Early Signs Of Diabetes You Must Know
Home » Type 2 Diabetes » 9 Early Signs of Diabetes You Must Know
Diabetes is sneaky.
The early symptoms can go unnoticed for months or years.
In fact, 1 in 3 people with type 2 diabetes dont know they have it.
1 in 3.
Most actually do experience the early signs but dont realise or understand what they are.
Early detection and treatment can have a profound impact on your long-term health. A 3-year delay in diagnosis increases your relative risk of heart disease by 29% .
Therefore by knowing what to look for, you can take control of the situation before it takes control of you.
Contents
What Kind Of Exercise Should Children With Diabetes Do
Exercise is the second major factor in controlling type 2 diabetes, and it is incredibly important for all children suffering from diabetes. Recommendations stand that children with diabetes should try to exercise every day. However, parents should be aware that physical activity lowers blood sugar levels.
It may be necessary for your child to reduce their dose of insulin, as in conjunction with exercise it can significantly lower blood sugar levels and result in hypos. When carrying out physical exercise your child should be near sugar.
Physical activity also governs how much your child can eat.
Children And Teenagers Coping With Diabetes
Living with and managing diabetes every day can be a struggle. Children are commonly concerned about:
- Feeling like they are a burden on the family.
- Being treated differently or delicately, as if they are ‘sick’.
- Coping with constant parental questions about their food intake, how they are feeling and whether or not they have taken their insulin.
- Getting extra attention from parents or others, which may cause jealousy among other siblings.
It’s normal for children or adolescents to feel sad, angry and fed up with their diabetes at times. After all, diabetes is a lifelong condition, so the tasks and skills needed to manage it must be continued over a lifetime. If children struggle with their diabetes management due to feeling depressed, anxious or overwhelmed, it is important to seek help from your diabetes healthcare team. A social worker or psychologist can help. In some cases, the involvement of a psychiatrist may be necessary.
Read Also: How I Reversed My Diabetes
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus In Children
HANNA XU, MD, Cook County Health and Hospitals System, Chicago, Illinois
MICHAEL C. VERRE, MD, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, Illinois
Am Fam Physician. 2018 Nov 1 98:590-594.
The prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents has increased worldwide over the past three decades. This increase has coincided with the obesity epidemic, and minority groups are disproportionately affected. The American Diabetes Association recommends screening for type 2 diabetes beginning at 10 years of age or the onset of puberty in children who are overweight or obese and have two additional risk factors. Diagnostic criteria include a fasting blood glucose level of 126 mg per dL or greater, a two-hour plasma glucose level of 200 mg per dL or greater during an oral glucose tolerance test, an A1C level of 6.5% or more, or a random plasma glucose level of 200 mg per dL or greater plus symptoms of polyuria, polydipsia, or unintentional weight loss. Management should be focused on a multidisciplinary, family-centered approach. Nutrition and exercise counseling should be started at the time of diagnosis and as a part of ongoing management. Metformin is the first-line therapy in conjunction with lifestyle changes. Insulin therapy should be initiated if there are signs of ketosis or ketoacidosis, or if the patient has significant hyperglycemia .
WHAT IS NEW ON THIS TOPIC
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
Excessive Thirst Is One Of The Classic Early Signs Of Diabetes

Drinking unusually large amounts of fluids throughout the day and even overnight is a glaring symptom.
Intake can be something like 4 litres or more per day. You can even start to feel thirsty immediately after youve just had a drink.
The more you drink, the more you urinate, which feeds back into the excessive urination cycle.
Why does this happen?: This is the bodys response to increased urination. With all that extra fluid loss, you become very dry and thirsty.
Don’t Miss: Diabetic Meal Plan To Gain Weight
Symptoms Of Type 1 Diabetes Onset In Adults
When an adult is diagnosed with diabetes, they are often mistakenly told that they have type 2 diabetes. This is because there may be a lack of understanding by some doctors that type 1 diabetes can start at any age, and in people of every race, shape and size. People with type 1 diabetes who have elevated blood glucose and classic risk factors for type 2 diabetes, such as being overweight or physically inactive, are often misdiagnosed. It can also be tricky because some adults with new-onset type 1 diabetes are not sick at first. Their doctor finds an elevated blood sugar level at a routine visit and starts them on diet, exercise and an oral medication.
Who Gets Juvenile Diabetes
About 23 million people in the United States have been diagnosed with diabetes, and 5% to 10% of those cases are juvenile . That works out to about one in 250 people of those, about three-quarters are diagnosed with juvenile diabetes during childhood or young adulthood.
The most common age for a juvenile diabetes diagnosis is between 10 and 16, possibly because puberty triggers an increase in hormone production and these hormones, including estrogen and testosterone, can affect blood sugar levels.
Recommended Reading: How Do People Get Type 1 Diabetes
How Is Type 1 Diabetes Diagnosed
To confirm a diagnosis, your childs doctor may order some or all of the following blood and urine tests:
- hemoglobin A1C test: a blood test that indicates your childs average blood sugar level for the past two to three months
- random blood sugar test: a blood sample taken at a random time
- fasting blood sugar test:a blood sample taken after an overnight fast
- To help distinguish between type 1 and type 2 diabetes, your childs doctor may also check for autoantibodies in the bloodthat are common in type 1 diabetes.
- ketones test: a test that measures ketones, byproducts from the breakdown of fat in children without enough insulin in the urine or blood
Your child may need to have blood drawn more than once so the test results can be confirmed with a second test on a different day. Distinguishing between type 1 and type 2 diabetes in children can sometimes be difficult, and your child’s doctor may need to do additional testing or monitor your child for some time before the type of diabetes can be confirmed.
Diabetes In Toddlers: Causes Signs And Treatment
Diabetes is a chronic condition that can appear at any age, even in the first year of a childâs life. Sometimes, the diagnosis is delayed in babies and young children because diabetes symptoms are similar to those of other illnesses. The most common signs of diabetes in toddlers include an increase in thirst and more frequent or increased urination. Read on to find out more about the signs of diabetes and how diabetes is diagnosed, as well as what treatments may be available, and what you can do day-to-day to manage diabetes in your toddler.
You May Like: Are Ketones Safe For Diabetics
Why Choose Children’s Colorado For Your Child’s Diabetes Treatment
At Children’s Colorado, your child has access to the experts they need, all in one place.
Children and teens with type 1 diabetes receive care by a dedicated diabetes team. Pediatric diabetes experts provide holistic, family-centered care for children with diabetes.
The care teams at the diabetes centers include board-certified pediatric endocrinologists, physician assistants, nurse practitioners and certified diabetes educators in nutrition, nursing and family counseling. This multidisciplinary team can devise plans to manage your child’s diabetes, which may include dietary changes, exercise and medicine.
Get Your Child Involved
One of the best things you can do for your child is to have them take part in managing their condition. The more they do, the more confident theyâll be.
Use your best judgment for what you think your child can handle. Even as they take on more responsibilities, keep an eye on things and give support when needed.
At ages 3-7, they can:
- Choose which finger to use to check blood sugar levels.
- Pick where to get the insulin shot.
- Count before taking out the insulin pen or syringe.
At ages 8-11, they may:
- Give themselves insulin while you watch.
- Notice low blood sugar symptoms and treat themselves.
- Learn carb counting and start picking some healthy food choices.
At age 12 and up, they may:
- Check blood sugar and take insulin increasingly on their own.
- Count carbs.
- Set reminders on when to take pills or check levels.
Teen years can bring new challenges. Physical changes during puberty that can make it harder to control blood sugar. Also, weight and body image issues may start to show up. Watch your child for emotional issues, like depression and anxiety, and look out for eating disorders, too. If you have concerns, talk to their doctor. You may want to consider therapy.
Don’t Miss: What’s New In Diabetes Treatment
What To Look For: Symptoms Of Pediatric Diabetes In Babies And Toddlers
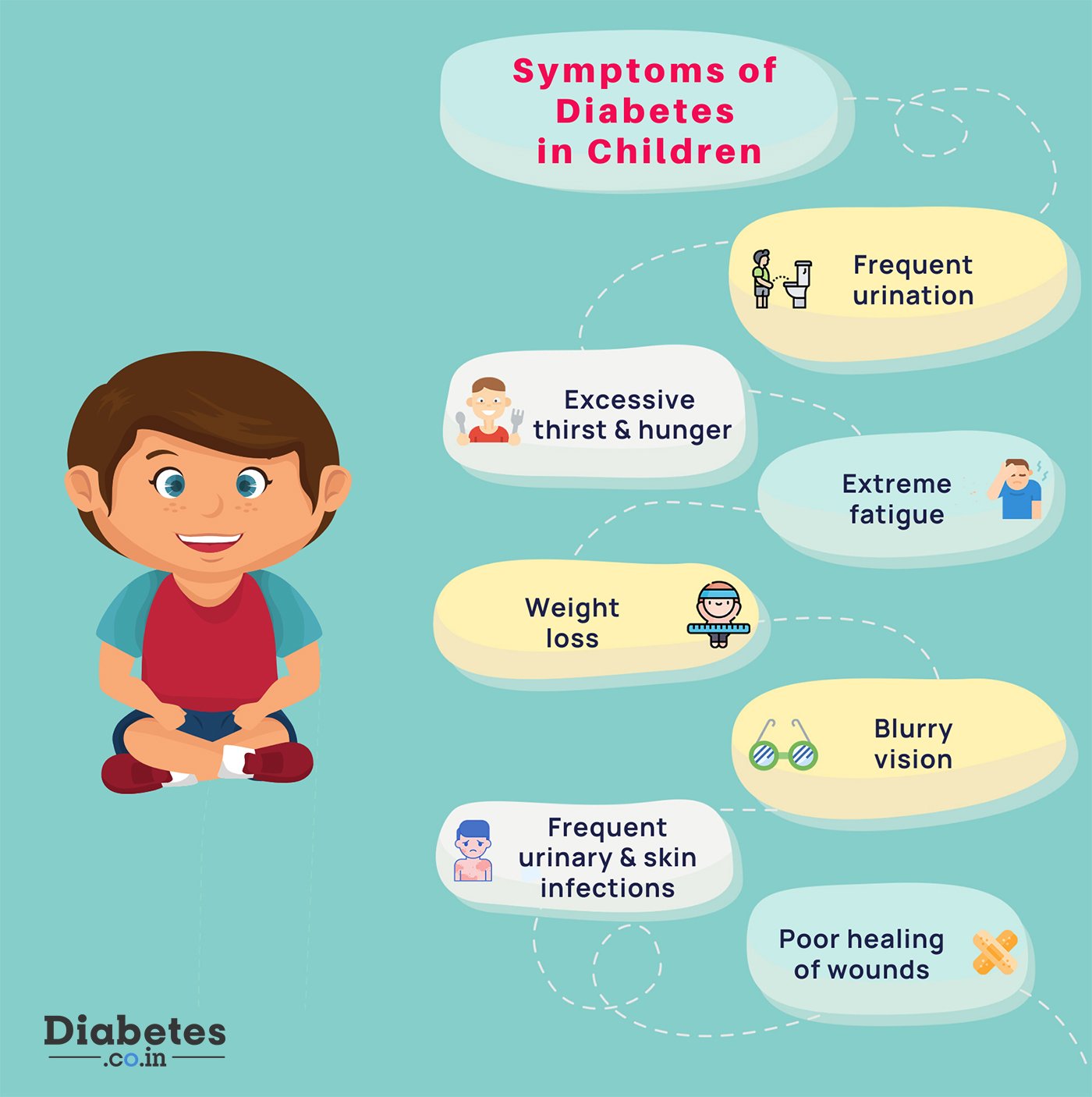
You may or may not be aware that increased thirst and frequent urination are common symptoms of type 1 diabetes in toddlers and other young children. The reason this happens is rising blood-sugar levels trigger a reaction in the body that pulls fluid from tissues. This will leave your son or daughter constantlyand understandablythirsty, which leads to increased urination. If your toddler is potty-trained you may also notice that they revert back or have bed-wetting issues.
But what else should you watch out for? Below are some other potential signs of pediatric diabetes:
Fatigue: This could be a sign that your childs body isnt able to turn the sugar in the bloodstream into energy.
Intense hunger and unexplained weight loss: If your kids muscles and organs arent receiving enough energy, it can trigger extreme hunger. And sudden weight lossespecially if he or she is eating morecould also be a major warning sign.
Changes in vision: High blood-glucose levels could lead to blurred vision or other eyesight issues. Unfortunately at a very young age, your son or daughter may not yet be able to articulate this.
Yeast infection: This type of infection can be one of the signs of diabetes in babiesbut it may present itself as a diaper rash caused by excessive yeast.
Fruity smelling breath or sugar in urine: This is a sign that your kids body is attempting to excrete sugar that it cant get into its cells.
Diagnosing Diabetes In Very Young Children
When a sick infant or toddler presents to their primary care physician, type I diabetes is generally not high on the list of possible diagnoses, given the relatively low incidence of the disease in this age group. Furthermore, the classical symptoms of polyuria and nocturia, polydipsia, polyphagia, and weight loss are often overlooked or ascribed to other causes until the disorder has progressed to frank diabetic ketoacidosis . Even then the diagnosis may not be made immediately, and other serous illnesses such as bronchiolitis or asthma , or meningitis or septicemia may be considered first. The presence of a candida diaper dermatitis may provide a significant tip-off of the presence of glycosuria.
Of note is that some young children who are given large volumes of fruit juice and other concentrated carbohydrate-containing fluids in response to the polydipsia may present with severe degrees of hyperglycemia and hyperosmolality . Extreme caution should be exercised in correcting the DKA and hyperosmolar state to prevent a rapid drop in serum osmolality and possible intracranial fluid shifts .
You May Like: Simple Diabetic Diet Meal Plan
Tests For Juvenile Diabetes
The first step in getting a diabetes diagnosis is a blood test to look for elevated glucose levels. If your child is diagnosed with high blood sugar, then the doctor will want to perform additional tests to identify the specific type of diabetes. Correct diagnosis is very important since treatment is different for each type. Your child may need one or more of the below:
When To Move Your Child To Diabetes Self
Moving from adolescent diabetes healthcare to an adult setting usually occurs around the age of 16-18 years, although the process is an ongoing one that should begin soon after diagnosis.
Some children may be transitioned to a Young Adults with Diabetes clinic staffed by paediatric specialists.
Once they are 18 or 19 years old, they will continue to attend their YADS clinic, but an adult diabetes specialist will take over their care. You and your child can prepare for this move by discussing it with your healthcare team.
The National Diabetes Services Scheme resource Moving on up transitioning to adult health care services provides further information about this transition.
It is important parents and carers use the transition process to encourage children to take a more proactive role in their diabetes care. Children can begin to schedule their appointments and be asked to think of things to discuss when they meet with their diabetes team.
It is also a good time to leave the room for part of your child’s appointment. This will allow your child to raise any issues they may not feel comfortable discussing with you in the room.
You May Like: Type 2 Diabetes When To Take Insulin
The Symptoms Of Diabetes In Children
As parents may not mention these symptoms a doctor must carefully draw out this information. Also, bedding wetting in a previously dry child can be one of the first symptoms in 89% of children over the age of 4 years. Recurrent infections can also be a presentation. Oral or genital thrush can be present.
If diabetic ketoacidosis has already occurred, the symptoms can include vomiting and abdominal pain deep sighing breathing called Kussmaul breathing and reduced levels of consciousness. All these symptoms can be misdiagnosed as acute asthma/pneumonia or possible gastroenteritis/appendicitis if the doctor is not aware of polyuria and polydipsia.
Teenagers With Diabetes And Driving
People with diabetes can hold a driver’s licence or learner’s permit as long as their diabetes is well managed, and they undertake certain diabetes self-management tasks before and during each trip.
A medical report must be provided before a driver’s licence or learners permit can be issued and two-yearly thereafter. This report should come from the persons treating doctor or diabetes specialist.The main concern of the licensing authorities is the possibility of hypoglycaemia occurring while driving. More information is available from VicRoads and the Diabetes Victoria page Driving and diabetes.
Read Also: Symptoms Of Low Blood Sugar In Type 2 Diabetes
Outbreak Of Small Reddish
When these bumps appear, they often look like pimples. Unlike pimples, they soon develop a yellowish color. Youll usually find these bumps on the buttocks, thighs, crooks of the elbows, or backs of the knees. They can form anywhere though.
Eruptive-xanthomatosis
These bumps appear suddenly and clear promptly when diabetes is well-controlled.
When these bumps appear, they often look like pimples. Unlike pimples, they soon develop a yellowish color. Youll usually find these bumps on the buttocks, thighs, crooks of the elbows, or backs of the knees. They can form anywhere though. No matter where they form, they are usually tender and itchy. The medical name for this skin condition is eruptive xanthomatosis.
Take action
- Tell your doctor about the bumps because this skin condition appears when you have uncontrolled diabetes.
- Talk with your doctor about how to better control your diabetes.
Yellow Reddish Or Brown Patches On Your Skin
Necrobiosis Lipoidica
This skin condition often begins as small raised solid bumps that look like pimples. As it progresses, these bumps turn into patches of swollen and hard skin. The patches can be yellow, reddish, or brown.
You may also notice:
- The surrounding skin has a shiny porcelain-like appearance
- You can see blood vessels
- The skin is itchy and painful
- The skin disease goes through cycles where it is active, inactive, and then active again
necrobiosis lipodica.
Take action
- Get tested for diabetes, if you have not been diagnosed.
- Work with your doctor to better control your diabetes.
- See a dermatologist about your skin. Necorbiosis lipodica is harmless, but it can lead to complications.
Don’t Miss: Type 1 Diabetes Require Insulin
Whats The Difference Between Signs Vs Symptoms Of Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes symptoms are experienced by a person with diabetes, but signs of type 1 diabetes can also be noted by friends and family even if the person who is having the symptoms may not notice them or may be unable to communicate because they are in the throes of diabetic ketoacidosis. Common signs of T1D to watch out for include:
- Weight loss, despite eating more
- Changes to menstruation
- Rapid heart rate
- Reduced blood pressure
- Low body temperature
- Acting or seeming drunk while sober, which is a sign of diabetic ketoacidosis
- Breath that is fruity or smells like nail polish remover which is another sign of ketosis
- Chronic skin infections
Managing Diabetes In Young Children

Your child will need insulin several times a day. This is given by injection or with an insulin pen. Another option is an insulin pump, a small device which is worn 24 hours a day and delivers insulin to the body through a plastic tube. A pump is not suitable for every child, so discuss this with your doctor. You may be eligible for a subsidy from the Australian Government to buy a pump. Visit the JDRF website for more information.
You will need to monitor your childs blood glucose levels regularly, up to 6 times throughout the day and night. You do this by testing a drop of your childs blood in a special testing kit. The aim is to keep the levels within a target range set by your doctor.
To keep blood glucose levels within the right range, you will need to carefully balance the food your child eats with the amount of physical activity they do and their insulin.
If their blood glucose levels fall too low, your child could develop hypoglycaemia, or if they are too high they could develop hyperglycaemia, which could lead to an even more serious condition known as ketoacidosis. Both of these conditions are medical emergencies and you will need to learn how to recognise and manage them.
You will also need to keep your child healthy by following an eating plan and making sure they get plenty of physical activity.
Don’t Miss: Diabetes Leading To Kidney Disease