Why Your A1c Matters
In a nutshell: your A1c is one of the clearest indicators of your risk for developing diabetes complications like neuropathy , retinopathy , nephropathy , and severe infection in any part of your body that requires healing.
For instance, a small cut on your toe could become infected due to high blood sugars, struggle to heal, and become severe enough that the infection could lead to an amputation.
The general guidelines from the American Diabetes Association recommend an A1c at or below 7.0 percent for the best prevention of diabetes complications. Your risk of developing a diabetes complication continues to drop as your A1c drops closer to 6 percent.
Some people with diabetes aim for A1c levels in the 5s and lower especially those who follow strict low-carb diets like the ketogenic diet and the Bernstein diet. However, this hasnt been proven in research as especially necessary, nor is it reasonably achievable for the larger population of people with diabetes.
Its also important to remember that your blood sugar levels and your A1c are just information that tells you whether your body needs more or less of factors like insulin, other diabetes medications, changes in your nutrition, and changes in your exercise.
If you dont like the number youre seeing on your glucose meter or your A1c results, use that number as motivation to make changes in how you safely manage your diabetes in order to get different results.
Risks Of Abnormal Fasting Blood Sugar Levels
As suggested earlier, the normal fasting blood sugar level is between 70-100mg/dl.
- If your blood sugar level is below 70mg/dl then you may have hypoglycemia or low blood sugar.
- A blood sugar level of 100 suggests prediabetes or borderline diabetes.
- A blood sugar of 120 mg/dl is an indication of diabetes.
Who Should Do The Test
According to the American Diabetes Association, screening for diabetes is recommended in people over 45 , or at any age if you have certain risk factors, including :
- Being overweight, obese, or physically inactive
- Having a close relative with diabetes
- Belonging to a certain race/ethnic group
- Having signs of insulin resistance or conditions associated with insulin resistance, such as high blood pressure , low good cholesterol and/or high triglycerides , and polycystic ovary syndrome
- Having had diabetes in pregnancy
Also Check: Does Being Diabetic Make You Gain Weight
Normal Ranges For Blood Sugar
People who dont have diabetes or pre-diabetes keep their blood sugars between 60 100 mg/dl overnight and before meals, and less than 140 mg/dl after meals. Although the ultimate goal of diabetes management is to return the blood sugar to the natural or non-diabetic level, this may be difficult without excessive low blood sugars or hypoglycemia.
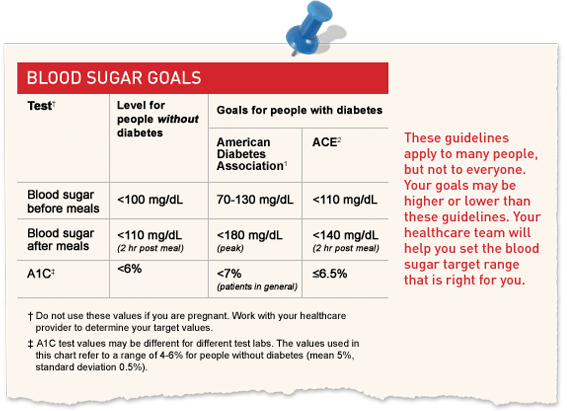
Goals For Blood Glucose Control
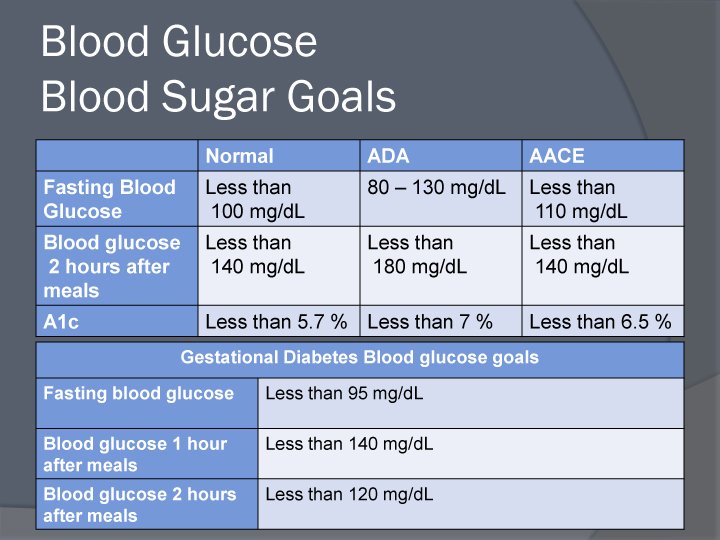
People who have diabetes should be testing their blood glucose regularly at home. Regular blood glucose testing helps you determine how well your diabetes management program of meal planning, exercising and medication is doing to keep your blood glucose as close to normal as possible. The results of the nationwide Diabetes Control and Complications Trial show that the closer you keep your blood glucose to normal, the more likely you are to prevent diabetes complications such as eye disease, nerve damage, and other problems. For some people, other medical conditions, age, or other issues may cause your physician to establish somewhat higher blood glucose targets for you. The following chart outlines the usual blood glucose ranges for a person who does and does not have diabetes. Use this as a guide to work with your physician and your healthcare team to determine what your target goals should be, and to develop a program of regular blood glucose monitoring to manage your condition. Time of Check Goal plasma blood glucose ranges for people without diabetes Goal plasma blood glucose ranges for people with diabetes Before breakfast < 100 70 – 130 Before lunch, supper and snack < 110 70 – 130 Two hours after meals < 140 < 180 Bedtime < 120 90- 150 A1C < 6% < 7% < = less than > = greater than > = greater than or equal to < = less than or equal to Information obtained from Joslin Diabetes Center’s Guidelines for Pharmacological Management of Type 2 Diabetes.Continue reading > >
You May Like: Best Sweetener For Baking For Diabetics
A Tool For Improving Our Knowledge On The Pathophysiology Of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a disease characterized by three main abnormalities : 1) a defect of -cell function , 2) a state of insulin resistance , and 3) an overproduction of glucose by the liver . Despite that currently available oral hypoglycemic agents are able to target deficiencies in either the endogenous insulin secretion or the insulin sensitivity at different target sites, the attainment of satisfactory diabetes control becomes more and more difficult the longer the duration of the disease .
Measurement Of Glycosylated Hemoglobin
Periodic Measurement of Glycated Hemoglobin. Another method to monitor the control of blood sugar in people with diabetes is through a blood test called hemoglobin A1c or glycohemoglobin .
This test can be done through a local laboratory or can be drawn at a doctor’s office, but unlike simple measurement of blood glucose levels, this cannot be done at home. The level of glycosylated hemoglobin correlates very well with a person’s recent overall blood sugar levels.
Hemoglobin A1c will tell what the diabetic’s blood sugar levels have been running for the past 2 to 3 months. If the blood sugars have generally been running high during the previous few months, the level of hemoglobin A1c will be high. If blood glucose concentrations have been running close to normal during this time, the hemoglobin A1c level will be close to values seen in normal persons.
It is an important value to monitor periodically. Studies have shown that glycohemoglobin values in the “better ranges” correlate with less incidence of diabetic complications later in life. People with type 1 diabetes will typically have hemoglobin A1c levels determined every 3 to 4 months, while people with type 2 diabetes will often require measurements less often.
Values vary from lab to lab but below is a common value system for hemoglobin A1c:
Hemoglobin A1cPoor: Greater than 9.5
Recommended Reading: Treatment Of Type 1 Diabetes In Child
What Should I Do After I Check My Blood Glucose
Write the blood glucose number in a log book or on a log sheet , and:
- Include all of your blood glucose numbers.
- Write a comment if there is a reason the blood glucose is above or below target.
- Take your blood glucose meter with you when you are away from home.
- Know your blood glucose numbers when you call the clinic or the doctor.
- Bring your blood glucose meter and blood glucose records to all your appointments.
- Bring a list of any questions that you may have.
How Is Blood Sugar Measured
In the United States, blood sugar is measured in milligrams per deciliter . This is abbreviated as mg/dl.
In Europe and Canada, blood sugar is measured a little differently, by millimole per liter, which is abbreviated mmol. However its measured, blood sugar is the concentration of sugar or glucose in the bloodstream.
If you multiply the Canadian or European mmol, by the number 18, you can calculate milligrams per deciliter.
In other words, if a person in Canada reports their blood sugar as an 8, multiply 8 times 18 to give you the number 144 . Using this calculation, this persons blood sugar = 144 mg/dl, .
Also Check: Diabetes How To Control Blood Sugar
Why Is It Important To Have Good Control Of Diabetes
Studies have recently shown that overall good control of blood sugar in diabetes does correlate with decreased incidence of diabetic complications. So, the answer is yes, it is important to control glucose levels as best as possible. In people with type 1 diabetes who are on insulin and in some people with type 2 diabetes, efforts to have control too tight may result in too many episodes of hypoglycemia . Therefore, the goal is to balance trying to have control as near normal as possible while trying to avoid hypoglycemic episodes.
Normal Blood Sugar Ranges In Healthy Non
For a person without any type of diabetes, blood sugar levels are generally between 70 to 130 mg/dL depending on the time of day and the last time they ate a meal. Newer theories about non-diabetic blood sugar levels have included post-meal blood sugar levels as high as 140 mg/dL.
Here are the normal blood sugar ranges for a person without diabetes according to the American Diabetes Association:
- Fasting blood sugar : under 100 mg/dL
- 1 hour after a meal: 90 to 130 mg/dL
- 2 hours after a meal: 90 to 110 mg/dL
- 5 or more hours after eating: 70 to 90 mg/dL
Also Check: Type 2 Diabetes Dry Mouth
Check Your Blood Sugar If:
- You have symptoms of low blood sugar . This includes dizziness, shaking, sweating, chills, and confusion.
- You have symptoms of high blood sugar , which include sleepiness, blurry vision, frequent urination, and excessive thirst.
- You have a job in which poor blood sugar control could cause safety problems.
- You need help deciding if its safe to drive or perform other tasks that require concentration if you are taking insulin or have had hypoglycemia in the past.
You need to learn how meals, physical activity, and medicine affect your blood sugar level.
What Is The A1c Test
The A1C test is a simple blood test that measures your average blood sugar levels over the past 2 or 3 months. The test is done at a lab or your doctors office in addition tonot instead ofregular blood sugar testing you do yourself.
A1C testing is part of the ABCs of diabetesimportant steps you can take to prevent or delay health complications down the road:
- A: Get a regular A1C test.
- B: Try to keep your blood pressure below 140/90 mm Hg .
- C: Manage your cholesterol levels.
- s: Stop smoking or dont start.
The A1C goal for most adults with diabetes is between 7% and 8%, but your goal may be different depending on your age, other health conditions, medicines youre taking, and other factors. Work with your doctor to establish a personal A1C goal for you.
Recommended Reading: What Is Diabetic Retinopathy Screening
Diagnosing Prediabetes Type 2 And Type 1 Diabetes
Depending on which country or medical organization you ask, the qualifying numbers for normal versus prediabetes versus diagnosed type 1 or type 2 diabetes can vary slightly. The following blood sugar and A1c the general results are used to diagnosed prediabetes and diabetes according to sources including the American Diabetes Association and Diabetes UK:
Prediabetes
- HbA1c: 5.7 to 6.4 percent
- Fasting: 100 to 125 mg/dL
- 2 hours after a meal: 140 mg/dL to 199 mg/dL
Type 1 or 2 diabetes
- HbA1c: 6.5 percent or higher
- Fasting: 126 mg/dL or higher
- 2 hours after a meal: 200 mg/dL or higher
Please note: Type 1 diabetes tends to develop very quickly which means that by the time symptoms are felt, blood sugar levels are generally well above 200 mg/dL all the time. For many, symptoms come on so quickly they are dismissed as the lingering flu or another seemingly ordinary virus.
By the time blood sugar levels are tested, many newly diagnosed type 1 patients will see levels above 400 mg/dL or higher. If you do suspect that you or a loved-one has type 1 diabetes, visit your primary care or urgent care immediately and ask for a urine test to measure ketones in addition to testing blood sugar levels and A1c.
Read more about ketones at diagnosis in Diabetes StrongsDiabetic Ketoacidosis Guide.
Translating Your A1c To A Blood Sugar Level
Using this easy calculator from the ADA, you can translate your most recent A1C result to an eAG or estimate average glucose level.
You can also use this translation when working to improve your A1c and achieving closer to normal blood sugar levels. If you know an A1c of 6.5 is an average blood sugar level of 126 mg/dL or a range of 100 to 152 mg/dL, then you can look at your current blood sugar results on your CGM and meter and pinpoint which time of day youre frequently higher than this range.12% = 298 mg/dL or range of 240 347 11% = 269 mg/dL or range of 217 31410% = 240 mg/dL or range of 193 2829% = 212 mg/dL or range of 170 2498% = 183 mg/dL or range of 147 2177% = 154 mg/dL or range of 123 1856% = 126 mg/dL or range of 100 1525% = 97 mg/dL or range of 76 120
Normal blood sugar levels in a person without diabetes can result in an A1c as low as 4.6 or 4.7 percent and as high as 5.6 percent.
Just a decade or two ago, it was rare for a person with type 1 diabetes to achieve an A1c result below 6 percent. Thanks to new and improved insulin and better technology like continuous glucose monitors and smarter insulin pumps, more people with diabetes are able to safely achieve A1c levels in the higher 5 percent range.
Also Check: Is Type 2 Diabetes Serious
Measurement Of Blood Glucose
When we speak about measuring blood glucose levels, it can be done 2 different ways. Blood glucose can be measured randomly from a sample taken at any time .
Blood glucose can also be measured in the “fasting” state, meaning that the person has not eaten or taken in any calories in the past 8 hours .
In a person with normal insulin production and activity blood sugar levels will return to “fasting” levels within 3 hours of eating. People with diabetes may not be able to get their blood glucose down this quickly after a meal or drinking a calorie-containing drink. More about this can be found on our Diagnosing Diabetes page.
Management Of Blood Glucose Levels
Insulin resistance, decreased insulin secretion, and increased hepatic glucose output are the hallmarks of type 2 diabetes. Medications target one or more of these defects .1113 Average absolute reductions in A1C for each class of medication range from 0.5 to 1.0 percent for exenatide , pramlintide , and alpha-glucosidase inhibitors to 1 to 2.5 percent for sulfonylureas and metformin.14 Reviews have reported that mono-therapy with any oral hypoglycemic agent is superior to dietary management or placebo in reducing A1C values, but the studies are so heterogeneous that the expected A1C reduction attributed to any class of medication should be interpreted with caution.15,16 For example, six trials that evaluated sulfonylureas for an average of 16 weeks reported mean A1C reductions of 1.8 percent ,15 whereas the 10-year United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study reported an A1C reduction of 0.9 percent with sulfonylureas.3 This suggests that short-term studies may not accurately reflect long-term results. It is also critical to remember that the goal of treatment is not only to reduce A1C levels, but also to prevent premature mortality and morbidity. Not all agents have been proven to achieve this goal.
You May Like: Type 1 Diabetes And Anxiety
Monitoring Your Blood Sugar Level
Last Updated February 2021 | This article was created by familydoctor.org editorial staff and reviewed by Robert “Chuck” Rich, Jr., MD, FAAFP
If you have diabetes, its important to monitor your blood sugar at different times of the day and throughout the year. There are 3 tools that can help you do this and, therefore, manage your diabetes: A blood test done every three months, blood tests taken every day, and a system that constantly monitors your blood glucose.
The 3-month blood test is called an A1C test. This test reflects your blood sugar control over the past 2-3 months. Testing your A1C level every 3 months is the best way for you and your doctor to understand how well your blood sugar levels are controlled. Your doctor will likely be the one who orders an A1C test. However, you can also purchase over-the-counter A1C testing kits that you can use at home. Your A1C goal will be determined by your doctor. However, the goal is generally less than 7% or 8%, depending on your age.
The daily blood test is done with a blood glucose monitor . This is also called a home blood sugar meter, a glucometer, or a glucose meter. This type of testing is often referred to as self-monitoring of blood glucose. Your doctor may prescribe a BGM, especially if your blood sugar fluctuates. They will show you how to use it.
Cgm Studies In Nondiabetic Individuals
One study from 2009 entitled Reference Values for Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Chinese Subjects looked at the glucose levels of 434 healthy adults using CGM and found the following:
- On average, their daily glucose levels stayed between 70140 mg/dl for 93% of the day, with very small portions of the day spent above 140 mg/dl or below 70 mg/dl.
- Also, their mean 24-hour glucose levels were around 104 mg/dl
- 1-hour post-meal glucose values average 121-123 mg/dl for breakfast, lunch, and dinner
- 3-hour post-meal glucose values were around 97-114 mg/dl.
- Peak post-meal values appeared to be around 60 minutes after eating.
- Mean fasting glucose was 86 ± 7 mg/dl.
- Mean daytime glucose was 106 ± 11 mg/dl.
- Mean nighttime glucose was 99 ± 11 mg/dl.
A 2010 study, Variation of Interstitial Glucose Measurements Assessed by Continuous Glucose Monitors in Healthy, Nondiabetic Individuals, looked at a healthy population of 74 individuals that included children, adolescents, and adults during daily living using CGM. This research showed that:
- Glucose levels stayed between 71-120 mg/dl for 91% of the day.
- Levels were lower than 70 mg/dl for 1.7% of the time and greater than 140 mg/dl, only 0.4% of the time.
- Mean 24-hour glucose was 98 ± 10 mg/dl.
- Mean fasting glucose of 86 ± 8 mg/dl.
Compared to the first study mentioned, these healthy, nondiabetic individuals appeared to have a tighter range of glucose, spending the vast majority of the 24-hour period between 71-120 mg/dl.
You May Like: Number Of Grams Of Sugar Per Day For Diabetic