When To See A Healthcare Provider
Getting professional medical advice from a healthcare provider like an endocrinologist is the best way to learn more about whether your blood sugar levels are where they should be. Not getting proper treatment for low or high blood sugar levels can be serious and lead to health complications, especially for those with diabetes. Diabetes complications include nerve damage, kidney disease, heart disease, or heart attacks.
If you see a healthcare provider about your blood sugar levels, be prepared to answer questions about risk factors like what you eat, how much you exercise, and about your family history. Some healthcare providers may want to take a blood sample to test your blood sugar levels. They may also order an A1C test, which is a blood test that measures blood sugar levels over several months. You may have to fast eight hours beforehand to get accurate test results, so its always a good idea to check before your appointment.
If your blood sugar level goes above 250 mg/dL, you should go to the ER for immediate medical attention, says Dr. Tarugu. Emergency rooms are equipped to handle high blood sugar levels and can administer treatments like insulin therapy and fluid or electrolyte replacement.
Normal Blood Sugar Levels
It is important to work with your healthcare provider to maintain healthy blood sugar levels. The following is a list of healthy blood sugar levels.
If an individual has type 1 diabetes the blood sugar should be the following:
- Before meals: From 90 to 130 mg/dL for adults
- After meals : Less than 180 mg/dL for adults
- At bedtime: From 90 to 150 mg/dL for adults
If an individual has type 2 diabetes, levels should be the following:
- Before meals: From 70 to 130 mg/dL for adults
- After meals : Less than 180 mg/dL for adults
Blood Sugar Target Ranges For Gestational Diabetes
The strictest and tightest control of blood sugars is necessary when a patient has gestational diabetes. This tight control is necessary to keep mother and baby safe when the mother has gestational diabetes.
In addition to increased complications for the mother, an infant born to a mother with gestational diabetes is at an increased risk of being born with a high birth weight . This condition is called macrosomia. Later on in life, the infant may be more prone to becoming obese, and to developing Type 2 Diabetes.
When the extra sugar in the mothers bloodstream crosses the placenta, the infants pancreas is signaled to make more insulin. Therefore, the infant grows too large in utero.
After birth, the infant is at increased risk of hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar related to the excessive amounts of insulin their pancreas produces.
Blood sugar target ranges for gestational diabetes from the American Diabetes Association
The blood sugar target ranges for gestational diabetes coincide with an A1C of less than 6 percent. As long as this is able to be achieved without episodes of low blood sugar or hypoglycemia, this tight control is sought out
- Fasting and pre-meal less than or equal to 95 mg/dl
- One-hour post-meal less than or equal to 140 mg/dl
- Two-hour post-meal less than or equal to 120 mg/dl
For women with preexisting diabetes who become pregnant, blood sugar target levels are as follows:
If you need more information:
You May Like: Does One High A1c Mean Diabetes
Inactivity Also Negatively Affects Blood Sugar
As if you needed more science-backed reasons to exercise, heres another: You can help regulate your glucose levels and reduce your risk of prediabetes and type 2 diabetes with exercise. Why is inactivity linked to higher blood sugar? Inactivity leads to a decrease in your insulin sensitivity and increases your insulin requirements, says Zuckerbrot. Exercise uses up your bodys glucose, making you more sensitive to insulin. According to the American Diabetes Association, physical activity can lower your blood glucose for up to 24 hours or more after you work out, and regular exercise can lower your overall blood glucose level . On the other hand, research published in the Journals of Gerontology found that two weeks of inactivity could increase the risk of blood sugar-control problems in older, overweight people who already had prediabetes.
A Note About Accuracy

In the USA, a blood glucose meter can be approved for sale so long as the results are consistently within 20% of the accurate value. That means that if your blood sugar is 180 mg/dL or 10 mmol/L, your meter may display a result of 216 mg/dL or 144 mg/dL . In practice, most meters are more accurate than that, but even an expensive hospital blood test using calibrated equipment has a 10% margin of error.
So dont panic if you check your blood sugar and its 140 mg/dL and a few minutes later, its 150 mg/dL . This may just be the normal discrepancy in the measurements. Look for trends over time to truly understand whats happening.
Similarly, CGM measurements also have a margin of error , and varies slightly depending on the specific system.
You May Like: What Is Considered Low Blood Sugar For Type 2 Diabetes
Managing Your Child’s Diabetes
One of the most important differences between children and adults with diabetes is day-to-day management, Quinn says. “As children grow, hormones human growth hormone in particular make them more resistant to insulin,” she says. “Insulin dosages need to be adjusted quite regularly .” She adds that it’s critical for children with diabetes to be seen regularly by a doctor, in order to keep their medication doses on track with their growth.
Read more:7 Foods That Won’t Cause Blood Sugar Spikes
Type 1 diabetes is typically treated through insulin injections. Type 2 is treated through lifestyle changes and possibly medication , according to KidsHealth. No matter which type of diabetes your child has, it’s critical to check their blood sugar regularly to make sure that their blood sugar levels are in the target range.
Uncontrolled diabetes can eventually lead to eye problems, nerve damage, kidney disease, high blood pressure and/or stroke, according to the American Diabetes Association. This may sound frightening, but the good news is that these complications can be avoided through proper diabetes management. Therefore, though it may be challenging at times, it’s very important that you as a parent help your child learn how to manage his or her own diabetes. After all, at some point, it will be your child’s responsibility to manage his or her own health.
Tip
The Right Blood Sugar Level At Bedtime
Routine blood sugar checks must be an essential part of your routine. You should not miss checking your sugar before bedtime as it helps to access which foods work and which dont for your diabetes. Ideally, your blood sugar must be between 90 to 150 mg/dL before you go to sleep. For a normal person, blood sugar levels should lie between 70 to 130 mg/dL.
You May Like: Is Insulin Used To Treat Type 2 Diabetes
Artificial Sweeteners Dont Benefit Blood Sugaror Do They
Theres mixed reviews about the impact of artificial sweeteners on blood sugar level. Some research has suggested that the sweet taste is enough to trick your bodys response, as if it was actually receiving sugar. But, the sweetener stevia may hold some promise for actually reducing blood sugar, according to one study. Some research suggests stevia may have a beneficial impact on blood glucose levels, however, more research needs to be done in this area, Palinski-Wade says.
When To See A Doctor
According to the University of Michigan, blood sugar levels of 300 mg/dL or more can be dangerous. They recommend calling a doctor if you have two readings in a row of 300 or more.
See your doctor if you have consistently high blood sugar levels. Symptoms of this include:
- increased thirst
- high levels of sugar in urine
Ask your doctor how often to check your blood sugar and about your ideal blood sugar levels.
If you dont currently see a doctor who specializes in diabetes, known as an endocrinologist, you can find one by searching the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists website.
You can find a certified diabetes educator by visiting the American Diabetes Associations website and searching by zip code.
Summary
Talk to your doctor if you have consistently high blood sugar readings or symptoms of chronic hyperglycemia.
Checking your blood sugar and then treating hyperglycemia early will help prevent any complications.
Health problems can arise when someone has high blood sugar regularly and without treatment.
Examples of complications include:
- nerve damage, called diabetic neuropathy, that may affect sensations in the feet and hands
- diabetic retinopathy, or damage to the blood vessels in the eyes that affects vision
- increased risks for kidney problems
- increased risks for heart problems
Taking steps to keep your blood sugar at target levels can help to minimize the likelihood that these complications will occur.
Read Also: How Much Sugar Can A Type 2 Diabetic Have
Get Educated About Diabetes Management
There are science-backed strategies to drop blood sugar back to a normal range, and Clement says she puts diabetes education at the forefront of what everyone should know about glucose. There is not enough emphasis on the consequences of uncontrolled diabetes and resulting complications such as neuropathy, heart disease, eye disease, and kidney disease, she says. In addition to good medical care, diabetes self-management education can help patients learn to take care of their disease.
What Is Blood Glucose
Blood glucose comes from food. When an individual eats, the food is broken down into sugar and sent to the blood. The insulin is what helps the sugar go into the cells. Once this happens, the sugar that has moved from the blood into the cells is used for energy or is stored.
Glucose is known as the bodys main energy source. Too much glucose in the blood, or if it is not absorbed properly, can create health issues both long and short term. To keep a healthy blood sugar level, it is important to:
- Eat healthily
- Check blood glucose levels
- Keep in contact with your healthcare provider
It is important to keep in contact with a healthcare professional, eat properly, check your blood glucose, and exercise regularly to keep a healthy blood sugar level.
Also Check: Do I Need Prescription For Insulin
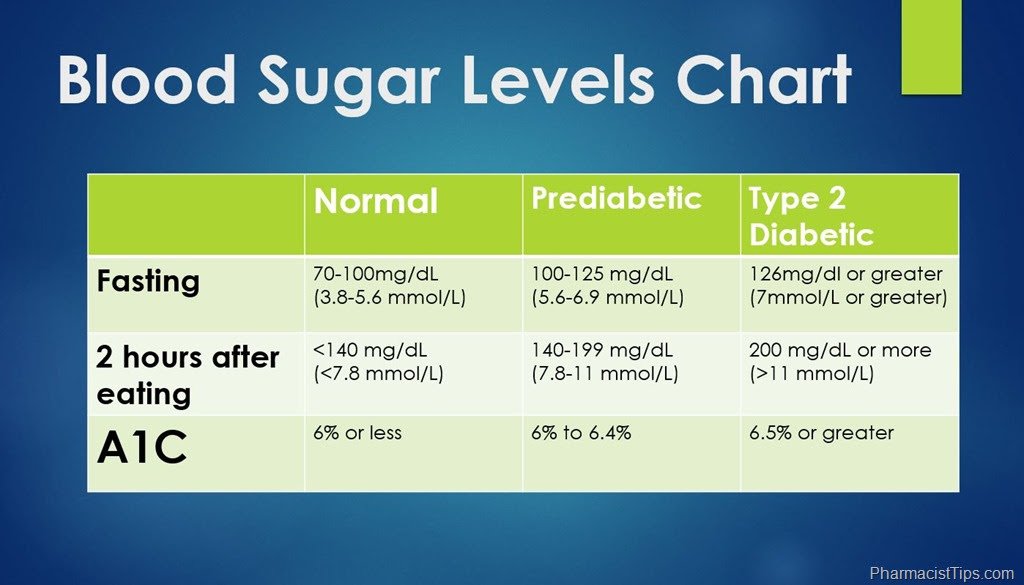
Normal Blood Sugar Ranges In Healthy Non
For a person without any type of diabetes, blood sugar levels are generally between 70 to 130 mg/dL depending on the time of day and the last time they ate a meal. Newer theories about non-diabetic blood sugar levels have included post-meal blood sugar levels as high as 140 mg/dL.
Here are the normal blood sugar ranges for a person without diabetes according to the American Diabetes Association:
- Fasting blood sugar : under 100 mg/dL
- 1 hour after a meal: 90 to 130 mg/dL
- 2 hours after a meal: 90 to 110 mg/dL
- 5 or more hours after eating: 70 to 90 mg/dL
Types Of Diabetes And Their Major Causes
Diabetes is mainly of 3 types, type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes, and with all 3 types of diabetes, the body is either not able to produce enough insulin or unable to use the insulin that it makes, leading to high blood sugar levels.Type 1 Diabetes usually starts in childhood and carries on for life. Type 1 Diabetes occurs when the patients pancreas stops making insulin. The causes of Type 1 Diabetes are:
- Family History and Genetics: A person having a close relative with Type 1 Diabetes usually has a high chance of getting the condition himself. So, it is imperative for every child with a parent or a sibling having Type 1 Diabetes to undergo a screening test for Type 1 Diabetes.
- Pancreatic Diseases: Persons with diseased pancreas may acquire Type 1 Diabetes because the pancreas may fail to produce insulin needed to maintain normal blood sugar levels.
- Infections or Illnesses that Cause Damage to the Pancreas: Viral infections such as German measles, mumps, and rotavirus may cause damage to the beta cells of the pancreas which produce insulin and lead to the development of Type 1 Diabetes.
Type 2 Diabetes occurs when the body develops insulin resistance and is not able to make use of the insulin produced by the pancreas, leading to uncontrolled blood sugar levels. Type 2 Diabetes usually affects adults, but it can occur in individuals of any age. The main causes of Type 2 Diabetes include:
Read Also: Why Are Insulin Prices So High
How To Improve Blood Test Results
Identifying the foods or meals that regularly spike your blood sugar too high, too fast, or too long can help you to individualize your diet for longevity.
After a few weeks of testing your blood sugar levels after eating various types of food, you should have a clear record of how your body responds.
A balanced blood sugar results in a greater sense of wellbeing, having more energy, preventing the afternoon crash and feeling hangry , and getting a better nights rest.
Heres what It feels like to have normal blood sugar:
- No extreme hunger between meals
- No sleepiness after meals or mid-day
- Balanced mood
How Is Blood Sugar Measured
In the United States, blood sugar is measured in milligrams per deciliter . This is abbreviated as mg/dl.
In Europe and Canada, blood sugar is measured a little differently, by millimole per liter, which is abbreviated mmol. However its measured, blood sugar is the concentration of sugar or glucose in the bloodstream.
If you multiply the Canadian or European mmol, by the number 18, you can calculate milligrams per deciliter.
In other words, if a person in Canada reports their blood sugar as an 8, multiply 8 times 18 to give you the number 144 . Using this calculation, this persons blood sugar = 144 mg/dl, .
Also Check: Symptoms Of Low Blood Sugar In Type 2 Diabetes
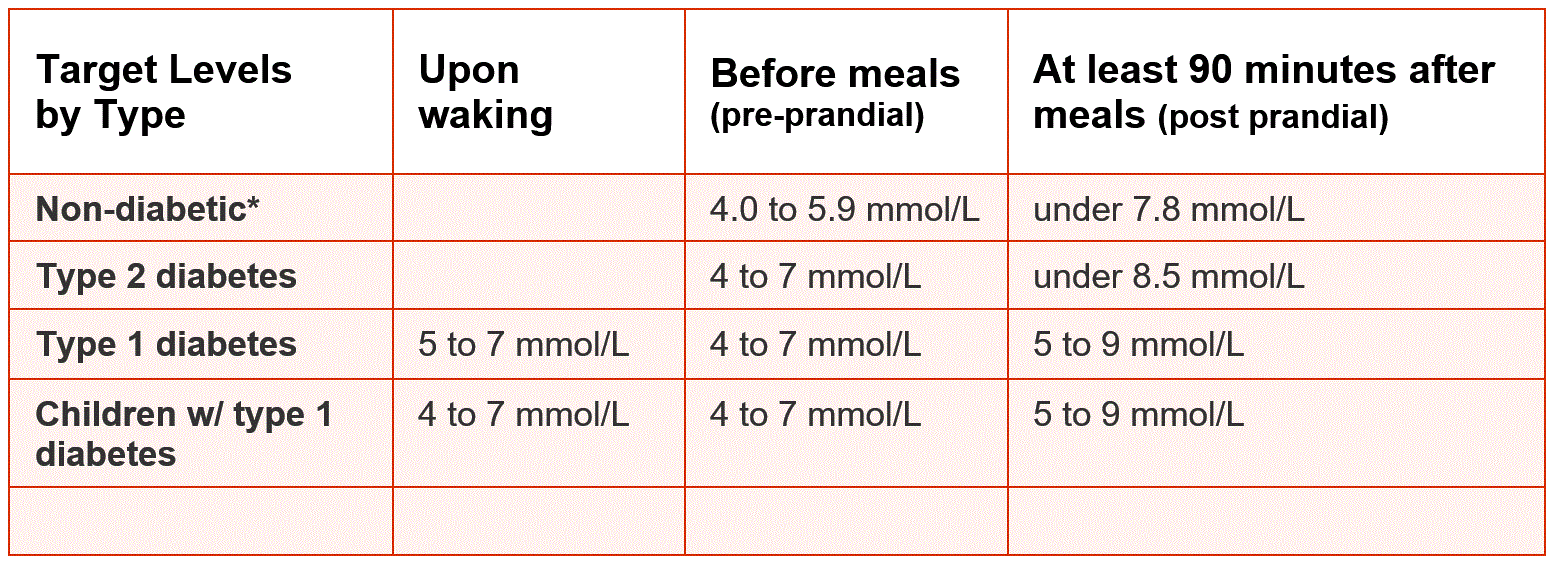
What Is Normal Blood Glucose
There is no one blood glucose level that defines a person as normal. The table of blood glucose levels below gives the appropriate values at different times and in different states, according to the American Diabetes Association. For example, insulin-dependent diabetics often use an upper limit of 7 mmol/L or 140 mg/dL, while non-insulin-dependent diabetics may aim for less than 6 mmol/L or 108 mg/DL.
The blood glucose levels range between less than 100-180 mg/dL for adults from 20 years or older. Depending on your age this may vary.
- Fasting: Less than 5.6 mmol/L or 100 mg/DL
- Before meal: 3.9-7.2 mmol/L or 70-130 mg/DL
- 1-2 hours after eating: Less than 10 mmol/L or 180 mg/DL
- Bedtime: 5.6-7.8 mmol/L or 100-140 mg/DL
Be aware that the above numbers might be different for everyone depending on your doctor’s recommendations.
Avoid Sweets Right Before Bed
We have discussed how insulin sensitivity decreases in the evening, as well as the potential reactive hypoglycemic effects of high sugar/starch foods. Avoiding sweets before bed can help circumvent both of those issues.
If you still find yourself craving something sweet, try switching to sources that include fiber or have a reduced sugar content . This can aid in smoothing out glucose levels.
Also Check: How To Care For Someone With Diabetes
Poor Sleep Isnt Great For Blood Sugar
Fact: You are more likely to eat more when youre sleep deprived. Plus, youll likely be craving junk food, which is not exactly great for your blood sugar level. According to the National Sleep Foundation, the connection may be because with lack of sleep, hormones get out of whack, and the stress hormone cortisol may prevent insulin from doing its job properly. With short-term sleep deprivation, levels can go back to normal with two nights of good sleep. But for long-term problems sleeping, including sleep apnea, see your doctor to reduce your diabetes risk.
Avoid Alcohol Before Nighttime
Another good habit is to avoid alcohol before going to bed. This can cause your blood sugar to increase quickly but leave you with low levels overnight. Avoiding alcohol for a few hours before bedtime will help keep the glucose in balance and prevent fluctuations.
If you do drink alcoholic beverages before going to bed try to eat a healthy snack with some carbohydrates to catch that low blood sugar after drinking alcohol.
Recommended Reading: How Many People In The Us Have Type 1 Diabetes
Best Ways To Lower Blood Sugar Quickly
When treated early, you can bring high blood sugar levels down and prevent complications, including DKA.
Some sources suggest that drinking water or eating a high protein snack can quickly lower your blood sugar levels, though there isnt enough research to support this.
If you have high blood sugar and need to lower it fast, try the following methods:
How Do Glucose Levels Change Overnight
As you sleep, your body is still working to regulate the fluctuations in your blood sugar levels from the day before.
The reason for this change in your blood sugar levels is the Somogyi effect which happens when someone with diabetes has too much insulin and it drops during sleep. The person also wakes up with higher blood sugar levels because of this phenomenon. Another reason is the Dawn phenomenon where people experience an increase in their blood sugar levels around the time that they wake up on any given morning. Eating your bedtime snack which can help regulate these changes and prevent too much fluctuation throughout the day and into the mornings.
Here are some tips for ensuring you have a restful night and don’t wake up feeling groggy-eat meals with healthy carbs at dinner time, eat a light snack before bedtime, or try to turn off electronics around two hours before bedtime.
Recommended Reading: How Does Diabetes Lead To Renal Failure