How Are Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes Treated
Theres no cure for type 1 diabetes. People with type 1 diabetes dont produce insulin, so it must be regularly injected into the body.
Some people take injections into soft tissue, such as the stomach, arm, or buttocks, several times per day. Other people use insulin pumps. Insulin pumps supply a steady amount of insulin into the body through a small tube.
Blood sugar testing is an essential part of managing type 1 diabetes, because levels can go up and down quickly.
Type 2 diabetes can be managed and even reversed with diet and exercise alone, but many people need extra support. If lifestyle changes arent enough, your doctor may prescribe medications that help your body use insulin more effectively.
Monitoring your blood sugar is an essential part of type 2 diabetes management too. Its the only way to know if youre meeting your target levels.
Your doctor may recommend testing your blood sugar occasionally or more frequently. If your blood sugar levels are high, your doctor may recommend insulin injections.
Managing And Treating Type 1 And Type 2
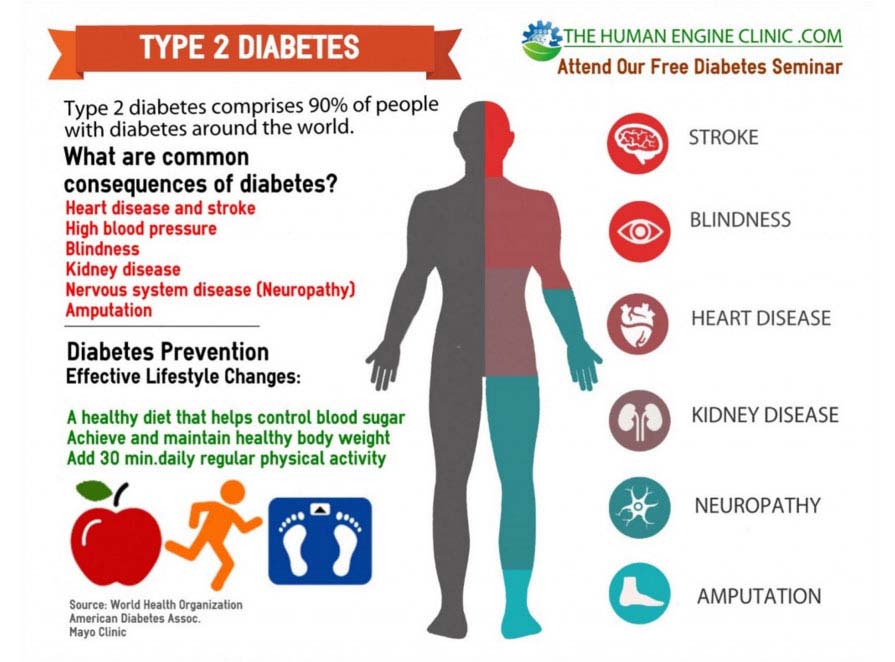
Managing and treating your diabetes is so important. This is because itll help you avoid serious health complications. And itll play a big part in your daily life regardless of if you have type 1 or type 2.
If you have type 1 diabetes, youll need to take insulin to control your blood sugar levels. Youll also need to test your blood glucose levels regularly. And count how many carbs you eat and drink. Counting carbs will help you work out how much insulin you should take when you inject with your meals.
And generally you should be trying to have a healthy lifestyle. That includes regular physical activity and a healthy balanced diet. These will help you reduce your risk of diabetes complications.
If you have type 2 diabetes, you also need to eat a healthy diet and be active. These things will help you manage your weight and diabetes.
But quite often people with type 2 also need to take medication. Such as tablets and insulin, or other treatments too. Whether you need to test your blood glucose level like someone with type 1, depends on the treatment you take. Your GP can tell you what you should do at home.
Symptoms Of Type 3c Diabetes
If you have type 3c then your pancreas may not be able to give you what you need to digest your food. This is pancreatic exocrine insufficiency and means that your pancreas isnt working properly.
The signs to look out for can include:
- losing weight without trying to
- stomach pain
- feeling more tired than usual
- frequently passing wind
- fatty or oily stools
- hypoglycaemia, also called low blood sugar.
There are also common signs and symptoms of diabetes that you might want to look out for as well.
If notice any of these symptoms or have any concerns then you should speak to your doctor.
You May Like: Are Omelettes Good For Diabetics
How Is Diabetes Treated
Treatments for diabetes depend on your type of diabetes, how well controlled your blood glucose level is and your other existing health conditions.
- Type 1 diabetes: If you have this type, you must take insulin every day. Your pancreas no longer makes insulin.
- Type 2 diabetes: If you have this type, your treatments can include medications , insulin and lifestyle changes such as losing weight, making healthy food choices and being more physically active.
- Prediabetes: If you have prediabetes, the goal is to keep you from progressing to diabetes. Treatments are focused on treatable risk factors, such as losing weight by eating a healthy diet and exercising . Many of the strategies used to prevent diabetes are the same as those recommended to treat diabetes .
- Gestational diabetes: If you have this type and your glucose level is not too high, your initial treatment might be modifying your diet and getting regular exercise. If the target goal is still not met or your glucose level is very high, your healthcare team may start medication or insulin.
Oral medications and insulin work in one of these ways to treat your diabetes:
- Stimulates your pancreas to make and release more insulin.
- Slows down the release of glucose from your liver .
- Blocks the breakdown of carbohydrates in your stomach or intestines so that your tissues are more sensitive to insulin.
- Helps rid your body of glucose through increased urination.
Other Types Of Diabetes
There are a handful of other illnesses that commonly fall under the category of diabetes, although not all of them are true diabetes mellitus.
Monogenic diabetes: This rare type of diabetes mellituswhich accounts for 1% to 5% of all casesis caused by a mutation in a single gene. Most of the time in monogenic diabetes, the pancreas struggles to make insulin. The condition is usually found in kids.
Secondary diabetes: Sometimes, certain other diseases can cause high blood sugar that leads to diabetes mellitus, such as Cushings syndrome and cystic fibrosis. Specific medications, including niacin, diuretics, HIV medicines, and anti-seizure drugs can also lead to high blood sugar.
Prediabetes: If your blood sugar is higher than normal but not high enough to be diabetes, thats considered prediabetes. People with prediabetes have an increased risk of developing type 2. Exercise and diet changes are often prescribed to reduce blood sugar and reduce the risk. In some cases, a doctor may also prescribe metformin, a blood-sugar-lowering drug that helps prevent type 2. An estimated 84 million Americans have prediabetes.
Diabetes insipidus: Despite its name, this disease is not related to diabetes mellitus and has nothing to do with high blood sugar. its a rare disorder caused by brain or kidney diseases that causes people to urinate up to 20 times more often than people without the condition.
Don’t Miss: Why Are Insulin Prices So High
How Can Parents Help
Now is the perfect time to help your child to create healthy habits for life. Heres how:
- Get involved with daily care. Help your child put their care plan into action every day. From counting carbs, to calculating insulin doses, and giving injections, theres a lot to learn at first. Share the responsibilities with your child. Over time, theyll be able to take on more on their own. Turn to your childs care team with any questions about the care plan or daily care.
- Learn all you can about diabetes. The more you know about type 1 diabetes, the more confident youll feel about helping your child manage it day to day. And a solid understanding of diabetes lets you advocate for your child. You can share your knowledge with important people in your childs life, like grandparents, teachers, coaches, and babysitters. Doing so helps you build a community of support for your child.
- Encourage your child. It can take a while to adjust to the new responsibilities that come with type 1 diabetes. Remind your child that many kids their age have type 1 diabetes, and they follow a similar care plan. If your child has concerns that youre not sure how to handle, ask the care team. Theyll connect you with the right resources.
Having a child with type 1 diabetes may seem overwhelming at times, but you’re not alone. If you have questions or problems, reach out to your childs diabetes care team they can help with all kinds of issues, and will guide your family through this journey.
Conditions Related To Type 3c
Type 3c is linked to many other conditions, all of which are to do with the pancreas, such as:
- pancreatitis
- haemochromatosis.
You can also develop type 3c if you have your pancreas removed because of any other damage.
Your doctor should be aware of your pancreatic issues if theyre testing you for diabetes. But make sure you mention it to them so that they know that you’re at risk for type 3c.
Organisations such as Pancreatic Cancer UK, Haemochromatosis UK and Cystic Fibrosis Trust can offer you support for some of the conditions related to type 3c.
Also Check: Diabetes And Heat Exhaustion Symptoms
What Is Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Nonketotic Syndrome
Hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic syndrome develops more slowly than diabetic ketoacidosis. It occurs in patients with Type 2 diabetes, especially the elderly and usually occurs when patients are ill or stressed.If you have HHNS, you blood glucose level is typically greater than 600 mg/dL. Symptoms include frequent urination, drowsiness, lack of energy and dehydration. HHNS is not associated with ketones in the blood. It can cause coma or death. Youll need to be treated in the hospital.
What Are The Risk Factors For Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
Risk factors for type 1 diabetes include:
- Family history: People with a parent or sibling with type 1 diabetes have a higher risk of developing it themselves.
- Age: Type 1 diabetes can appear at any age, but its most common among children and adolescents.
- Geography: The prevalence of type 1 diabetes increases the farther away you are from the equator.
- Genetics: The presence of certain genes points to an increased risk of developing type 1 diabetes.
Youre at risk of developing type 2 diabetes if you:
- have prediabetes, or slightly elevated blood sugar levels
- are carrying excess weight or have obesity
- are Black, Hispanic, American Indian, or Alaska Native
- have an immediate family member with type 2 diabetes
You May Like: Protein Shake For Diabetic Patients
Do I Have Other Treatment Options For My Type 1 Diabetes
The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases has played an important role in developing artificial pancreas technology. An artificial pancreas replaces manual blood glucose testing and the use of insulin shots. A single system monitors blood glucose levels around the clock and provides insulin or a combination of insulin and glucagon automatically. The system can also be monitored remotely, for example by parents or medical staff.
In 2016, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved a type of artificial pancreas system called a hybrid closed-loop system. This system tests your glucose level every 5 minutes throughout the day and night through a continuous glucose monitor, and automatically gives you the right amount of basal insulin, a long-acting insulin, through a separate insulin pump. You still need to manually adjust the amount of insulin the pump delivers at mealtimes and when you need a correction dose. You also will need to test your blood with a glucose meter several times a day. Talk with your health care provider about whether this system might be right for you.
The illustration below shows the parts of a type of artificial pancreas system.
Starting in late 2016 and early 2017, the NIDDK has funded several important studies on different types of artificial pancreas devices to better help people with type 1 diabetes manage their disease. The devices may also help people with type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes.
Normal And Diabetic Blood Sugar Ranges
For the majority of healthy individuals, normal blood sugar levels are as follows:
- Between 4.0 to 5.4 mmol/L when fasting
- Up to 7.8 mmol/L 2 hours after eating
For people with diabetes, blood sugar level targets are as follows:
- Before meals : 4 to 7 mmol/L for people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes
- After meals : under 9 mmol/L for people with type 1 diabetes and under 8.5mmol/L for people with type 2 diabetes
Read Also: Best Sweetener For Baking For Diabetics
Can Diabetes Be Cured Or Reversed
Although these seem like simple questions, the answers are not so simple. Depending on the type of your diabetes and its specific cause, it may or may not be possible to reverse your diabetes. Successfully reversing diabetes is more commonly called achieving remission.
Type 1 diabetes is an immune system disease with some genetic component. This type of diabetes cant be reversed with traditional treatments. You need lifelong insulin to survive. Providing insulin through an artificial pancreas is the most advanced way of keeping glucose within a tight range at all times most closely mimicking the body. The closest thing toward a cure for Type 1 is a pancreas transplant or a pancreas islet transplant. Transplant candidates must meet strict criteria to be eligible. Its not an option for everyone and it requires taking immunosuppressant medications for life and dealing with the side effects of these drugs.
Its possible to reverse prediabetes and Type 2 diabetes with a lot of effort and motivation. Youd have to reverse all your risk factors for disease. To do this means a combination of losing weight, exercising regularly and eating healthy . These efforts should also lower your cholesterol numbers and blood pressure to within their normal range. Bariatric surgery has been shown to achieve remission in some people with Type 2 diabetes. This is a significant surgery that has its own risks and complications.
Diagnosis For Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
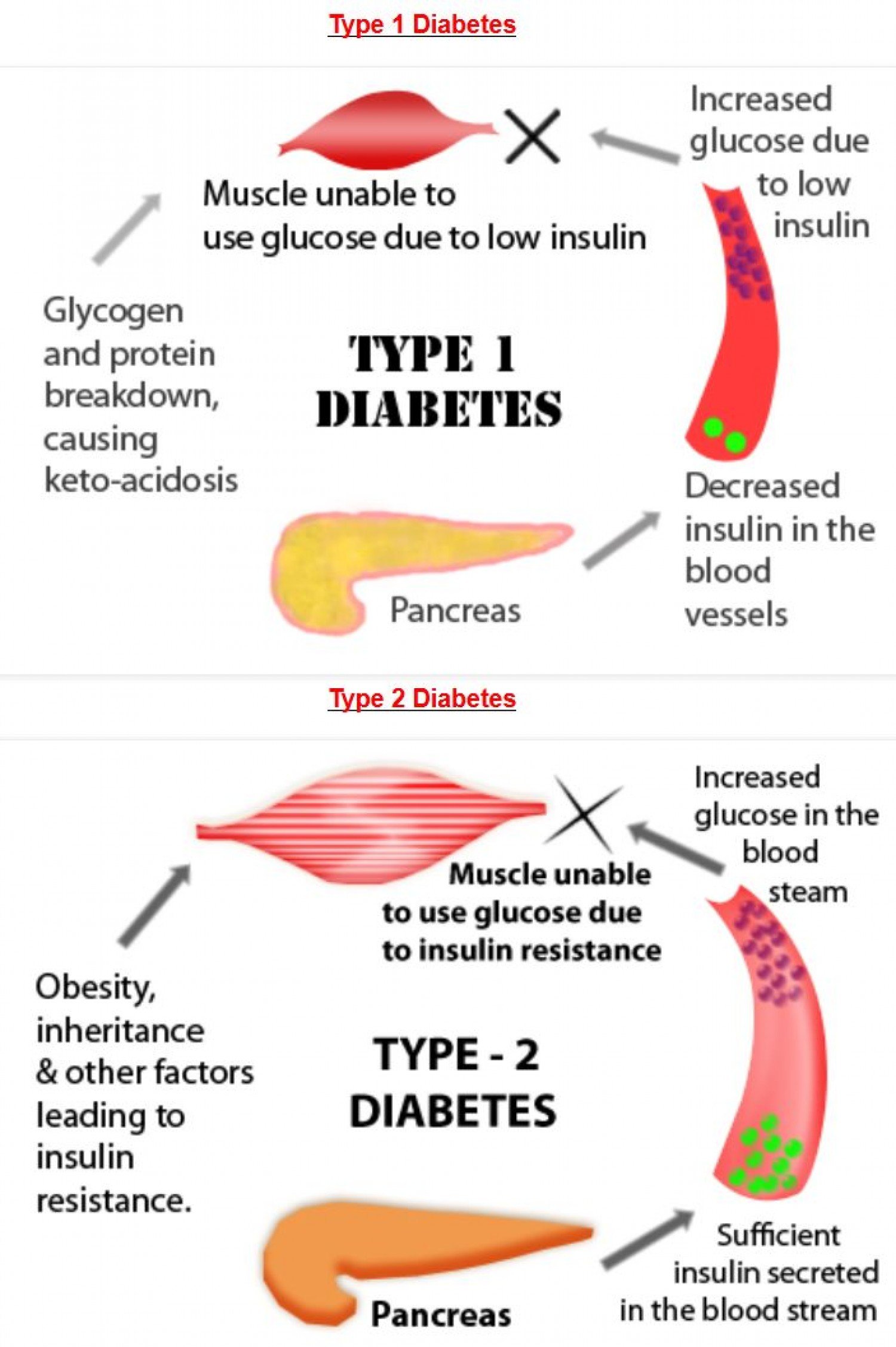
The development of type 1 diabetes is usually abrupt. If a person experiences symptoms, they should seek medical attention as soon as possible.
A person with type 2 diabetes in its initial stages, on the other hand, may have no symptoms. A normal blood test, however, will reveal high blood sugar levels at this point.
Obese people and others who are at risk for type 2 diabetes ought to have their glucose concentrations checked on a regular basis. They may have diabetes or prediabetes if their blood sugar levels are high.
Prediabetes is a condition in which a persons blood sugar levels are elevated but not elevated enough to be detected with type 2 diabetes.
The tests listed below can help identify type 1 or type 2 diabetes, however not all of them are appropriate for both:
The chart below indicates which test findings suggest diabetes:
| A1C | |
| Below 200 | Below 100 |
It is advised that patients aged 45 and up to be screened for type 2 diabetes on a routine basis. Younger people who are more at risk of developing diabetes, such as those with a family history of the disease, should be tested for type 2 diabetes on a frequent basis.
At home, people can monitor their blood sugar levels. A person who does not have diabetes but is concerned about readings from a home test should see their doctor.
Don’t Miss: Chromium Picolinate Dosage For Diabetes
Can Diabetes Be Prevented Or Cured
“As of now there is no way to prevent or cure type 1 diabetes,” Drincic notes. “There is lots of promising research, but it is still in the early stages.” Some of the initiatives involve targeting the cells in the immune system that cause the autoimmune response. Other possibilities include the use of stem cells or pancreas transplants.
Another area of research is diet and its effects on both prevention and diabetes maintenance. A study published in March 2017 in the British Journal of Nutrition reported that following a diet high in plant nutrients and low in meat consumption lowers a person’s risk of developing type 2 diabetes. The results indicated that certain compounds found in meat, rather than specific proteins, increased the risk of type 2 diabetes. Aside from eating healthy foods rich in plant nutrients, a large number of studies indicate that exercise is paramount not only for weight control, but also for maintaining a healthy, optimistic outlook.
Type 1 Diabetes Symptoms
Signs are often subtle, but they can become severe. They include:
- Extreme thirst
- Heavy, labored breathing
- Frequent infections of your skin, urinary tract, or vagina
- Crankiness or mood changes
- Bedwetting in a child whoâs been dry at night
Signs of an emergency with type 1 diabetes include:
- Shaking and confusion
- Loss of consciousness
Read Also: Foods Good For Kidney Disease And Diabetes
Outlook For Type 3 Diabetes
Type 3 diabetes is a way of describing Alzheimers thats caused by insulin resistance inside the brain. So, your outlook will vary according to several factors, including your diabetes treatment and the severity of your dementia.
If you can treat your diabetes with diet, exercise, and medication, researchers who promote the diagnosis of type 3 diabetes suggest that you may be able to slow the progression of Alzheimers or vascular dementia, but evidence is uncertain.
Your outlook will also vary according to how soon your symptoms were discovered and what your healthcare provider thinks about your specific case. The sooner treatment begins, its likely the better your outlook will be.
According to the Mayo Clinic, the average life expectancy for a person with Alzheimers is around 3 to 11 years from the time that theyre diagnosed. But some people with Alzheimers can live as many as 20 years post-diagnosis.
If you already have type 2 diabetes, there are ways that you can better manage it and lower your risk for developing type 3 diabetes.
Here are some of the proven methods for managing type 2 diabetes and minimizing organ damage:
- Try to exercise four times per week for 30 minutes per day.
Treating Type 1 Diabetes
It’s important that diabetes is diagnosed as early as possible. If left untreated, type-1 diabetes is a life-threatening condition. It’s essential that treatment is started early.
Diabetes can’t be cured, but treatment aims to keep your blood glucose levels as normal as possible and control your symptoms, to prevent health problems developing later in life.
If you’re diagnosed with diabetes, you’ll be referred to a diabetes care team for specialist treatment and monitoring.
As your body can’t produce insulin, you’ll need regular insulin injections to keep your glucose levels normal. You’ll be taught how to do this and how to match the insulin you inject to the food you eat, taking into account your blood glucose level and how much exercise you do.
Insulin injections come in several different forms, with each working slightly differently. You’ll most likely need a combination of different insulin preparations.
Insulin is given to some patients by a continuous infusion of fast acting insulin . This is where a small device constantly pumps insulin into your bloodstream through a plastic tube that’s inserted under the skin with a needle.
There are alternatives to insulin injections and pumps, but they’re only suitable for a small number of patients. They are:
Read more about diagnosing diabetes and treating type 1 diabetes
Recommended Reading: Diagnosing Type 1 Diabetes In Children