How Will I Know If I Have Diabetes
You should get tested for it. A simple blood test to check your blood sugar levels is the best way to find diabetes or pre-diabetes. Pre-diabetes is a condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal, but not high enough for a diagnosis of diabetes. Finding and controlling diabetes early is important. Talk to your healthcare provider about getting tested for diabetes.
Pancreas After Kidney Transplant For Type 1 Diabetic Patients
Pancreas after kidney transplant modality has the shortest waiting time for pancreas transplant in Brazil, since many teams capture the pancreas, but do not perform the pancreas transplant surgical procedure, which results in a shorter waiting time in comparison to simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplant. The life expectancy rate is reported to be 17.2 years . However, the greatest challenge is to monitor the pancreatic rejection, inasmuch as asynchronous pancreas rejection may occur.
Furthermore, PAKT indications are still controversial in the literature, but they may be certainly indicated for cases of severe asymptomatic hypoglycemia and ketoacidosis of difficult control . Therefore, the probability of hypoglycemia greater than 5% and the probability of death from hypoglycemia greater than 9% justify the PAKT performance . The PAKT is also indicated in cases when ketoacidosis becomes a frequent event .
In addition, it was recently demonstrated that the 1-year patient survival after PAKT was similar to the simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplant , as well as the 1-year pancreas graft survival . The immunosuppressive regimen included rabbit anti-thymocyte globulin , early steroid withdrawal and maintenance with tacrolimus and sirolimus or mycophenolate mofetil. Interestingly, the acute cellular rejection was present in only 2% of the groups described. However, further studies are necessary to evaluate the long-term pancreas graft survival rates after the PAKT.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Coordination of care among all team members, including nurses, internists, nutritionists, surgeons, endocrinologists, nephrologists and, infectious disease specialists, is an essential factor in the management of pre-existing diabetes or NODAT in transplant patients. Adequate blood glucose control, as well as treatment of comorbidities, is the backbone in the management of NODAT as it increases patient survival and decreases the risk of graft rejection. Selecting the right immunosuppressants with the appropriate dose is one of the steps to prevent NODAT, but the risk of developing diabetes after transplantation should be weighed against the risk of transplant rejection. At the time of discharge, each caring team’s responsibility is to explain the above to the patient. Also, education coordination by the nurses and clinicians of the patient and the family about the medical therapies and their side effects is critical as it can impact the patient survival.
Article Details
Also Check: What Insulin Pumps Are Covered By Medicaid
Efficacy Study Of Sitagliptin To Prevent New
| The safety and scientific validity of this study is the responsibility of the study sponsor and investigators. Listing a study does not mean it has been evaluated by the U.S. Federal Government. Read our disclaimer for details. |
| First Posted : August 23, 2013Results First Posted : June 29, 2021Last Update Posted : November 23, 2021 |
- Study Details
| Phase 4 |
This will be a single-center, randomized, double-blind trial to evaluate the efficacy of sitagliptin to prevent the development of new-onset diabetes after transplant in previously non-diabetic patients with post-operative hyperglycemia following living-donor or deceased-donor kidney transplant. In this trial, previously non-diabetic adult patients with hyperglycemia in the first 72 hours following kidney transplant will be screened to determine eligibility based on inclusion/exclusion criteria. Patients that meet study entry criteria will be stratified based on HbA1c and randomized in a 1:1 ratio to one of two treatment groups: sitagliptin versus placebo. Fifty patients will be enrolled. Dosing period will be 3 months at which time study drug will be discontinued and patients will be followed for an additional 3 month period.
Screening period
Randomization
Drug dosing period
Follow-up
Lifestyle Modification Prevents Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Lifestyle interventions promoting reduced fat/reduced energy diets, daily moderate-intensity physical activity, and modest weight loss reduce incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus. In the largest such study, the DPP, a lifestyle weight-reduction intervention reduced diabetes incidence by 58% compared with a group receiving only standard advice about diet and exercise . In the Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study, a similar lifestyle intervention had almost identical effects, reducing the incidence rate of diabetes by 58% . In smaller studies of Chinese, Japanese, and Asian Indian populations, lifestyle intervention was efficacious in preventing or delaying type 2 diabetes mellitus in high-risk individuals .
Impact of dietary and physical activity modifications on risk of development of type 2 diabetes mellitus in five randomized clinical trials
Although studies of the general population show that intensive modification of diet and physical activity can prevent or delay progression of prediabetes to overt type 2 diabetes mellitus, the question of whether NODAT can be prevented using a similar strategy has not, to our knowledge, been tested.
Don’t Miss: Three Risk Factors For Type 2 Diabetes
Summary And Conclusion: The Way To The Best Quality In Diabetic Patient Care With Ckd
The prognosis of the diabetic patient with ESRD and without the possibility of LDKT or early DDKT is still poor. It is necessary to face a list of problems with prognostic implications and whose proper management may improve life expectancy and life quality.
Cardiovascular disease is the most frequent cause of morbidity and mortality in this population. Peripheral vascular disease, infections and malnutrition strongly impact in prognosis as well. Therefore, the adequate control of blood pressure , glycemia , lipid profile and nutrition are essential.
Isolated Kidney Transplant From A Living Donor For Type 1 Diabetic Patients
The awaiting time is shorter in this transplant modiality than in other ones because it takes just the time to prepare the living donor. Imunossuppressive regimen may be tailored according to the Human Leucocytes Antigens compatibility. If there is is an identical donor, the dose of the immunosuppressors will be lower, which minimizes their side effects. This is the transplant modality that has the greatest life expectancy rate, around 18.3 years .
You May Like: How To Treat Diabetes Insipidus
Clinical And Economic Significance Of Nodat
Kidney transplantation is the best therapy for end-stage renal disease , but subsequent development of impaired glucose regulation or NODAT undermines the many benefits of kidney transplantation by lowering allograft and patient survival and impairing quality of life . In a U.S. Renal Data System study of 11,659 patients who received a transplant between 1996 and 2000, NODAT was associated with a more than 60% increase in incidence of graft failure and an almost 90% increase in mortality rate . Another analysis of USRDS data demonstrated frequent occurrence of diabetes complications, including ketoacidosis, hyperosmolarity, ophthalmic complications, neurologic complications, and hypoglycemic shock, in patients with NODAT . NODAT also increases the annual cost of care from $15,000 to $36,500 .
Sglt2i And Cv Protection
SGLT2i reduce 3-point major adverse CV events , all-cause mortality and HF hospitalizations in the general population in varying combinations. SGLT2i significantly reduced MACE in those with established CVD. Potential beneficial mechanisms include naturietic diuresis, reduced inflammation, and increased hematocrit from erythropoietin production with enhanced myocardial tissue oxygen delivery.
Several trials specifically examined HF as a primary outcome. Many patients did not have T2DM, and SGLT2i reduced CV death and HF hospitalization or progression regardless of diabetes status. Patients with HFrEF of < 40% showed a significantly lower CV death or HF hospitalization again regardless of T2DM status, and a slower eGFR decline in T2DM. With T2DM and recent worsening HF there was lower CV mortality and HF hospitalization.
LVH has not been studied to the same extent as CV mortality and HF. However, a substudy of the EMPA-HEART CardioLink-6 RCT showed that empagliflozin was associated with significant reduction in LV mass index, possibly from increased red cell mass and improved myocardial tissue oxygen delivery.
Don’t Miss: What Is Stage 2 Diabetes
Drug Therapy After Transplant
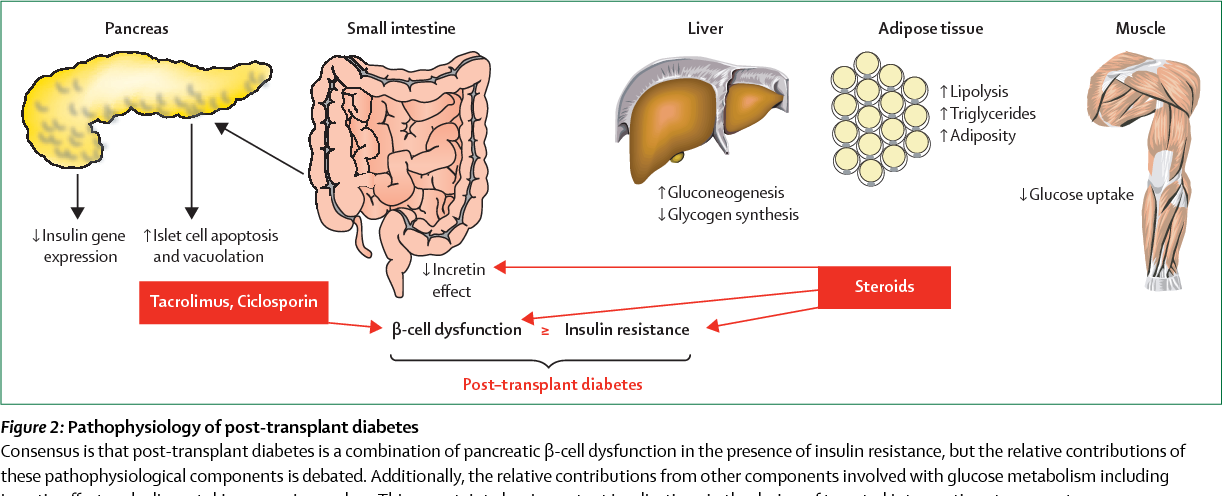
Previous studies have reported a high incidence of de novo hyperglycemia immediately after transplant . The pancreatic -cell is exposed to several stressors immediately after kidney transplant surgery, including the surgical procedure itself, high-dose corticosteroids, and initiation of CNIs. Thus, resting the -cell with basal insulin and optimizing -cell protection with tighter control to near-normoglycemic treatment goals could further reduce the number of patients with future impaired glucose tolerance and NODAT. A recent study randomized nondiabetic patients to two groups in the immediate postoperative period. The first was the basal insulin group , in whom basal insulin treatment was initiated with a morning dose of 6, 8, or 10 IU isophane insulin for previous evening blood glucose measurements of 140180, 180240, or 240 mg/dL, respectively. The normoglycemic goal was 110120 mg/dL. In addition, short-acting insulin was used for corrections of hyperglycemia during the postoperative period, followed by appropriate increase in isophane insulin. The control or standard arm received short-acting insulin, oral antidiabetic therapy for hyperglycemia, or both. Treatment was administered in those with blood glucose 180 mg/dL. The treatment group had lower odds of NODAT than the control group, and HbA1C was, on average, 0.38% lower in the treatment group than the control group .
C Preventing Cardiovascular Disease
As anyone who takes care of diabetes patients already knows, diabetes care extends beyond glucose management alone. Because cardiovascular events are the most common cause of mortality, smoking should be discouraged in all recipients. Although most programs require smoking cessation before transplant, some recipients return to smoking and may not report it unless asked. Dyslipidemia and hypertension are frequent if not ubiquitous accompaniments to diabetes of all types and are often exacerbated by many of the immunosuppressants, as well as reduced renal function, common to the post-transplant setting. Treatment must be mindful of drug-drug interactions because many of the immunosuppressants are metabolized through the same pathways as most of the lipid-lowering agents and some blood pressure medications.
You May Like: Difference Between Diabetes Mellitus 1 And 2
Besides Medication What Other Factors Increase My Risk For Diabetes
Many things can put you at risk for diabetes. Some factors are things you cannot change, like your age or ethnic background. But others are things you can change, like being overweight or not getting enough exercise. Some common factors that are associated with diabetes are:
- Being overweight
- Being African-American/Black, American Indian, Alaskan Native, Hispanic, Pacific Islander or Asian
- Being age 45 or older
- Having a family history of diabetes
- Having had diabetes during pregnancy
- Having high blood pressure or abnormal blood fats
- Having had an hepatitis C virus infection
Dpp4i Cv And Kidney Protection
All major CV trials of DPP4i including linagliptin, sitagliptin, saxagliptin, and alogliptin revealed non-inferiority compared to placebo for the risk of major events. Non-inferiority was also evident when linagliptin was compared to glimepiride. However, in the SAVOR-TIMI 53 trial, saxaliptin was associated with an increased risk of hospitalization for HF in patients with elevated N-terminal pro B-type natriuretic peptide levels, a history of HF, or CKD with eGFR < 60 mL/min. Linaglipitin and saxagliptin reduce the risk for albuminuria progression, or even improve albuminuria, regardless of baseline eGFR. This benefit was not demonstrated with sitagliptin. The KDIGO 2020 guidelines highlight the role of DPP4i in T2DM and CKD. Therefore, while DPP4i may be useful adjuncts to control blood glucose and favorably affect albuminuria at best, their effect on CVD outcomes and CKD progression remains uncertain.
Also Check: What To Do If You Think Your Diabetic
Pancreas Or Islet Transplantation
Curr Opin Organ Transplant.Curr Opin Organ Transplant.Pancreatology.
Transplantation.
- de Koning EJP
- et al.
Transplantation.Am J Transplant.Endocr Rev.
Endocr Rev.Endocr Rev.
Endocr Rev.
Transplantation.Transplantation.JAMA.Diabetes.
Am J Transplant.
- Diez A.
- et al.
Clin Transplant.
- Brockmann J.
- et al.
Diabetes Care.
- Brockmann J.
- et al.
Diabetes Care.
- Brockmann J.
- et al.
Diabetes Care.
- Brockmann J.
- et al.
Diabetes Care.
Diabetes Med.
Study Cohort Generation And Data Source
This is an ancillary study to the Deceased Donor Study , an ongoing multicenter, observational, cohort study of deceased donors and their kidney recipients. The DDS study population and methods has been described in detail elsewhere . Briefly, five organ procurement organizations enrolled donors between May 2010 and December 2013 and followed their own protocols for research authorization and donor management. Clinical variables were abstracted from OPO donor charts. Recipients of these kidneys were identified at 13 participating transplant centers where detailed chart review was performed. All exposures and outcomes were assessed by usual care practices. Trained site coordinators reviewed medical records and recorded detailed recipient characteristics, treatments, and outcomes. Study staff at the data coordinating center validated abstracted data to confirm data quality and accuracy . In addition, data for all kidney recipients and donors were obtained from the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network . We excluded recipients on the basis of the following criteria: age < 16 years, without any follow-up data, en bloc transplant, or multiorgan transplants. We also excluded recipients with known history of pretransplant diabetes, defined as need for insulin or oral hypoglycemic medications at time of transplant, including patients with DM as the cause of ESKD.
Don’t Miss: What Is An Average Blood Sugar Level For Diabetics
Transplantation In People With Pre
People with pre-existing diabetes often experience hyperglycemia following transplantation and may need additional anti-hyperglycemic therapy. Insulin may be required, at least temporarily. No controlled studies have examined treatment strategies for glycemic management after transplantation in people with pre-existing diabetes .
Patients With Severe Disease Not Managed By Medication Are Now Diabetes And Dialysis Free
Jeffrey Edwards of Washington, D.C., can hardly believe that his 17 year battle with diabetes is over. His debilitating three-times-a-week dialysis sessions are finished.
Im no longer doing finger sticks to check my blood sugar, I can eat what I want, when I want and I feel great. Its almost as if the diabetes never existed, said Edwards, age 53.
Edwards, a letter carrier for the U.S. Postal Service of 31 years, is one of an increasing number of patients at the MedStar Georgetown Transplant Institute to receive a life-changing kidney/pancreas transplant as a treatment for severe diabetes.
Because the regulation of insulin is performed by the pancreas, transplanting the pancreas in someone with severe diabetes cures them of their disease, said Peter Abrams, M.D., a kidney and pancreas transplant surgeon at the MGTI. When we transplant the kidney at the same time, then the patient is no longer ruled by dialysis. And the new pancreas protects the new kidney from further damage due to the diabetes. We call that a kidney/pancreas transplant. Mr. Edwards is doing great. He has no diabetes. He functions as a normal non-diabetic human being now.
Jeffrey Edwards had suffered through the many ravages of diabetes. A two week diabetic coma in 1999 almost ended his life. Congestive heart failure due to his diabetes necessitated heart surgery. Dialysis frequently resulted in serious complications.
Then in 2013 Ruzanic received a kidney from a friend, a living donor.
Read Also: How To Reverse Ed In Diabetics
Influencing Factors Of New
-
Affiliation Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, P.R. China
-
Affiliations Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, P.R. China, Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, People’s Hospital Affiliated to Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine , Fuzhou, P.R. China
-
Affiliation Department of Urology, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai Key Laboratory of Organ Transplantation, Shanghai, P.R. China
-
Affiliations Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, P.R. China, Department of Cadre’s Ward, Fujian Provincial Hospital, Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou, Fujian, P.R. China
-
Affiliation Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, P.R. China
-
Affiliation Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, P.R. China
-
Affiliation Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, P.R. China
-
Affiliation Evidence Base Medicine Center, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, P.R. China
-
* E-mail:
Affiliation Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, P.R. China
-
* E-mail:
Affiliation Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, P.R. China
Can Lifestyle Modification Be Adapted For Prevention Of Nodat
Patients with CKD self-report low levels of physical activity , and in-center hemodialysis, three times per week for 34 h per treatment, strongly promotes inactivity. Patients receiving chronic hemodialysis have lower physical activity on dialysis days than nondialysis days, and a majority of the reduced activity is explained by less movement recorded during dialysis treatment . Other factors, such as anemia, hypervolemia, and uremic cachexia, may contribute to decreased physical activity. A lifestyle intervention similar to the DPP may safely reverse the inactivity of patients before transplant.
Because current antirejection therapies, including glucocorticoids, CNIs, and mTOR inhibitors, are well-established risk factors for NODAT and yet are not easily substituted, the potential effectiveness of lifestyle intervention assumes even greater importance however, to our knowledge, the feasibility or efficacy of a lifestyle intervention to lower the incidence of NODAT has not been described.
You May Like: Side Effects From Taking Insulin
C Role Of Immunosuppression Agents
Corticosteroids are well established to cause hyperglycemia through several mechanisms: by inducing or worsening pre-existing insulin resistance, increasing hepatic gluconeogenesis, and long-term, by stimulating appetite and weight gain . The impact is dose-dependent. High-dose corticosteroids, often used as part of induction protocols in the immediate post-transplant hospitalization, have much greater impact than chronic low-dose corticosteroids that are common to many maintenance immunosuppression protocols. A recent prospective randomized trial of early withdrawal of corticosteroids vs remaining on low-dose chronic prednisone from 6 months to 5 years after kidney transplant showed that incidence of PTDM was minimally impacted .
The remaining available immunosuppressive agents vary with respect to risk for PTDM. Mycophenolate mofetil and azathioprine have not been shown to have a large impact on insulin action or glucose metabolism and so do not appear to have a major role in PTDM. There is increasing evidence that the other commonly used immunosuppressants, particularly CNIs and inhibitors of the mammalian target of rapamycin , may contribute to PTDM. Our work in animals suggests a dose-dependent effect of both tacrolimus and sirolimus on glucose metabolism , although there are no comparable human studies. However, there are reports that both glucose intolerance and the dyslipidemia that occurs predominantly with mTOR inhibitors improve as the dose is reduced.