Managing Type 2 Diabetes
Managing type 2 diabetes requires teamwork. Youll need to work closely with your doctor, but a lot of the results depend on your choices.
Your doctor may want to perform periodic blood tests to determine your blood glucose levels. This will help determine how well youre managing the condition. If you take medication, these tests will help gauge how well its working.
Your doctor may also recommend a home monitoring system to test your own blood glucose levels between visits. Theyll explain to you how often you should use it and what your target range should be.
Because diabetes can increase your risk of cardiovascular disease, your doctor may want to monitor your blood pressure and blood cholesterol levels. If you have symptoms of heart disease, you may need additional tests. These tests may include an electrocardiogram or a cardiac stress test.
It may also be helpful to bring your family into the loop. Educating them about the warning signs of blood glucose levels that are too high or too low will allow them to help in an emergency.
Why Take Care Of Your Diabetes
Taking care of yourself and your diabetes can help you feel good today and in the future. When your blood sugar is close to normal, you are likely to:
- have more energy
-
Ask your health care team what type of diabetes you have.
-
Learn where you can go for support.
-
Learn how caring for your diabetes helps you feel good today and in the future.
Ophthalmologist To Prevent Eye Diseases Caused By Diabetes
Your eye specialist will help you maintain healthy vision and monitor you for any complications caused by elevated or uncontrolled blood sugar levels, including diabetic retinopathy, diabetic macular edema, cataracts, and glaucoma, according to the American Academy of Ophthalmology. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that people who have diabetes get a dilated eye exam annually.
Also Check: Diagnosing Type 1 Diabetes In Children
What Insulin Medications Are Approved To Treat Diabetes
There are many types of insulins for diabetes. If you need insulin, you healthcare team will discuss the different types and if they are to be combined with oral medications. To follow is a brief review of insulin types.
- Rapid-acting insulins: These insulins are taken 15 minutes before meals, they peak at one hour and work for another two to four hours. Examples include insulin glulisine , insulin lispro and insulin aspart .
- Short-acting insulins: These insulins take about 30 minutes to reach your bloodstream, reach their peak effects in two to three hours and last for three to six hours. An example is insulin regular .
- Intermediate-acting insulins: These insulins reach your bloodstream in two to four hours, peak in four to 12 hours and work for up to 18 hours. An example in NPH.
- Long-acting insulins: These insulins work to keep your blood sugar stable all day. Usually, these insulins last for about 18 hours. Examples include insulin glargine , insulin detemir and insulin degludec .
There are insulins that are a combination of different insulins. There are also insulins that are combined with a GLP-1 receptor agonist medication .
What Is Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy

Peripheral neuropathy is a type of nerve injury that is common in people living with diabetes. Often affecting the distal extremities like the toes, feet, fingers, and hands, diabetic neuropathy can cause a variety of unpleasant symptoms that can impact a persons ability to participate in day-to-day activities.
When combined with other common symptoms of diabetes like edema and swelling, diabetic peripheral neuropathy can have a profoundly negative impact on a persons overall health and wellness if not adequately addressed.
Read Also: What Do You Do If You Think You Have Diabetes
How Often Do I Need To See My Primary Diabetes Healthcare Professional
In general, if you are being treated with insulin shots, you should see your doctor at least every three to four months. If you are treated with pills or are managing diabetes through diet, you should be seen at least every four to six months. More frequent visits may be needed if your blood sugar is not controlled or if complications of diabetes are worsening.
Your Inner Circle To Support Good Habits
Letting your loved ones know whats going on with your health and how they can help you will go a long way in relieving the burden of a diabetes diagnosis. If they offer a source of positive support, friends and family can help buffer some of the stress that comes from managing diabetes, says Bereolos. In other words: Youre not alone.
Read Also: Why Are Insulin Prices So High
What Does It Mean If Test Results Show I Have Protein In My Urine
This means your kidneys are allowing protein to be filtered through and now appear in your urine. This condition is called proteinuria. The continued presence of protein in your urine is a sign of kidney damage.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Theres much you can do to prevent the development of diabetes . However, if you or your child or adolescent develop symptoms of diabetes, see your healthcare provider. The earlier diabetes is diagnosed, the sooner steps can be taken to treat and control it. The better you are able to control your blood sugar level, the more likely you are to live a long, healthy life.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 03/28/2021.
References
How Diabetes Causes Peripheral Neuropathy
To better understand what causes diabetic neuropathy, we must first understand how diabetes impacts the health and function of other areas of our body. As an endocrine disorder, diabetes affects the function of the hormone insulin. Created in the pancreas, insulin is the hormone primarily responsible for lowering our blood sugar levels after we eat. In normal conditions, insulin is released from the pancreas after a meal and is able to bind to our cells to increase sugar intake, effectively reducing the amount of excess sugar in our bloodstream.
In people with diabetes, either the amount of insulin created or its ability to bind to our cells is impeded, resulting in increased difficulty in regulating our blood sugar levels. When this occurs, our blood sugar levels can remain high for prolonged periods of time, resulting in significant damage to the other essential organs in our bodies.
Our neurological system is an incredibly complex and intricate collection of nerves that stretches around our entire body. Designed to be highly sensitive to small electrical impulses and charges, the cells that make up our nervous system are vulnerable to damage when exposed to chronically high blood sugar levels. Capable of permanently injuring our nerve cells, this is why people living with diabetes are at an elevated risk of developing neuropathy.
Also Check: Is Insulin Used To Treat Type 2 Diabetes
Iii Diabetic Retinopathy Screening And Treatment
Diabetic retinopathy is a highly specific vascular complication of both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. The prevalence of retinopathy is strongly related to the duration of diabetes. Diabetic retinopathy is estimated to be the most frequent cause of new cases of blindness among adults aged 2074 years.
Intensive diabetes management with the goal of achieving near normoglycemia has been shown in large prospective randomized studies to prevent and/or delay the onset of diabetic retinopathy . In addition to glycemic control, several other factors seem to increase the risk of retinopathy. The presence of nephropathy is associated with retinopathy. High blood pressure is an established risk factor for the development of macular edema and is associated with the presence of proliferative diabetic retinopathy . Lowering blood pressure, as shown in the UKPDS, has been shown to decrease the progression of retinopathy. Several case series and a controlled prospective study suggest that pregnancy in type 1 diabetic patients may aggravate retinopathy . During pregnancy and 1 year postpartum, retinopathy may be transiently aggravated laser photocoagulation surgery can minimize this risk .
For a detailed review of the evidence and further discussion, see the ADAs technical review and position statement on this subject .
Can Diabetes Kill You
Yes, its possible that if diabetes remains undiagnosed and uncontrolled it can cause devastating harm to your body. Diabetes can cause heart attack, heart failure, stroke, kidney failure and coma. These complications can lead to your death. Cardiovascular disease in particular is the leading cause of death in adults with diabetes.
Read Also: Why Do Diabetics Legs Swell
Diabetes Can Be Managed But People Need Medication
The burden of diabetes is increasing globally. There are about half a billion people in the world living with the disease. In sub-Saharan Africa, 23 million people had diabetes in 2021. This number is expected to increase to 33 million by 2030 and 55 million by 2045.
As part of its 2013-2020 Global Action Plan the World Health Organisation set targets for prevention and control of noncommunicable diseases. It said essential medicines and basic technologies should be at least 80% available in public or private healthcare facilities. For diabetes, these medicines include insulin and oral agents that reduce blood sugar. There should also be medicines like aspirin and statins that reduce the risk of related heart diseases. The technology includes glucometers and test strips for urine protein and ketones.
Sub-Saharan Africa faces the dual burden of communicable and noncommunicable diseases straining countries’ health resources and fragile health systems. Access to essential medicines and diagnostic tests remains a challenge in the region. Public health facilities are faced with frequent stock-outs of medicines and patients often pay for medicines themselves writes Richard E. Sanya for The Conversation.
Currently, diabetes has no cure. But it can be controlled using medicines, diet, and lifestyle modification.
How Do I Check My Blood Glucose Level Why Is This Important
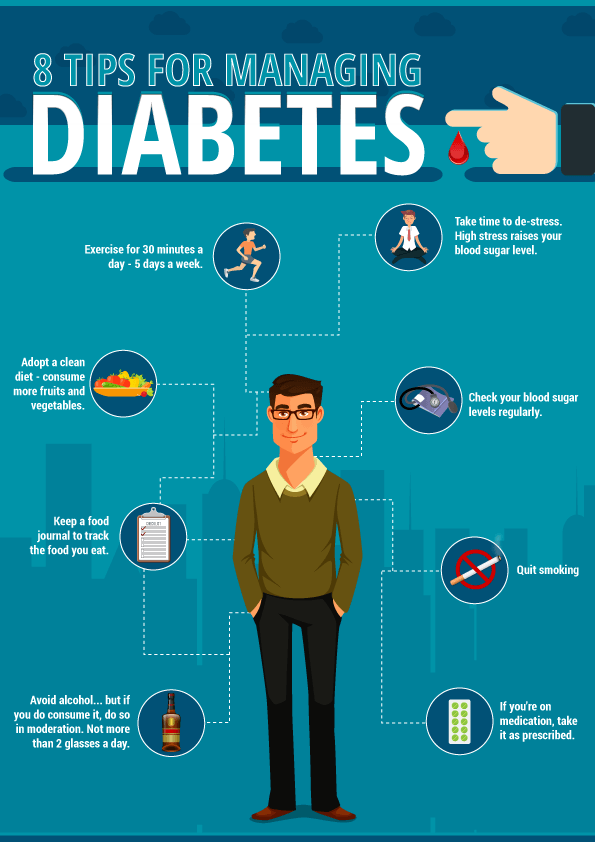
Checking your blood glucose level is important because the results help guide decisions about what to eat, your physical activity and any needed medication and insulin adjustments or additions.
The most common way to check your blood glucose level is with a blood glucose meter. With this test, you prick the side of your finger, apply the drop of blood to a test strip, insert the strip into the meter and the meter will show your glucose level at that moment in time. Your healthcare provider will tell you how often youll need to check your glucose level.
You May Like: How Much Is Insulin Out Of Pocket
I Care Of Older Adults With Diabetes
Diabetes is an important health condition for the aging population at least 15% of patients over the age of 65 years have diabetes. The number of older persons with diabetes can be expected to grow rapidly over the coming decades. Unfortunately, there are no long-term studies demonstrating the benefits of tight glycemic control in persons over 65 years of age. In approaching the elderly patient, a thoughtful individualized approach, consistent with the heterogeneity of the aging process, should be used. However, patients who can be expected to live long enough to reap the benefits of long-term glycemic control and who are active, cognitively intact, and willing to undertake the responsibility of self-management should be encouraged to do so.
Cardiovascular risk reduction continues to be important as in younger patients there is strong evidence from clinical trials of the value of treating hypertension in the elderly. There is less evidence for lipid-lowering and aspirin therapy, although diabetes patients have such an elevated risk for CVD that aggressive management of lipids and aspirin use when not contraindicated are probably reasonable interventions.
Learning To Live With Diabetes
- Helping them understand exactly what diabetes is and how it affects their body
- Determining the best type of glucose monitoring device for their circumstances
- Explaining how diabetes medications work and when or why they may be indicated
- Helping people understand how different foods affect their blood sugar and how to plan meals including culturally appropriate meals that fit their life
- Helping them learn how to recognize, treat and prevent high and low blood sugar
- Determining how much and which kinds of exercise are appropriate
Also Check: Diabetes And Lower Back Pain
What Are The Different Types Of Diabetes
The types of diabetes are:
- Type 1 diabetes: This type is an autoimmune disease, meaning your body attacks itself. In this case, the insulin-producing cells in your pancreas are destroyed. Up to 10% of people who have diabetes have Type 1. Its usually diagnosed in children and young adults . It was once better known as juvenile diabetes. People with Type 1 diabetes need to take insulin every day. This is why it is also called insulin-dependent diabetes.
- Type 2 diabetes: With this type, your body either doesnt make enough insulin or your bodys cells dont respond normally to the insulin. This is the most common type of diabetes. Up to 95% of people with diabetes have Type 2. It usually occurs in middle-aged and older people. Other common names for Type 2 include adult-onset diabetes and insulin-resistant diabetes. Your parents or grandparents may have called it having a touch of sugar.
- Prediabetes: This type is the stage before Type 2 diabetes. Your blood glucose levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be officially diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes.
- Gestational diabetes: This type develops in some women during their pregnancy. Gestational diabetes usually goes away after pregnancy. However, if you have gestational diabetes you’re at higher risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later on in life.
Less common types of diabetes include:
Diabetes insipidus is a distinct rare condition that causes your kidneys to produce a large amount of urine.
Alternative Treatments For Diabetes
There have been some small, limited studies as well as anecdotal reports that certain alternative or natural treatments can help control blood glucose levels in people with diabetes or otherwise prevent the condition or prevent its complications. These can include herbs or dietary supplements. Examples include garlic, cinnamon, alpha-lipoic acid, aloe vera, chromium, ginseng, and magnesium.
These substances are not considered to be medications by the US FDA and are therefore not regulated as such. This means that there are no standards in place to ensure that a given product contains the substance or dose as described on the label. There are also no requirements to perform studies showing that the products are safe or effective. Side effects of supplements are typically not well understood, and some supplements can interfere with the action of medications.
The American Diabetes Association publishes treatment guidelines for physicians based on all available scientific evidence. In the 2018 guidelines document, Standard of Medical Care in Diabetes, the ADA states that there is not sufficient evidence to support the use of any of the proposed alternative treatments for diabetes. These guidelines state that:
Also Check: What’s The Treatment For Type 2 Diabetes
What Are The Symptoms Of Diabetes
Symptoms of diabetes include:
- In women: Dry and itchy skin, and frequent yeast infections or urinary tract infections.
- In men: Decreased sex drive, erectile dysfunction, decreased muscle strength.
Type 1 diabetes symptoms: Symptoms can develop quickly over a few weeks or months. Symptoms begin when youre young as a child, teen or young adult. Additional symptoms include nausea, vomiting or stomach pains and yeast infections or urinary tract infections.
Type 2 diabetes and prediabetes symptoms: You may not have any symptoms at all or may not notice them since they develop slowly over several years. Symptoms usually begin to develop when youre an adult, but prediabetes and Type 2 diabetes is on the rise in all age groups.
Gestational diabetes: You typically will not notice symptoms. Your obstetrician will test you for gestational diabetes between 24 and 28 weeks of your pregnancy.
How Can I Check My Blood Sugar
Use a blood sugar meter or a continuous glucose monitor to check your blood sugar. A blood sugar meter measures the amount of sugar in a small sample of blood, usually from your fingertip. A CGM uses a sensor inserted under the skin to measure your blood sugar every few minutes. If you use a CGM, youll still need to test daily with a blood sugar meter to make sure your CGM readings are accurate.
You May Like: Can You Get Rid Of Diabetes Type 1
Is One Medication Better Than Another
In recent years, many new medicines for treating type 2 diabetes have been developed.
According to international guidelines, patients should take metformin as their first-line type 2 diabetes treatment unless there is a medical reason that it should not be prescribed.
However, various factors should be taken into account when choosing a ‘second-line’ medication to add to metformin. You can find out more about the individual medicines later in this leaflet.
- If it is important to avoid low blood glucose – DPP-4 inhibitor, SGLT-2 inhibitor, pioglitazone or GLP-1 mimetic.
- For people with a history of heart attack, stroke, etc – SGLT-2 inhibitor or GLP-1 mimetic with proven heart benefit.
- For people with a history of heart failure or chronic kidney disease – SGLT-2 inhibitor or, if not suitable, GLP-1 mimetic.
- For people where weight loss or avoiding weight gain is important – SGLT-2 inhibitor or GLP-1 mimetic .
- In the UK, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence recommends that with some exceptions, GLP-1 mimetics should only be prescribed for people with a body mass index over 35.
Preventing And Treating Diabetes

Do you have risk factors for diabetes? Does your family have a history of diabetes? Or do you have prediabetes? Then check out these healthy living tips. They may prevent diabetes and/or heart disease and stroke. Lifestyle changes such as losing weight, eating healthy and engaging in regular, moderate physical activity may reduce the progression of prediabetes and Type 2 diabetes and control Type 1 diabetes. They can also minimize other risk factors such as high blood pressure, blood cholesterol and even heart attacks and strokes.
In many instances, lifestyle changes must be accompanied by medications to control blood glucose levels, high blood pressure and cholesterol. This complementary regimen may also prevent heart attack and stroke.
You May Like: What Should My Sugar Level Be With Type 2 Diabetes