Complications Of Type 2 Diabetes Treatment
Medications for type 2 diabetes, like most other medications, can cause side-effects in some people. You can find out more about diabetes medications and their side-effects from our separate leaflet called Type 2 Diabetes Treatment.
However, one important side-effect which can affect people taking insulin and/or certain diabetes tablets is hypoglycaemia . This occurs when the level of glucose becomes too low, usually under 4 mmol/L. Not all tablet medicines used for diabetes can cause a hypo – for example, metformin does not cause this.
A hypo may occur if you have too much diabetes medication, have delayed or missed a meal or snack, or have taken part in unplanned exercise or physical activity. You can find out more about the symptoms and treatments of hypos from our separate leaflet called Hypoglycaemia .
Until about 20 years ago, the medication options for treatment of type 2 diabetes were fairly limited. Insulin, along with a group of medicines called the sulfonylureas, can cause hypos . In the last 20 years, as newer medication has been developed, many people do not need to take sulfonylureas. In fact, more and more people never need to take insulin as newer agents offer more options for type 2 diabetes treatment.
Note: hypoglycaemia cannot occur if you are treated with diet alone.
Assessment Of Vital Signs
Baseline and continuing measurement of vital signs is an important part of diabetes management. In addition to vital signs, measure height, weight, and waist and hip circumferences.
In many cases, blood pressure measurement will disclose hypertension, which is particularly common in patients with diabetes. Patients with established diabetes and autonomic neuropathy may have orthostatic hypotension. Orthostatic vital signs may be useful in assessing volume status and in suggesting the presence of an autonomic neuropathy.
If the respiratory rate and pattern suggest Kussmaul respiration, diabetic ketoacidosis must be considered immediately, and appropriate tests ordered. DKA is more typical of type 1 diabetes, but it can occur in type 2.
Type 2 Diabetes In Older Adults
Your risk of type 2 diabetes goes up as you age because your body can become resistant to insulin and your pancreas might not work as well as it used to.
Diabetes is more likely to cause complications in people 65 and older, especially heart attacks, eye problems, loss of a leg , and kidney disease.
You May Like: What Problems Can Diabetes Cause
Differentiation Of Type 2 From Type 1 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be differentiated from type 1 diabetes mellitus on the basis of history and physical examination findings and simple laboratory tests . Patients with type 2 diabetes are generally obese, and may have acanthosis nigricans and/or hirsutism in conjunction with thick necks and chubby cheeks.
References
Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2010 Jan. 33 Suppl 1:S62-9. . .
American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes–2012. Diabetes Care. 2012 Jan. 35 Suppl 1:S11-63. .
U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Adults. Available at .
Tucker ME. Diabetes Care 2022: Screen More, Personalize, Use Technology. Medscape Medical News. 2021 Dec 20. .
American Diabetes Association. Introduction: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care. 2022 Jan 1. 45 :S1-S2. . .
Keller DM. New EASD/ADA Position Paper Shifts Diabetes Treatment Goals. Medscape Medical News. Available at . Accessed: October 15, 2012.
Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, Diamant M, Ferrannini E, Nauck M, et al. Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes: a patient-centered approach. Position statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes . Diabetologia. 2012 Jun. 55:1577-96. .
Managing Blood Glucose Levels
Maintain blood glucose levels within the recommended range. You can help keep your blood glucose levels as near as possible to normal by:
- eating healthily
- achieving and maintaining a healthy weight
- doing regular physical activity, including sitting less.
Glucose-lowering medications, and insulin, may also be needed to manage blood glucose levels. If you are taking diabetes tablets or insulin, the recommended blood glucose levels are 68 mmol/L before meals, and 610mmol/L two hours after meals. Blood glucose targets are individualised. Check with your doctor or diabetes educator about the targets recommended for you.
Keeping your blood glucose levels within the target range can help prevent long-term problems that can affect your heart, blood vessels, eyes, kidneys and nerves.
Read Also: What Is Worse Diabetes 1 Or Diabetes 2
Itching And Yeast Infections
Excess sugar in the blood and urine provides food for yeast, which can lead to infection. Yeast infections tend to occur on warm, moist areas of the skin, such as the mouth, genital areas, and armpits.
The affected areas are usually itchy, but a person may also experience burning, redness, and soreness.
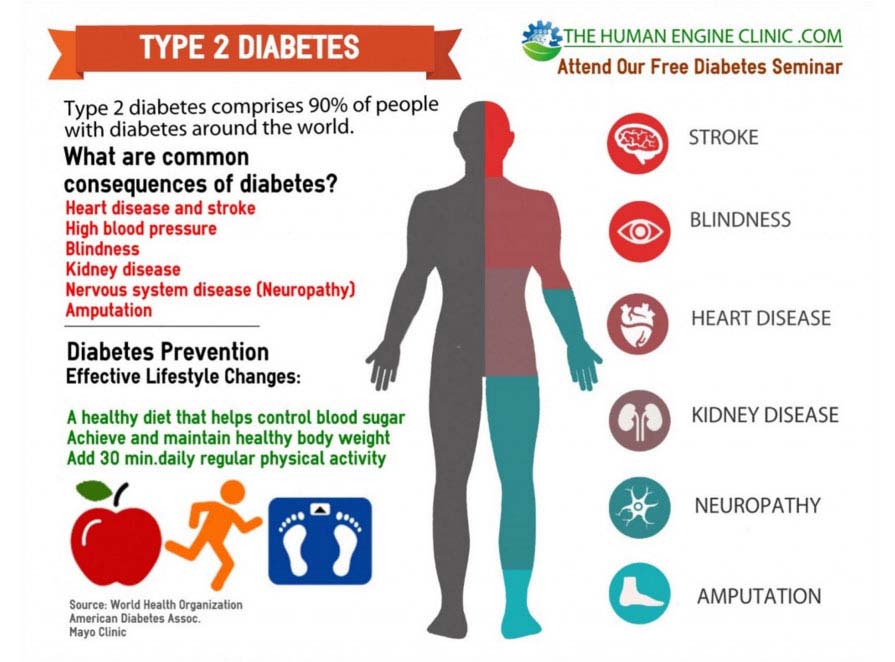
Complications Of Type 2 Diabetes
Itâs important to get your blood sugar under control to avoid these serious conditions:
- Hypoglycemia. If your blood sugar falls below 70 milligrams per deciliter , it can lead to accidents, coma, and death.
- Hyperglycemia. Blood sugar that goes above 180 to 200 mg/dL can give you heart, nerve, kidney, and vision problems. Over the long term, it also can cause coma and death.
Over time, people with type 2 diabetes may have other health problems:
- Diabetic ketoacidosis. When you donât have enough insulin in your system, your blood sugar rises, and your body breaks down fat for energy. Toxic acids called ketones build up and spill into your urine. It can cause coma and death if you donât treat it.
- Heartand blood vessel diseases. People with diabetes are more likely to have conditions like high blood pressure and high cholesterol, which play a role in heart disease. Also, high blood sugar can damage your blood vessels and the nerves that control your heart.
- High blood pressure. Diabetes doubles your risk of high blood pressure, which makes you more likely to have heart disease or stroke.
- Nerve damage . This can cause tingling and numbness, most often in your feet and legs. But it can also affect your digestive system, urinary tract, blood vessels, and heart.
- Eyedamage. Diabetes can cause:
- Glaucoma, a buildup of pressure in your eyes
- Cataracts, a cloudiness of your lens
- Retinopathy, which is damage to the blood vessels in your eyes
Recommended Reading: What’s The Normal Diabetes Level
Type 2 Diabetes Complications
With type 2 diabetes , if you dont work hard to keep your blood glucose level under control, there are short- and long-term complications to contend with. However, by watching the amount and types of food you eat , exercising, and taking any necessary medications, you may be able to prevent these complications.
And even if you have some of the long-term, more serious complications discussed below when youre first diagnosed, getting tight control of your blood glucose will help prevent the complications from becoming worse.
Short-term complications of type 2 diabetes are hypoglycemia and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic nonketotic syndrome , which is very high blood glucose.
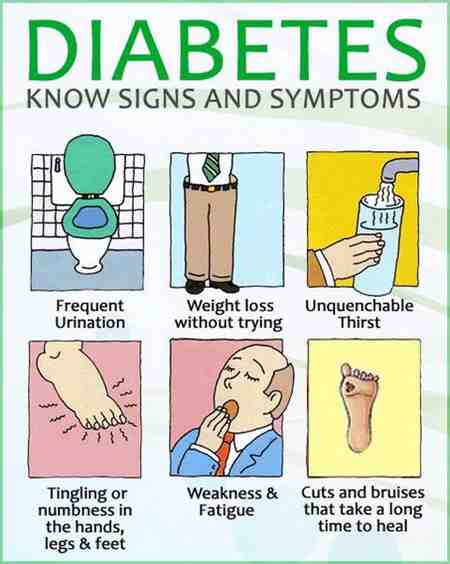
What Are The First Symptoms Of Type 2 Diabetes
Many people with type 2 diabetes do not experience any symptoms at first and it may go undiagnosed for years. If they do have symptoms, these may include:
- being very thirsty
- having cuts that heal slowly
Over time, diabetes can lead to complications, which can then cause other symptoms.
Blood glucose testing is important for detecting pre-diabetes and type 2 diabetes before complications arise.
Read Also: What Is The Best Treatment For Type 2 Diabetes
Can Type 2 Diabetes Be Prevented
You can take steps to help prevent or delay type 2 diabetes by losing weight if you are overweight, eating fewer calories, and being more physically active. If you have a condition which raises your risk for type 2 diabetes, managing that condition may lower your risk of getting type 2 diabetes.
NIH: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
Who Develops Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes used to be known as maturity-onset, or non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Type 2 diabetes develops mainly in people older than the age of 40 . Over 462 million people are living with diabetes in the world, which is estimated to be 1 in 11 of the world’s adult population. It is estimated that by 2030, that figure will have risen to 540 million people. Type 2 diabetes is now becoming far more common in children and in young people.
The number of people with type 2 diabetes is increasing in the UK, as it is more common in people who are overweight or obese. It also tends to run in families. Type 2 diabetes is around five times more common in South Asian and African-Caribbean people . It is estimated that there are around 750,000 people in the UK with type 2 diabetes who have not yet been diagnosed with the condition.
You May Like: Type 1 Diabetes Emergency Kit
Increase In Frequency Of Urination
The kidneys help process and filter glucose, with much of it normally being reabsorbed into the body. However, when blood glucose gets very high, it can be too demanding for the kidneys to process, causing glucose to spill over into the urine and be excreted from the body.
If you notice you or your child are urinating more than is normal for you, it is worth investigating, especially if other early signs of diabetes accompany it.
For children, sometimes this can present as nighttime bedwetting and having accidents after they have been potty trained and normally stay dry at night. In adults, you might not notice the increased frequency at first, but be aware if it leads to waking at night to urinate.
Pa And Prevention Of Type 2 Diabetes
Participation in regular PA improves BG control and can prevent or delay onset of type 2 diabetes . Prospective cohort and cross-sectional observational studies that assessed PA with questionnaires showed that higher PA levels are associated with reduced risk for type 2 diabetes, regardless of method of activity assessment, ranges of activity categories, and statistical methods . Both moderate walking and vigorous activity have been associated with a decreased risk, and greater volumes of PA may provide the most prevention . Observational studies have reported that greater fitness is associated with a reduced risk of developing type 2 diabetes , even if only moderate-intensity exercise is undertaken.
Data show that moderate exercise such as brisk walking reduces risk of type 2 diabetes , and all studies support the current recommendation of 2.5 h/week of a moderate aerobic activity or typically 30 min/day for 5 days/week for prevention. A meta-analysis of 10 cohort studies that assessed the preventive effects of moderate-intensity PA found that risk reduction for type 2 diabetes was 0.70 for walking on a regular basis . The preventive effects of resistance training have not been studied.
Evidence statement.
At least 2.5 h/week of moderate to vigorous PA should be undertaken as part of lifestyle changes to prevent type 2 diabetes onset in high-risk adults. ACSM evidence category A. ADA A level recommendation.
Recommended Reading: Why Do Diabetics Legs Swell
What Health Problems Can People With Diabetes Develop
Following a good diabetes care plan can help protect against many diabetes-related health problems. However, if not managed, diabetes can lead to problems such as
- heart disease and stroke
- gum disease and other dental problems
- sexual and bladder problems
Many people with type 2 diabetes also have nonalcoholic fatty liver disease . Losing weight if you are overweight or obese can improve NAFLD. Diabetes is also linked to other health problems such as sleep apnea, depression, some types of cancer, and dementia.
You can take steps to lower your chances of developing these diabetes-related health problems.
About Type 2 Diabetes
Diabetes is usually a lifelong condition that causes a person’s blood glucose level to become too high.
The hormone insulin produced by the pancreas is responsible for controlling the amount of glucose in the blood
There are two main types of diabetes:
- type 1 where the pancreas doesn’t produce any insulin
- type 2 where the pancreas doesn’t produce enough insulin or the body’s cells don’t react to insulin
This topic is about type 2 diabetes.
Read more about type 1 diabetes
Another type of diabetes, known as gestational diabetes, occurs in some pregnant women and tends to disappear after birth.
Also Check: How Does Diabetes Affect Your Feet
Exercise With Nonoptimal Bg Control
Hyperglycemia.
While hyperglycemia can be worsened by exercise in type 1 diabetic individuals who are insulin deficient and ketotic , very few persons with type 2 diabetes develop such a profound degree of insulin deficiency. Therefore, individuals with type 2 diabetes generally do not need to postpone exercise because of high BG, provided that they are feeling well. If they undertake strenuous physical activities with elevated glucose levels , it is prudent to ensure that they are adequately hydrated . If hyperglycemic after a meal, individuals with type 2 diabetes will still likely experience a reduction in BG during aerobic work because endogenous insulin levels will likely be higher at that time .
Evidence statement.
Individuals with type 2 diabetes may engage in PA, using caution when exercising with BG levels exceeding 300 mg/dl without ketosis, provided they are feeling well and are adequately hydrated. ACSM evidence category C. ADA E level recommendation.
Hypoglycemia: causes and prevention.
Evidence statement.
Persons with type 2 diabetes not using insulin or insulin secretagogues are unlikely to experience hypoglycemia related to PA. Users of insulin and insulin secretagogues are advised to supplement with carbohydrate as needed to prevent hypoglycemia during and after exercise. ACSM evidence category C. ADA C level recommendation.
Symptoms Of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes symptoms often take several years to develop. Some people dont notice any symptoms at all. Type 2 diabetes usually starts when youre an adult, though more and more children and teens are developing it. Because symptoms are hard to spot, its important to know the risk factors for type 2 diabetes. Make sure to visit your doctor if you have any of them.
Don’t Miss: Nature Made Diabetes Health Pack Side Effects
Medication Effects On Exercise Responses
Current treatment strategies promote combination therapies to address the three major defects in type 2 diabetes: impaired peripheral glucose uptake , excessive hepatic glucose release , and insufficient insulin secretion. Medication adjustments for PA are generally necessary only with use of insulin and other insulin secretagogues . To prevent hypoglycemia, individuals may need to reduce their oral medications or insulin dosing before exercise . Before planned exercise, short-acting insulin doses will likely have to be reduced to prevent hypoglycemia. Newer, synthetic, rapid-acting insulin analogs induce more rapid decreases in BG than regular human insulin. Individuals will need to monitor BG levels before, occasionally during, and after exercise and compensate with appropriate dietary and/or medication regimen changes, particularly when exercising at insulin peak times. If only longer-acting insulins such as glargine, detemir, and NPH are being absorbed from subcutaneous depots during PA, exercise-induced hypoglycemia is not as likely , although doses may need to be reduced to accommodate regular participation in PA. Doses of select oral hypoglycemic agents may also need to be lowered in response to regular exercise training if the frequency of hypoglycemia increases .
Evidence statement.
Healthy Eating For Type 2 Diabetes
A dietitian or your doctor will be able to advise you on what to eat to meet your nutritional needs and control your blood sugar. Your doctor should be able to refer you to a registered dietitian for personalised advice.
Eating healthy foods with a low glycaemic index can help to optimise your blood sugar levels. This includes wholegrain breads, minimally processed breakfast cereals like rolled or steel cut oats, legumes, fruit, pasta and dairy products.
Avoid high-carbohydrate, low-nutrient foods such as cakes, lollies and soft drinks, and eat a diet low in saturated fat.
You should eat at regular times of the day and may also need snacks. Try to match the amount of food you eat with the amount of activity you do, so that you dont put on weight.
If you are overweight or obese, losing even 5-10 per cent of your body weight can significantly improve blood sugar control.
Read Also: What Are The Best Frozen Meals For Diabetics
What Does Undiagnosed Diabetes Feel Like
I remember feeling really tired and sleepy, but I didnt think anything of it as I was trying to juggle work and caring for my three children. When I got diagnosed, it made me think about my mum and her health. I thought she might have had diabetes too. She always used to feel tired and she had a boil on her leg that never seemed to heal. Read Saritas story in full.
Who Is More Likely To Develop Type 2 Diabetes

You can develop type 2 diabetes at any age, even during childhood. However, type 2 diabetes occurs most often in middle-aged and older people. You are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes if you are age 45 or older, have a family history of diabetes, or are overweight or obese. Diabetes is more common in people who are African American, Hispanic/Latino, American Indian, Asian American, or Pacific Islander.
Physical inactivity and certain health problems such as high blood pressure affect your chances of developing type 2 diabetes. You are also more likely to develop type 2 diabetes if you have prediabetes or had gestational diabetes when you were pregnant. Learn more about risk factors for type 2 diabetes.
Recommended Reading: How Many People In The Us Have Type 1 Diabetes