Get The Medicine Ready To Use:
- Check the label. Check that you have the correct medicine. Also check the expiration date. Use a new pen if the expiration date has passed.
- Check the color of the medicine. The medicine in the cartridge should be clear, colorless, and free of particles or clumps. Use a new pen if the medicine is cloudy or has particles in it.
Cardiovascular Effects Of The New Compounds
While he main physiologic benefits demonstrated from exenatide therapy have been on indexes of glycemic control, cardiovascular effects have also been described. In experimental models, GLP-1 receptors have been demonstrated in cardiac myocytes and in certain regions of the brain that regulate autonomic function . In some cases the use of GLP-1 infusion was associated with a doubling of stroke volume and an increase in cardiac output by > 50%, as well as significant decreases in left ventricular end-diastolic volume . Encouraging results were also documented in humans , but long-term safety data are required before we fully understand any potential benefits or risks derived from the hemodynamic influences of GLP-1-based therapies.
Regarding DPP-4 inhibitors, few data are available concerning cardiovascular markers or clinical outcomes. Given the preliminary data they might be considered in individuals with impaired ventricular function. However, no clinical trials using these agents have yet been reported in this or any other group of patients with cardiovascular disease. Glitazars may yield some reduction in blood pressure . The amylin mimetic drug pramlintide did not show cardiovascular advantages or risks .
What Are Oral Diabetes Medications And How Do They Work
Insulin is a hormone produced by cells in the pancreas called beta cells. Insulin helps the body use blood glucose for energy. People with type 2 diabetes do not make enough insulin and/or their bodies do not respond well to it, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. Oral diabetes medications bring blood sugar levels into the normal range through a variety of ways.
Read Also: How Does Diabetes Lead To Renal Failure
Global Non Insulin Anti Diabetes Drugs Market Size Status And Forecast 2021
Published on: Dec 2021 | From USD $3500 | Published By: QY RESEARCH JAPANESE | Number Of Pages: 95
MediPoint: Bariatric Surgery Devices – Global Analysis and Market ForecastsSummaryBariatric Surgery Devices is an ever growing specialty area within General Surgery. This report focuses on the Bariatric Surgery Devices diagnostics market in t…
USD $5995
United States Bariatric Procedures Outlook to 2023SummaryGlobalDataÂs new report, “United States Bariatric Procedures Outlook to 2023”, provides key procedures data on the United States Bariatric Procedures. The report provides procedure vol…
USD $2995
United States Transcervical Resection of the Endometrium Procedures Outlook to 2023SummaryGlobalDataÂs new report, “United States Transcervical Resection of the Endometrium Procedures Outlook to 2023”, provides key procedures d…
USD $2995
United States Uterine Fibroid Embolization Procedures Outlook to 2023SummaryGlobalDataÂs new report, “United States Uterine Fibroid Embolization Procedures Outlook to 2023”, provides key procedures data on the United States Uteri…
USD $2995
United Kingdom Bariatric Procedures Outlook to 2023SummaryGlobalDataÂs new report, “United Kingdom Bariatric Procedures Outlook to 2023”, provides key procedures data on the United Kingdom Bariatric Procedures. The report provides procedure …
USD $2995USD $2995USD $2995USD $2995USD $2995
What You Need To Know:
A pen is a device used to inject diabetes medicines. The pen contains a cartridge of diabetes medicine. The medicine in the pen helps control your blood sugar levels. Some medicines may also help you maintain or lose weight. The pen may be used with or without an insulin pen to control your diabetes.
You May Like: Cheapest Insulin In The World
Your Treatment Needs Can Change
Over time, your condition and treatment needs can change. If youve found it difficult to manage your blood sugar with lifestyle changes and other medications, your doctor might prescribe insulin. Following their recommended treatment plan can help you manage your condition and lower your risk of complications.
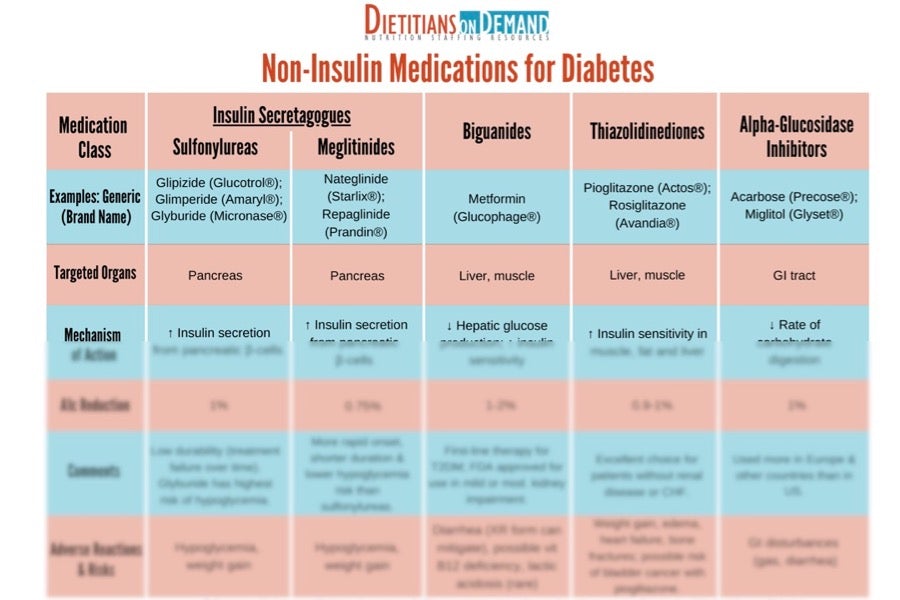
Glimepiride Glyburide Glipizide Gliclazide
These are drugs that stimulate the release of insulin from the beta cells of the pancreas. First generation sulfonylureas are rarely used. However, the second generation sulfonylureas like glimepiride, glyburide , glipizide, and gliclazide are widely used for the management of diabetes mellitus. There are other insulin secretagogues like repaglinide and nateglinide.
These drugs, its actions, side effects and contraindications are discussed in detail under Sulfonylurea Drug Information.
Recommended Reading: Are Omelettes Good For Diabetics
Approach To The Patient
Guidelines from the ADA and the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists recommend a comprehensive, patient-centered approach for achieving and maintaining glycemic control. Figure 1 provides multiple pharmacotherapy options based on A1C levels, fasting or postprandial glucose control, weight loss, and adverse effects.1,12,32 Although glycemic control is important, addressing other cardiovascular risk factors, such as hyperlipidemia and hypertension, is at least as important but is beyond the scope of this article.
Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Figure 1.
Algorithm for the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Information from references 1,12, and 32.
Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Figure 1.
Algorithm for the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Information from references 1,12, and 32.
Store The Pen As Directed:
Do not store your pen with a needle attached. Follow the storage directions on the label or package insert that came with the pen. Unopened pens can be stored in the refrigerator until you are ready to use them. Most pens can be opened and kept at room temperature. Store your pen in a cool, dry place. Do not keep your pen in direct sunlight or in your car. Throw away pens that have been frozen or exposed to temperatures above 85° F . If you travel, keep the pen in a cool pack.
You May Like: Why Are Insulin Prices So High
Weight Loss Surgery May Be An Option
If your body mass index a measure of weight and height meets the criteria for obesity, your doctor might recommend weight loss surgery to help treat type 2 diabetes. This procedure is also known as metabolic or bariatric surgery. It can help improve your blood sugar levels and lower your risk of diabetic complications.
In a joint statement issued in 2016, multiple diabetes organizations recommended weight loss surgery to treat type 2 diabetes in people with a BMI of 40 or higher. They also recommended weight loss surgery for people who have a BMI of 35 to 39 and a history of unsuccessfully trying to manage their blood sugar with lifestyle and medications.
Your doctor can help you learn if weight loss surgery is an option for you.
Combined Treatment With Classical Drugs
Figure 1
Histographical display of crude all-cause mortality over a mean 7.7-year follow-up in 11,322 CAD patients nondiabetic and diabetic on several therapeutic regimens. Mortality in patients on a combined glibenclamide/metformin regimen was significantly higher and almost quadrupled the figures documented for nondiabetic CAD patients. Significant statistical differences were still present when comparing the group on combined pharmacotherapy with the groups on other antidiabetic regimes. ND nondiabetics diet patients solely on diet gliben patients on glibenclamide metfor patients on metformin comb patients on a combined glibenclamide/metformin regimen. .
Hence, the combined antihyperglycemic treatment with classical drugs leads to a peculiar entanglement since sulfonylureas and metformin are 1) the most powerful antiabetic drugs 2) those presenting the most unfavorable cardiac effects 3) the most frequently employed combination in routine clinical practice .
Don’t Miss: What’s The Treatment For Type 2 Diabetes
Management Of Blood Glucose Levels
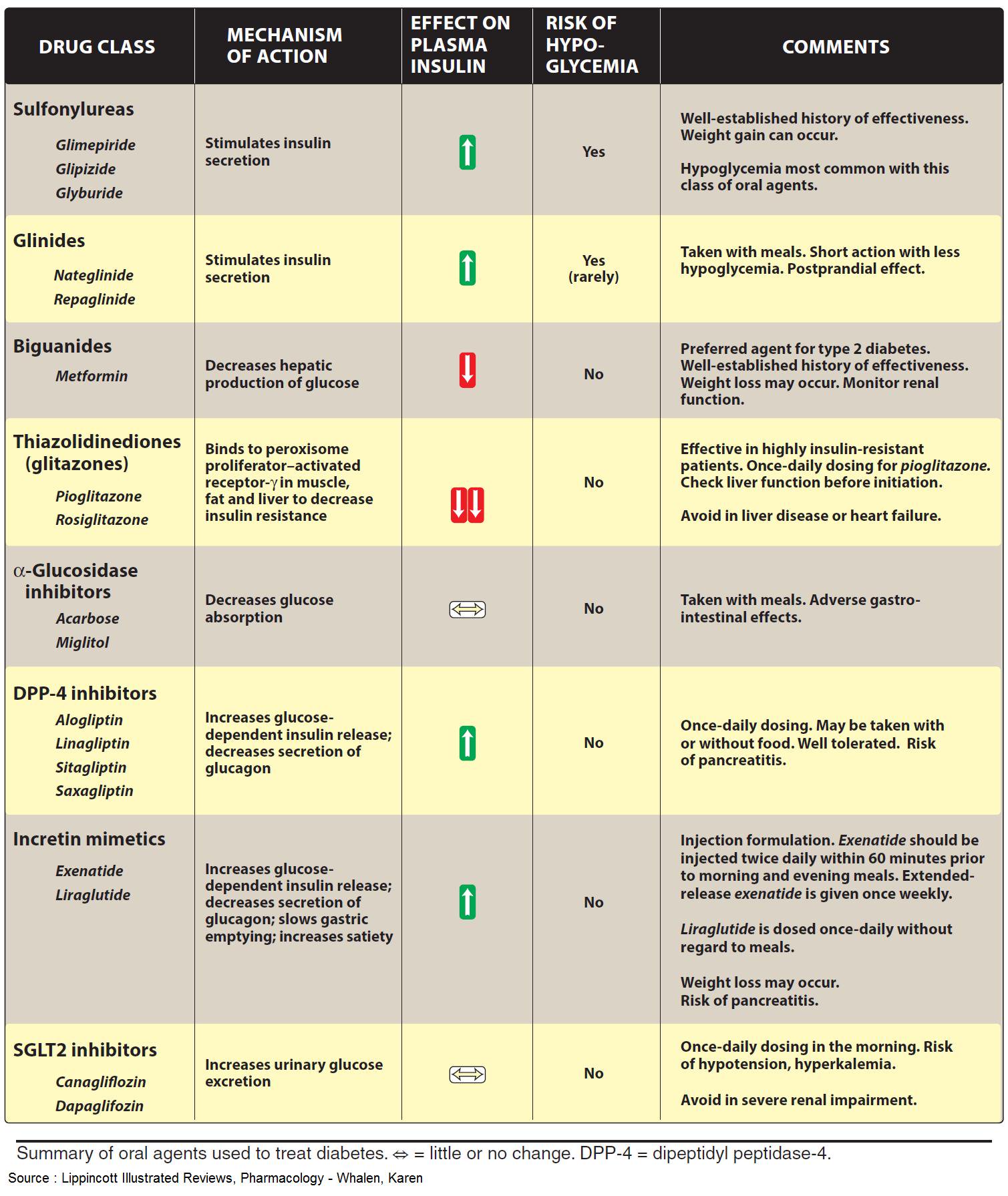
Medications for type 2 diabetes target multiple sites throughout the body to lower blood glucose levels . The ADA recommends starting therapy with metformin, because it is the only medication shown to reduce mortality and complications in randomized controlled trials .7 Additional medications should be added in a patient-centered, individualized fashion, although there is no evidence from RCTs that any of these medications reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications, cardiovascular mortality, or all-cause mortality.1 A 2011 comparative effectiveness review showed that metformin, second-generation sulfonylureas, thiazolidinediones, and repaglinide lowered A1C levels by about 1% when used as monotherapy and that combination therapies showed an additive effect on A1C levels.8 Table 1 lists common hypoglycemic agents for treating type 2 diabetes.1,9 Table 2 lists typical doses and costs of common hypoglycemic agents.10
Mechanisms of Action of Medications for Treating Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Information from:
American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes2014. Diabetes Care. 2014 37:S14-S80.
Powers AC, D’Alessio D. Chapter 43. Endocrine pancreas and pharmacotherapy of diabetes mellitus and hypoglycemia. In: Brunton LL, Chabner BA, Knollmann BC, eds. Goodman & Gilman’s Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 12th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill 2011.
Mechanisms of Action of Medications for Treating Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Information from:
Some Treatments Can Cause Side Effects
Different types of medication, surgery, and other treatments can cause side effects. The type and risk of side effects varies, from one treatment to another.
Before you start taking a new medication, talk to your doctor about the potential benefits and risks of using it. Ask them if it can interact with any other medications or supplements that you take. You should also let your doctor know if youre pregnant or breastfeeding, since some medications arent safe for pregnant or breastfeeding people to use.
Surgery can also put you at risk of side effects, such as infection at an incision site. Before you undergo any operation, ask your doctor about the potential benefits and risks. Talk to them about the recovery process, including steps you can take to reduce your risk of postsurgery complications.
If you suspect that youve developed side effects from treatment, contact your doctor. They can help pinpoint the cause of your symptoms. In some cases, they might adjust your treatment plan to help relieve or prevent side effects.
Don’t Miss: How Long Does Thc Stay In A Diabetics System
What Are The Side Effects Of The Non
Many people with type 2 diabetes will take a combination of medications to help control their diabetes. With combination therapy, there is increased risk for low blood sugar.
The sulfonylureas may cause hypoglycemia , skinrash or itching, sensitivity to sunlight, upset stomach, and weight gain.
The meglitinides may cause hypoglycemia and weight gain.
People taking biguanides may develop lactic acidosis, a rare but severe side effect. Excessive alcohol intake while on metformin can contribute to development of lactic acidosis. Other side effects include metallic taste in the mouth and diarrhea.
Thiazolidenediones can increase risk of heart failure and should not be used in patients with symptoms of heart failure. Liver enzymes should be checked regularly with use. Other side effects include weight gain, fatigue, swelling of the legs or ankles, increased risk for fractures in female patients. Avandia may have a potential increased risk for heart attack.
Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors may cause gastrointestinalproblems , although they are usually fleeting.
The DPP-4 inhibitor sitagliptin may cause serious allergic reactions, sore throat, upper respiratory infection, and headache.
Pramlintide may cause gastrointestinal problems , slight weight loss, headache, fatigue, dizziness, coughing, sorethroat, and skin reactions at the injection site.
Side effects of exenatide may include slight weight loss, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
- Cholesterol medications
Management Of Blood Glucose With Noninsulin Therapies In Type 2 Diabetes
CHRISTA M. GEORGE, PharmD, and LUCY L. BRUIJN, MD, MPH, University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, Tennessee
KAYLEY WILL, PharmD, Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, Abilene, Texas
AMANDA HOWARD-THOMPSON, PharmD, University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, Tennessee
Am Fam Physician. 2015 Jul 1 92:27-34.
Treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus begins with a comprehensive and collaborative approach. The American Diabetes Association treatment guidelines focus on medical nutrition therapy, exercise, pharmacologic therapy, and the prevention and management of diabetes-related complications.1 Selected major trials that form the basis for treatment recommendations are listed in eTable A. There is no evidence demonstrating the impact on complications or mortality for the newer agents described in this article.
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
Metformin should be used as first-line therapy to reduce microvascular complications, assist in weight management, reduce the risk of cardiovascular events, and reduce the risk of mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
A = consistent, good-quality patient-oriented evidence B = inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence C = consensus, disease-oriented evidence, usual practice, expert opinion, or case series. For information about the SORT evidence rating system, go to .
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
UKPDS 33A1
UKPDS 33A1
Don’t Miss: Financial Help With Diabetic Supplies
Contact Your Healthcare Provider If:
- You feel or see hard lumps in your skin where you inject your medicine.
- You think you gave yourself too much or not enough medicine.
- Your injections are very painful.
- You see blood or clear fluid on your injection site more than once after you inject medicine.
- You have questions about how to give the injection.
- You cannot afford to buy your diabetes supplies.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Pramlintide Is An Injected Medicine For People With Diabetes
In type 1 diabetes, Pramlintide can be taken in addition to insulin to help control mealtime blood sugars.
If you have type 2 diabetes, and lifestyle changes are not enough to control your blood sugar, typically, your provider will first start you on a single medicine. For people who are overweight, metformin is usually the first medicine prescribed.
If the single therapy doesnt work, additional medicines can be added. Many people require treatment with 2, 3 or more different medicines. If pill combinations dont work, an injected medicine such as an incretin-based medicine, amylin analog or insulin may be prescribed. Medicine combinations are used because different drugs target different parts of your bodys sugar regulation system.
Rarely, and usually due to other medical conditions, it may be necessary to start medical treatment of type 2 diabetes with insulin therapy. Usually, however, insulin therapy is the last treatment prescribed and is added only after the oral medications or non-insulin injections dont work.
In this section, you will learn about the non-insulin treatment options for glucose control in type 2 diabetes including the different medicines, how they work, doses, and side effects.
Don’t Miss: Can You Reverse Diabetic Neuropathy
What Are The Warnings And Precautions For Non
Diabetes medications can have interactions with other medications or supplements being used. Use of more than one diabetes medication can increase the risk for hypoglycemia. Beta-blocker medications can mask the symptoms of hypoglycemia.
Sulfonylureasmay increase the risk of death from cardiovascular disease. Prolonged exercise and alcohol intake increase the risk for hypoglycemia.Patients undergoing surgery or who have had recent trauma, stress, or infection may need to switch from a sulfonylurea to insulin to manage blood sugar levels. People with kidney or liver disease need to take precaution.
Because meglitinides may cause hypoglycemia, they should be taken right before meals to minimize the possibility of hypoglycemia. If a meal is to be skipped, the dose of the medication should also be skipped.
Thiazolidinediones may cause or exacerbate heart failure. Trouble breathing, rapid weight gain and fluid retention may indicate the onset of heart failure.
Avandia may potentially increase the risk of heart attack.
Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors should not be used in people with intestinal diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease or intestinal obstruction. People with kidneydysfunction may not be able to these medications.
Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors should be taken with the first bite of each meal.
Patients with kidney disease may require dosage adjustment if they are using a DPP-4 inhibitor.
Severe hypersensitivity reactions have occurred during use of sitagliptin.
Where To Inject Medicine:
- You can inject medicine into your abdomen, upper arm, and the front or side of the thigh.
- Do not inject medicine into areas where you have a wound or bruising. Medicine injected into wounds or bruises may not get into your body correctly.
- Inject your medicine at least 2 inches away from where you inject insulin.
- Use a different area within the site each time you inject medicine. For example, inject medicine into different areas in your abdomen. Medicine injected into the same area can cause lumps, swelling, or thickened skin.
You May Like: Does Insulin Cause Erectile Dysfunction
If You Take Too Much Or The Wrong Type Of Medicine
If you have taken too much or the wrong type of diabetes medicine, its important that you contact your doctor or diabetes nurse or educator for advice.
Taking too much diabetes medicine can cause your blood glucose level to drop too low. This is known as hypoglycaemia or a hypo, and can lead to a serious situation if not addressed.
- If you think you may have taken too much diabetes medicine and you monitor your blood glucose at home, test your blood glucose level as soon as possible. If you dont monitor glucose levels routinely, contact your doctor or seek other medical advice straight away.
- If you find your blood glucose level is low, you will need to address this straight away.
Get helpful tips about non-insulin devices.
Noninsulin Antidiabetic Drugs For Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Are We Respecting Their Contraindications

Josep Franch-Nadal
1Primary Health Care Center La Torrassa, Consorci Sanitari Integral, Ronda Torrassa 151-153, 08903 LHospitalet de Llobregat, Spain
2DAP-Cat Group, Unitat de Suport a la Recerca Barcelona Ciutat, Institut Universitari dInvestigació en Atenció Primària Jordi Gol , Sardenya 375, 08006 Barcelona, Spain
3Primary Health Care Center Raval Sud, Gerència dÀmbit dAtenció Primària Barcelona Ciutat, Institut Català de la Salut, Avinguda Drassanes 17-21, 08001 Barcelona, Spain
4CIBER of Diabetes and Associated Metabolic Diseases , Instituto de Salud Carlos III , Monforte de Lemos 3-5, 28029 Madrid, Spain
5Primary Health Care Center La Mina, Gerència dÀmbit dAtenció Primària Barcelona Ciutat, Institut Català de la Salut, Mar S/N, 08930 Sant Adrià de Besòs, Spain
6Department of Endocrinology & Nutrition, Health Sciences Research Institute and Hospital Universitari Germans Trias i Pujol, Carretera Canyet S/N, 08916 Badalona, Spain
7Primary Health Care Center Sant Martí de Provençals, Gerència dÀmbit dAtenció Primària Barcelona Ciutat, Institut Català de la Salut, Fluvià 211, 08020 Barcelona, Spain
8Primary Health Care Center Anglès, Gerència dÀmbit dAtenció Primària Girona, Institut Català de la Salut, Carretera de Girona S/N, 17160 Anglès, Spain
9Primary Health Care Center Salt, Gerència dÀmbit dAtenció Primària Girona, Institut Català de la Salut, Manel de Falla 35, 17190 Salt, Spain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Design
2.2. Studied Variables
Also Check: What Can People With Type 2 Diabetes Eat