Control Blood Pressure And Slow Progression Of Kidney Disease
People with IgA nephropathy that is causing high blood pressure may need to take medications that lower blood pressure and can also significantly slow the progression of kidney disease. Two types of blood pressure-lowering medicationsangiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers have proven effective in slowing the progression of kidney disease. Many people require two or more medications to control their blood pressure. A person may also need beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, and other blood pressure medications.
How Common Is Iga Nephropathy And Who Is More Likely To Get The Disease
IgA nephropathy is one of the most common kidney diseases, other than those caused by diabetes or high blood pressure.1
IgA nephropathy can occur at any age, although the first evidence of kidney disease most frequently appears when people are in their teens to late 30s.2 IgA nephropathy in the United States is twice as likely to appear in men than in women.3 While found in people all over the world, IgA nephropathy is more common among Asians and Caucasians.4
A person may be more likely to develop IgA nephropathy if
- he or she has a family history of IgA nephropathy or IgA vasculitisa disease that causes small blood vessels in the body to become inflamed and leak
- he is a male in his teens to late 30s
- he or she is Asian or Caucasian
Effect Of Glycemic Control
The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial and the United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study have definitively shown that intensive diabetes therapy can significantly reduce the risk of the development of microalbuminuria and overt nephropathy in people with diabetes. The glycemic control recommendations for all patients with diabetes in the American Diabetes Associations Standards of Medical Care for Patients with Diabetes Mellitus should be followed in this regard.
Recommended Reading: How Much Sugar A Day To Get Diabetes
What Are The Symptoms Of Diabetic Kidney Disease
You are unlikely to have symptoms with early diabetic kidney disease – for example, if you just have microalbuminuria . Symptoms tend to develop when the kidney disease progresses. The symptoms at first tend to be vague and nonspecific, such as feeling tired, having less energy than usual and just not feeling well. With more severe kidney disease, symptoms that may develop include:
- Difficulty thinking clearly.
- Needing to pass urine more often than usual.
- Being pale due to anaemia.
- Feeling sick .
As the kidney function declines, various other problems may develop – for example, anaemia and an imbalance of calcium, phosphate and other chemicals in the bloodstream. These can cause various symptoms, such as tiredness due to anaemia, and bone ‘thinning’ or fractures due to calcium and phosphate imbalance. End-stage kidney failure is eventually fatal unless treated.
Eating Diet And Nutrition

Researchers have not found that eating, diet, and nutrition play a role in causing or preventing IgA nephropathy. Health care providers may recommend that people with kidney disease, such as IgA nephropathy, make dietary changes such as
- limiting dietary sodium, often from salt, to help reduce edema and lower blood pressure
- eating a diet low in saturated fat and cholesterol to help control high levels of lipids, or fats, in the blood
Health care providers may also recommend that people with kidney disease eat moderate or reduced amounts of protein, although the benefit of reducing protein in a persons diet is still being researched. Proteins break down into waste products the kidneys must filter from the blood. Eating more protein than the body needs may burden the kidneys and cause kidney function to decline faster. However, protein intake that is too low may lead to malnutrition, a condition that occurs when the body does not get enough nutrients. People with kidney disease on a restricted protein diet should receive blood tests that can show nutrient levels.
People with IgA nephropathy should talk with a health care provider about dietary changes to best manage their individual needs.
Read Also: Signs Your Kid Has Diabetes
What Is The Outlook
- If you have microalbuminuria , this may clear away, especially with treatment.
- If you have proteinuria , over time the disease tends to become worse and progress to end-stage kidney failure. However, the length of time this takes can vary and it may take years. If your kidneys do begin to fail you should be referred to a kidney specialist.
- Once the kidney function goes below a certain level then you will need kidney dialysis or a kidney transplant.
- A main concern is the increased risk of developing cardiovascular diseases. Cardiovascular diseases, such as heart attack and stroke, are the main causes of death in people with diabetic kidney disease. The treatments outlined above will reduce the risk of these occurring.
Risk Factors And Pathogenesis
Diabetic nephropathy develops in, at most, 40% of patients with diabetes, even when high glucose levels are maintained for long periods of time. This observation raised the concept that a subset of patients have an increased susceptibility to diabetic nephropathy. Furthermore, epidemiological and familial studies have demonstrated that genetic susceptibility contributes to the development of diabetic nephropathy in patients with both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. The main potentially modifiable diabetic nephropathy initiation and progression factors in susceptible individuals are sustained hyperglycemia and hypertension . Other putative risk factors are glomerular hyperfiltration , smoking , dyslipidemia , proteinuria levels , and dietary factors, such as the amount and source of protein and fat in the diet.
Also Check: Type 2 Diabetes Occurs When
What Is The Function Of The Kidneys
The kidneys are organs comprised of millions of small blood vessels that work to filter the blood and remove waste products. When the human body metabolizes protein, waste products are produced these waste products are normally filtered through the kidneys.
The kidneys filtering system involves millions of minute blood vessels with very small holes. The common waste products such as urea, ammonia, and creatinine go through the holes and are excreted into the urine. Larger molecules and cells, such as proteins, red blood cells, and white blood cells stay in the blood because they are too large to be filtered into the urine.
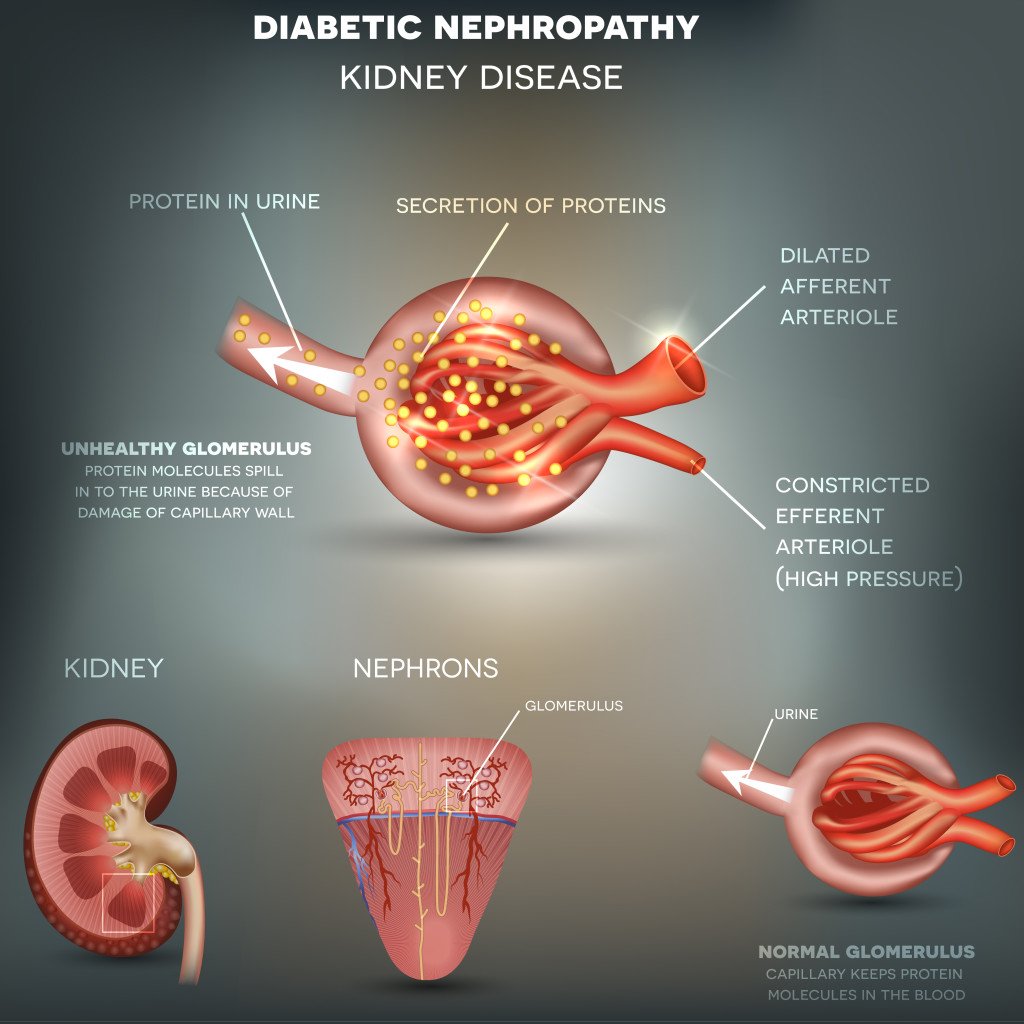
High blood glucose levels such as seen in diabetes can damage organs, including the kidneys’ filtering system, allowing leakage of proteins into the urine. This condition is called diabetic nephropathy. When left untreated, it can lead to kidney failure.
What Causes Kidney Disease
One of the main jobs of your kidneys is to filter your blood. They get rid of extra fluid and waste products from your body through your urine.
High blood glucose levels can damage the small blood vessels and tiny filters in your kidneys. High blood pressure can also do this too. This can cause them to leak and not work as well. When this happens, abnormal amounts of protein from the blood can leave your body in your urine. This is often an early sign of kidney disease.
Recommended Reading: How To Lose Weight When You Are Diabetic
What Happens To The Kidneys In Diabetes
The main function of the kidneys is to filter waste products and excess water from the bloodstream so that they can be excreted in the form of urine. This is carried out by a system of tubes and blood vessels known as nephrons. Inside the nephrons are tiny blood vessels called capillaries and tiny urine-collecting tubes. One of the major structures in the nephron is a group of blood vessels known as the glomerulus, which acts as a filter.
Having high blood glucose levels can interfere with the function of the glomerulus. The filtering function of the kidneys doesnt work properly and proteins start to leak from the blood into the urine.
High blood glucose levels can also cause scarring of the glomerulus . As the scarring gets worse, the kidneys stop being able to filter waste products from the blood.
When enough glomeruli have been damaged, kidney failure results.
People who have diabetic nephropathy also often have high blood pressure. High blood pressure can further contribute to kidney damage.
Treatment For Diabetic Nephropathy
Early detection and treatment of diabetic nephropathy can not only stop the progression of kidney disease in people with diabetes, but during the early stages can actually reverse it. Treatment involves controlling both your blood glucose levels and your blood pressure.
Blood glucose levels should be kept in the normal range as much as possible to prevent or slow the progression of diabetic nephropathy. Lifestyle measures in combination with oral diabetes medicines or insulin can be used to control blood glucose levels.
People with type 2 diabetes who have microalbuminuria or proteinuria are usually also treated with medicines called angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers . These medicines are also used to control blood pressure, but even if your blood pressure is normal, your doctor may prescribe an ACE inhibitor or ARB because they decrease the amount of protein in the urine and can prevent or slow the progression of diabetic kidney disease.
Other medicines may also be prescribed to help control high blood pressure.
Also Check: How Close Are We To Curing Diabetes
What Are Some Preventive Measures You Can Take Along With The Treatment
There are some guidelines that you can follow during ayurvedic treatment for diabetic nephropathy.
Control your diabetes. Work on your blood sugar goals to prevent the risk of diabetic nephropathy later in life. You can do this by following a diet plan and taking ayurvedic treatment.
Regulate your blood pressure. Hypertension and other conditions may damage kidney function abruptly and severely. To regulate your blood pressure, make sure that you do not consume alcohol and do running.
Follow instructions on over-the-counter medicines. Over-the-counter medicines like aspirin and ibuprofen substantially increase the risk of kidney damage.
Do not smoke. The attributed factor is â the waste produced because of smoke from the cigarette starts to build up in the body. And over time, the kidneys may lose their function when eliminating them.
Maintain a healthy weight. If youâre obese, work to maintain your weight by being physically active most days of the week. Along with the measures, make sure to rely on Ayurvedic Treatment For Diabetic Nephropathy for a healthy recovery.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Iga Nephropathy
In its early stages, IgA nephropathy may have no symptoms it can be silent for years or even decades. Once symptoms appear, the most common one is hematuria, or blood in the urine. Hematuria can be a sign of damaged glomeruli. Blood in the urine may appear during or soon after a cold, sore throat, or other respiratory infection. The amount of blood may be
- visible with the naked eye. The urine may turn pink or the color of tea or cola. Sometimes a person may have dark or bloody urine.
- so small that it can only be detected using special medical tests.
Another symptom of IgA nephropathy is albuminuriawhen a persons urine contains an increased amount of albumin, a protein typically found in the blood, or large amounts of protein in the urine. Albumin is the main protein in the blood. Healthy kidneys keep most proteins in the blood from leaking into the urine. However, when the glomeruli are damaged, large amounts of protein leak out of the blood into the urine.
When albumin leaks into the urine, the blood loses its capacity to absorb extra fluid from the body. Too much fluid in the body may cause edema, or swelling, usually in the legs, feet, or ankles and less often in the hands or face. Foamy urine is another sign of albuminuria. Some people with IgA nephropathy have both hematuria and albuminuria.
After 10 to 20 years with IgA nephropathy, about 20 to 40 percent of adults develop end-stage kidney disease.5 Signs and symptoms of end-stage kidney disease may include
Also Check: Diabetic Fasting Blood Sugar Goal
Treating Kidney Disease Safely The Sick
Several classes of medications used commonly in people with diabetes can reduce kidney function during periods of intercurrent illness, and should be discontinued when a person is unwell, in particular, when they develop significant intravascular volume contraction due to reduced oral intake or excessive losses due to vomiting or diarrhea. Diuretics can exacerbate intravascular volume contraction during periods of intercurrent illness. Blockers of the RAAS interfere with the kidney’s response to intravascular volume contraction, namely the ability of angiotensin II to contract the efferent arteriole to support glomerular filtration during these periods. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatories cause constriction of the afferent arterioles, which can further reduce blood flow into the glomerulus, especially in people who are volume contracted. For these reasons, all of these drugs can reduce kidney function during times of intercurrent illness. Consideration should be given to providing people with a sick-day medication list, instructing the patient to hold these medications if they feel that they are becoming dehydrated for any reason. A number of additional medications need to be dose-adjusted in people with renal dysfunction, and their usage and dosage should be re-evaluated during periods where kidney function changes .
Medications For Diabetic Nephropathy
- SGLT2 inhibitors: this controls high blood glucose levels
- Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme inhibitors: However, some of the medicines under this drug category, such as ramipril , quinapril , and lisinopril are the medicines given to blood pressure patients. But to lower the complications, diabetes patients also rely on these.
- Angiotensin Receptor Blockers : If the patient suffers from any side effects of ACE inhibitors, these medications help instead.
If left untreated, the kidneys will fail to function and the only option left to you will be either Dialysis or go for a kidney transplant.
You May Like: Diabetes Kidney Failure Life Expectancy
Intensive Blood Glucose Control
Clinical trials have consistently demonstrated that A1c levels < 7% are associated with decreased risk for clinical and structural manifestations of diabetic nephropathy in type 1 and type 2 diabetic patients. In the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial , intensive treatment of diabetes reduced the incidence of microalbuminuria by 39% . It is interesting to note that patients randomized to strict glycemic control had a long-lasting reduction of 40% in the risk for development of microalbuminuria and hypertension 78 years after the end of the DCCT . In the UKPDS, a 30% risk reduction for the development of microalbuminuria was observed in the group intensively treated for hyperglycemia . Moreover, in the Kumamoto Study, intensive glycemic control also reduced the rate of development of micro- and macroalbuminuria . Therefore, intensive treatment of glycemia aiming at A1c < 7% should be pursued as early as possible to prevent the development of microalbuminuria.
Workup In Diabetic Nephropathy
Diabetic nephropathy is characterized by the following:
- Persistent albuminuria that is confirmed on at least two occasions 3-6 months apart
- A relentless decline in the glomerular filtration rate
- Elevated arterial blood pressure
A 24-hour urinalysis for urea, creatinine, and protein is extremely useful in quantifying protein losses and estimating the GFR.
Blood tests, including calculation of GFR , are helpful in monitoring for the progression of kidney disease and in assessing its stage.
Renal ultrasonography is performed to observe for kidney size, which is usually normal to increased in the initial stages and, later, decreased or shrunken with chronic renal disease. Rule out obstruction. Perform echogenicity studies for chronic renal disease.
You May Like: Do Type 2 Diabetics Take Insulin Shots
What Is The Treatment For Diabetic Kidney Disease
Treatments that may be advised are discussed below. Treatments aim to:
- Prevent or delay the disease progressing to kidney failure. In particular, if you have early diabetic kidney disease it does not always progress to the proteinuria phase of the disease.
- Reduce the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases such as heart disease and stroke.
Use Of Antihypertensive Agents
The positive response to antihypertensive treatment coupled with the concept that often there is a progressive deterioration of renal function regardless of the underlying etiology gave rise to the idea that hemodynamic factors may be critical in furthering the fall in GFR. In this hypothesis, damage to glomeruli causes changes in the microcirculation that result in hyperfiltration occurring in the remaining glomeruli with increased intraglomerular pressure and increased sensitivity to angiotensin II the single-nephron hyperfiltration with intraglomerular hypertension is itself damaging. Many studies have shown that in hypertensive patients with type 1 diabetes, ACE inhibitors can reduce the level of albuminuria and the rate of progression of renal disease to a greater degree than other antihypertensive agents that lower blood pressure by an equal amount. Other studies have shown that there is benefit in reducing the progression of microalbuminuria in normotensive patients with type 1 diabetes and normotensive and hypertensive patients with type 2 diabetes.
Because of the high proportion of patients who progress from microalbuminuria to overt nephropathy and subsequently to ESRD, use of ACE inhibitors or ARBs is recommended for all patients with microalbuminuria or advanced stages of neuropathy. The effect of ACE inhibitors appears to be a class effect, so choice of agent may depend on cost and compliance issues.
Also Check: Are Protein Shakes Good For Diabetics
Review Of Your Medication
Certain medicines can affect the kidneys as a side-effect which can make diabetic kidney disease worse. For example, you should not take anti-inflammatory medicines unless advised to by a doctor. You may also need to adjust the dose of certain medicines that you may take if your kidney disease becomes worse.
Age Distribution For Diabetic Nephropathy
Diabetic nephropathy rarely develops before 10 years duration of type 1 DM. The peak incidence is usually found in persons who have had diabetes for 10-20 years. The mean age of patients who reach end-stage kidney disease is about 60 years. Although in general, the incidence of diabetic kidney disease is higher among elderly persons who have had type 2 diabetes for a longer generation, the role of age in the development of diabetic kidney disease is unclear. In Pima Indians with type 2 diabetes, the onset of diabetes at a younger age was associated with a higher risk of progression to end-stage kidney disease.
Recommended Reading: How To Count Carbs For Type 1 Diabetes