For People With Type 1 Diabetes
Microalbuminuria or proteinuria is rarely present at the time when the diabetes is first diagnosed. By five years after the diagnosis of diabetes, about 1 in 7 people will have developed microalbuminuria.
After 30 years, about 4 in 10 people will have developed microalbuminuria. Some people with microalbuminuria progress to proteinuria and kidney failure.
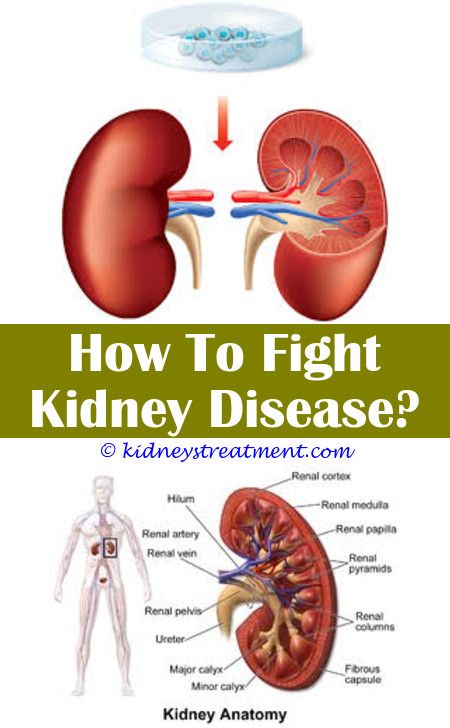
Treatment Of Kidney Disease Stage 3
Once you are diagnosed with stage 3 kidney disease, there is no way to treat the damage that has already been done to your kidneys. The following steps for your treatment have to do with treating the issues caused by decreased kidney functioning and preventing further damage.
These treatments include:
- Monitoring your weight to remain healthy
- Attending to anemia
Additionally, you may need to take medications. Which medications and even if you need to take them entirely depends on the cause of your kidney disease. Some of these medications could be:
- An angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor which lowers your blood pressure
- An angiotensin receptor blocker which would also lower your blood pressure
- Diuretics to help flush out waste
- Any type of medication that could help lower your cholesterol
- Erythropoietin which helps build red blood cells for people who struggle with anemia
- Vitamin D to strengthen the bones and avoid bone loss
- A phosphate binder
Trends In Life Expectancy
A review of annual reports from the USRDS in the period 19962013 reveals that the life expectancy for a 36-year-old man on haemodialysis has improved steadily and linearly from 7.2 years in 1996 to 11.5 years in 2013 . Thus, one can anticipate that our current projections of life expectancy probably err on the pessimistic side of reality. This is supported by a detailed analysis of paediatric outcome over the period 19902010 .
You May Like: How Much Sugar Can A Type 2 Diabetic Have
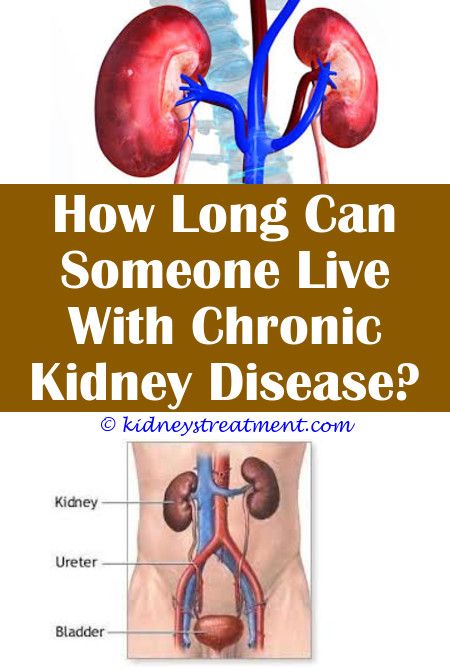
How Long Can You Live With Chronic Kidney Disease
The life expectancy of the chronic kidney disease depends on the stage at the time of diagnosis. It is a condition that affects old people differently from young adults. Life expectancies decrease with age when diagnosis occurred.
People with a diagnosis at the age of 30 have a possibility of living 10 to 20 years. However, due to renal treatment and technology improvement, the lifespan may go up with a few years.
Studies show that patients with a GFR of 60 and above and aged between 30 and 50 years when diagnosed. They have a life expectancy of between 24 years and 12 years.
Those patients facing stage 4 of the disease have a life expectancy of 20 years for those with 30 years old and 7 years for those with 50 years old.
When these patients reach end-stage renal disease or stage 5, the life expectancy shortens even further. Individuals aged 60 years and 85 years have a life expectancy of 6 years and between twelve and eighteen months, respectively.
These statistics are only approximated and averages, these are not absolute numbers as the situation. Life expectancy varies from case to case, but as people grow older, life expectancy reduces.
How Long Does It Take To Die From Kidney Failure Kidney Failure
Kidneys are the organs that filter waste products from the blood. When kidney failure occurs, the waste products accumulate in the blood leading to fatal outcomes.
Kidney failure can be due to acute or chronic kidney disease. It is a condition that can have multiple causes depending on the type of failure. Within this article, you will find answers to some of the most common questions about the treatment options and how long anyone can live with this disease. Before reaching that point, there will be brief explanations about the basic concepts of the disease.
By reading this article, you will obtain critical insights about Kidney failure like how it happens, its signs and symptoms, and the complications. Please continue reading to get pearls on this specific topic by the hand of a doctor.
Also Check: Chromium Picolinate Dosage For Diabetes
What Is The Outlook
- If you have microalbuminuria , this may clear away, especially with treatment.
- If you have proteinuria , over time the disease tends to become worse and progress to end-stage kidney failure. However, the length of time this takes can vary and it may take years. If your kidneys do begin to fail you should be referred to a kidney specialist.
- Once the kidney function goes below a certain level then you will need kidney dialysis or a kidney transplant.
- A main concern is the increased risk of developing cardiovascular diseases. Cardiovascular diseases, such as heart attack and stroke, are the main causes of death in people with diabetic kidney disease. The treatments outlined above will reduce the risk of these occurring.
What Do Your Kidneys Do
You have two kidneys. They are bean-shaped organs that are located toward your back, on either side of your spine, just underneath the rib cage. Each kidney is about the size of your fist.
Your kidneys have many jobs, but their main job is to filter your blood, getting rid of toxins and excess salt and water as urine. If your kidneys are damaged and dont work as they should, wastes can build up in your blood and can make you sick. Your kidneys also balance the amount of salts and minerals in your body, make hormones that control blood pressure, make red blood cells and keep your bones strong.
Also Check: Why Are Diabetic Supplies So Expensive
What Is Diabetic Kidney Disease
Diabetic kidney disease is a complication that occurs in some people with diabetes. In this condition the filters of the kidneys, the glomeruli, become damaged. Because of this the kidneys ‘leak’ abnormal amounts of protein from the blood into the urine. The main protein that leaks out from the damaged kidneys is called albumin.
In normal healthy kidneys only a tiny amount of albumin is found in the urine. A raised level of albumin in the urine is the typical first sign that the kidneys have become damaged by diabetes. Diabetic kidney disease is divided into two main categories, depending on how much albumin is lost through the kidneys:
- Microalbuminuria: in this condition, the amount of albumin that leaks into the urine is between 30 and 300 mg per day. It is sometimes called incipient nephropathy.
- Proteinuria: in this condition the amount of albumin that leaks into the urine is more than 300 mg per day. It is sometimes called macroalbuminuria or overt nephropathy.
How Is Kidney Disease Diagnosed
First your healthcare provider will take your medical history, conduct a physical exam, ask about any medication you are currently taking, ask about any symptoms you have noticed, and inquire if any of your family members have kidney disease.
Your healthcare provider will order blood tests, a urine test and will also check your blood pressure.
The blood tests will check:
- Your glomerulofiltration rate . This describes how efficiently your kidneys are filtering blood how many milliliters per minute your kidneys are filtering. Your GFR is used to determine the stage of your kidney disease.
- Your serum creatinine level, which tells how well your kidneys are removing this waste product. Creatinine is a waste product from muscle metabolism and is normally excreted in your urine. A high creatinine level in your blood means that your kidneys are not functioning well enough to get rid it in your urine.
A urine protein test will look for the presence of protein and blood in your urine. Well-functioning kidneys should not have blood or proteins in your urine. If you do, this means your kidneys are damaged.
Read Also: How Do Diabetics Check Their Blood Sugar
Everyone Who Has Gone Through Dialysis Has Different Experiences Health Problems And Opinions Debbie Who Went Through Two Years Of Dialysis Talks About The Mental Physical And Emotional Aspects Of Her Journey
I became a Type one diabetic at the age of 13. At this time I was 42 years old and 29 years of living with diabetes had started to affect my kidneys.
In October 2008 I attended an appointment with a kidney specialist. My diabetic nurse had referred me as my kidneys were beginning to fail. The doctor sent me for various scans, one of which revealed that my kidney function was only 50 per cent and another discovered a growth on my right kidney.
In March 2009 the growth was removed. Three weeks later I was told that it was only a cyst. This was a great relief, but the operation had unfortunately caused further kidneys damage.
In October 2009 I attended another appointment with a kidney specialist. Blood tests had revealed that it would not be long before I would have to start dialysis and that he would like to refer me for a kidney-pancreas transplant. This would mean that I would have to pass several different scans before I could be placed on the transplant list.
At this stage I became quite emotional, I had not been aware that a pancreas transplant was possible. After being a diabetic for so many years, being told that it could be possible to have a life without diabetes came as a big shock.
In December 2009 I had to decide which type of dialysis to go for. I was shown around the hemodialysis unit whilst patients were undergoing treatment. This type of dialysis meant I would have to go to the renal unit three times week and over a matter of hours have my blood cleaned.
The Impact Of Cardiovascular Disease And Chronic Kidney Disease On Life Expectancy And Direct Medical Cost In A 10
Diabetes Care
Eric Yuk Fai Wan, Weng Yee Chin, Esther Yee Tak Yu, Ian Chi Kei Wong, Esther Wai Yin Chan, Shirley Xue Li, Nico Kwan Lok Cheung, Yuan Wang, Cindy Lo Kuen Lam The Impact of Cardiovascular Disease and Chronic Kidney Disease on Life Expectancy and Direct Medical Cost in a 10-Year Diabetes Cohort Study. Diabetes Care 1 August 2020 43 : 17501758.
The relative effects of various cardiovascular diseases and varying severity of chronic kidney disease on mortality risk, direct medical cost, and life expectancy in patients with diabetes are unclear. The aim of this study was to evaluate these associations.
This was a retrospective cohort study that included 208,792 adults with diabetes stratified into 12 disease status groups with varying combinations of heart disease, stroke, moderate CKD and severe CKD in 20082010. The effect of risk of mortality, annual direct medical costs, and life expectancy were assessed using Cox regression, gamma generalized linear method with log-link function, and flexible parametric survival models.
Also Check: How Many People In The Us Have Type 1 Diabetes
Diabetic Kidney Disease: Diagnosis Treatment And Prevention
KATHRYN MCGRATH, MD, Sidney Kimmel Medical College at Thomas Jefferson University Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
RINA EDI, MD, University of California, San Diego, California
Am Fam Physician. 2019 Jun 15 99:751-759.
Patient information: A handout on this topic is available at .
Globally, more than 400 million people have diabetes mellitus and almost 600 million may be affected by 2035.1 In the United States, approximately 12% of the population has diabetes, and up to 25% of these individuals may be undiagnosed.2 The disease affects patients across all age groups, sexes, racial or ethnic groups, education levels, and income levels.2 Diabetic kidney disease affects about 20% of patients with diabetes.3 DKD is associated with increased risks of morbidity and mortality and is the leading cause of end-stage renal disease in the United States.4,5
Prevention of diabetes in the general population is the most effective means of minimizing the impact of DKD understanding risk factors for DKD development can help with early identification and intervention. Effectively using screening guidelines, treatment strategies, and subspecialty referral can help prevent progression of DKD. The role of primary care physicians in the management of patients with DKD secondary to type 2 diabetes is reviewed.
Causes Of Renal Failure
As we have said, diabetes is the cause of renal failure in almost half of all cases. From the chart below, we can see that the most prevalent cause of kidney failure is diabetes, followed by high blood pressure, glomerulonephritis, cystic diseases, urological diseases, and other factors.
How many people with diabetes actually get kidney failure?
From a study of veterans, we can see the prevalence of renal disease in those with diabetes is largely male and Caucasian. When looking at ESRD associated with diabetes, the prevalence was higher among males, and higher among those of the black population.
44,671 of the 415,910 veterans with diabetes had a diagnosis of any renal disease. With the average age of 67 years, about 98% were male and 60% were of white ethnicity. The prevalence of diabetic nephropathy was 6.0%. ESRD was present in 4.2% of subjects. ESRD caused by diabetes-associated prevalence was higher amongst black compared to white veterans and male compared female veterans.
Also Check: What Is An Insulin Pump
What To Expect With Stage 3 Kidney Disease
As stated earlier, stage 3 kidney disease does not often statistically lead to stage 4 kidney disease. However, it also does predispose someone to mortality more than not having any kidney disease at all.
âIf you have stage 3 kidney disease, you shouldnât expect to feel many severe symptoms. It should be a time to reevaluate your habits, make treatment plans with your doctor or doctors, and focus on staying healthy. The most important elements to preventing kidney failure are keeping medical appointments, taking your medications, having a healthy lifestyle, and monitoring your blood pressure and blood sugar.
Show Sources
What Is Chronic Kidney Disease
Chronic kidney disease is the disease in which the gradual loss of kidney functions found to get occur. Our kidneys play very important jobs in the body and protect the other organs from damage. It helps in the excretion of waste and toxins from the body which can be much dangerous for our overall health. At the time of kidney disease, all the functions performed by the kidneys found to get affected and cause the waste build up inside the body. Here are the causes of chronic kidney disease, every individual need to be aware of:
- Diabetes and frequent hypertension
- Urine backs up inside the kidneys
- Kidney infection
Recommended Reading: Type 1 Diabetes Immune System
Study Design And Population
We performed a population based retrospective cohort study of members of Clalit Health Services , the largest medical service provider in Israel, who began MD from January 1, 2003 to December 31, 2015 and had a prior diagnosis of diabetes. The study was approved by CHS Soroka hospital IRB and all data collection methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines. As this was a retrospective study where the data was de-identified, it was exempt by the IRB from the need for informed consent.
Patients were excluded if their dialysis treatment period or total follow-up time were shorter than 90 days. Patients were followed up until renal transplantation, death, or 31 December 2016. To improve accuracy, data were collected starting from 2002, when computerized registration began.
To include only MD patients with a high probability of diabetic nephropathy, patients with other known primary renal disease or those who developed diabetes only AD or patients that started MD prior to the age of 40, were excluded.
Diabetes And Kidney Failure
Before understanding about dialysis, let us first understand what causes kidney failure in diabetes. If you are not able to manage your diabetes in an effective manner, the process of smooth blood circulation is hindered. Besides, you could also experience damage to the various nerves and blood vessels. When the damage is caused by the nerves and the blood vessels of the kidney, the kidneys stop doing the normal activities that they are responsible for. As a result, you experience the following problems:
- Accumulation of harmful wastes in your body
- Inability to make the required number of red blood cells
- Accumulation of fluid in the body
As a result, the body suffers from a lot of complications. Hence, it is imperative that the condition of kidney failure is appropriately treated. There are various ways of treating the same. But we shall concentrate on dialysis in this article.
Also Check: 30 Carb Meals For Diabetics
What Is Kidney Disease
Having kidney disease means that there is damage to your kidneys and they arent working as well as they should. Kidney disease is called chronic because kidney function slowly gets worse over time. Kidney disease leads to kidney failure, which is also called end-stage kidney disease. At this point, youll need dialysis or a kidney transplant.
Good Control Of Your Blood Pressure
Strict blood pressure control is likely to reduce the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases and prevent or delay the progression of kidney disease. Most people should already be taking an ACE inhibitor or AIIRA . These medicines lower blood pressure.
However, if your blood pressure remains at 130/80 mm Hg or more then one or more additional medicines may be advised to lower your blood pressure to below this level.
Also Check: What Is Considered Low Blood Sugar For Type 2 Diabetes
Diet For Renal Failure
If you already have chronic renal failure, your doctor or dietician will want you to start on an eating plan called the Renal Diet.
Your kidneys are damaged therefore, your kidneys cannot handle a regular amount of protein as they could in the past. Your kidneys also cant handle excessive amount of salt or potassium, due to the kidneys role in regulating these electrolytes. If you choose not to decrease your protein, sodium, and potassium levels, it makes your kidneys work harder to filter waste, and you will experience ESRD sooner. A renal diet is lower in protein, fat, sodium or salt, and potassium. You will most likely be asked to:
- cut back on protein containing foods, especially animal products such as milk, eggs, and cheese
- eat a low fat diet that is also low in cholesterol, as your body cannot handle high cholesterol foods like it used to, and you will get plaque build-up in your arteries from all of the excessive cholesterol in your bloodstream
- avoid high salt or sodium in your diet, and keep sodium to 1500 mg/day to keep your blood pressure in a better range to protect your kidneys
- avoid excess potassium since your kidneys can no longer regulate this electrolyte. Potassium keeps your heart beating regularly and helps your muscles to work right, but kidney disease may result in high potassium levels, an irregular heartbeat, or even cardiac arrest. Avoid foods like apricots, oranges, potatoes and bananas, which are all high in potassium