What Causes People With Diabetes To Get Diarrhea
The cause for the connection between diabetes and diarrhea isnt clear, but research suggests that neuropathy may be a factor. Neuropathy refers to numbness or pain resulting from nerve damage. If you have diabetes, high blood sugar levels can damage your nerve fibers. This generally occurs in the hands or feet. Issues with neuropathy are common causes for many of the complications that accompany diabetes.
Another possible cause is sorbitol. People often use this sweetener in diabetic foods. Sorbitol has proven to be a potent laxative in amounts as small as 10 grams.
An imbalance in your enteric nervous system can also cause diarrhea. Your ENS regulates the functions of your gastrointestinal system.
Researchers have also looked at the following possibilities:
- bacterial overgrowth
- fecal incontinence resulting from anorectal dysfunction
- Celiac disease
Can Diabetes Cause Headaches Or Dizziness
Yes, its possible to develop headaches or dizziness if your blood glucose level is too low usually below 70 mg/dL. This condition is called hypoglycemia. You can read about the other symptoms hypoglycemia causes in this article.Hypoglycemia is common in people with Type 1 diabetes and can happen in some people with Type 2 diabetes who take insulin or medications such as sulfonylureas.
Are There Any Other Treatments For Gastroparesis
A newer treatment for gastroparesis is called per oral pyloromyotomy . This is a nonsurgical procedure in which the doctor inserts an endoscope into the patients mouth and advances it to the stomach. The doctor then cuts the pylorus, the valve that empties the stomach, which allows food to move from the stomach to the small intestine more easily.
In a severe case of gastroparesis, your doctor may decide you would benefit from a feeding tube, or jejunostomy tube. The tube is inserted in a surgical procedure through your abdomen into your small intestine. To feed yourself, you put nutrients into the tube, which go directly into your small intestine this way, they go around the stomach and get into your bloodstream more quickly. The jejunostomy tube is usually a temporary measure.
Another treatment option is intravenous, or parenteral, nutrition. This is a feeding method in which nutrients go directly into your bloodstream through a catheter placed into a vein in your chest. Like a jejunostomy tube, parenteral nutrition is meant to be a temporary measure for a severe case of gastroparesis.
Read Also: What Should Be Fasting Blood Sugar Level
You May Like: Can You Eat After Taking Insulin
How Diabetes Affects The Skin
Diabetes affect on the skin is usually a result of its affect on the nerves and circulation which can lead to dry skin, slow healing of cuts, burns and wounds, fungal and bacterial infections and loss of feeling in the foot.
People with diabetes are recommended to have their feet checked at least once a year. The effect of diabetes on the feet is often referred to as diabetic foot
What Does It Mean If Test Results Show I Have Protein In My Urine
This means your kidneys are allowing protein to be filtered through and now appear in your urine. This condition is called proteinuria. The continued presence of protein in your urine is a sign of kidney damage.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Theres much you can do to prevent the development of diabetes . However, if you or your child or adolescent develop symptoms of diabetes, see your healthcare provider. The earlier diabetes is diagnosed, the sooner steps can be taken to treat and control it. The better you are able to control your blood sugar level, the more likely you are to live a long, healthy life.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 03/28/2021.
References
Also Check: How Can Diabetes Be Managed
Diabetes And Nerve Damage
Nerve damage can affect your hands, feet, legs, and arms.
High blood sugar can lead to nerve damage called diabetic neuropathy. You can prevent it or slow its progress by keeping your blood sugar as close to your target range as possible and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Managing your blood sugar is an essential part of your diabetes care plan. Not only does it help you with day-to-day wellness, it can help prevent serious health problems down the road.
Nerve damage is one possible complication from having high blood sugar levels for a long time. High blood sugar damages your nerves, and these nerves may stop sending messages to different parts of your body. Nerve damage can cause health problems ranging from mild numbness to pain that makes it hard to do normal activities.
Half of all people with diabetes have nerve damage. The good news is that you can help prevent or delay it by keeping your blood sugar as close to your target levels as possible. When you do this, youll also have more energy, and youll feel better!
Symptoms of nerve damage usually develop slowly, so its important to notice your symptoms early so you can take action to prevent it from getting more serious.
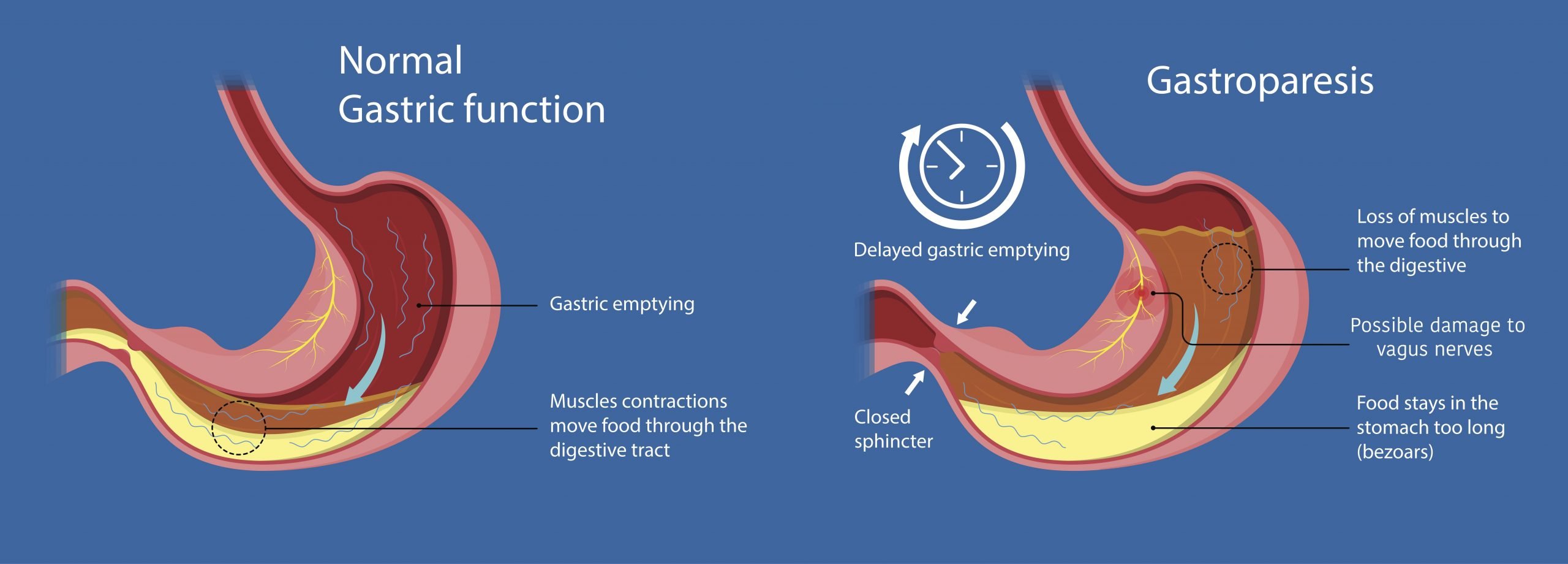
How Diabetes Affects The Stomach
According to doctors, the other term for gastroparesis is diabetic stomach. Autonomic neuropathy that is the damaging of the vagus nerve, makes the movement of the food slow, thus retaining it for an extended period. This accumulation of solid mass in the stomach leads to awful pain and discomfort.
The principal cause of this has been owed to diabetes. Although it occurs in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes, but according to WHO, type 1 patients are more frequented by it. Type 1 diabetes stomach problems include irregular bowel movements, accidental bowel leakage, prolonged removal of the stomachs content and bloating of the stomach.
Normally, the surplus glucose in the body, if any, is flushed out through urine. However, a diabetic patient with high glucose level can acquire urinary tract infection due to the bacterial development in the excretory system. It can also result in the damage of nerves and kidney.
Don’t Miss: Printable Low Carb Food List For Diabetics
Lauras Story Managing My Blood Sugars Around Gastroparesis
The most common pattern of otherwise irrational blood sugar fluctuations Laura experiences as a result of her gastroparesis are severe low blood sugars after eating because the insulin dose kicked-in but the food she ate wasnt being digested.
Then it causes very high sugars hours later, which take a long time to come down, especially throughout the night.
One tactic shes developed to manage this is by using the multiwave bolus on her insulin pump for meals.
I take an upfront amount of insulin before I eat, and then have the pump deliver the rest of the dose over the course of a few hours, explains Laura. Trying to estimate how many hours it will take for my food to digest is complete guesswork though, which is why I use a Freestyle Libre to track my blood sugars.
While the Freestyle Libre isnt a continuous glucose monitor like a DexCom or Medtronic CGM, it still provides instant data every time she swipes the device over the sensor site on her body.
If I see a sharp rise in my blood sugar, then I take more insulin and try my best to monitor everything.
Its an incredibly difficult balance act, which I feel, without a CGM or something like the Freestyle Libre, is impossible to manage.
Questions To Ask Your Doctor
- Ive never been diagnosed with diabetes, but I have many of the symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis. Do I have diabetes?
- Im having a hard time controlling my blood sugar levels. Am I at risk of diabetic ketoacidosis?
- Will diet and exercise help me to avoid diabetic ketoacidosis?
- If I notice Im having symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis, what should I do first?
- Is it safe for me to exercise?
- How often should I check my blood sugar level if Im sick?
- What is the best way for me to check the ketone level in my body?
- I missed a dose of insulin. Should I start testing my blood sugar level and ketone level right away?
Recommended Reading: What Is Diabetic Retinopathy Screening
How Does Type 1 Diabetes Affect The Digestive System
diabetesaffectOnedigestion
. People also ask, can Type 1 diabetes cause stomach problems?
Many children and adolescents with Type 1 diabetes suffer with delayed gastric emptying. exclusively in those individuals with long- standing diabetes. Gastroparesis can be evident early in the diagnosis of diabetes. Various regions of the diabetic stomach may be affected or hampered.
Furthermore, can high blood sugar cause digestive problems? Diabetes and GastroparesisHigh blood sugar from diabetes can cause chemical changes in the vagus nerve, which connects the brainstem to the gastrointestinal tract. Gastroparesis symptoms include nausea, vomiting, reduced appetite, feeling full after eating small amounts of food, abdominal pain, and heartburn.
Besides, how does Type 1 diabetes affect the urinary system?
Diabetics are prone to urinary tract infections , bladder issues and sexual dysfunction. Diabetes can often make your urologic conditions even worse because it can impact blood flow, nerves and sensory function in the body. But, in people with type 1 diabetes, the body doesnt make insulin at all.
How does diabetes affect other body systems?
The excess blood sugar in diabetes can wreak havoc on blood vessels all over the body and cause complications. It can severely damage the eyes, kidneys, nerves, and other body parts cause sexual problems and double the risk of heart attack and stroke.
Darker Area Of Skin That Feels Like Velvet
A dark patch of velvety skin on the back of your neck, armpit, groin, or elsewhere could mean that you have too much insulin in your blood. This is often a sign of prediabetes.The medical name for this skin condition is acanthosis nigricans.
Acanthosis Nigricans
Often causing darker skin in the creases of the neck, AN may be the first sign that someone has diabetes.
Take action
- Get tested for diabetes
Don’t Miss: What Is The Most Common Form Of Diabetes
Pathogenesis Of Gi Symptoms In Diabetes
In the broadest sense, GI symptoms in diabetes can be regarded as the outcome of a disordered gut-brain axis. Potential pathogenic factors include autonomic and peripheral neuropathy, structural and functional central nervous system changes , acute and chronic dysglycemia, psychological dysfunction, and pharmacotherapy. Specific pathogenic factors relevant to each section of the GI tract are discussed subsequently.
The putative association of GI symptoms with disordered GI motor function arising from irreversible autonomic neuropathy is long-standing . The few tests that specifically evaluate GI autonomic function are not widely available , and standardized tests of cardiovascular reflexes typically are used as a surrogate . Autonomic neuropathy, as assessed by these tests, is closely associated with symptoms and signs of peripheral neuropathy in diabetes . However, the relationships between GI symptoms and the presence of autonomic or peripheral neuropathy are weak .
Structural and functional changes in the CNS may influence the perception and generation of symptoms, with evidence of both gastric hypersensitivity and rectosigmoid hyposensitivity . Brock et al. investigated neurophysiological changes in a predominantly type 1 diabetes cohort and reported evidence of rectosigmoid hyposensitivity and bilateral anterior shifting of the insula and cingulate sources of brain activity, which correlated positively with postprandial fullness and nausea.
Healthy Digestion And Converting Foods Into Energy
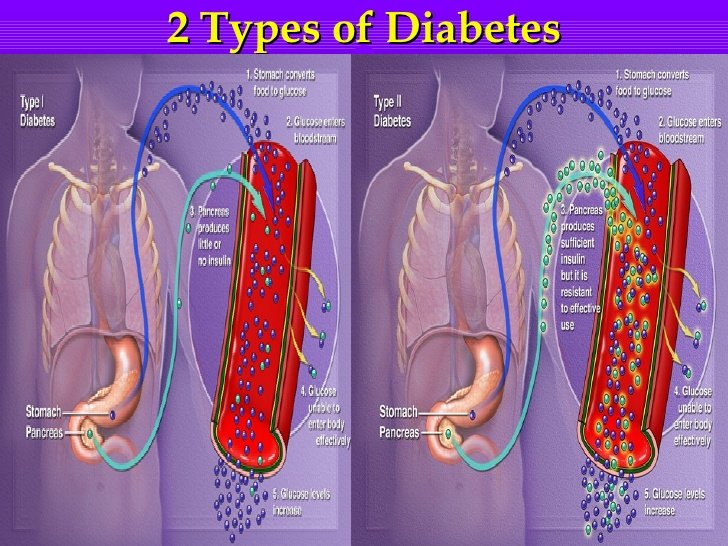
To understand diabetes, it helps to know how our bodies handle the sugars and energy found in our food and drinks.
In people with diabetes, this process can go wrong in two ways. Either:
People with diabetes may have the following symptoms when their blood sugar is extremely high:
- Confusion
- Increased urination
- Lethargy
Recommended Reading: Sure Comfort Insulin Syringes 30 Gauge
Gastroparesis In People With Diabetes Despite Healthy Blood Sugar Levels
While its usually associated with high blood sugar levels, diabetic gastroparesis can sometimes develop even if your HbA1c is in a healthy range and blood sugars are in your goal range.
Generally, a person who develops complications of diabetes despite healthy blood sugar levels will experience a combination of conditions rather than just one. For example: gastroparesis and retinopathy, or peripheral neuropathy and retinopathy.
Can You Have Neuropathy In Your Stomach
Neuropathy in the stomach occurs when the nerves supplying it are damaged due to do any cause. The stomach contains two layers of nervous tissue in it in the form of plexus formation. One layer is present in submucosa known as Meissners plexus and the other layer is present in between the muscular layer known as myenteric plexus or Auerbach plexus. The plexus controls glandular secretions like secretions of parietal cell, chief cell, etc., alters electrolyte and water transport across the luminal membrane, and regulates capillary blood flow of the local vessels and sometimes may also change the configuration of the luminal surface of the stomach. The myenteric plexus controls the muscles of the stomachthe including both circular and longitudinal muscles. It is responsible for the gastric emptying, churning of food, etc.
The most common cause of gastric neuropathy is diabetes mellitus. It causes dysfunction of the autonomic nerves known as autonomic neuropathy. Other causes of gastric neuropathy include HIV, amyloidosis, inherited neuropathies, botulism, autoimmune causes like systemic lupus erythematosus, etc. These causes can affect both the plexuses of the stomach and in turn affect the normal functioning of the stomach. Since diabetes is a modern epidemic and has a very high number of cases, the cases of uncontrolled diabetes are not uncommon which is frequently seen associated with autonomic neuropathy.
Also Check: Diagnosing Type 1 Diabetes In Children
How Is Diabetic Gastroparesis Treated
Your healthcare provider may change one or more of your current medicines. Do not change your medicines without direction from your provider. Any of the following may also be used to treat gastroparesis:
- Medicines:
- Motility medicines help your stomach muscles move food and liquids out of your stomach faster. These medicines also may help you digest food better.
- Nausea medicine helps calm your stomach and prevent vomiting.
- An antibiotic may be given for a short time to help your stomach empty more quickly.
Who Gets Diabetes What Are The Risk Factors
Factors that increase your risk differ depending on the type of diabetes you ultimately develop.
Risk factors for Type 1 diabetes include:
- Having a family history of Type 1 diabetes.
- Injury to the pancreas .
- Presence of autoantibodies .
- Physical stress .
- Exposure to illnesses caused by viruses.
Risk factors for prediabetes and Type 2 diabetes include:
- Family history of prediabetes or Type 2 diabetes.
- Being African-American, Hispanic, Native American, Asian-American race or Pacific Islander.
- Being overweight.
Risk factors for gestational diabetes include:
- Family history of prediabetes or Type 2 diabetes.
- Being African-American, Hispanic, Native American or Asian-American.
- Being overweight before your pregnancy.
- Being over 25 years of age.
Read Also: Why Are Diabetic Supplies So Expensive
What Is The Relationship Between Liver And Metabolism
The liver is the only organ that metabolizes sugar. Only the liver can transport sugar. Active people or athletes can consume a lot of fructose without any worries. Their liver converts the fructose into glycogen and stores it.
If you have diabetes, it is either your body does not use insulin properly or it lacks it. Carbohydrates are essential in your body as all the cells in the body use it for energy.
The only organ that requires glucose for energy is your brain. Carbohydrates supply your brain with energy. Carbohydrates are also necessary for fat metabolism.
The endocrine system is a network of glands that regulates metabolism. The system comprises of pineal, hypothalamus, thymus, testis, thyroid, ovaries, adrenal glands, and pancreases to mention but a few. These glands work as a team. They release several hormones that operate as chemical messengers to manage metabolism.
Pancreases in the endocrine region produce insulin and glucagon. The endocrine system influences metabolism a great deal. Endocrine plays a direct and indirect role in changing several bodily functions such as inflammation, immune system, energy expenditure, mineral regulation, cellular repair, stomach, and intestines and functional of all organs.
When To Contact A Medical Professional
- Chest pain or pressure
- Shortness of breath
- Red, painful skin that is spreading quickly
These symptoms can quickly get worse and become emergency conditions .
Also call your provider if you have:
- Numbness, tingling, or pain in your feet or legs
- Problems with your eyesight
- Sores or infections on your feet
- Symptoms of high blood sugar
- Symptoms of low blood sugar
- Frequent feelings of depression or anxiety
Don’t Miss: What Do You Do If You Think You Have Diabetes