Evidence Synthesis And Next Steps
Given the highly consistent results from the existing longitudinal observational studies, it is unlikely that new observational studies would modify the conclusion that vitamin D status is inversely associated with diabetes risk. A search of clinicaltrials.gov did not identify ongoing or planned randomized controlled trials specifically designed and being conducted to test the effect of vitamin D supplementation for the prevention of type 2 diabetes. Many large trials testing the effect of vitamin D supplementation on nondiabetes outcomes in populations at average risk for diabetes have been recently published or will be completed soon . We expect many of these trials to present secondary results on incident diabetes however, these reports will require careful interpretation due to several limitations . Therefore, the conclusions we draw on the role of vitamin D for the prevention of type 2 diabetes will depend on data we already have.
We also expect many of the completed trials to publish secondary results on the effect of vitamin D supplementation on micro- and macrovascular complications of diabetes. However, these trials are not powered for detecting an effect because the risk of developing micro- and macrovascular complications in these trial populations is very low.
Comparison Of 25d Levels And Prevalence Of Nafld In T2dm Patients With Different Levels Of Bmi
Patients who underwent combined NAFLD still conferred a statistically significant lower level of 25D and a higher proportion of patients with vitamin D deficiency compared with T2DM patients without NAFLD . NAFLD prevalence in T2DM patients with 25 D deficiency was higher than in those without 25 D deficiency, and the difference was statistically significant .
|
Figure 1 Comparison of 25D between the NAFLD group and the non-NAFLD group in participants with T2DM: all participants participants with BMI > 23kg/m2 participants with BMI 23kg/m2. |
|
Figure 2 Comparison of the prevalence of NAFLD in T2DM patients with and without vitamin D deficiency: all participants participants with BMI > 23kg/m2 participants with BMI 23kg/m2. |
BMI was categorized as BMI 23kg/m2 and BMI 23 kg/m2. We also carried out separate analyses for these two subgroups. In T2DM patients with BMI > 23kg/m2, the level of 25D was significantly lower in T2DM patients with NAFLD compared with those without NAFLD . The NAFLD prevalence in patients with 25 D deficiency was higher than in those without 25 D deficiency, and the difference was statistically significant in T2DM patients with BMI> 23kg/m2 . However, no difference was observed in the levels of 25 D between NAFLD and non-NAFLD groups in T2DM patients with BMI 23kg/m2 . There was no difference in the prevalence of NAFLD between VDND and VDD groups in T2DM patients with BMI 23kg/m2 .
Patients And Study Design
The study was conducted following the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Ethics Committee of Hebei General Hospital. Our study included 434 patients diagnosed with T2DM who were hospitalized in Hebei General Hospital of Shijiazhuang in China. All subjects had signed written informed consent. Studies were independently assessed by the two researchers and evaluated against inclusion and exclusion criteria by consensus.
Recommended Reading: Lesser Known Symptoms Of Diabetes
Research Design And Study Patients
We collected electronic medical records of 797 inpatients at Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University between June 24, 2019 and December 24, 2020. Inclusion criteria: 1) All selected candidates must have complete electronic medical records for the index of study interest 2) 18 years old and above 3) All enrollees were able to eat and drink normally, were not in the acute phase of disease or with serious life-threatening illness, and do not come from an ICU unit 4) All selected candidates do not come from hospitalized persons during pregnancy or puerperium. Electronic medical records that do not meet the above requirements will be deleted. At last, 201 people whose medical records lacked information such as height, weight and blood pressure were excluded and a total of 596 subjects were enrolled . T2DM group should be diagnosed as T2DM according to the 1999 World Health Organization standard . The ethics Committee of Dalian R& S Kangtai Medical Testing Laboratory Co. authorized the ethics of this study and approved a waiver of informed consent due to the nature of the study. This is consistent with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Article Flow Chart.
Vitamin D Supplementation Has A Modest Impact On A1c Levels
A 2017 study from Baltimore, MD set out to determine if consistent consumption of vitamin D supplements helped improve glucose metabolism and lower patients A1c levels.
The study saw a modest reduction in the A1c levels of the group taking D3 supplementation compared to the placebo group, but no noticeable changes in their fasting blood sugar levels.
Recommended Reading: Where Can I Put My Insulin Shot
Data Extraction And Quality Assessment
Data from each study were extracted by one of the reviewers and confirmed by the other. The extracted data included: study design participant characteristics cohort source longest reported follow-up period method of assessing vitamin D status or details of vitamin D supplementation association between vitamin D and outcome potential confounding variables adjusted for, with particular emphasis on age, race, weight and variables related to sun exposure method of ascertaining glycemia outcome, and statistical analysis.
Vitamin D Supplements Do Not Significantly Reduce Risk Of Developing Type 2 Diabetes According To Research Presented Today At The Adas Scientific Sessions
New research shows that daily oral vitamin D supplementation does not effectively reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes among vitamin D-sufficient adults at high risk for developing the disease, according to the The Vitamin D and Type 2 Diabetes Study A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial for Diabetes Prevention study presented today at the American Diabetes Associations® 79th Scientific Sessions® at the Moscone Convention Center in San Francisco.
More than 84 million Americans have prediabetes, which is a precursor of symptoms indicating higher risk of progression to type 2 diabetes. The prevalence of type 2 diabetes and related costs are expected to continue to increase in the next quarter century, resulting in a need for effective prevention interventions for populations at high risk. Vitamin D insufficiency has emerged as a potential key contributor to the development of T2D. Observational studies have consistently reported an inverse association between blood 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration and incident diabetes however, data from long-term trials are lacking. D2d, a multicenter randomized controlled trial focused on diabetes prevention, was conducted in 22 U.S. cities to determine whether vitamin D supplementation is safe and effective in delaying the onset of TD2 in people at risk for the disease and to gain a better understanding of how vitamin D affects glucose metabolism.
Also Check: Where To Get Diabetic Supplies
Multivariate Logistic Regression Analyses Of Nafld And Associated Factors
Multiple logistic regression analysis was employed to examine whether vitamin D deficiency was independently and significantly associated with the presence of NAFLD in T2DM patients. For all T2DM patients, vitamin D deficiency was significantly associated with a higher prevalence of NAFLD. Specifically, T2DM patients with vitamin D deficiency had a 2.045 times higher risk of developing NAFLD than those without vitamin D deficiency .
|
Table 3 Logistic Regression Analysis of Vitamin D Deficiency for NAFLD in Patients with T2DM |
Vitamin D deficiency was not associated with high NAFLD preference in T2DM patients with BMI 23 kg/m2, . Vitamin D deficiency was associated with high NAFLD preference in T2DM patients with BMI > 23kg/m2, regardless of whether an unadjusted or adjusted model was used .
|
Table 4 Logistic Regression Analysis of Vitamin D Deficiency for NAFLD in T2DM Patients with BMI 23kg/m2 |
|
Table 5 Logistic Regression Analysis of Vitamin D Deficiency for NAFLD in T2DM Patients with BMI > 23kg/m2 |
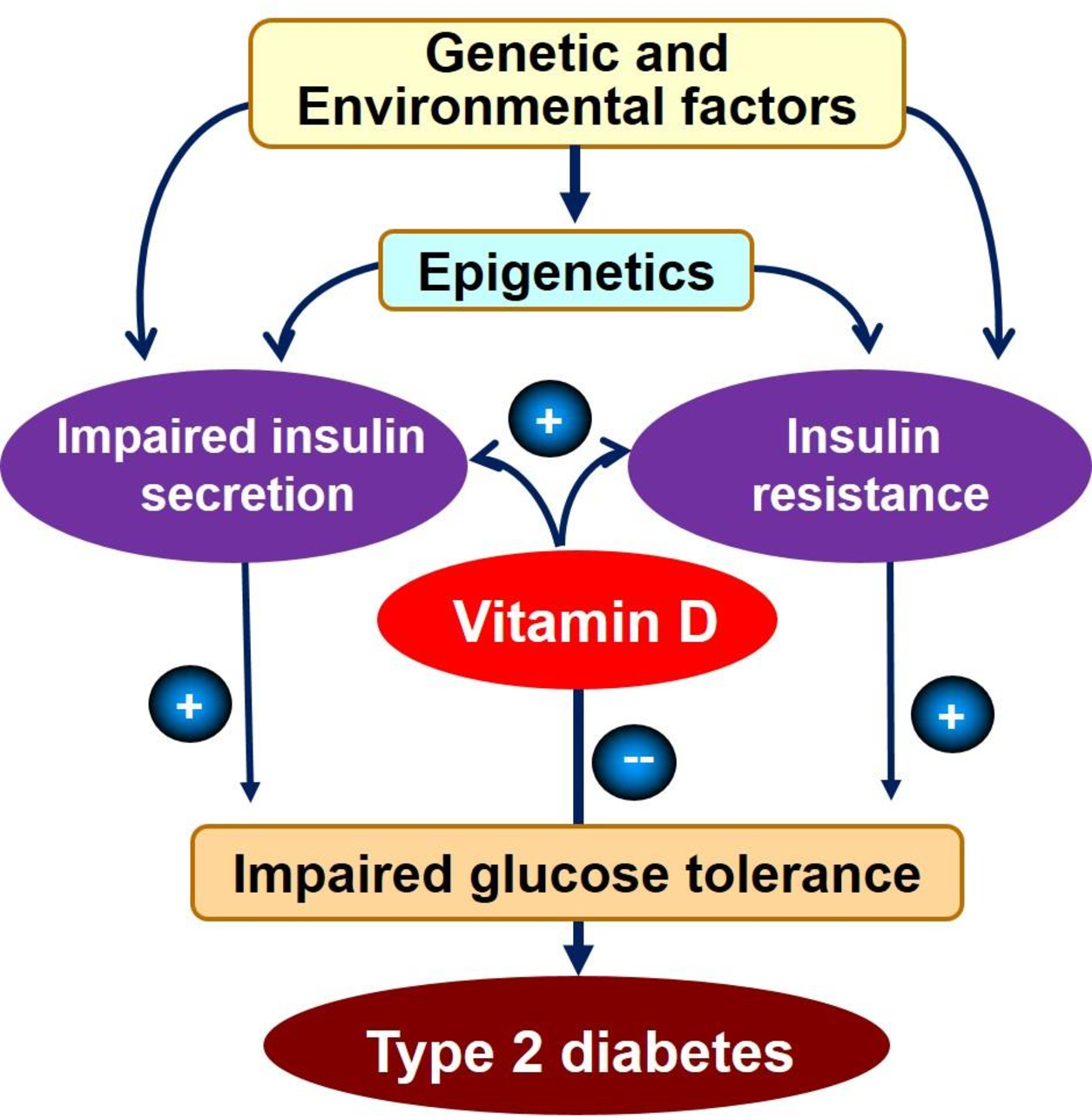
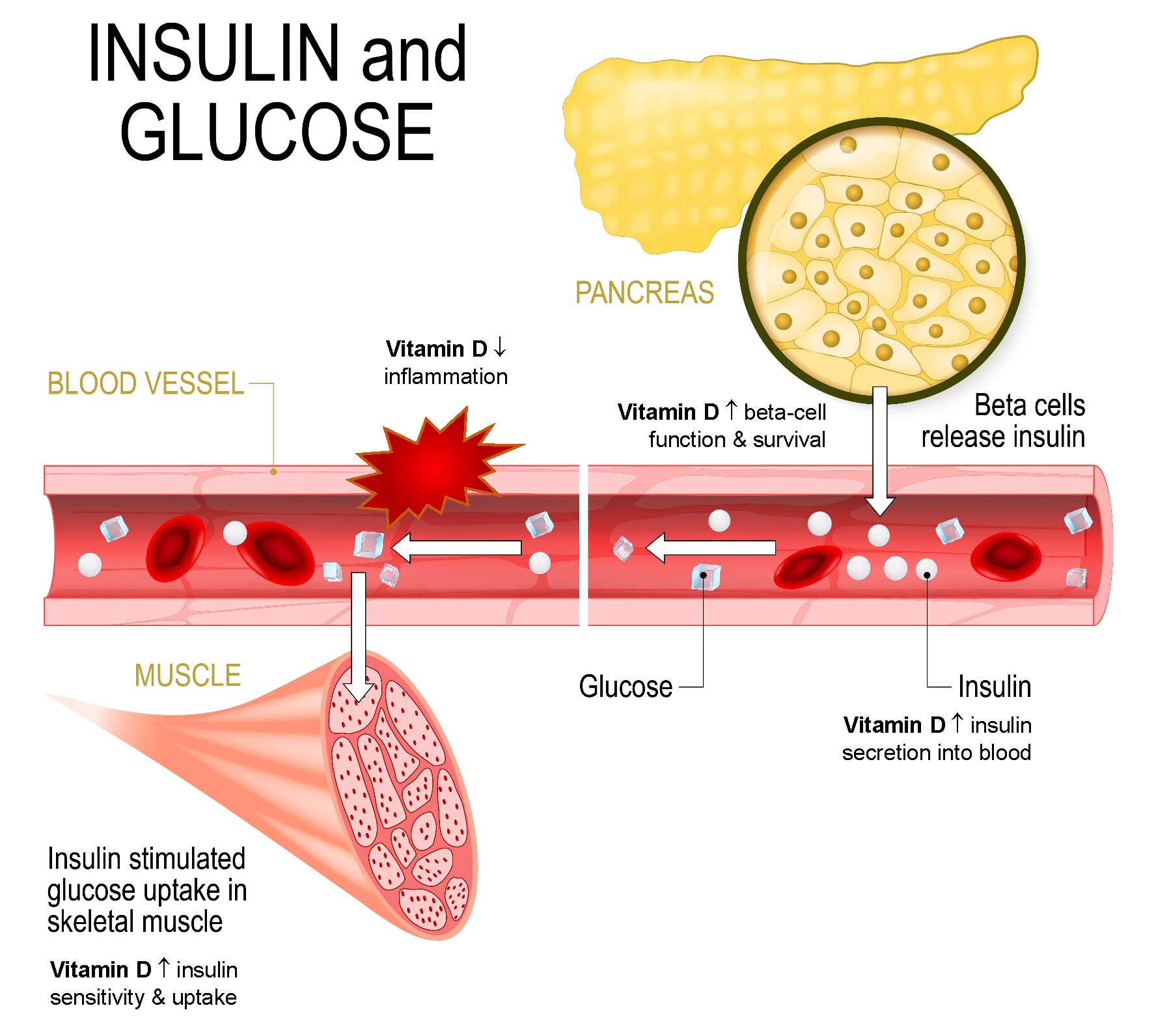
Overview Of Vitamin D Physiology And Plausible Mechanistic Links To The Pathophysiology Of Type 2 Diabetes
Vitamin D, obtained either from oral sources or cutaneous biosynthesis upon sun exposure, is hydroxylated first in the liver to 25D, and then in the kidneys to become the active form 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D . These vitamin D metabolites are transported in the circulation bound primarily to vitamin D binding protein and only a small fraction circulates in the free form. The free 1,252D form binds to the nuclear vitamin D receptor , which regulates hundreds of genes . Circulating 25D has a long half-life, can be readily measured, and correlates well with known vitamin D effects therefore, it is used in clinical and research settings as a marker of vitamin D status.
The main effect of vitamin D is to increase the intestinal absorption of calcium. Severe vitamin D deficiency leads to rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults. However, due to the wide tissue distribution of the VDR and extrarenal activation of 25D to 1,252D, it is believed that vitamin D has extraskeletal effects . Accordingly, low blood 25D levels have been associated with numerous diseases, including the risk of developing type 2 diabetes .
Despite basic research studies providing some support for mechanisms in favor of vitamin D having an effect on the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes, one needs to be careful of arguments in favor of biologic rationale, as the research history is filled with large trials that did not confirm a hypothesis that had a strong biological rationale from basic research.
Also Check: Causes Of Hypoglycemia In Diabetics
Vitamin D And Diabetes
Teresa Martin, RD, CDE, LD, is a diabetes educator for Novo Nordisk based in Bend, Ore. R. Keith Campbell, RPh, CDE, FASHP, is a distinguished professor in diabetes care at Washington State University College of Pharmacy in Pullman.
Diabetes Spectr
Teresa Martin, R. Keith Campbell Vitamin D and Diabetes. Diabetes Spectr 1 May 2011 24 : 113118.
Renewed interest in vitamin D, the so-called sunshine vitamin, has occurred recently because it has been linked to everything from cancer and heart disease to diabetes. Research studies continue to pour into the literature stating that vitamin D is a superstar when it comes to health. However, most of the research is based on observational, epidemiological studies, which are important for generating hypotheses but do not prove causality.
A PubMed search in 2011 using the term vitamin D and selecting articles published in the past 2 years resulted in more than 2,864 hits. The following diseases and conditions have been researched to assess their relationship with vitamin D status: osteomalacia/osteoporosis, muscle function and falls, cancer, multiple sclerosis, hypertension, type 1 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, tuberculosis,, mental health, cardiovascular events,, infection,, seasonal affective disorder, obesity, aging, and overall mortality.
Vitamin D And Inflammation
During the exposure to sunlight, ultraviolet B photons penetrate into the skin and are absorbed by 7-dehydrocholesterol inducing the formation of previtamin D . This is an unstable form of vitamin D that rapidly undergoes rearrangement to form vitamin D3 . Vitamin D2 is the form of vitamin D that occurs in plants and is used to fortify certain foods, such as fluid milk. Both vitamin D forms eventually enter the circulation bound to a vitamin D binding protein and are metabolized in the liver by the vitamin D-25-hydroxylase enzyme to 25-hydroxyvitamin D , the main vitamin D form circulating in plasma and a substrate for production of the hormonally active metabolite 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D, 1,252D3 .
Don’t Miss: Ginger For Diabetes Type 2
Randomized Controlled Trials In Relation To Type 1 Diabetes
There are no trials that have reported the effect of vitamin D2 or D3 supplementation on prevention or treatment of type 1 diabetes. In a pilot, open-label trial in 70 children, mean age of 14 years, with recent-onset type 1 diabetes, calcitriol had a modest favorable effect on residual pancreatic beta-cell function however, the reduction in hemoglobin A1c concentration after 1 year was not statistically significant .
Vitamin D Analog Does Not Affect Incidence Rates Of Type 2 Diabetes In Adults
Disclosures: We were unable to process your request. Please try again later. If you continue to have this issue please contact .
Eldecalcitol, a vitamin D analog, is not associated with a reduced incidence of type 2 diabetes among adults with prediabetes, though it may have a beneficial effect in those with lower insulin secretion, according to study data.
Tetsuya Kawahara
We were surprised at the findings because our pilot study showed eldecalcitols preventive effect on the development of type 2 diabetes,Tetsuya Kawahara, MD, PhD, of the University of Occupational and Environment Health and Shin Komonji Hospital in Kitakyushu, Japan, told Healio. We think that these findings are a result of lack of statistical power, an unbalanced distribution of 2-hour plasma glucose concentrations between participants in the eldecalcitol and placebo groups, or both. Treatment with eldecalcitol was effective in increasing bone mineral densities and serum osteocalcin concentrations.
The findings were published in The BMJ.
During the follow-up period, 79 adults in the eldecalcitol group and 89 in the placebo group developed diabetes. There was no significant difference in diabetes incidence between the two groups. There was also no difference in the percentage of participants achieving normoglycemia.
Eldecalcitol lowers diabetes risk in adults with low insulin secretion
Larger intervention studies needed
Reference:
Read Also: What Do You Do If You Think You Have Diabetes
People With Dark Skin
The darker your skin, the more protected your skin is from ultraviolet rays. This means it will take more sun exposure for a person with darker skin to synthesize vitamin D from sunlight. Fortunately, research has shown that people with darker skin still have lower rates of bone fractures and osteoporosis compared to the Caucasian population.
Vitamin D And Risk Of Type 2 Diabetes
Supplements had no clinically meaningful effect in the latest trial
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is a public health disaster it affects approximately 480 million people worldwide, predicted to increase to 700 million by 2045.1 Another half a billion people have impaired glucose tolerance,2 an intermediate stage in T2DM development but amenable to interventions that halt disease progression and lead to remission.3
Weight loss and exercise decrease risk of progression to T2DM in people with impaired glucose tolerance.4567 However, lifestyle interventions are difficult to sustain.8 The possibility that a vitamin might prevent T2DM development is attractive to both healthcare professionals and patients. Interest in vitamin D is based on epidemiological evidence showing an association between low vitamin D status and increased risk for T2DM.9
A link is also biologically plausible: pancreatic cells have vitamin D receptors, and animal studies show improved production of and sensitivity to insulin associated with vitamin D treatment1011 also, vitamin D has immunomodulatory effects and may modify risk of T2DM by suppressing inflammation, a known risk factor.12 Until recently, however, scant evidence has been available from interventional studies.
Don’t Miss: How To Control Pre Diabetic Condition
Conclusions And Future Directions
An inverse association between vitamin D status and both types of diabetes is suggested by observational studies. However, the lack of large prospective observational studies that have measured 25D as the exposure variable prior to ascertainment of the outcome and the lack of randomized trials specifically designed to test the effects of vitamin D on diabetes limits drawing any definitive conclusions. To better define the clinical role of vitamin D as a potential intervention for prevention and management of diabetes, high quality observational studies that measure 25D as the exposure variable and randomized controlled trials specifically designed to test such an hypothesis are needed.
Were The Studys Results Truly Significant
Despite the hopeful results, some diabetes experts are skeptical of this recent researchs claim that noticeable changes in insulin sensitivity and insulin production were demonstrated.
This seems to me to be a rather fuzzy result, Gretchen Becker, medical journalist and author of The First Year: Type 2 Diabetes, told Healthline.
There are so many studies showing that Factor X or Factor Y or Food A or Food B improves insulin sensitivity that Ive stopped paying attention to them, said Becker.
Becker also points to a study reported on by Healthline warning of the dangers of consuming too much vitamin D.
And yes, vitamin D helps your body take up calcium, but too much calcium is not good either.
Smith agrees.
Caution should be taken with vitamin D dosages, for people with or without diabetes, said Smith. The standard dosage is 400 IUs per day, but for those with diabetes, the current recommended safe daily dose to maintain optimal vitamin D levels is 1,000 to 2,000 IUs per day.
For patients whose bloodwork reveals a vitamin D deficiency, Smith said larger doses 4,000 daily or 50,000 IUs weekly can be taken for short periods of time to adequately improve vitamin D levels.
Taking high doses of vitamin D for long periods of time can lead to some troubling side effects, especially higher levels of calcium in the blood, explained Smith.
Recommended Reading: Diabetes Feeling Hot All The Time
What We Dont Yet Know About The Benefits Of Vitamin D For Diabetes
Yet more research is still needed in this area. Importantly, the American Diabetes Association notes that theres insufficient evidence to recommend the routine use of vitamin D to improve blood sugar control in people who have diabetes, and not all research suggests that vitamin D is useful when it comes to preventing diabetes. For example, a study published in June 2019 in The New England Journal of Medicine looked at close to 2,500 people at risk for type 2 diabetes who either received vitamin D supplementation of 4,000 international units or received a placebo. After two years, the people receiving the supplements did not have a significantly lower risk of diabetes than people receiving the placebo.
Its important to review the scientific evidence with a critical lens, says Devje. Much of the research has focused on observational and epidemiological studies, which illustrate an association between vitamin D and diabetes, and do not prove causality.
RELATED: What Vitamin D Can and Cant Do for Your Health