What Does An Insulin Pump Do
An insulin pump is intended to act like a human pancreas outside the body. Your pancreas releases insulin in response to changes in your blood sugar level. But when you have diabetes, your body doesnt release insulin or use it properly. As a result, you have to find another way to get the insulin you need.
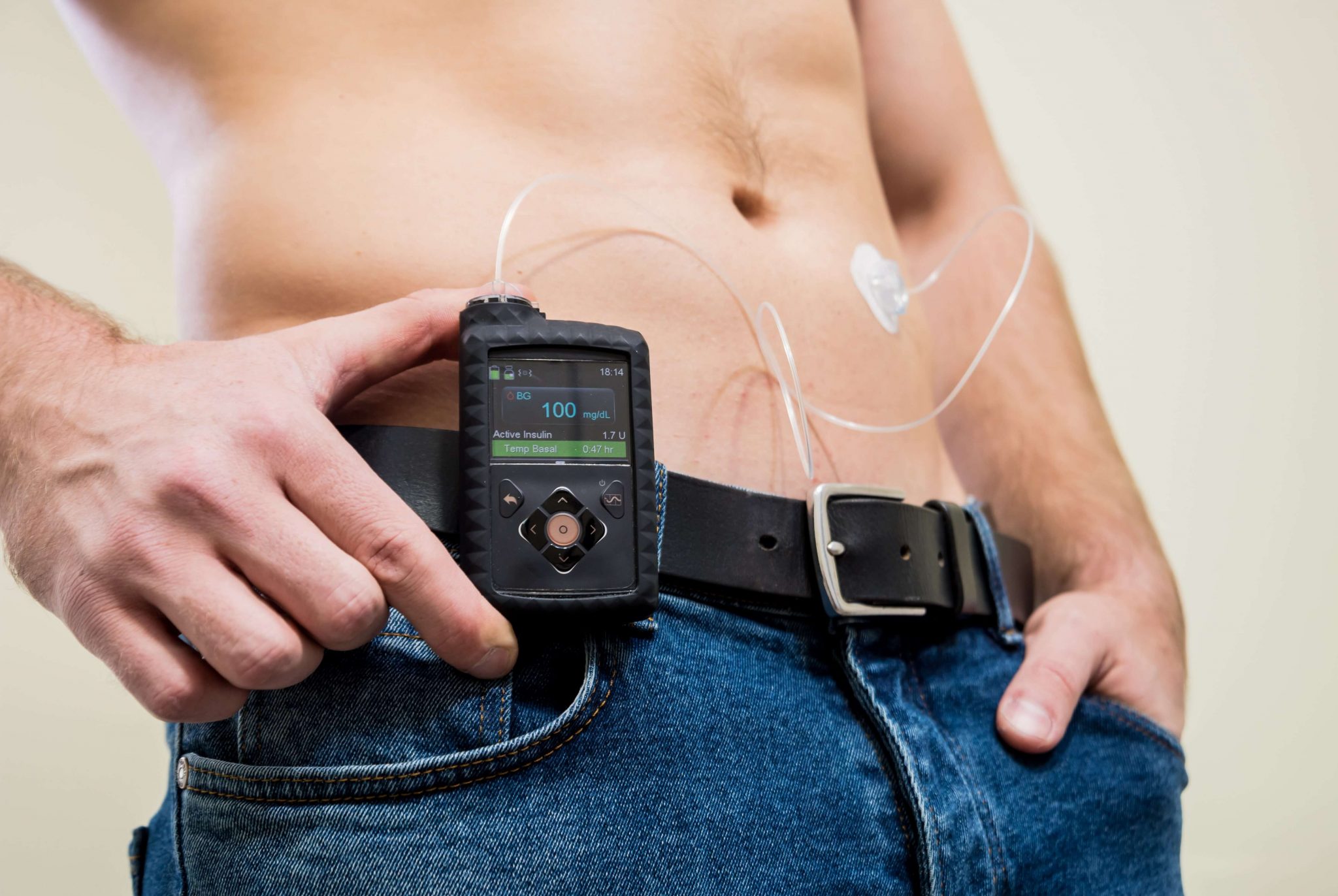
Insulin pumps work by delivering a basal, or set, rate of insulin through a tube called a cannula. The cannula is inserted just under the top layer of your skin. Your doctor will work with you to determine the amount of insulin you need each day.
Insulin pumps can also deliver an insulin bolus. This is an extra dose of insulin besides your basal rate. A pump wont automatically give you this extra dose of insulin, though. You need to tell the pump to administer the bolus dose.
Some insulin pumps will also monitor your blood sugar level. The pump will tell you in real time what your blood sugar is, so you can give yourself insulin.
Insulin pumps give you insulin according to how you program them. They dont adjust on their own to your changing insulin levels.
They require special training on your part to make sure you can use them safely and effectively.
An insulin pump is usually about the size of a deck of cards, although the size can vary depending on the model. You wear the pump outside your body.
The pump usually consists of:
- a display screen
- a place for an insulin container
- a thin cannula, or tube, that attaches to your body
Advantages Of Using A Pump With Type 2 Diabetes
Have You Ever Wondered How Does The Omnipod Work So Have We We Scoured The Internet And Talked To Some Of Our Favourite Podders To Learn As Much As We Could About How The Omnipod Works And Wanted To Share What We Learned With You
Disclaimer: Please check out CIMs Partners Page to learn more about the companies we work with. Its important for CIM to recognize and to disclose that our writing may be biased based on the fact that the Omnipod provides sponsorship and support to CIM. We work hard to get information into the hands of the diabetes community whenever we feel it may help people live life without limits.
What is different about the Omnipod Insulin Management System? If you are brand new to Omnipod , we suggest checking out Connected in Motions Tech Update blog about the Omnipod Insulin Management System. In short, Omnipod is a tubeless insulin pump made by Insulet, a company whose mission is to make the lives of people with diabetes easier. Insulet was founded in Massachusetts back in 2000 and officially brought to Canada in 2011. Interested in learning more about how the Omnipod came to be? Read more about what inspired Insulets co-founder to create the product one that is now used by 140,000 adults and youth around the world today.
There are two parts of the Omnipod System: The Pod and the PDM .
The Pod and Personal Diabetes Manager communicate wirelessly to deliver continuous insulin based on your personal settingsgiving you what you ask for, when you ask for it. Youll need to keep the PDM within 5 feet of the Pod to program a bolus or make a change to your settings, otherwise, you dont need the PDM with you at all times.
Recommended Reading: How Do I Get My Diabetic Supplies Through Medicare
What Should My Expectations Be When Considering The Pump
Often times people have wrong expectations of what a pump can do, so lets set the record straight. Its not something that you can just hook up and let it go.yet. It requires just as much, if not more attention than giving insulin injections. There are three main areas to think about when it comes to transitioning to a pump:
Insulin Pumps For Type 2 Diabetes
Insulin pumps can be incredibly helpful for people with diabetes. While many people still prefer the traditional method of taking multiple daily injections , insulin pumps can truly change life with diabetes.
- Traditional insulin pumps:Todays insulin pumps are small, computerized machines that deliver insulin through a tiny catheter inserted into the skin with a small needle or cannula. They can be programmed with very specific, detailed hours and dosages to cover both your basal and bolus insulin needs.
- Disposable patch pumps:Disposable insulin patch pumps offer a very simple method of delivering insulin without injections. Determining which type of patch pump is right for you may depend on whether you need both basal and bolus insulin or just bolus insulin. Options include a 3-day wearable patch and a 1-day wearable patch. Disposable insulin patches offer easy insulin dosing with a simpler system.
Also Check: Symptoms For Low Sugar Diabetes
Tips On Disconnecting The Pump
Now, lets talk about when you should or can disconnect:
First, the actual act of disconnecting can sometimes be challenging. A light touch is the best advice. If you are struggling to disconnect stop, take a breath, relax, and try again. After the first few times, you will have the hang of it and it will be no problem.
Once you are disconnected, ideally you are not staying off the pump for more than an hour or so, and if you are, you should check your blood sugar after an hour and reconnect and give a bolus if needed, then disconnect and go back to what you were doing.
Inpatient Cgm Use In The Sars
The rapid outbreak of novel coronavirus 2019 , which arose from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection, has recently become an international public health emergency. Various cardiovascular and metabolic comorbidities, including diabetes, have been reported as a risk factor for unfavorable prognosis . Anecdotal reports suggest that patients with severe COVID-19 can present with marked hyperglycemia, even DKA, and can be very insulin resistant, whether or not there was a prior history of diabetes . Given this information, maintaining optimal glucose levels in hospitalized patients is a key component of care. However, the need for multiple fingerstick glucose measurements per day contradicts efforts to conserve personal protective equipment and reduce healthcare professionals repeated exposure to the novel coronavirus and workload.
Recommended Reading: Healthy Diet Plan For Diabetic Patient
How Much Does A Pump Cost
The answer to this is different for every one. A pump may cost you anywhere from $0-$7000 depending on your insurance coverage. Dont let that stop you! The first step after deciding that you want a pump and which one, is letting the pump company help you figure out your out of pocket cost . You will give the pump company your insurance information and they will contact them to check your coverage. They may cover the full amount or maybe only 80%, but the company should be able to give you a good idea of what it will cost you. Also, know that some companies wont cover certain pumps.
Most pump companies have payment plans to help make having a pump more affordable. If you prefer to call your insurance company on your own, remember that a pump is considered durable medical equipment . Its not like a normal prescription drug that you just pick up at the pharmacy. You will also need to ask about the ongoing cost for supplies. Supplies will be shipped to you typically, every month or 3 months. Many of the insulin pumps have an integrated continuous glucose monitor and checking coverage for CGM is important as well. To get the best quote and save you the most time, you are better off letting the pump company check your benefits for you, they know the lingo and will be able to get you accurate information.
First, this is your medical device that you life will depend on, do you really want to buy it from a random person on the internet?
Differences In Usage Of Iis Between Countries
In view of the differences between patients with respect to age, sex, BMI, physical activities, and insulin pump variations, a clear need for a variety of IIS types exists. However, many pump wearers remain on the same IIS that is shipped with their pump or that the diabetes nurse supplied during their introduction to insulin pump therapy.
Most IIS are manufactured by a single company in Denmark. There is a scarcity of published data about how many pump wearers in different countries use steel versus Teflon IIS, and about which brands or styles are used in various locations. Survey data suggest that steel sets are more commonly used in Germany and Europe than in the United States , and this may correlate with the market share for various brands of insulin pumps used in different countries.6
Don’t Miss: Does Diabetes Affect Your Stomach
How Much Does An Insulin Pump Cost
If you meet the criteria for a pump, you should be able to get your pump on the NHS for free.
If you dont meet the criteria, they cost around £2000 to £3000 and should last between 4 to 8 years. This is a lot of money, and is a big commitment. If you want to talk to us about your options then give our helpline a call. But remember to speak to your healthcare team too.
Its important to remember that youll also have to buy other things that make the pump work, like your infusion set. These cost around £1500 a year. This doesnt include your prescription insulin, which you get for free.
Other Factors To Consider:
- The insulin pump doesnt take away the need to check blood sugar.
- There are technical aspects to using a pumpsetting it up, putting it in, interacting with itthat are more complicated in some ways than using injections.
- If it breaks or falls off, the person wearing it needs to be ready to give insulin by injection any time it is needed.
- It can be expensive, so find out which pumps are covered by your insurance and if those pumps meet your needs.
- All pumps are an extra piece of hardware attached to your body, either with tubing or attached to your skin. There are many clever ways to wear pumps and hide them from view, but they do take a bit of getting used to at first.
Don’t Miss: Dinner For Diabetics Type 1
A Pump May Be A Good Choice For:
- People who like the idea of a pump. If this is what you want, or what you want for your child, and it can be used it safely, then it should be used.
- Active people, who benefit from changes in basal rates or suspending the pump when exercising.
- People who have frequent low blood sugar reactions.
- Anyone who has delays in absorption of food from the stomach .
- Women planning pregnancy.
- People who want to use the pumps bolus calculator functions to determine insulin doses.
Do Pumps Take Blood Glucose Readings

Traditionally, pumps have not taken blood glucose readings but it is now possible to get pumps that have sensors which measure sugar levels.
It should be noted that these sensors actually measure the level of sugar in interstitial fluid, a fluid which acts as a reservoir of nutrients, including glucose.
Some people may also wear a continuous glucose monitor in addition to an insulin pump.
A continuous glucose monitor also is worn on the body and provides regular interstitial fluid sugar level readings. The sugar level of our interstitial fluid is generally proportional to the sugar level of our blood
Also Check: Insulin Plant For Type 1 Diabetes
Advantages Of An Insulin Pump
- Youâll need fewer needle sticks. A pump requires one shot every few days when you change your infusion set.
- A pump is more accurate than shots, helping you better manage blood sugar levels.
- Youâll have fewer blood sugar lows, which is important if you often have hypoglycemia.
- It may improve your A1c levels.
- Dosing for meals and snacks is easier.
- Itâs easier to plan for exercise.
- Itâs easier to bolus.
- It helps manage early morning high blood sugar, also called the âdawn phenomenon.â
One thing to keep in mind: Youâll always need to have regular injectable insulin on hand in case the pump stops working.
How To Get An Insulin Pump
To get a pump for free, youll have to meet certain criteria set by the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence .
If you live in England and Wales, youre over 12 years old and have type 1 diabetes, you need to meet one or more of the following criteria:
- You cant get to your target HbA1c without severe hypos.
- Your HbA1c remains high despite carefully trying to manage your diabetes.
If you live in Scotland or Northern Ireland, the criteria is different. Your healthcare team will give you advice on whether you meet your local criteria for getting a pump and what the next steps are.
If youre thinking about an insulin pump for your child, the criteria is different. Pumps are recommended for children under 12 when multiple daily insulin injections arent practical or appropriate. Make sure you speak to your diabetes specialist about if this is the best option for your child.
We understand that trying to get an insulin pump can be very frustrating, and you might feel disappointed if you cant get one. If you have any questions at all, or you just need someone to talk to, call our helpline.
Pumps are currently not available for people with Type 2 on prescription. You can self-fund, but make sure you have a discussion with your healthcare professional if youre thinking of trying one.
Don’t Miss: Where Can I Get Free Diabetic Supplies
What Is Involved In Starting The Pump
Pump starts are usually done in 2 long office visits. The first visit is a pump start without insulin. The patient inserts the pump and learns all the basic features then uses the pump for a week with saline, while continuing the usual insulin regimen by injection. Patients spend the first week practicing pump site insertions, trouble-shooting, and making changes and adjustments in basal and bolus doses. The second visit is for the pump start with insulin. This visit is done in the morning. The long acting insulin is held the night before and insulin is initiated by pump is the office. Patients usually spend at least through lunch at the Berrie Center on their first day of pump therapy. Patients are in close contact with the educator for several weeks after initiation of pump therapy.
Traveling With A Pump
When traveling , you should always carry several days of extra supplies and all supplies and medications should be kept in your carry on. Make sure all medications, including insulin are in their original container with the prescription label on it. It doesnt hurt to have a letter from your provider stating you are wearing a medical device. Carry syringes and back up long-acting insulin with you when you travel, just in case. Dont forget extra batteries or your charger cable for you pump or CGM.
Your pump is OK to go through screening, but not through the Xray machine. You can also request a pat down rather than having to remove your pump.
If you are going out of the country, many pump companies will offer you a loaner pump to take with you just in case of a malfunction. Its also helpful to change the time on your insulin pump once you arrive at your destination, otherwise you basal rates will not be programmed correctly.
Further reading:
If you are going through a very large time change, talk to your educator about how and when to change the time for your basal. Also, if you are going to be more active on your vacation, you may just plan to set a complete separate basal pattern for while you are away. Just make sure to set an alarm in your phone or leave yourself a note at home to change your time or basal pattern back when you return.
Also Check: Where To Go To Get Tested For Diabetes
What Cant The Pump Do
Its important to recognize what the pump can and cannot do. Patients may be able to obtain good glucose control from insulin injections or from an insulin pump. The pump cannot automatically give patients excellent diabetes control without effort. Patients still need to monitor their blood sugars and count carbohydrates.