How Is Diabetes Diagnosed In Toddlers
If your toddlerâs healthcare provider suspects diabetes, she may recommend testing to check your toddlerâs blood glucose levels. Here are some common tests your provider may perform:
-
Random blood sugar test. A blood test is done at a random time to measure glucose levels.
-
Glycated hemoglobin blood test. This test measures the percentage of glucose attached to the hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen.
-
Fasting blood sugar test. For this test, a blood sample is taken after an overnight fast.
-
Oral glucose tolerance test. If your healthcare provider suspects type 2 diabetes, an oral glucose tolerance test may be recommended. The first blood test is taken after an eight-hour or overnight fast. Then your little one will drink a sugary solution and his blood sugar levels will be rechecked via a blood test several times over the next few hours.
Your toddlerâs healthcare provider will explain the testing process and go over the results with you.
Treatment Of Diabetes In Children And Adolescents
-
Nutrition and exercise
-
For type 1 diabetes, injections of insulin
-
For type 2 diabetes, metformin by mouth and sometimes injections of insulin or liraglutide
The main goal of diabetes treatment is to keep blood glucose levels as close to the normal range as can be done safely. However, no treatment completely maintains blood glucose at normal levels. When people try very hard to keep blood glucose levels normal, they increase the risk that their blood glucose levels will sometimes become too low. Low blood glucose is called hypoglycemia Hypoglycemia Diabetes mellitus is a disorder in which blood sugar levels are abnormally high because the body does not produce enough insulin or fails to respond normally to the insulin produced… read more and can be dangerous.
Children with either type of diabetes need to
-
Make healthy food choices
-
Lose weight if overweight
-
Exercise regularly
General nutritional management and education are particularly important for all children with diabetes. Dietary recommendations for children with diabetes are based on healthy eating recommendations for all children and aim to maintain ideal body weight and optimal growth and to prevent short-term and long-term complications of diabetes.
Once The Diagnosis Has Been Made
Traditionally, most children with new onset type I diabetes, and particularly the youngest ones, have been hospitalized to stabilize their hyperglycemia and to provide the initial education of their families. In more recent years, there has been a trend away from hospitalization at diagnosis except under certain circumstances . The Hospital for Sick Children has found this to be no less true for infants and toddlers than for older children and teens. Indications for hospitalization include the severity of their condition at diagnosis , family living far from the hospital with difficulty attending on a daily basis, or if the responsible physician is not certain that the family understands the significance of the diagnosis or may be unlikely to attend the day care education program. The latter may be due to the presence of a language barrier or part of a severe emotional response to the diagnosis.
Also Check: Advanced Diabetes Supply Freestyle Libre
How Is Type 1 Diabetes Diagnosed
Doctors use a blood test that measures the amount of sugar in the blood. High blood sugars show that a child has diabetes. Then, the doctor will do more blood tests to find out what type it is.
Kids with type 1 diabetes often go to a pediatric endocrinologist. This kind of doctor finds and treats problems affecting hormones, like diabetes.
What Is Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes, or diabetes mellitus, is a disorder in which the body cannot properly use glucose as an energy source. In type 1 diabetes, the body does not make enough of the hormone insulin, which enables the body to properly utilize glucose. Type 1 diabetes develops when the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas are destroyed due to an autoimmune process in which the bodys immune system mistakenly destroys its own organs or tissues. People with type 1 diabetes need daily insulin shots. This is the more prevalent form of diabetes in children and young adults. In type 2 diabetes, the pancreas produces enough insulin but the body cannot use it effectively, referred to as insulin resistance. Gradually, insulin production slows down, as is the case in type 1 diabetes. Previously unheard of in children and teens, type 2 diabetes is now being diagnosed more often in youngsters, which many public health experts blame on the rising tide of childhood obesity.
You May Like: What Does Type 1 Diabetes Do
How Can You Tell The Difference
Sometimes it’s hard to distinguish between high and low blood sugar symptoms, especially if your child is very young. Test your child’s blood sugar whenever you think it may be high or low so that you can treat it appropriately. If your child has symptoms of very high blood sugar, such as a fruity breath odour, vomiting, and/or belly pain, seek emergency care. These symptoms may point to diabetic ketoacidosis, which is a life-threatening emergency.
In England Diabetes Occurs In 1 In Every 450 Children
In England diabetes occurs in 1 in every 450 children. 97% of children with diabetes have type 1 diabetes mellitus. Type 2 diabetes in children is still uncommon.
Nearly 30% of newly diagnosed children have had at least one related medical visit before diagnosis. Doctors and parents are missing the early signs.
Doctors may fail to ask about frequent urination and excessive drinking Adolescents may ignore the symptoms.
Recommended Reading: Why Do I Need Insulin
How Long Will Diabetes Last
Both forms of diabetes are lifelong conditions. Once diagnosed as having type 1 or type 2 diabetes, your child will always have it.
Long-term risks and complications can be minimised by:
- keeping blood glucose levels normal as much as possible
- participating in your child’s care and ongoing good health
- learning as much as you can about diabetes
- having good medical care
- providing good family support
- having a healthy lifestyle
While type 2 diabetes is a lifelong condition, the symptoms may lessen if the person with diabetes loses weight, becomes physically active and engages in a healthier lifestyle.
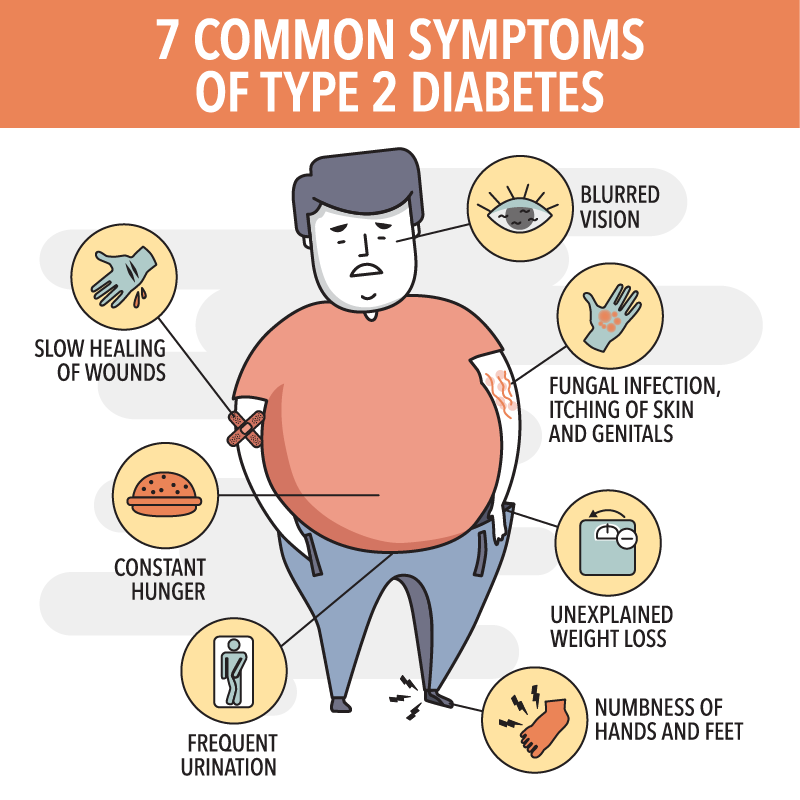
Tingling Or Numbness In Hands Or Feet
A tingling or numb sensation in the bodys extremities such as hands and feet is a common early sign of diabetes.
It tends to occur first thing in the morning after you wake up, and can even feel more like a burning sensation.
Why does this happen?: Sugar that lingers in the blood will begin to damage nerves and nerve-endings. Nerves that are furthest from the heart are not well repaired due to circulation problems.
Read Also: How Much Insulin Should I Take
Do Children With Type 1 Diabetes Will Require Insulin
Children with type 1 diabetes will require insulin. There are various regimens and insulin will be started on the day of referral. Support and Education are carried out by a multidisciplinary team consisting of doctors, diabetes specialist nurses, and dieticians.
In Italy, a hard-hitting, inexpensive campaign of information aimed at doctors and the public about the early symptoms of type 1 diabetes in children, greatly reduced the incidence of DKA at diagnosis. A similar campaign is needed in the UK
How To Manage Your Own Needs
Finding out your child has diabetes can be overwhelming. Your childs needs will vary from day to day, depending on what they eat, whether theyre sick, whether theyre growing and how much sleep theyve had. You will manage better on some days than others and should try to take one day at a time.
Remember that having diabetes can affect your childs behaviour. They may feel different from other children. Involve your child in their own care and teach them how to make good choices for their health. Its also a good idea to introduce them to other children who have diabetes.
You are not alone. You will have a team of professionals to help you, which may include your GP, endocrinologist, diabetes educator dietitian, podiatrist and eye specialist. A credentialed diabetes educator is a specially trained health professional who will show you how to manage your childs diabetes. To find a credentialed diabetes educator near you, visit the Australian Diabetes Educators Association website.
Make sure everyone who cares for your child knows they have diabetes and how to manage it. And make sure that glucose is always available in case of hypoglycaemia.
You May Like: Diabetic Recipes For Picky Eaters
Sign : Changes In Eyesight
A high blood glucose level causes fluid to be pulled from other body tissues, including eye lenses. This may lead to blurred vision or other eyesight problems. However, a young child may not complain to you about it.They dont know what normal is, the way adults would, says Clement. And some of them arent even reading yet.
Effective Treatments For Type 1 Diabetes

Insulin
Children with type 1 diabetes need insulin to replace the insulin that the body cannot make anymore. Insulin is a hormone which you cannot take as an oral medicine – you must inject it into the layer of fat under the skin.
Healthy diet
A child with type 1 diabates needs to eat a healthy diet, just like a child without diabetes. They need a regular intake of carbohydrates for growth and development.
Physical activity
Physical activity is the best foundation for management of type 1 diabetes. Physical activity is part of a healthy lifestyle.
Matching insulin to carbohydrates and physical activity
The amount of insulin a child with type 1 diabetes needs depends on the amount of carbohydrates they eat and the amount of physical activity they do. This is called matching insulin to carbohydrates and physical activity.
Learning about diabetes
There is a lot to learn about how to care for a child or young person with diabetes.
This learning involves the whole family, extended family, and other people that are involved in the life of a child or young person – school staff, friends, neighbours, sports coaches, etc.
Education and learning about type 1 diabetes is an ongoing process.
Check Diabetes – physical activity.
You May Like: Financial Help With Diabetic Supplies
How Can You Manage Diabetes
The key to managing diabetes is to keep blood sugar levels in a target range. To do this, your child needs to take insulin, eat about the same amount of carbohydrate at each meal, and exercise. Part of your child’s daily routine also includes checking his or her blood sugar levels at certain times, as advised by your doctor.
The longer a person has diabetes, the more likely he or she is to have problems, such as diseases of the eyes, heart, blood vessels, nerves, and kidneys. For some reason, children seem protected from these problems during childhood. But if your child can control his or her blood sugar levels every day, it may help prevent problems later on.
Signs Of Type 2 Diabetes Found In Children As Young As Eight
The early signs of type 2 diabetes are visible in children as young as eight years old, according to new research.
Authored byMilly Evans
18-Sep-19·3 mins read
New findings presented at the 2019 Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes have found that the signs of adulthood type 2 diabetes may be visible in children, decades before it is likely to be diagnosed.
The researchers analysed genetic information known to increase the chances of someone developing adult type 2 diabetes. They found that a child’s levels of high-density lipoprotein , cholesterol, amino acids and a chronic inflammatory trait measure in the blood were all affected by their susceptibility to type 2 diabetes.
Targeting these factors early in life could be key to preventing children from developing type 2 diabetes.
Unlike type 1, type 2 diabetes develops later in life and is more common in people who are obese and older people, although it is becoming increasingly common in young people. It affects the body’s ability to make and use insulin to control blood sugar levels.
Management of the condition usually involves changes to diet and exercise. In England, about one in 10 people aged 45-54 years have diabetes and about one in four people aged over 75 years have diabetes. Nine in 10 cases of diabetes are type 2.
“Knowing what early features of type 2 diabetes look like could help us to intervene much earlier to halt progression to full-blown diabetes and its complications.”
You May Like: Are Diabetic Test Strips Universal
Excessive Thirst Is One Of The Classic Early Signs Of Diabetes
Drinking unusually large amounts of fluids throughout the day and even overnight is a glaring symptom.
Intake can be something like 4 litres or more per day. You can even start to feel thirsty immediately after youve just had a drink.
The more you drink, the more you urinate, which feeds back into the excessive urination cycle.
Why does this happen?: This is the bodys response to increased urination. With all that extra fluid loss, you become very dry and thirsty.
The Goals Of Treatment
The elements of treatment from the time the diagnosis is made include insulin therapy, individual self-monitoring of blood sugar, age-adapted and structured patient education, and the psychosocial care of the family . The target HbA1c value is < 7.5% without simultaneous hypoglycemia . It is currently being discussed whether the target should be lowered to HbA1c< 7.0% , because modern treatment methods are associated with a lower risk of hypoglycemia .
Further parameters for the assessment of metabolic control that have recently come into wide use are the so-called time in range and other measures of glycemic variability .
Also Check: How Much Is Insulin Out Of Pocket
Sign : Diabetic Ketoacidosis
DKA can happen in a child with undiagnosed diabetes and is a medical emergency. As the body runs out of insulin for breaking down glucose, it starts to burn fat for energy instead. This leads to a buildup of acidic byproducts called ketones. DKA changes the pH of your blood and is a very dangerous condition, notes Clement.
Signs your child is in crisis can include vomiting, stomach pain, fast breathing, flushed face, fruity breath odour and fatigue. DKA may progress very quickly and can be fatal. But its also preventable. The more that parents, teachers and camp counsellors are aware of the early signs of diabetes in children, the more likely it is that DKA can be averted.
Dont miss out! and get nutritious recipes, healthy weight-loss tips, easy ways to stay in shape and all the health news you need, delivered straight to your inbox.
How We Care For Type 1 Diabetes
The Diabetes Program at Boston Childrens Hospital is one of the largest pediatric diabetes centers in North America. We treat over 2,000 patients with diabetes each year and have demonstrated success in improving diabetes outcomes. Our integrated team brings together pediatric endocrinologists, diabetes nurse educators, registered dietitians, and behavioral specialists who work with you and your child to develop an appropriate diabetes treatment plan.
We provide comprehensive services for infants, children, adolescents, and young adults with all types of diabetes. This includes type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, cystic fibrosis-related diabetes, steroid-induced diabetes, and other, rare forms of diabetes.
Our services include:
- management of the acute complications of diabetes
- long-term management and follow-up care
Also Check: Is Atkins Diet Good For Diabetics
Living With Type 1 Diabetes
With the right care and support, a child with type 1 diabetes can lead a healthy and happy life.
Type 1 diabetes needs careful daily management to ensure glucose levels remain stable and within a healthy range. This involves a careful balance between food intake, exercise and medication.
Type 1 diabetes is treated by replacing the bodys missing insulin and people with this condition must:
- use insulin every day
- regularly test their blood glucose or use a glucose sensor
- eat a healthy diet matched with the insulin dose
- take exercise as any other child of the same age.
Education to enable self-management is the cornerstone of diabetes care and continues at all ages and for the duration of the illness.
Diabetes Queensland has a wealth of information for children and teens who have recently been diagnosed with, or are living with diabetes, including information about school action and management plans for students with diabetes, exams, sport days and school camps, as well as resources for schools, parents and carers.
Having a child diagnosed with type 1 diabetes can be scary and upsetting for parents and carers. Diabuddies is a supportive community for parents and carers of children living with type 1 diabetes, where you can connect, ask questions, and feel supported.
Mood Changes And Irritability
The continually fluctuating blood sugar levels create havoc on the mood of a person. Children are no different. When the sugar levels are low, we feel morose and irritable. When they are high, we feel full of energy and are in a better mood. When the levels dip too low or go too high, it could make one feeling depressed or manic. Frequent and unexplained mood swings in kids could be a warning sign of type 1 diabetes.
Recommended Reading: Best Low Carb Diet For Diabetics
What To Watch For
Symptoms of type 1 diabetes in infants and children can start very suddenly. Keep an eye out for these signs in your baby or child:
- Sudden strange behavior
- Breath that smells fruity, sweet, or like wine
- Extreme drowsiness or lack of energy
- Ongoing, intense thirst
- Peeing more often
- Difficulty breathing
Type 2 Diabetes In Children
We include products we think are useful for our readers. If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission. Heres our process.
For decades, type 2 diabetes was considered an adults-only condition. In fact, type 2 diabetes was once called adult-onset diabetes. But what was once a disease mainly faced by adults is becoming more common in children.
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how the body metabolizes sugar, also known as glucose.
Between 2014 and 2015, about 24 percent of new diabetes diagnoses in children were type 2 diabetes.
Read on to learn the symptoms of type 2 diabetes in children and what you can do about it.
Symptoms of type 2 diabetes arent always easy to spot. In most cases, the disease develops gradually, making the symptoms hard to detect. Many people dont feel any symptoms. In other cases, children may not show any.
If you believe your child has diabetes, keep an eye out for these six symptoms:
Recommended Reading: How Can I Know If I Am Diabetic