What Causes Hypoglycemia In A Child
Hypoglycemia can be a condition by itself. Or it can be a complication of diabetes or other disorder. Its most often a problem in someone with diabetes. It occurs when theres too much insulin. This is also called an insulin reaction.
Causes in children with diabetes may include:
-
Too much insulin or oral diabetes medicine
-
The wrong kind of insulin
-
Incorrect blood-glucose readings
-
Tingling feelings around the mouth
-
Seizure
-
Nightmares and confusion on awakening
The symptoms of hypoglycemia can be like other health conditions. Make sure your child sees his or her healthcare provider for a diagnosis.
Blood Sugar Target Levels For People Without Diabetes
In a person without diabetes, the body makes enough insulin to bring down the blood sugar after a meal. There is enough insulin made by the islet cells in the pancreas to deal with blood sugar. The insulin that is made by the islet cells in the pancreas works well. It is used by the bodys cells efficiently.
The blood sugar ranges listed below for the nondiabetic coincide with an A1C of 4.8 5.6 percent. This is in normal range for this laboratory value. The A1C is the average of blood sugars over a two to three-month period. A person with no diabetes and a fully working pancreas will have an A1C in this range.
Fasting blood sugar and before meal blood sugar target levels for a person without diabetes
In a person with the absence of diabetes, a normal blood sugar before eating or drinking anything upon rising in the morning would be 80-99 mg/dl. This is the range for blood sugars fasting and before meals .
If we convert the same number to mmol, the value in mmol . Now that you have a good idea of how to convert mg/dl to mmol, we will continue discussing blood sugars in terms of milligrams per deciliter, or mg/dl, for simplification. Again, this is the measurement used in the United States.
Two-hour post-prandial blood sugar for a person without diabetes
There is no insulin resistance in the person with no diabetes, so the bodys cells take the insulin up, and use it for energy. Everything is as it should be, and working properly.
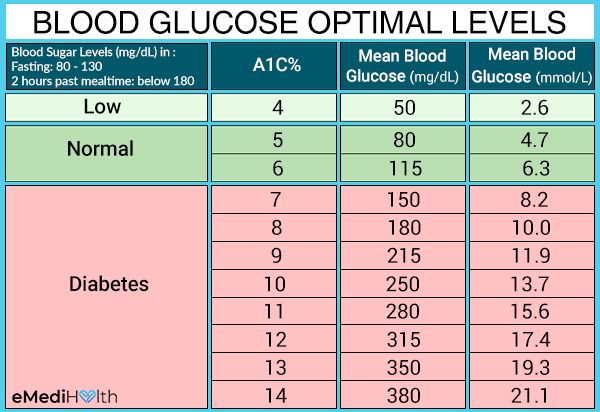
Hba1c The Big Picture On Blood Glucose
Your GP or specialist may request you to have a HbA1c blood test. This blood test provides an average measure of your blood glucose over the previous two to three months.
HbA1c is an important complement to selfmonitoring at home . Understanding your HbA1c levels can help you and your health care team make more informed decisions about your diabetes management. Some medications, treatments and inherited blood conditions can affect HbA1c results. Your doctor should be aware of your medical history to ensure an accurate HbA1c.
Your doctor will recommend a HbA1c target based on your life stage and particular circumstances. Usually this will be around 7% , although this can vary depending on your personal circumstances.
Also Check: Can You Get Rid Of Diabetes Type 1
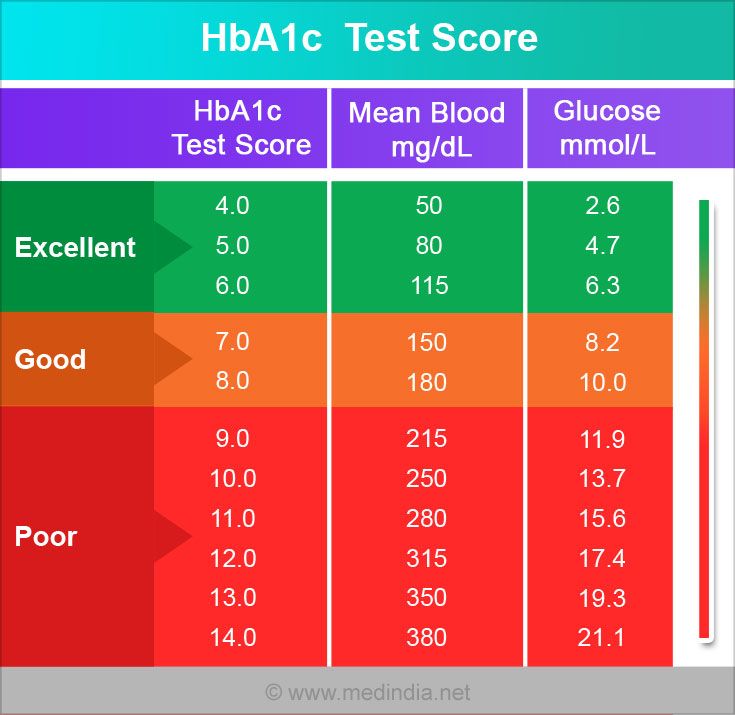
Why Your A1c Matters
In a nutshell: your A1c is one of the clearest indicators of your risk for developing diabetes complications like neuropathy , retinopathy , nephropathy , and severe infection in any part of your body that requires healing.
For instance, a small cut on your toe could become infected due to high blood sugars, struggle to heal, and become severe enough that the infection could lead to an amputation.
The general guidelines from the American Diabetes Association recommend an A1c at or below 7.0 percent for the best prevention of diabetes complications. Your risk of developing a diabetes complication continues to drop as your A1c drops closer to 6 percent.
Some people with diabetes aim for A1c levels in the 5s and lower especially those who follow strict low-carb diets like the ketogenic diet and the Bernstein diet. However, this hasnt been proven in research as especially necessary, nor is it reasonably achievable for the larger population of people with diabetes.
Its also important to remember that your blood sugar levels and your A1c are just information that tells you whether your body needs more or less of factors like insulin, other diabetes medications, changes in your nutrition, and changes in your exercise.
If you dont like the number youre seeing on your glucose meter or your A1c results, use that number as motivation to make changes in how you safely manage your diabetes in order to get different results.
What Should My Bgl Be
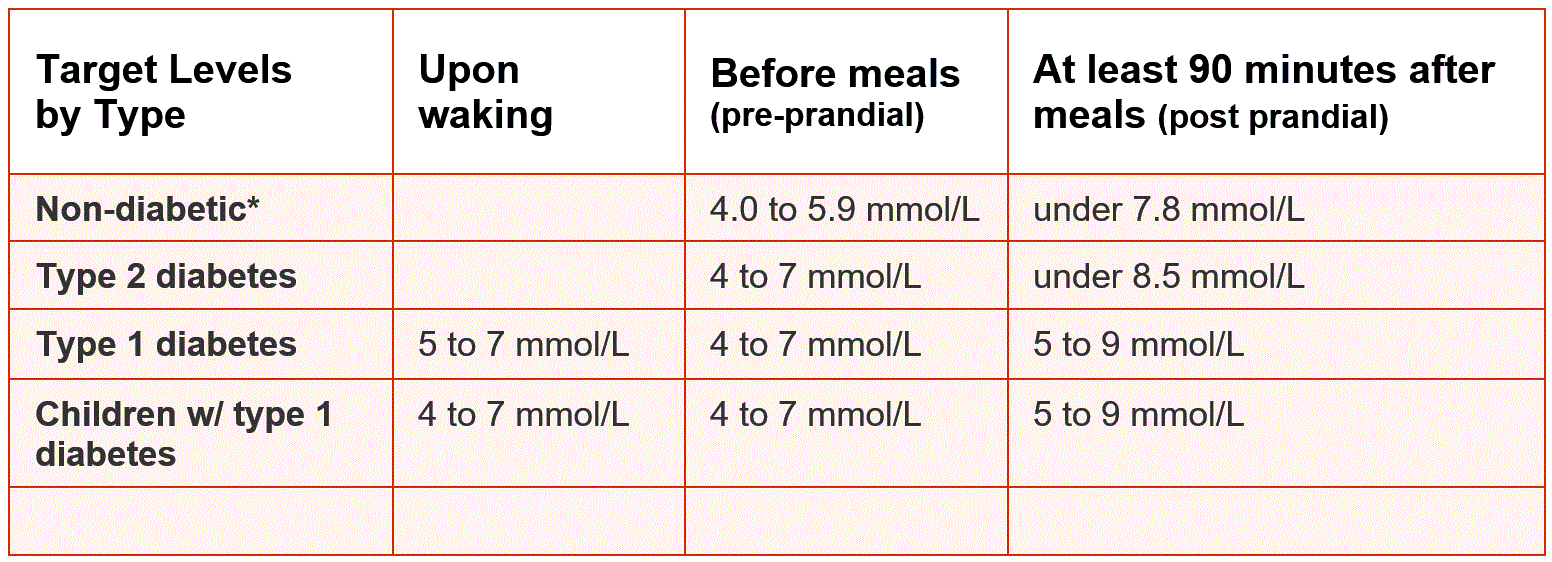
For a person without diabetes, throughout the day blood glucose levels will generally range between 4.0 7.8 millimoles of glucose per litre of blood regardless of how they eat or exercise, or what stress theyre under.
When youre living with diabetes your body cannot, or finds it hard to, keep your BGLs within a healthy range.
Because each person living with diabetes is different, your GP or specialist will set target BGLs that are right for you. However, here is some information you can use as a general guide.
Also Check: How To Treat Diabetes Insipidus
How Is Hypoglycemia Diagnosed In A Child
The healthcare provider will ask about your childs symptoms and health history. He or she may also ask about your familys health history. He or she will give your child a physical exam. Your child may also have blood tests to check blood sugar levels.
When a child with diabetes has symptoms of hypoglycemia, the cause is most often an insulin reaction.
For children with symptoms of hypoglycemia who dont have diabetes, the healthcare provider may:
-
Measure levels of blood sugar and different hormones while the child has symptoms
-
See if symptoms are relieved when the child eats food or sugar
-
Do tests to measure insulin action
Your child may need to do a supervised fasting study in the hospital. This lets healthcare providers test for hypoglycemia safely.
Other Tips For Checking:
- With some meters, you can also use your forearm, thigh, or fleshy part of your hand.
- There are spring-loaded lancing devices that make sticking yourself less painful.
- If you use your fingertip, stick the side of your fingertip by your fingernail to avoid having sore spots on the frequently used part of your finger.
Also Check: Where To Get Diabetic Supplies
Your Task: 21 Day Lower Blood Sugar Challenge
Commit to yourself and apply what we share because we know what we share can help you get results.
Well there you have it. Hope you find this information helpful and if you do please pin it and share it around to help others. Thanks!
References
Who Is At Risk Of Low Blood Glucose
- Insulin and some diabetes medications increase your risk of a hypoglycaemia .
- Hypos occur when the blood glucose level has dropped too low, below 4mmol/L.
- Hypo symptoms can sometimes occur with higher blood glucose levels, especially in children, older people and those who have had blood glucose levels above the target range for a long time.
Recommended Reading: Type 2 Diabetes After Kidney Transplant
What Can You Do If Your Blood Sugar Levels Are Too Low
It is important to react quickly enough and eat or drink something, like dextrose sugar or a sugary drink .
If someone has severe hypoglycemia they may feel drowsy and confused, and might even become unconscious. People who have type 1 diabetes often carry a pre-filled syringe on them in case that happens, containing the hormone glucagon. Glucagon makes the liver release sugar into the bloodstream. Someone else can then inject the hormone if necessary. If this is not possible, it is important to call the emergency services immediately and ask for medical help.
If your blood sugar levels keep on dropping too low, you should see your doctor. It could then be a good idea to change your lifestyle or medication.
Blood Glucose And A1c Targets For Frail Elderly People
The Diabetes Canada clinical practice guidelines were recently updated to recommend different blood glucose targets in the frail elderly. These are seniors who have three or more of the following conditions:
- Unintended weight loss of more than 4.5 kilograms during the past year
- Constant fatigue or exhaustion
- Weakness in their arms and legs
- A slow walking speed
- Low levels of physical activity
In these people, the A1C target is 8.5% , and pre-meal blood sugar levels should be 5.0 to 12.0 mmol/L .
One of the main reasons why blood sugar and A1C targets are higher for frail elderly people is that studies have shown that tighter blood sugar control is associated with mortality in this population. The Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes study a very large trial of more than 10,000 adults with type 2 diabetes found that very tight glycemic control in older patients was associated with an increased risk of death.
As well, frail elderly adults are more inclined to suffer from moderate to severe hypoglycemia. This is because they may not be eating a nutritionally balanced diet they are also more likely to have other ailments for which they take medications that may contribute to episodes of hypoglycemia.
Recommended Reading: Low Carb Cake Recipes For Diabetics
What Can I Do To Prevent Hypoglycemia In My Child
Not all episodes of hypoglycemia can be prevented. Most children with type 1 diabetes will have hypoglycemia. The chances of severe hypoglycemia go down as your child gets older. But you can help prevent severe episodes by:
-
Testing your childs blood glucose often, including at night
-
Checking that the glucose test strips are not outdated and match the glucose meter
-
Recognizing symptoms
Other ways to minimize or prevent hypoglycemia include making sure your child:
-
Takes medicines at the right time
-
Eats enough food
-
Doesnt skipping meals
-
Checks blood glucose before exercising
-
Eats a healthy snack if needed. The snack should include complex carbohydrates and some fat, if possible.
Interested In Learning More Read About Normal Blood Glucose Numbers Getting Tested For Type 2 Diabetes And Using Blood Sugar Monitoring To Manage Diabetes
Want to keep track of your blood glucose readings to help you better manage your condition? With our free printable diabetes logbook sheets, youll be able to monitor the effects of food, exercise, medicines and more. One sheet tracks levels for a week. Download your free blood sugar logbook today to start analyzing your patterns!
Also Check: How Long You Can Live With Diabetes
How To Use A Blood Glucose Meter:
- After washing your hands, insert a test strip into your meter.
- Use your lancing device on the side of your fingertip to get a drop of blood.
- Touch and hold the edge of the test strip to the drop of blood and wait for the result.
- Your blood glucose level will appear on the meter’s display.
Note: All meters are slightly different, so always refer to your user’s manual for specific instructions.
Normal Blood Sugar Ranges In Healthy Non
For a person without any type of diabetes, blood sugar levels are generally between 70 to 130 mg/dL depending on the time of day and the last time they ate a meal. Newer theories about non-diabetic blood sugar levels have included post-meal blood sugar levels as high as 140 mg/dL.
Here are the normal blood sugar ranges for a person without diabetes according to the American Diabetes Association:
- Fasting blood sugar : under 100 mg/dL
- 1 hour after a meal: 90 to 130 mg/dL
- 2 hours after a meal: 90 to 110 mg/dL
- 5 or more hours after eating: 70 to 90 mg/dL
Don’t Miss: Can Keto Diet Cause Diabetes
What Are Normal Blood Sugar Levels
April 19, 2018 by Diabetes Care
When you or someone you care for is diagnosed with diabetes, a three-worded phrase quickly becomes part of everyday conversation: that is, blood sugar levels or blood glucose levels.
Blood glucose is the amount of glucose in a persons blood at a given time. An individual with diabetes can gain valuable information by knowing how their levels compare with targeted healthy blood sugar levels at various times in the day.
Lets start by clarifying the generally agreed upon blood glucose targets.
Diabetes Canadas 2018 Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Prevention and Management of Diabetes in Canada is a guide issued to healthcare professionals to help direct an agreed standard of diabetes care in Canada. The chart below shows the recommendations for blood glucose levels for most people with diabetes.
Fasting Plasma Glucose Test
A fasting plasma glucose test is taken after at least eight hours of fasting and is therefore usually taken in the morning.
The NICE guidelines regard a fasting plasma glucose result of 5.5 to 6.9 mmol/l as putting someone at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes, particularly when accompanied by other risk factors for type 2 diabetes.
Read Also: Is Diabetic Macular Edema The Same As Diabetic Retinopathy
How Can I Treat High Blood Sugar
Talk to your doctor about how to keep your blood sugar levels within your target range. Your doctor may suggest the following:
- Be more active. Regular exercise can help keep your blood sugar levels on track. Important: dont exercise if ketones are present in your urine. This can make your blood sugar go even higher.
- Take medicine as instructed. If your blood sugar is often high, your doctor may change how much medicine you take or when you take it.
- Follow your diabetes meal plan. Ask your doctor or dietitian for help if youre having trouble sticking to it.
- Check your blood sugar as directed by your doctor. Check more often if youre sick or if youre concerned about high or low blood sugar.
- Talk to your doctor about adjusting how much insulin you take and what types of insulin to use.
Lets Crunch Some Numbers
Ill give these numbers to you in a written, chart, and visual format because it will make sense to you depending how you read it.
Depending where you live in the world, numbers can vary slightly. And your numbers will either be mg/dl or mmol/l. Youll find the numbers for both of these readings below.
Normal Blood Sugar Levels
Fasting glucose 70-99 mg/dl or 4-6 mmol/l
2 hours post meal glucose Less than 140 mg/dl or less than 7.8 mmol/l
Pre-diabetes diagnostic ranges also called impaired fasting glucose or impaired glucose tolerance
Fasting glucose 100-125 mg/dl or 6.1-6.9 mmol/l
2 hours post meal glucose level 140-199 mg/ dl or 7.8-11 mmol/l
Type 2 Diabetes diagnostic ranges
Fasting glucose More than 126 mg/dl or more than 7.0 mmol/l
2 hours glucose level More than 200 mg/dl or more than 11.1 mmol/l
Don’t Miss: How To Get Rid Of Diabetes Stomach Fat
What Is Happening In The Body Of Someone With T2dm
When we eat carbohydrate foods, our bodies break them down into glucose which enters into our bloodstream from our digestive system. Our pancreas produces a hormone called insulin which also enters our bloodstream and takes this glucose from our blood and into our cells to be stored or to be used as energy.
In someone with T2DM, the amount of glucose in the blood is higher than normal, so more insulin is required to transport this glucose into the cells. When this goes on for an extended period of time, a few different things happen. Firstly, the cells that produce insulin in the pancreas can become damaged from working overtime and so start to work less efficiently. Secondly, the bodys cells can become desensitised to insulin as they are constantly exposed to high levels of it in the blood. This means that the insulin that is being produced is unable to do its job, a term called insulin resistance.
These two factors in combination are what lead to consistent high Blood Glucose Levels and a diagnosis of T2DM.
What Causes Low Blood Sugar
Low blood sugar has many causes, including missing a meal, taking too much insulin, taking other diabetes medicines, exercising more than normal, and drinking alcohol. Blood sugar below 70 mg/dL is considered low.
Signs of low blood sugar are different for everyone. Common symptoms include:
- Shaking.
- Dizziness.
- Hunger.
Know what your individual symptoms are so you can catch low blood sugar early and treat it. If you think you may have low blood sugar, check it even if you dont have symptoms. Low blood sugar can be dangerous and should be treated as soon as possible.
Recommended Reading: Glucerna Meal Replacement For Diabetics
What Are The Main Treatments For T2dm
The main treatments for managing T2DM include a combination of lifestyle interventions and medications.
The first step, or primary intervention, in managing someone who is at risk of developing or has been newly diagnosed with T2DM, is dietary modification. This also includes modifying physical activity patterns and is the first attempt to correct the blood glucose imbalance that is occurring in the body.
Secondary interventions include the use of oral and injectable medications such as Metformin, Sulfonylureas, GLP-1 agonists, DPP-4 inhibitors and insulin. The appropriate dosage and selection of medications depends on the severity and length of time you may have had diabetes and will be individualised to each person by their doctor or endocrinologist.
What Is Hypoglycemia In Children
Hypoglycemia is when the level of sugar in the blood is too low. Glucose is the main source of fuel for the brain and the body. The normal range of blood glucose is about 70 to 140 milligrams per deciliter . The amount differs based on the most recent meal and other things, including medicines taken. Babies and small children with type 1 diabetes will have different goal ranges of blood glucose levels than older children.
Don’t Miss: Is Sorghum Good For Diabetics