Diabetes Type 2 Symptoms
Diabetes type 2 symptomsA1CHbA1cDiabetes type 2measuring the glucose hemoglobin
| diabetes type 2 symptoms and treatment |
I was diagnosed as HEPATITIS B carrier in 2013 with fibrosis of theliver already present. I started on antiviral medications whichreduced the viral load initially. After a couple of years the virusbecame resistant. I started on HEPATITIS B Herbal treatment fromULTIMATE LIFE CLINIC in March, 2020. Theirtreatment totally reversed the virus. I did another blood test afterthe 6 months long treatment and tested negative to the virus. Amazingtreatment! This treatment is a breakthrough for all HBV carriers.
How Can I Prevent Hypoglycemic Episodes
The key to preventing hypoglycemic events is managing diabetes:
- Follow your healthcare providers instructions about food and exercise.
- Track your blood sugar regularly, including before and after meals, before and after exercise and before bed.
- Take all your medications exactly as prescribed.
- When you do have a hypoglycemic event, write it down. Include details such as the time, what you ate recently, whether you exercised, the symptoms and your glucose level.
Impaired Awareness Of Hypoglycaemia
Impaired Awareness of Hypoglycaemia occurs when people do not feel the early warning symptoms of hypoglycaemia and only realise they are hypo when their BGLs drop very low or when they check their BGL. If you have had diabetes and hypos for many years the risk of not feeling the symptoms of hypos is more common. IAH can be dangerous because by the time you realise you are having a hypo you may find it hard to treat it and you could become unconscious.
If you have hypos without symptoms or your symptoms change, you may need to check your blood glucose more often. Always treat BGLs at 4mmol/L or below, even if you feel fine. If you have low BGLs without any symptoms you need to discuss this with your doctor or Credentialled Diabetes Educator.
Recommended Reading: Can You Eat After Taking Insulin
Exercise Food And Alcohol
For people with type 1 diabetes, maintaining the correct blood glucose level involves balancing how much insulin you inject, the amount of food you eat, and how much energy you burn during exercise.
Hypoglycaemia may occur if you’ve taken your dose of insulin as usual, but your carbohydrate intake is lower than normal or has been used up more quickly. This may happen if you delay or miss a meal or snack, don’t eat enough carbohydrate, or exercise more than usual.
People with diabetes who’ve drunk too much alcohol, or drank alcohol on an empty stomach, can also get hypoglycaemia.
However, it’s not always possible to identify why a particular episode of hypoglycaemia has occurred, and sometimes it happens for no obvious reason.
How Are You Sweetening Your Coffee What You Add To Your Cup May Affect Your Blood Sugar Levels
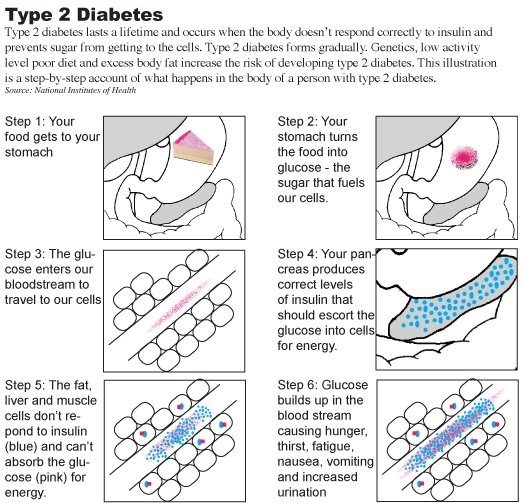
Whether you were recently diagnosed with type 2 diabetes or have been living with the condition for several years, you know how fickle blood sugar levels can be, and how important it is that they stay controlled.
Proper blood sugar control is key for warding off potential diabetes complications, such as kidney disease, nerve damage, vision problems, stroke, and heart disease, according to the National Institutes of Health . Plus, keeping your levels in check on a daily basis can help you stay energized, focused, and in a good mood, explains Lisa McDermott, RD, CDCES, a diabetes specialist with the Pittsburgh-based Allegheny Health Network.
According to the American Diabetes Association , proper medication, effective meal planning, regular exercise, and regular blood sugar checks can all help you keep your levels within a healthy range. The ADA recommends blood glucose stay within 80 to 130 milligrams per deciliter before meals and below 180 mg/dL two hours after the start of a meal. Furthermore, the organization recommends getting an A1C test, which measures your average blood glucose over the past two to three months, at least twice per year if your levels are stable and you are meeting treatment goals.
Don’t Miss: Number Of Grams Of Sugar Per Day For Diabetic
What Causes Hypoglycemic Unawareness
Sometimes people treated with insulin releasing pills or insulin lose the ability to detect a low blood sugar a condition known as hypoglycemic unawareness.
Your brain has a trigger point that tells it when to release stress hormones from other organs in the body. When there are frequent low blood sugars, this set point gets reprogrammed to lower and lower blood sugar levels. And the stress hormones which cause blood sugar levels to rise and cause symptoms arent released until the blood sugar is dangerously low.
Because the symptoms of low blood sugar alert you to the problem, not having any symptoms requires that you be especially vigilant. Remember: Frequent monitoring is the only way to know if you are low and need to take corrective action.
Keep in mind, too, that hypoglycemic unawareness is not a permanent condition. For many people, symptoms of low blood sugar will return and act as your warning signal once you stop having chronic low blood sugars.
What Should I Do If I Experience A Hypoglycemia
Low blood sugar can be treated quickly with fast-acting glucose. If you are at risk for lows, you should always have something fast and sweet with you. Glucose tabs, for example, are available at any pharmacy, are relatively affordable, and are designed to digest quickly and raise blood glucose fast.
Other options are fruit juice, regular soda, candies , or other . It is important that whatever you use to treat the low does not contain a lot of fat or fiber, which slows digestion and takes longer to raise blood sugar.
The general guidelines are to eat 15-20 grams of glucose or simple carbohydrates then check your blood sugar again in 15 minutes. If you are still low, repeat.
If you experience low blood sugars often, talk to your doctor. Together, you’ll be able to figure out why they are happening and then make adjustments, so they don’t happen so often.
Read Also: Patho Of Type 2 Diabetes
Not Eating Enough Carbohydrates
The digestive system breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which raises blood sugar levels.
Individuals need to eat enough carbohydrates to balance their medication and avoid hypoglycemia. They should therefore seek guidance from a healthcare professional about how to reach that balance.
Additionally, the protein, fat, and fiber content in meals affects the absorption of carbohydrates and can slow down the release of blood sugar into the bloodstream.
What Are Treatments For Type 2 Diabetes
Unless its absolutely necessary, insulin should not be used to treat type 2 diabetes. Dr. Bergquist explains, Injecting insulin improves blood sugar but worsens underlying insulin resistance. Insulin is a fat-storage hormone. Higher insulin leads to more fat storage in organs where its toxic, making them more insulin resistant.
Insulin should only be used when the pancreas fails and the B cells cannot be regenerated, says Dr. Apovian. When type 2 diabetes is caught early enough, you can reverse it with lifestyle, medication, and bariatric surgery. In certain cases, when a person is severely overweight, bariatric surgery is a successful treatment for type 2 diabetes, because it effectively decreases a persons body weight set point and can reverse hormonal imbalances that underlie obesity and fuel type 2 diabetes.
Additionally, new type 2 diabetes medications have been approved by the FDA, including a class of drugs known as glucagon-like-peptides , which aid the pancreas in producing more insulin by decreasing glucose production in the liver. Researchers are also working to understand the role that inflammation and hormonal imbalances have in the development of T2D.
Recommended Reading: How Many People In The Us Have Type 1 Diabetes
How To Recognize Hypoglycemia
The first signs of hypoglycemia include feeling sweaty, shaky, and hungry. However, not everyone has these symptoms or notices them in time to prevent low blood sugar from getting worse. Its also important to know that your symptoms of hypoglycemia will change the longer you have T1D.
As hypoglycemia gets worse, symptoms can include:
- Feeling weak
- Having difficulty walking or seeing clearly
- Acting strange or getting disoriented
- Having seizures
Severe hypoglycemia may make you faint or pass out. This is dangerous if you are driving, climbing stairs, or doing other activities where you need to stay aware of things around you.
Hypoglycemia can happen at night. If it does, you are likely to wake up, but its important not to rely on your body to wake you up. A continuous glucose monitor, or CGM, can alert you and those around you with an alarm to let you know if your blood sugar starts getting low while you are sleeping.
Its a good idea to check your blood sugar often when lows are likely, such as in hot weather or when you travel. Your CGM can also let you know when your blood sugar is getting lower.
Watch out for hypoglycemia unawareness.
You might not have early warning signs of low blood sugar. This is called hypoglycemia unawareness, and it raises the risk of having severe lows. It is more likely if:
- You have had diabetes longer than 5 or 10 years
- You have frequent episodes of hypoglycemia
- You take certain medicines, such as beta blockers for high blood pressure
How Can I Be Better Prepared For Hypoglycemia
You can take some steps to be ready for hypoglycemia:
- Be aware of the symptoms and treat them early.
- Carry some fast-acting carbs with you all the time.
- Check your glucose levels frequently, especially around meals and exercise.
- Inform family, friends and co-workers so they know what do if you need help.
- Talk to your healthcare provider regularly to make and update your plan.
- Wear a medical bracelet that lets people know you have diabetes. Carry a card in your purse or wallet with instructions for hypoglycemia.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Hypoglycemia is quite common in people with diabetes. If not treated, it can cause troubling symptoms, and even serious health problems. Fortunately, you can avoid hypoglycemic episodes by monitoring your blood sugar. You can also make small adjustments to eating and exercising routines.
You May Like: Diabetes And Heat Exhaustion Symptoms
Most Of The Time You Can Prevent Hypoglycemia By:
- Monitoring your blood sugar often
- Staying alert for the first symptoms
- Keeping some sugar or sweet handy
Despite all the safety planning, you still may get a low blood sugar when you are treated with insulin releasing pills or insulin. So always wear your medical alert identification. And if you are taking insulin, have family members or friends trained to use a Glucagon Emergency kit.
How Serious Is Hypoglycemia
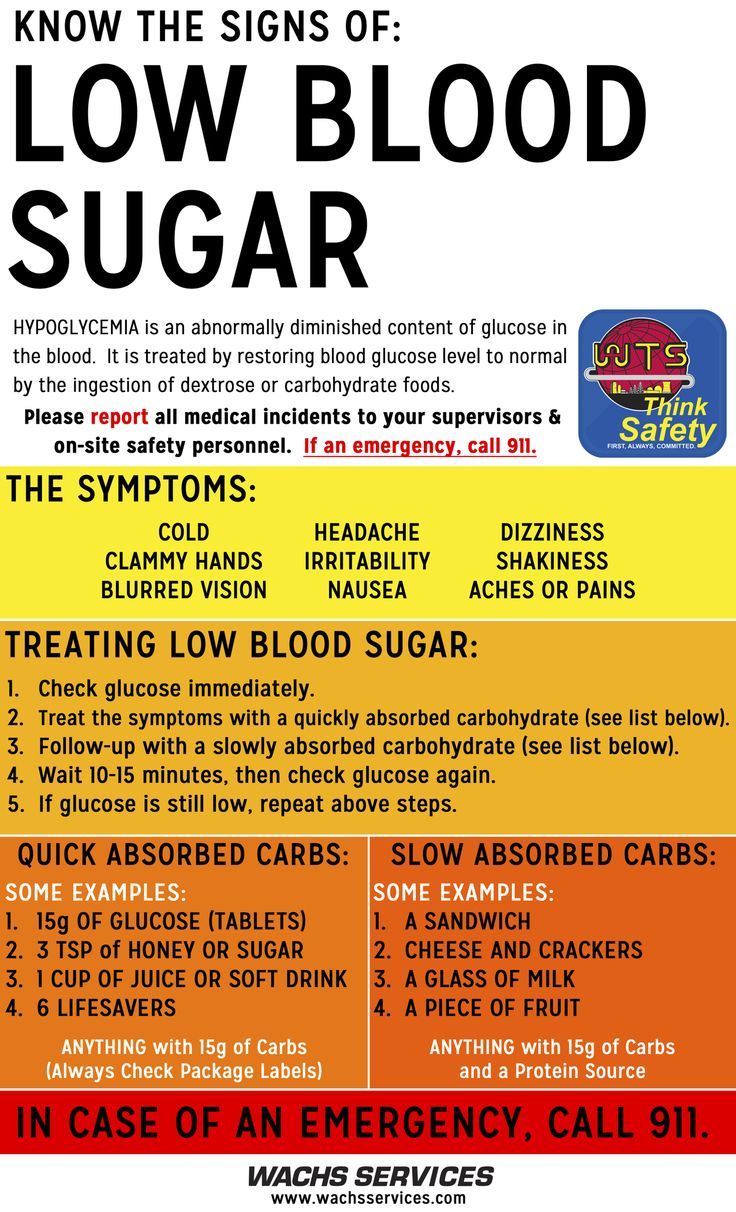
Hypoglycemic episodes can range from mild to severe.
Mild hypoglycemia can usually be treated by the individual and are to be expected to some degree in people on insulin. Mild hypos are not associated with significant long term health problems unless they are occurring very regularly or for long periods of time.
Severe hypoglycemia, however, will require treatment from someone else and may require an ambulance. Severe hypos can lead to immediate danger if not treated immediately. Whilst rare, severe hypos can potentially lead to coma and death.
- What is dead in bed syndrome ?
Also Check: Nursing Care Plan For Diabetes
What Else Should I Do
- Always carry fast acting carbohydrates with you
- Wear identification that says you have diabetes
- Make a note of any hypos you have and discuss it with your doctor or Credentialled Diabetes Educator
- Make sure your family, friends, co-workers, school staff and carers know how to recognise and treat hypoglycaemia
- Look for the cause of your hypo so you can try to prevent it from occurring again
- Contact your doctor or Credentialled Diabetes Educator if you are having hypos often
- If youre taking medication called Acarbose carry pure glucose with you such as glucose tablets, glucose gel or Lucozade
- Eat carbohydrates if you are drinking alcohol
- Test your blood glucose level and ensure it is above 5mmol/L before driving a motor vehicle.
Why Do These Symptoms Matter For Diabetics
These symptoms are essential for diabetics to understand, because they may encounter high or low blood sugar levels from time to time.
A cold or virus can cause sudden high blood sugar levels, and understand the symptoms means knowing how to deal with hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia.
People with diabetes who can recognise the symptoms can avoid levels that lead to medical emergencies such as diabetic ketoacidosis
You May Like: What Is Considered Low Blood Sugar For Type 2 Diabetes
Hypoglycemia Means Low Blood Sugar Symptoms Include:
- Shaking, sweating, rapid heartbeat
- Headache
- Sudden moodiness
As the term implies, low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia, occurs when your brain and body are not getting enough sugar. For most people whose blood sugar is kept in the near normal range, less than 70 mg/dl can be considered low, or hypoglycemic. When you have type 2 diabetes and are treated with insulin releasing pills or insulin, you are at risk for low blood sugars or hypoglycemia. It is very unlikely for individuals with type 2 diabetes who are only treated with lifestyle changes or blood sugar normalizing medications to have a low blood sugar.
How To Treat Someone Who’s Unconscious Or Very Sleepy
Follow these steps:
They may need to go to hospital if they’re being sick , or their blood sugar level drops again.
Tell your diabetes care team if you ever have a severe hypo that caused you to lose consciousness.
Read Also: Type 2 Diabetes Dry Mouth
When Your Blood Sugar Gets Low
Check your blood sugar whenever you have symptoms of low blood sugar. If your blood sugar is below 70 mg/dL, treat yourself right away.
1. Eat something that has about 15 grams of carbohydrates. Examples are:
- 3 glucose tablets
- One half cup of fruit juice or regular, non-diet soda
- 5 or 6 hard candies
- 1 tablespoon or 15 mL of sugar, plain or dissolved in water
- 1 tbsp of honey or syrup
2. Wait about 15 minutes before eating any more. Be careful not to eat too much. This can cause high blood sugar and weight gain.
3. Check your blood sugar again.
4. If you do not feel better in 15 minutes and your blood sugar is still lower than 70 mg/dL , eat another snack with 15 g of carbohydrates.
You may need to eat a snack with carbohydrates and protein if your blood sugar is in a safer range — over 70 mg/dL — and your next meal is more than an hour away.
Ask your provider how to manage this situation. If these steps for raising your blood sugar do not work, call your doctor right away.
What Are The Symptoms Of Low Blood Sugar How Do I Know I’m Experiencing A Low Blood Sugar
All this talk about lows, and we haven’t told you what to watch out for! Shame on us.
The signs and symptoms of low blood sugars happen quickly, can vary a lot, and can even be different each time. The American Diabetes Association has a comprehensive list:
- Shakiness
- Tingling or numbness in the lips or tongue
- Headaches
Also Check: Can You Get Rid Of Diabetes Type 1
A Low Blood Sugar Level Without Diabetes
A low blood sugar level is uncommon in people who do not have diabetes.
Possible causes include:
- a gastric bypass
- other medical conditions, such as problems with your hormone levels, pancreas, liver, kidneys, adrenal glands or heart
- some medicines, including quinine
See a GP if you think you keep getting symptoms of a low blood sugar level. They can arrange some simple tests to check if your blood sugar level is low and try to find out what’s causing it.
Hypoglycemia Symptoms With Normal Glucose Levels
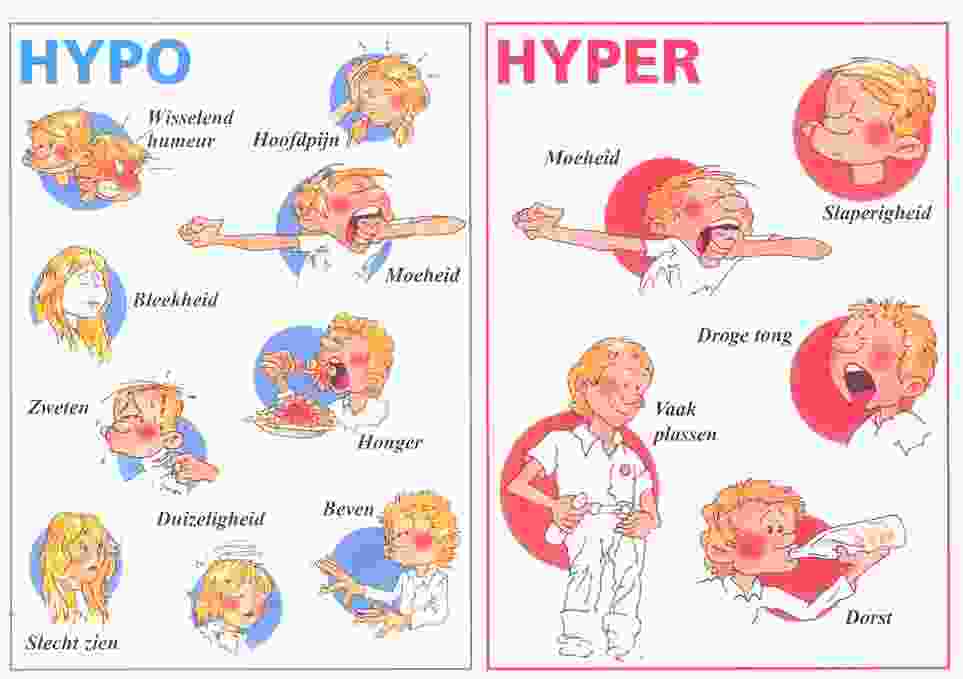
There is such a thing as pseudo-hypoglycemia. This happens when glucose levels are continuously high for a long time then are suddenly brought down to normal. It’s as if the body becomes accustomed to the higher range, then panics when levels drop to normal, responding with hormones like cortisol and adrenaline.
Info:Hypoglycemia is usually defined as blood glucose levels below 70 mg/dl . However, your doctor may give you a different blood glucose number that is considered too low for you.
Also Check: Diabetes And Lower Back Pain
If A Person Is Unconscious
If a person loses consciousness because of severe hypoglycaemia, they need to be put into the recovery position and given an injection of the hormone glucagon . The injection will raise their blood glucose level.
The injection should be carried out by a friend or family member who knows what they’re doing, or by a trained healthcare professional.
You should dial 999 to request an ambulance if:
- a glucagon injection kit isn’t available
- there’s nobody available who’s trained to give the injection
- the injection is ineffective after 10 minutes
Never try to put food or drink into the mouth of someone who’s unconscious as they could choke.
If you’re able to give a glucagon injection and the person regains consciousness, they should eat some longer-acting carbohydrate food, such as a few biscuits, a cereal bar or a sandwich.
You should continue to monitor the person for signs of recurring symptoms in case they need to be treated again.