insulin in 1955, was awarded the 1958 . received the 1977 Nobel Prize in Medicine for the development of the for insulin.
You May Like: What Do You Do If You Think You Have Diabetes
Yellowish Scaly Patches On And Around Your Eyelids
These develop when you have high fat levels in your blood. It can also be a sign that your diabetes is poorly controlled.The medical name for this condition is xanthelasma.
Take action
- Tell your doctor about the yellowish scaly patches around your eyes.
- Talk with your doctor about how to better control your diabetes. Controlling diabetes can clear the scaly patches.
Current Benefits Of Staging Type 1 Diabetes
There are beneficial short-term clinical outcomes for subjects followed prospectively in natural history studies. In DAISY, a study of genetically at-risk children, only 3% of study participants were hospitalized at diagnosis compared with 44% of age- and sex-matched children diagnosed in the community . In the TEDDY study, 30% of children aged < 5 years were presymptomatic at the time of diagnosis of type 1 diabetes based on ADA diagnostic criteria and, if symptomatic, were significantly less likely to experience DKA at onset than comparable populations . Similarly, in the German BABYDIAB and the Munich Family Study, children who were followed after screening positive for islet autoantibodies had a lower prevalence of DKA . A majority of DPT-1 study participants were diagnosed with type 1 diabetes based on laboratory metabolic parameters without symptoms, with only 3.67% developing DKA . In contrast, DKA at onset of type 1 diabetes was observed in 30% of youth in the population-based SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth study and affected 46% of youth at diagnosis in Colorado in 2012, representing a 55% increase from 1998 to 2012 . DKA at onset of type 1 diabetes is associated with increased mortality and longer hospitalizations is less likely to be associated with a partial remission, or honeymoon phase and is more commonly associated with lower residual -cell function, worse metabolic control, higher insulin requirements, and adverse short-term neurocognitive outcomes .
Don’t Miss: Body Wash For Diabetic Skin
What Problems Can Happen With Type 1 Diabetes
Not having the right amount of sugar in the blood can lead to:
- hyperglycemia: This is when blood sugars are too high. Kids with hyperglycemia may be extra thirsty, pee more than usual, and lose weight. High blood sugars can be treated. If they arent, kids can develop health issues later in life.
- diabetic ketoacidosis : This serious condition needs treatment right away. When theres not enough insulin in the body to let the glucose into the cells, the body starts to break down fat instead of sugar. Symptoms of DKA can include nausea, vomiting, belly pain, fast breathing, and, in severe cases, unconsciousness.
- hypoglycemia: This is when blood sugars are too low and can sometime happen when people are being treated for diabetes. Symptoms can include headache, weakness, shakiness, anxiety, and sweating.
- growth and development problems: Some kids might grow slower than their peers or start puberty later than usual.
Type 1 Diabetes In Children
Type 1 diabetes was once known as juvenile diabetes. That is because its frequently diagnosed in children and young adults. By comparison, type 2 diabetes is typically diagnosed in older adults. However, both types can be diagnosed at almost any age.
According to a
The ketogenic diet has shown some benefits for people with type 2 diabetes.
The high fat, low carb diet may help manage blood sugar levels, according to 2018 research . It can even lead to weight loss, a goal for many people with type 2.
For type 1 diabetes, however, the keto diet hasnt been well-studied. To date, the general dietary recommendation for this type of diabetes is a low carb diet. However, researchers are looking at the possible benefits and safety of a diet that restricts carbs even more for people with type 1 diabetes.
One small study found that people with type 1 diabetes who followed the keto diet for more than 2 years showed better A1C results and glycemic control. However, these individuals also had higher blood lipids and more low blood sugar episodes. Long-term safety is unknown.
If youre interested in trying the keto diet and you have type 1 diabetes, start by talking with your doctor. They may refer you to a registered dietitian or nutritionist to help you find a plan that is right for you.
Recommended Reading: How Much Does It Cost To Make Insulin
What Is Type 1 Diabetes In Children
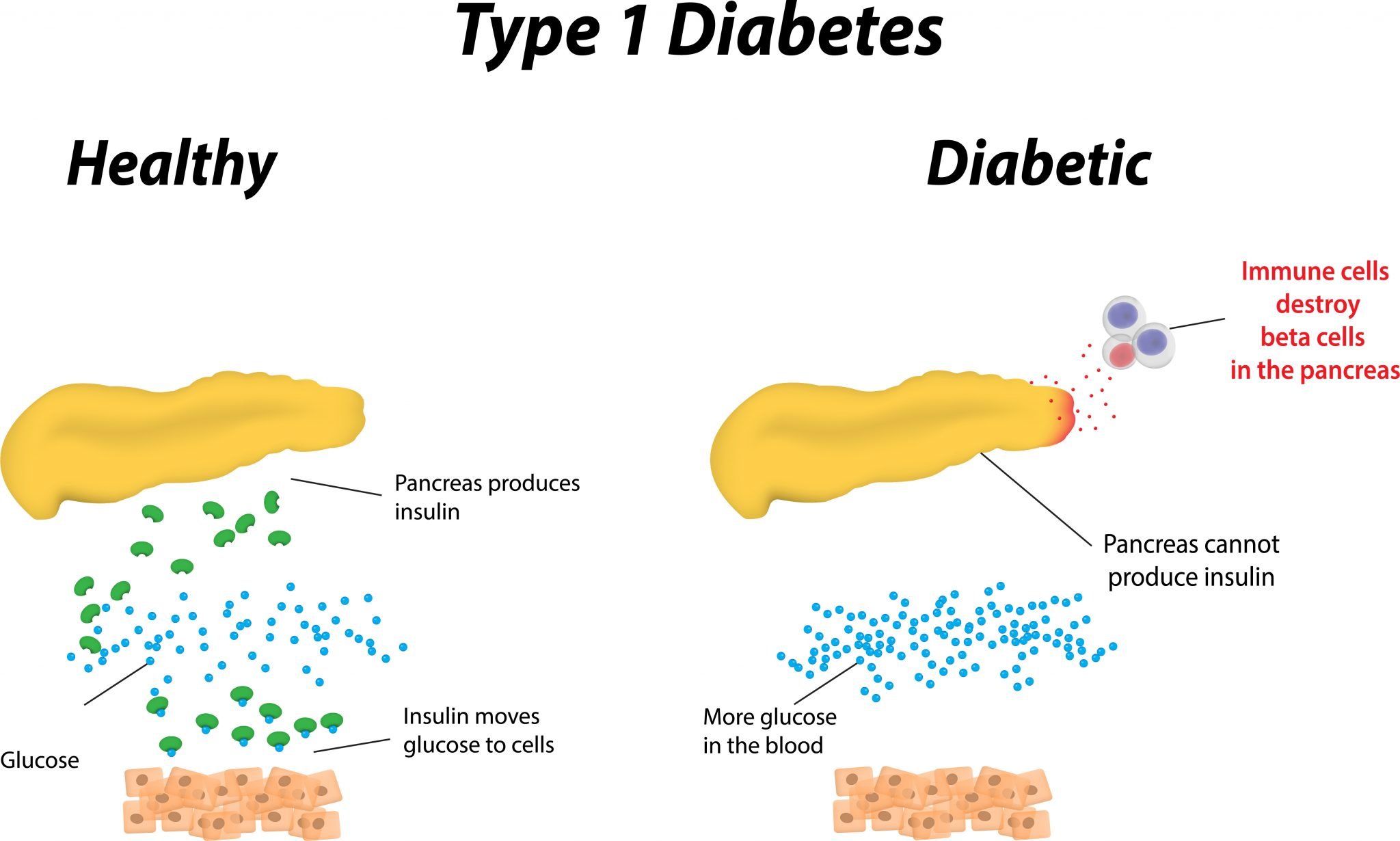
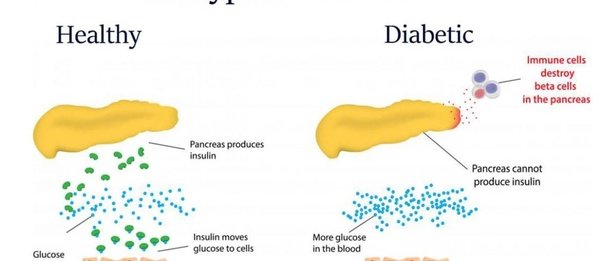
Type 1 diabetes in children, or juvenile diabetes, is a disease that requires lifelong management. Type 1 diabetes occurs when the autoimmune system attacks and destroys cells in the pancreas called beta cells, which produce insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps sugar, or glucose, enter cells to give them energy.
When there is no insulin, too much sugar stays in the bloodstream. This can lead to a life-threatening condition.
Staging Presymptomatic Type 1 Diabetes: A Scientific Statement Of Jdrf The Endocrine Society And The American Diabetes Association
Diabetes Care
Richard A. Insel, Jessica L. Dunne, Mark A. Atkinson, Jane L. Chiang, Dana Dabelea, Peter A. Gottlieb, Carla J. Greenbaum, Kevan C. Herold, Jeffrey P. Krischer, Åke Lernmark, Robert E. Ratner, Marian J. Rewers, Desmond A. Schatz, Jay S. Skyler, Jay M. Sosenko, Anette-G. Ziegler Staging Presymptomatic Type 1 Diabetes: A Scientific Statement of JDRF, the Endocrine Society, and the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 1 October 2015 38 : 19641974.
Also Check: Financial Help With Diabetic Supplies
Treating Type 1 Diabetes
It’s important that diabetes is diagnosed as early as possible. If left untreated, type-1 diabetes is a life-threatening condition. It’s essential that treatment is started early.
Diabetes can’t be cured, but treatment aims to keep your blood glucose levels as normal as possible and control your symptoms, to prevent health problems developing later in life.
If you’re diagnosed with diabetes, you’ll be referred to a diabetes care team for specialist treatment and monitoring.
As your body can’t produce insulin, you’ll need regular insulin injections to keep your glucose levels normal. You’ll be taught how to do this and how to match the insulin you inject to the food you eat, taking into account your blood glucose level and how much exercise you do.
Insulin injections come in several different forms, with each working slightly differently. You’ll most likely need a combination of different insulin preparations.
Insulin is given to some patients by a continuous infusion of fast acting insulin . This is where a small device constantly pumps insulin into your bloodstream through a plastic tube that’s inserted under the skin with a needle.
There are alternatives to insulin injections and pumps, but they’re only suitable for a small number of patients. They are:
Read more about diagnosing diabetes and treating type 1 diabetes
Ensuring A Long Life With Diabetes
Death is an unpleasant subject and no one wants to die of any disease. Hence, taking a certain precaution is a must as this can increase the life expectancy to a great extent. The following paragraphs deal with the subject as to how can you increase the life expectancy even if you suffer from a chronic condition like diabetes.
Hence, ensure a long life with diabetes by taking the following simple steps:
- The first and foremost thing which is of prime importance in diabetes is to maintain healthy and recommended levels of blood glucose.In this regard, the following should be kept in mind:
The most important consideration, while you try to manage type 1 diabetes in your child is to regularly monitor the level of blood sugar or blood glucose. The following prescribed range of blood glucose should be kept in mind:
- For a diabetic patient, the fasting blood sugar is under 126mg/dl or even higher.
- As per the American Diabetes Association, the normal blood sugar for a diabetic should be around 80-130mg/dl before the meals and around 200mg/dl a couple of hours after meals.
The recommended levels for type 2 diabetes include:
Recommended Reading: How Does Diabetes Cause Kidney Failure