Is There Anything In Between Rapid
Yes. There are short-acting and intermediate-acting insulins available.
-
Short-acting insulins are used like rapid-acting insulin to cover blood sugar elevation from eating.
-
Intermediate-acting insulins are similar to long-acting insulins as they are used to cover blood sugar elevations when the rapid-acting or short-acting insulins finish working.
Always Choosing The Same Spot To Inject Insulin
Insulin is absorbed at different rates depending on where you inject it. It enters your blood fastest when you inject it into your abdomen, a little more slowly when you inject it into the upper arms, and even more slowly when you inject it into the thighs and buttocks, according to the ADA. Youll get the best results by injecting your basal or bolus insulin into the same general body area, but rotating the side of the body where you inject if from day to day. Injecting insulin in the same spot over and over can cause hard, fatty lumps to form. These lumps dont absorb insulin well. You could be injecting your usual dose of insulin into one of these areas but potentially 50 percent or less of the insulin is absorbed, Port says. She recommends checking for these hard lumps from time to time.
For more on how to use insulin properly, check out Diabetes Dailys article Habits of a Great A1C: Insulin Use Strategies!
Newer Insulins & Peak Times
As insulin has evolved over time from animal insulin to human insulin to analog insulin, concerns around peak times have also changed. These days, human and analog insulin are the most common types of insulin available. Newer analog insulins offer a variety of peak times, which helps make insulin peak times more predictable.
With the development of analog insulin came the advent of rapid-acting insulin. Rapid-acting insulins are popular because they can cover the carbohydrate in your meal, and then leave your body fairly quickly. Rapid-acting insulin injections are usually taken at mealtimes they work quickly, which eliminates the guesswork around when their peak times take place.
Although analog insulin offers many benefits, it is more expensive than human insulin. For that reason, some people choose to use human insulin, instead, because its more affordable. If youre considering switching to human insulin, be sure to consult a healthcare professional who has experience managing patients on human insulin and to discuss any changes to your dosing regimen that may be necessary. Dosing and timing for human insulin is different than those for analog insulin in order to account for fluctuations in peak time.
Also Check: How Do You Treat Diabetes 2
Insulin Analogs Are Now Replacing Human Insulin In The Us
Insulins are categorized by differences in onset, peak, duration, concentration, and route of delivery.
Human Insulin and Insulin Analogs are available for insulin replacement therapy. Insulins also are classified by the timing of their action in your body specifically, how quickly they start to act, when they have a maximal effect and how long they act.Insulin analogs have been developed because human insulins have limitations when injected under the skin. In high concentrations, such as in a vial or cartridge, human clumps together. This clumping causes slow and unpredictable absorption from the subcutaneous tissue and a dose-dependent duration of action . In contrast, insulin analogs have a more predictable duration of action. The rapid acting insulin analogs work more quickly, and the long acting insulin analogs last longer and have a more even, peakless effect.
Different Types Of Insulin
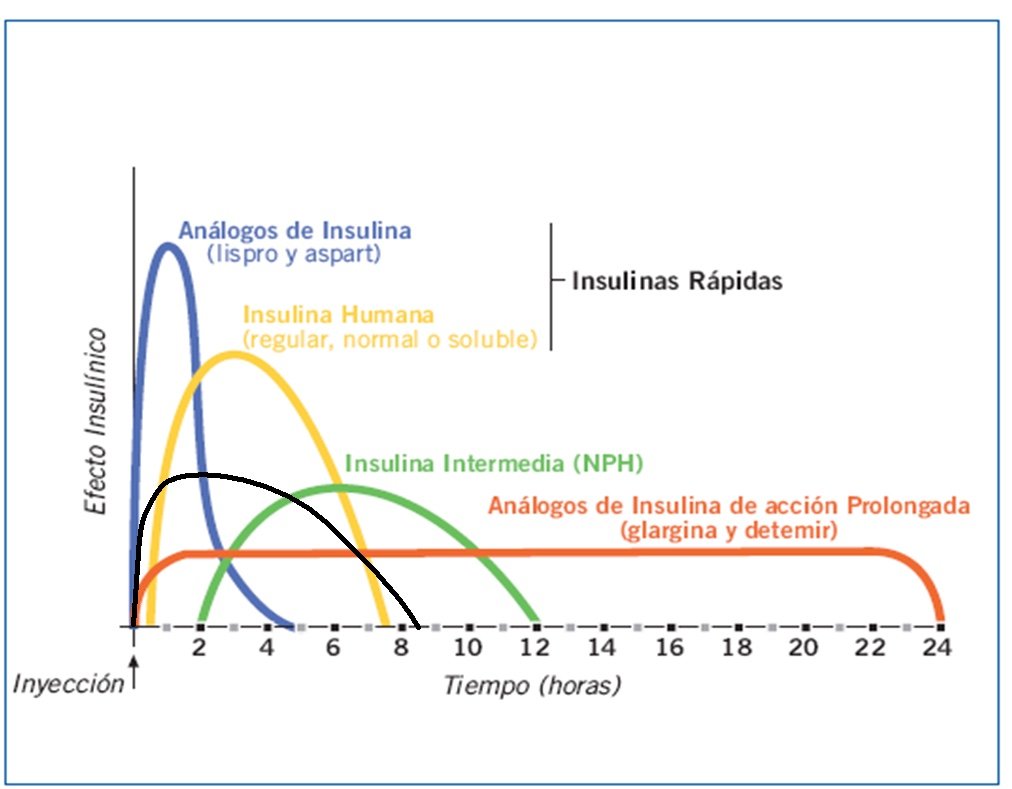
Insulin A to Z: A Guide on Different Types of Insulin Elizabeth Blair, A.N.P., at Joslin Diabetes Center, helps break down the different types of insulin and how they work for people with diabetes. Types of Insulin for People with Diabetes Rapid-acting: Usually taken before a meal to cover the blood glucose elevation from eating. This type of insulin is used with longer-acting insulin. Short-acting: Usually taken about 30 minutes before a meal to cover the blood glucose elevation from eating. This type of insulin is used with longer-acting insulin. Intermediate-acting: Covers the blood glucoseelevations when rapid-acting insulins stop working.This type of insulin is often combined with rapid- or short-acting insulin and is usually taken twice a day. Long-acting: This type of insulin is often combined, when needed, with rapid- or short-acting insulin. It lowers blood glucose levels when rapid-acting insulins stop working. It is taken once or twice a day. A Guide on Insulin Types for People with DiabetesContinue reading > >
Read Also: Once Per Week Diabetes Injection
What Are The Different Types Of Insulin
Basal vs. Prandial. Insulins are categorized by how quickly they act , when they peak, and how long they act . There are two main categories of insulin, based on function: basal and prandial . Most basal insulin is designed to be injected once or twice daily to provide a constant level of insulin action throughout the day and to provide adequate levels of insulin throughout the night. Basal insulin helps keep blood sugars at a consistent level when you are not eating but it is not enough to cover glucose spikes after meals. Prandial insulins, on the other hand, are taken at mealtime and act rapidly in the body, serving to manage the elevation of glucose levels following meals. Prandial insulins can also be used as correction doses between meals or during the night if glucose levels are high and out of range on the high side.
A newer approach to basal insulin for people with type 2 diabetes is an injectable drug that combines basal insulin with GLP-1 agonist medication. Taken as one daily injection, GLP-1/basal treatments effectively lower glucose levels while reducing weight gain and risk of hypoglycemia . Learn more here.
In A Person With Type 1 Diabetes Or Type 2 Diabetes
In a person with type 1 diabetes: the pancreas constantly tries to produce beta cells in order to make insulin, but the immune system continues to attack and destroy most or all of those beta cells.
For those with type 1 diabetes, the evolution of the disease and the attack on the beta cells occurs very quickly, which means people get sick very quickly. Often mistaken at first for the lingering flu, a simple blood test and urine test can determine and diagnose type 1 diabetes.
Immediately upon diagnosis, patients should begin taking pharmaceutical insulin via pump, pen, or syringe.
In a person with type 2 diabetes: the body is either struggling to produce a normal amount of insulin , or the body is struggling with severe insulin resistance which makes it difficult to manage healthy blood sugar levels with the available amount of insulin.
For those with type 2, the struggle to properly produce or make use of their own insulin is usually a slower process, sometimes taking years before you show strong enough symptoms to warrant an HbA1c test,a diagnosis, and eventual treatment.
Also Check: Reversing Type 2 Diabetes With Ketogenic Diet
What Is Basal Insulin
Insulin is produced by the beta cells inyour pancreas. Normally, the pancreas produces a steady amount of insulinduring the day, whether you are sleeping or awake. This is called basalinsulin. After you eat, your pancreatic beta cells produce a burst of insulin,called bolus insulin.
When you have diabetes, your pancreaticbeta cells no longer produce enough basal and/or bolus insulin. For thisreason, you need to use long-acting insulin to replacethe basal insulin, and short-acting mealtime insulin to replace your bolusinsulin.
Both long and ultra-long-acting insulinshave chemical modifications that allow them to release into your bloodstream ata steady rate to mimic basal insulin. These modifications include changes toamino acids, which are the building blocks of all proteins including insulin.
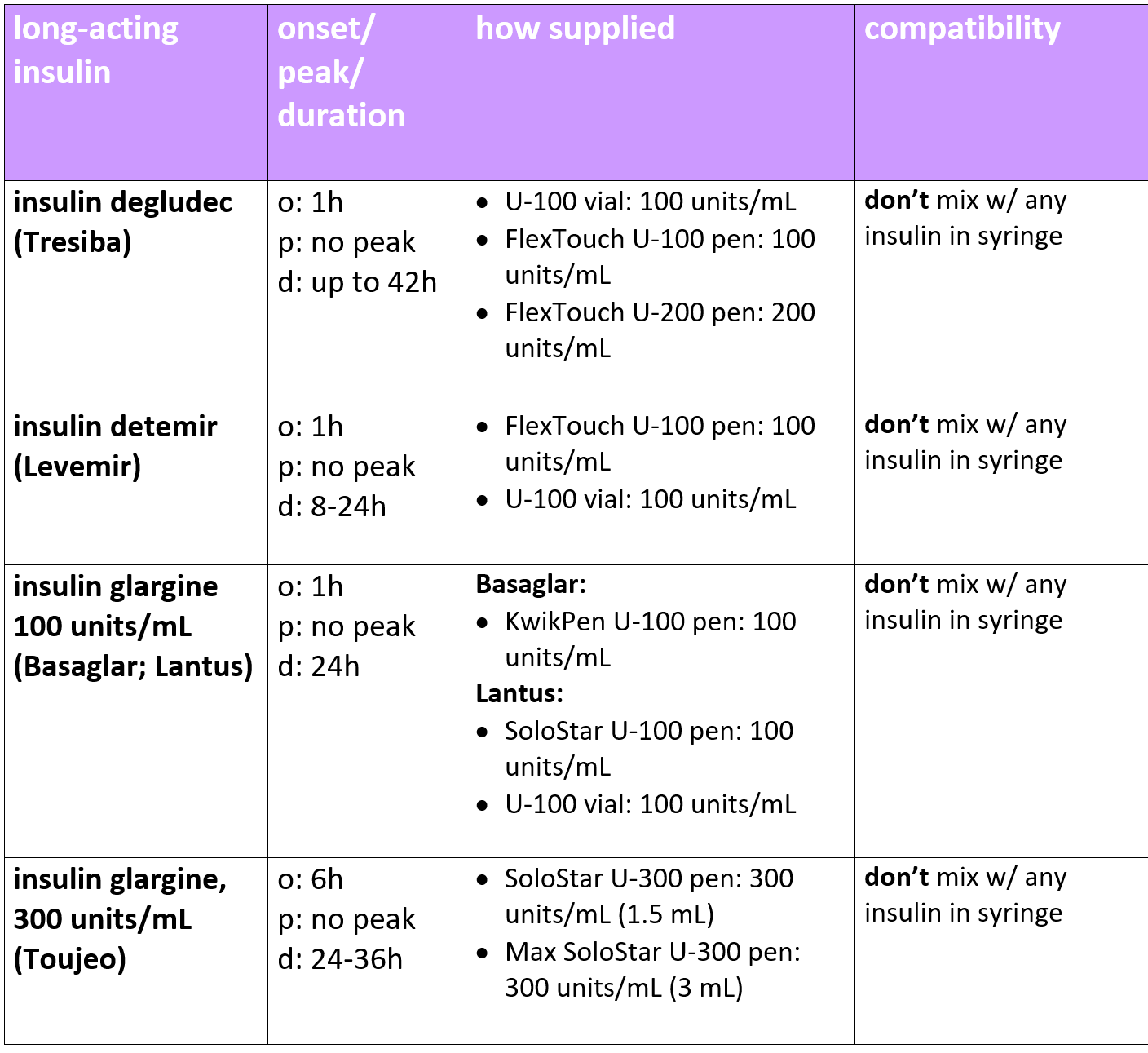
Are There Any Insulin Products That Last Longer Than Long
Yes. There are 2 ultra-long-acting insulin products that are availableToujeo and Tresiba.
The ultra-long-acting insulin, Toujeo, was approved by the FDA in February 2015. Toujeo will begin working within 6 hours of injecting and last for 36 hours with no peak.
The ultra-long-acting insulin, Tresiba, was approved by the FDA in September 2015. Tresiba will begin working within 1 hour of injecting and last at least 42 hours with no peak.
Don’t Miss: Freestyle Libre For Type 2 Diabetes
When Is The Right Time To Take Your Insulin
Posted on December 4, 2014 by DiabetesDigest.com Staff in Blogs, Diabetes Digest
If you take insulin and struggle to manage high and low blood glucose numbers, one reason may be the timing of your injections. Coordinating when you take your insulin with the timing of your meals, your physical activity, and other parts of your diabetes care plan can help. Here are some tips to help you time your insulin just right.
Take insulin at regularly scheduled times. The more often you are able to take your insulin at the same time each day, the easier it becomes to keep your blood glucose in control. This isnt always easy. If you want a more flexible insulin plan, talk with your health care provider about taking more injections, using a long-acting and rapid-acting insulin plan, using an insulin pen or switching to an insulin pump.
Eat at about the same times each day. Doing so also makes it easier to manage your blood glucose.
When you eat, you need insulin readily available. This will help to keep your blood glucose level from going too high. Carbohydrates in food make blood glucose rise. Its easier to keep blood glucose from going too high by having insulin in your body when you eat rather than trying to lower blood glucose that has already gotten too high.
Paying attention to timing wont solve all of the ups and downs of blood glucose levels, but it can help to make managing your diabetes a bit easier.
Diabetes and Arthritis
MEDICATIONS
How Does Ozempic Affect My Blood Sugar
In clinical studies conducted by the manufacturer, Ozempic was studied as a single treatment compared to placebo as well as when combined with other type 2 diabetes medications such as metformin, metformin plus a sulfonylureas, and metformin plus thiazolidinediones.
The effectiveness of Ozempic was compared to sitagliptin, exenatide extended-release, and insulin glargine. Ozempic 0.5 mg and 1 mg injected weekly significantly reduced the A1C levels in all studies ranging from 30 weeks to 56 weeks.
However, reducing your A1C below 7 may take at least 8 weeks, depending upon where your hemoglobin A1C is when you start Ozempic. In a 56-week study comparing semaglutide to sitagliptin, Ozempic lowered the mean baseline A1C of 8% down to 7% by week 8 of the study. A1C levels were at or below 6.5% by week 16.
In another clinical study, Ozempic monotherapy lowered the A1C by 1.4% to 1.6% after 30 weeks of treatment. It also reduced fasting blood sugar levels by 41 to 44 mg/dL after 30 weeks. The percent of patients achieving an A1C of less than 7% was 70% to 73% of patients using Ozempic compared to 28% of patients using a placebo.
Dont Miss: List Of Insulins For Diabetes
Also Check: Best Diet Pills For Diabetes Type 2
Pregnant Women With Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes refers to diabetes that is diagnosed during a womans pregnancy. Similar to Type 2 diabetes, the insulin present may not be sufficient to maintain normal blood glucose levels and ensure the cells are receiving the fuel they need. Often insulin injections are necessary for the duration of the pregnancy to protect both the mother and the babys health.
Are Insulins Safe
The most serious risk of taking insulin is low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia. If untreated, low blood sugar can be a medical emergency. Low blood sugar can usually be treated quickly by drinking or eating a food high in sugar . There are also products, such as glucose tablets or glucagon for injection, that healthcare providers may recommend for insulin users to have on hand. Other serious risks with taking insulin are hypersensitivity reactions and hypokalemia .
Don’t Miss: Hiv And Diabetes Life Expectancy
How To Take Long
Usually, you inject long-acting insulin once a day to keep your blood sugar levels steady. You use a needle or pen device to give yourself the injection. Be sure to inject your long-acting insulin at the same time every day to avoid lags in insulin coverage or stacking your insulin doses. Stacking means taking your doses too close together, causing their activity to overlap.
Your doctor might recommend adding short-acting insulin before a meal to prevent a blood sugar spike after you eat.
If you change brands of long-acting insulin, you may need a different dose. Talk to your doctor for advice if you change brands of any insulin.
As with any medicine you take, insulin injections can cause side effects.
One possible side effect is low blood sugar . Symptoms of low blood sugar include:
- dizziness
- headache
- fainting
Other possible side effects of insulin injections include pain, redness, or swelling of the skin at the injection site.
Sometimes insulin is given in combination with thiazolidinediones. This drug group includes oral diabetic drugs like Actos and Avandia. Taking insulin with thiazolidinediones increases the risk of fluid retention and heart failure.
For those taking degludec, precautions may be necessary because of its long effect in the body. You doctor may need to increase your dose at a very gradual rate, at least three to four days apart. It will also take longer to clear the drug from your body.
Avoiding Injection Bruises And Lumps
Bruising can happen when you catch a tiny blood vessel under the skin where you have injected. It is quite normal for this to happen occasionally when you are injecting regularly and youre not doing anything wrong.
If you are concerned, you could make an appointment with your diabetes specialist nurse who will be able to do a review of your injection technique. In some cases, bleeding and bruising can be reduced by something as simple as using a different sized needle or changing your needle after each injection.
Some people notice hard lumps that can form if you inject in the same place too often. This might be lipohypertrophy , or could be something called cutaneous amyloidosis. These lumps can stop the insulin from working properly, so make sure you rotate where you inject and choose a different spot each time. If you notice any lumps, especially if theyre not going away, speak to your healthcare professional for more advice.
Other side effects from injecting a lot can be itching, rashes and other skin irritations. Changing where you inject helps with this too. You can also get treatments from your local pharmacy that can will help with the irritation.
Also Check: Once A Week Shot For Type 2 Diabetes
How Much Do Insulins Cost
The cost of insulin can vary significantly based on the type used , and the delivery method Insulin costs also may vary depending on the type of insurance, since many plans utilize formularies that may price similar insulin products differently depending on the preferred supplier . For people without health insurance, insulin can cost anywhere from $25 to more than $300 per vial. Underinsured or uninsured patients can use free SingleCare coupons to save money on insulin and other diabetes needs.
Know Your Insulins And Their Timing
A good way to improve glucose levels is to track the peaks and drops in your glucose and relate how the peak and action times of your insulins correspond to low or high patterns in your glucose. Identify your glucose patterns , and work to understand when each of your insulins is active. This allows you to adjust your insulin doses or food choices to stop unwanted ups and downs in your readings.
The table below shows the start, peak, and end times for various insulins.
| Action Times for Insulins | |
|---|---|
| covers meals and lowers high BGs | |
| Regular | covers meals and lowers high BGs |
| NPH | |
| very flat, long-acting background insulin action |
You May Like: What Is The Price Of Novolog Insulin
Are There Any Side Effects To Taking Insulin
The most common side effect of taking insulin is low blood sugar levels, also called hypoglycemia. Symptoms of severe hypoglycemia include feeling shaky, sweating, fast heartbeat, and hunger. You can treat the symptoms of hypoglycemia by eating or drinking a quick source of sugar such as fruit juice, hard candy, honey, or milk. You can lower your risk of hypoglycemia by actively managing your blood sugar levels and increasing the frequency of glucose monitoring.
Other less common side effects of insulin include weight gain and allergic reactions, which can also happen at the injection site if you are not using an inhaler. Allergic reactions can cause shortness of breath, wheezing, fast heartbeat, and sweating. If you have an allergic reaction to insulin, stop using it and call your doctor right away. If you think you or someone else is having a medical emergency, call 911 immediately.
Factors That Speed Insulin Absorption
Variation in insulin absorption can cause changes in blood glucose levels. Insulin absorption is increased by:
- injecting into an exercised area such as the thighs or arms
- high temperatures due to a hot shower, bath, hot water bottle, spa or sauna
- massaging the area around the injection site
- injecting into muscle this causes the insulin to be absorbed more quickly and could cause blood glucose levels to drop too low.
Don’t Miss: Does Diabetes Affect Your Stomach
Why Do Diabetics Need Insulin
Diabetes, also called diabetes mellitus, is a condition where your body cant properly use the insulin it produces, or cant produce enough insulin which causes high blood sugar levels. Type 1 diabetes is when your pancreas stops producing any insulin and you will need to take insulin to supplement your lack of insulin for the rest of your life. Type 2 diabetes is when your cells lose their insulin sensitivity and stop reacting to it, also called insulin resistance, which allows your blood glucose levels to rise. One of the main differences between the two types of diabetes is that type 2 diabetes can usually be prevented and the symptoms lessened with healthy lifestyle choices. The other most common type of diabetes is gestational diabetes which occurs when you are pregnant but usually disappears after pregnancy. If you have diabetes, monitoring of blood glucose levels is necessary as is making healthy lifestyle choices and taking insulin if necessary. Over time, the complications of diabetes can damage your heart, kidneys, nerves, and eyes among other medical conditions such as diabetic ketoacidosis which is when your blood becomes too acidic.