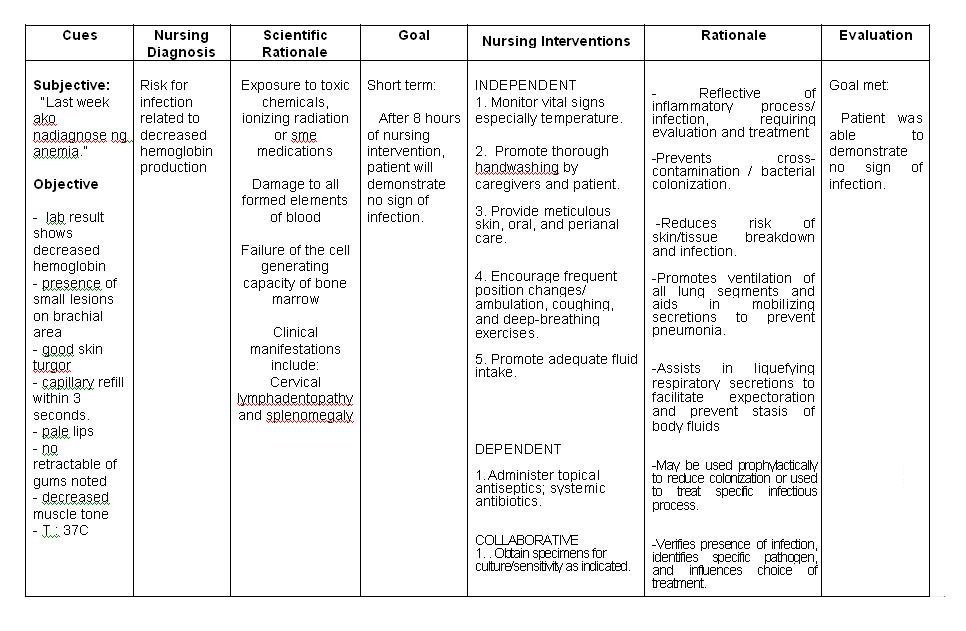
Does Insurance Cover A Type 2 Diabetes Care Plan
Some insurance providers may cover type 2 diabetes care plans within the context of DSM training.
For example, Medicare covers DSM training to prepare individuals to cope with and manage their condition. A care plan could also be part of this.
People with Medicare pay 20% of the Medicare-approved amount after the yearly deductible.
Many states require that insurers cover DSM training. This means that state-mandated insurers, such as Medicaid, are also likely to provide coverage.
However, individuals should check their policy documents to find details of coverage for their specific policy.
Nursing Care Plans Nursing Interventions
- The nurse will have to explain and engage the patient in verbalizing the relationship between diet and diabetes. The nurse will also give a return explanation in his/her own choice of words.
- Patients shall consult with dietitians to identify their optimal caloric intake, activity level, and potential.
- Patient to keep a journal for tracking caloric intake for food items consumed.
- A patient shall display a clear working knowledge of reading food labels after nurse demonstrates .
- Promote caregiver or family member participating in the healthy lifestyle routine as recommended in nursing care plans.
- The nurse will keep a record of the patients exercise long to enhance accountability.
- Patients shall have a schedule of goals and targets particularly for those targets related to reducing overall intake of calories.
The most vital thing to remember when dealing with type 2 diabetes is that healthy living can completely negate the diabetic disease process. Research has shown that human behavior dictates whether the problem exacerbates or not. Lack of proper nutrition and physical activity can lead to type 1 diabetes which has more severe symptoms including premature death, vision loss, and neuropathy.
Nursing Care Plans Goal Statements
1.Patient to acknowledge their behaviors and feelings that exacerbate improper nutrition within 8 hours. .
2.Patient to design a diet plan which will realistically help them adjust caloric intake within 24 hours. .
3.Patient to incorporate 30 minutes of exercise into daily schedule within 48 hours. .
You May Like: How Many People In The Us Have Type 1 Diabetes
What Is A Nursing Care Plan For Type 2 Diabetes
This is a plan, guide, and a checklist to help you provide proper care for an individual or family with type 2 diabetes. This nursing plan is explicitly allotted to diabetic patients.
The nursing plan merely focuses on methods proven to work with proper comprehensive treatment tactics offered to patients at hospitals and nursing home facilities, which can be used at individual and family levels.
The care plan involves diagnosis, monitoring, and planning the management that detains on effective recovery from type 2 diabetes through regular sugar monitoring, diets, exercises, and timely medications .
Deficient Knowledge R/t New Onset Of Diabetes Mellitus
Expected Outcome: The patient will identify learning needs and exhibit the motivation to learn about health conditions.
| Assess the patients knowledge about diabetes and insulin management. The patients knowledge base creates a baseline in developing an education and treatment plan. |
| Identify barriers to receiving care or necessary equipment. Patients may have various reasons for being noncompliant with their insulin treatment regimen. For example, there may be financial, social, cultural, or even psychological reasons for not complying with medication regimens. |
| Explore the factors leading to DKA. Knowing the chain of events helps identify strategies to avoid subsequent episodes of DKA. |
| Teach the patient and family to check blood glucose levels at designated times.Upon awakening |
Recommended Reading: How Many Carbs Should A Pre Diabetic Eat Per Day
Nursing Care Plan For Diabetic Foot Ulcer
Following is the nursing care plan for diabetic foot ulcers:
- Take care of the skin integrity which is generally caused because of immobilization.
- Take care of the pain which can either be associated with any infection or with any surgery.
- Keep an eye on the prevalent infection risks in your patients.
- Encourage your patients to seek proper treatment on time.
Sometimes patients also suffer from depression and stress.
Addressing these issues is important because it can impact the blood glucose levels in a very bad way.
Your Diabetes Care Plan
The annual diabetes review is an ideal time to have your care planning review. Care planning is a process that should be available to all people with diabetes. It:
- allows you to be more involved in decisions about how your diabetes is managed
- gives you a say in every aspect of the care you get
- helps you to work towards goals that are personal to you
- helps you to work in partnership with your diabetes team.
The care planning appointment is a chance to talk about the results of your annual diabetes checks with your healthcare professional, talk about your experiences and discuss how you feel, set goals, and create an action plan to help you manage your diabetes.
Your healthcare professional can help you to understand the results of your diabetes checks, provide you with information and advice, talk about different options for example, different types of medication available to you and refer or signpost you to support in your local area.
A care plan is a written document of all these discussions, goals and actions.
The short film below will help you to understand what care planning is, and how you can get more involved in your diabetes care.
You May Like: What Is Considered Low Blood Sugar For Type 2 Diabetes
Reversal Of Type 2 Diabetes
Inspired by the results from the ground-breaking Diabetes Remission Clinical Trial study, the year-long programme aims to help people recently diagnosed with diabetes lose weight and put their condition into remission.
For three months, people with type 2 diabetes provided with low-calorie total diet replacement products, such as shakes and soups. After this, theyll be supported to reintroduce solid foods and maintain their weight loss.
Alongside making changes to their diet, people taking part in the programme will also be provided with support to increase their exercise levels. And theyll be able to take part in virtual one-to-ones and group sessions throughout the year too.
Recommendations for weight management and remission for people living with type 2 diabetes:
- for overweight or obese people with Type 2 diabetes
- for remission, aim for weight loss of 15kg as soon as possible after diagnosis this may be achieved by total diet replacement or meal replacement plans providing 800-1200 Kcal per day for 12 weeks
- to improve glycaemic control and CVD risk, aim for at least 5% weight loss achieved by reducing calorie intake and increasing energy expenditure.
Risk For Unstable Blood Glucose Level
Related to
- Inadequate blood glucose control, food intake and medication management.
- Weight gain or loss
- Physical health status stress .
Possibly evidenced by.
- Increased urine output, dilute urine
- Weakness, fatigue, lack of muscle tone
- Altered level of consciousness Increased ketones.
Desired results:
- Blood glucose level.
- Maintain glucose in satisfactory range. .
- Fasting blood glucose reading less than 140 mg/dL when hospitalized. Hemoglobin A1C level less than 7.
- Self-management: Diabetes
- Recognize factors leading to glucose instability and DKA.
- Verbalize understanding of body and energy needs.
- Verbalize plan to modify factors to prevent or minimize complications.
Nursing intervention
Monitor blood glucose before meals and at bedtime.
Rationale
This monitors the effectiveness of blood glucose control at times when the patients glucose is not increased by digestion of food.
Nursing intervention
Assess for changes in mentality, apprehension, erratic behavior, tremors, slurred speech, staggering gait, and seizure activity. Treat hypoglycemia as prescribed.
Rationale
These are signs of hypoglycemia. Patients with hypoglycemia may experience vasodilation and decreased myocardial contractility, which decreases cerebral circulation and impairs cognition.
Nursing intervention
Administer basal, prandial, and correction insulin doses as prescribed.
Rationale
Nursing intervention
Encourage and teach the patient to perform regular home blood glucose monitoring.
Rationale
Rationale
Don’t Miss: Number Of Grams Of Sugar Per Day For Diabetic
When Should Blood Glucose Levels Be Measured
The number of times per day the individual with diabetes should measure their blood glucose levels will vary from patient to patient depending entirely on their condition. The following is a useful general guideline however it doesn’t apply to everyone and each case should be given individual advice.
Individuals with type 1 diabetes using insulin should check their blood glucose levels before every meal, sometimes as often as ten times per day.
Individuals with type 2 diabetes may measure their glucose levels if they are taking medications that can lead to hypoglycaemia . The frequency varies depending on the medication they are taking.
Type 2 diabetes is a progressive condition and even with metformin and diet only, individuals may need to test their blood glucose periodically to observe trends in rising blood glucose.
Focus 5 Diabetes Management
Medicine management for type 2
Firstly, not compromising on your medicine is your first ever priority.
Medicines assist in stabilizing your blood sugar levels and also prevent from causing serious health problems and diabetes complications.
Remember, if not managed well, diabetics might bring some serious issues. So, as noted above, keep a track by maintaining a journal in relation to your medicines and changes to your medications.
Consult your doctor at first sight when you have observed some new symptoms or changes to symptoms.
Right medicines taken at the correct time without missing any dose is important to help to heal the wounds.
Tip: Think again if you use hydrogen peroxide on wounds.
For example, Metformin is one of the commonly used medications used for treating type 2 diabetes in an early year of the disease. However, its mostly used when other medicines are not working.
After you have to consult a doctor, he will probably tell you how to take drugs and their cause of action.
Remember, some drugs might cause some disturbance in your body, which will also result in some symptoms. Although side-effects are not for all, it also can have an effect based on individual persons and other medical conditions they have.
Signs like sudden weight loss/weight gain, swollen ankles, bloating, or frequent feeling of being sick shouldnt be ignored.
Actions
Nursing Care Plan Diabetes
Bellow you will find a copy of one of the nursing care plans for type 2 diabetes authored by myself . An detailed commentary by myself can be found below the nursing care plan. Please read through the care plan to better understand standards of type 2 diabetes care.
Please refer to the link at the end of this article for more in-depth Diabetes information for both patients and medical professionals!
Nursing Care Plan NANDA Nursing Diagnosis
Imbalanced nutrition r/t excessive intake of nutrients as evidenced by Type II Diabetes:
Nursing Care Plan Goal Statements:
Nursing Interventions for Imbalanced Nutrition :
The Nurse shall explain and have patient verbalize the relationship of diabetes and diet, and the patient shall give a return explanation is his / her own words. .
Patient will consult with a dietician to find out what an optimal caloric intake for her size, activity level and goal of weight loss is, so that she knows where to start in planning her dietary needs. .
Patient will keep a journal of total intake every time food is consumed and mark where improvement can be made.
Deficient Fluid Volume / Risk For Shock
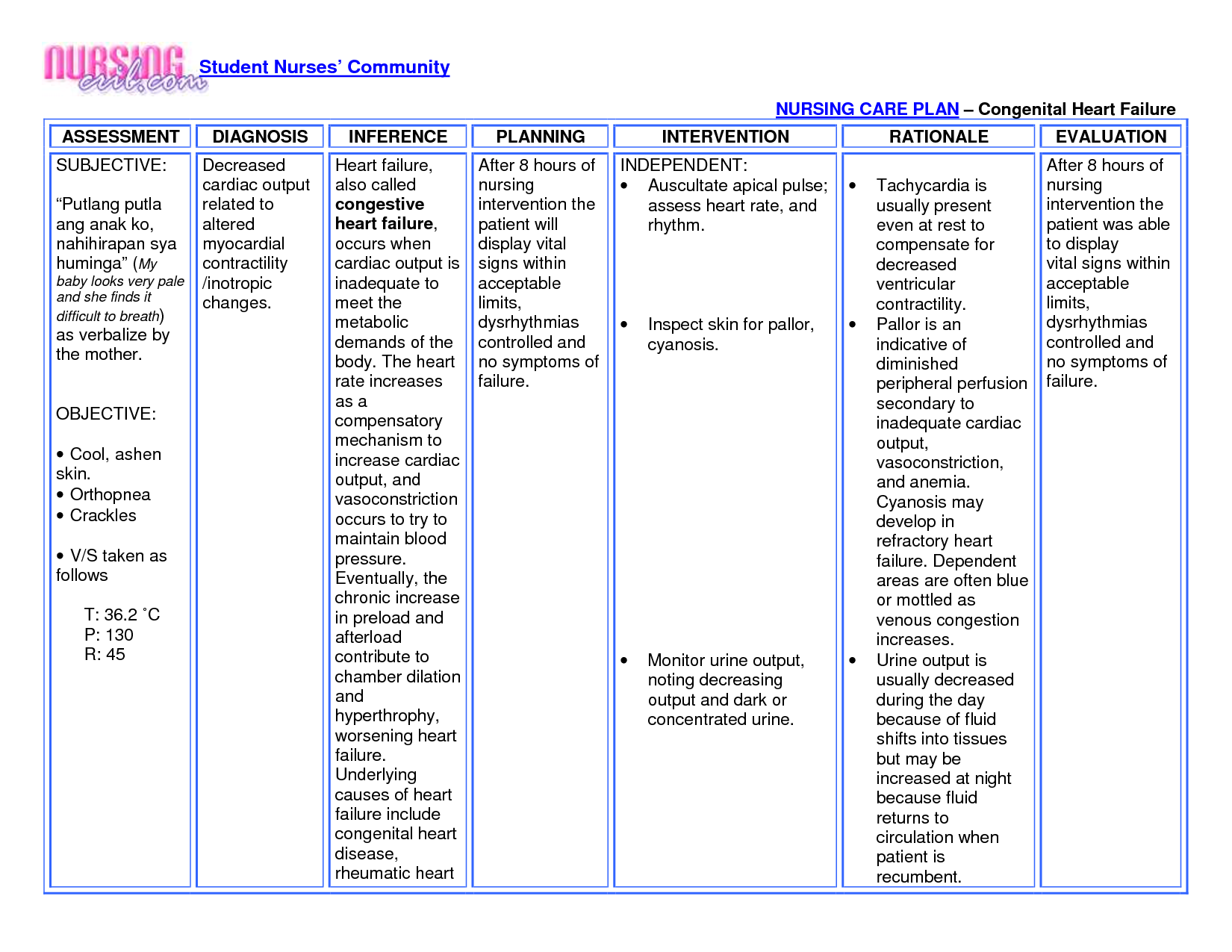
Related to
- Active loss that occurs with polyuria
- Possibly evidenced by
- Weakness, thirst, sudden weight loss.
Desired outcome:
Patient becomes normovolemic within 7 days of symptom onset, evidenced by
- Stable weight,
- Good skin turgor, moist tongue and oral mucosa,
- Blood pressure of 90-120/60-80 mm Hg heart rate of 60-100 bpm,
- Urine specific gravity greater than 1.010, and central venous pressure of 8-12 mm Hg.
Nursing intervention
Assess hypovolemia by monitoring I& O, specific gravity, and vital signs hourly. Check weight daily.
Rationale
Signs of hypovolemic include weight loss, inadequate fluid intake to balance output, thirst, poor skin turgor, decreased specific gravity, furrowed tongue, hypotension, and tachycardia.
Nursing intervention
Immediately report the following to the physician.
A diuresis greater than 200 mL in each of 2 consecutive hours.
Urine output greater than 500 mL in any 2-hour period.
Urine specific gravity less than 1.002.
Rationale
These are signs of extreme diuresis.
Diuresis can result in hypotension, hypokalemia, and dehydration, resulting in very viscous blood. The
Patient is at increased risk for hypovolemic shock, stroke, dysrhythmias and myocardial infarction.
Nursing intervention
Keep the water pitcher full and within easy reach of the patient. Explain the importance of consuming as much water as the patient can tolerate.
Rationale
Wearable Glucose Monitoring Sensors
There are two types of wearable glucose monitoring technologies intermittently scanned flash glucose monitoring and continuous glucose monitoring which are described in this section. They are only funded by the NHS for people with type 1 diabetes who meet NHS England criteria.
Healthcare professionals who will be working with flash and continuous glucose monitoring are directed to these webinars. It is important you are able to help your patients access wearable glucose monitoring devices appropriately, interpret their data and improve their glycaemic outcomes.
Nursing Care Plan For Diabetes Insipidus
Following is the nursing care plan for diabetes insipidus:
- Monitor the daily weights and determine the weight loss/gain.
- Monitor polydipsia.
- Monitor the symptoms of hypovolemia. When there is extreme fluid loss, the circulatory volume is decreased. The detection of the signs of hypovolemia prevents worse conditions.
- Monitor the stress and hypotension and educate your patients about ambulation.
- Record the changes at the time of providing mediations. It will give an idea about the changes in blood pressure due to the fluctuations in fluid balance.
- Make sure your patients have easy access to the bathrooms otherwise the frequent bathroom visits can be frustrating for your patients.
- Try to prevent injuries as well as you can. Frequent bathroom visits may subject your patients to fall. Hence, provide enough assistance to them.
Also, apply barriers to avoiding skin issues due to polyuria. This condition increases the risk of skin breakouts.
Focus 1 Important Past Health Information
Just to remind you of the complexity of diabetes, hence the importance of keeping a record of your past diabetes information, lets touch on to some diabetes background.
What is diabetes?
Diabetes is a medical condition known to be chronic in other words lasting for years, if not a lifetime. In this disease, the blood sugar level increases to a higher level.
Risk For Unstable Blood Glucose
May be related to lack of adherence to diabetes management inadequate blood glucose monitoring practices fluctuating physical activity level
blood glucose levels below or above normal levels
Desired Outcome identifies factors that may lead to unstable blood glucose levels verbalizes understanding of balancing body and energy needs verbalizes plan in modifying identified risk factors to prevent shifts in glucose level maintains blood glucose levels within the normal range
S To Developing A Nursing Care Plan
The purpose of creating professional nursing care plans is to identify problems of a patient and find solutions to the problems. This is usually done basically in five main steps including assessment, diagnosis, planning, intervention, and evaluation.
Step One: Assessment
The first step involves comprehensive and accurate assessment. This is usually accompanied by a routine assessment of the patients health status demand. For a comprehensive assessment, you should ask yourself questions such as: Why is the patient seeking medical care? What is the overall look of the patient?
Step Two: Diagnosis
Also referred to as a diagnostic statement, nursing diagnosis involves professional judgment concerning the patients response to either potential or actual health problems or needs. It, therefore, acknowledges the potential or actual health condition and labels it. Some questions nurses should ask themselves at this stage include: What problem is the patient facing? How does the patient response to particular conditions? The answers to such questions should lie in the assessment data for nursing care plans.
Step Three: Planning
Step Four: Intervention
Nursing care intervention is instituted based on the structure and components of a projected care plan. This process is usually based on the documented patients records. The goal is to ensure that the selected intervention helps solve or minimizes the patients existing condition.
Step Five: Evaluation
Treatment For Type 2 Diabetes
It is possible for a person to initially control the symptoms of type 2 diabetes by following a healthy diet, taking regular exercise and keeping their blood glucose levels within an agreed target range. Type 2 diabetes is a progressive condition so they may eventually need to take diabetes medication which will usually be in tablet form. A treatment programme will be tailored to suit the person’s needs by the diabetes team and will typically include one or a combination of the following:
- changing to a healthier diet
- medication such as metformin
- injectable GLP-1
- insulin therapies.
Keeping blood glucose levels under control is vital in reducing the risk of diabetes complications. If a person is overweight, weight loss can often help to reduce the extent of diabetes symptoms. Type 2 diabetes is effectively controlled when a person is involved in the management of their own programme of treatment. Effective ‘self-management’ is essential to successfully achieving their healthy targets for HbA1c, blood pressure and cholesterol levels. A person with type 2 diabetes may need medication that reduces high levels of blood glucose. In the first instance this will usually be glucose-lowering tablets and it may also include injectable insulin. Some oral medications for lowering blood glucose levels can cause hypoglycaemia for example, Gliclazide, Glipizide and Glimpiride.
Further resources
What Is The Nursing Care Plan For Diabetes
As you probably know, diabetes is one of the most common diseases. Maybe a part of the patients you saw today are diabetic.
According to the research studies more than 34 million US residents are diabetic.
This data shows that diabetes is very much prevalent and because of this reason, nurses need to have the proper knowledge about the disease and the skills to take care of their patients.
And at this point, a well-framed nursing care plan for diabetes comes into play.
So, before moving to the nursing care plans, first discuss diabetes and its types.
What is diabetes?
Diabetes or diabetes mellitus is a health problem where the levels of blood glucose are high. The most common symptoms of diabetes include:
- Weight loss
Generally, there are three types of diabetes and the treatment and nursing care plan for diabetes depends upon these types.
TYPE 1 DIABETES
Type 1 diabetes is also known as juvenile-onset and insulin-dependent diabetes. This type is very common in children.
In general, it is an autoimmune problem in which the body starts attacking the pancreas which in turn impacts insulin production.
TYPE 2 DIABETES
Type 2 diabetes is more prevalent than type 1.
In this health condition, the pancreas can not produce enough insulin required by the body.
In simple words, the body becomes resistant to insulin.
This type of diabetes can be easily controlled by making some changes in the lifestyle and regular intake of oral hypoglycemic agents.
GESTATIONAL DIABETES