What Are The Symptoms Of Type 2 Diabetes
Many people with type 2 diabetes have no symptoms at all. If you do have them, the symptoms develop slowly over several years. They might be so mild that you do not notice them. The symptoms can include:
- Increased thirst and urination
- Numbness or tingling in the feet or hands
- Sores that do not heal
- Unexplained weight loss
Major Exogenous Factors That Raise The Blood Glucose
Dietary carbohydrate is the major exogenous factor that raises the blood glucose. When one considers that it is common for an American in 2021 to consume 200300 grams of carbohydrate daily, and most of this carbohydrate is digested and absorbed as glucose, the body absorbs and delivers this glucose via the bloodstream to the cells while attempting to maintain a normal blood glucose level. Thinking of it in this way, if 200300 grams of carbohydrates is consumed in a day, the bloodstream that holds 510 grams of glucose and has a concentration of 100 milligrams/deciliter, is the conduit through which 200,000300,000 milligrams passes over the course of a day.
How Do I Check My Blood Glucose Level Why Is This Important
Checking your blood glucose level is important because the results help guide decisions about what to eat, your physical activity and any needed medication and insulin adjustments or additions.
The most common way to check your blood glucose level is with a blood glucose meter. With this test, you prick the side of your finger, apply the drop of blood to a test strip, insert the strip into the meter and the meter will show your glucose level at that moment in time. Your healthcare provider will tell you how often youll need to check your glucose level.
Don’t Miss: Best Way To Eat For Diabetes
Insulin Is Already Elevated In Ir And T2dm
Clinical experience of most physicians using insulin to treat T2DM over time informs us that an escalation of insulin dose is commonly needed to achieve glycemic control . When more insulin is given to someone with IR, the IR seems to get worse and higher levels of insulin are needed. I have the clinical experience of treating many individuals affected by T2DM and de-prescribing insulin as it is no longer needed after consuming a diet without carbohydrate .
What Are The Complications Of Diabetes
If your blood glucose level remains high over a long period of time, your bodys tissues and organs can be seriously damaged. Some complications can be life-threatening over time.
Complications include:
- Dental problems.
Complications of gestational diabetes:
In the mother:Preeclampsia , risk of gestational diabetes during future pregnancies and risk of diabetes later in life.
In the newborn: Higher-than-normal birth weight, low blood sugar , higher risk of developing Type 2 diabetes over time and death shortly after birth.
Recommended Reading: How Can I Tell I Have Diabetes
Possible Driving Factors Behind Health Disparities
Annals of EpidemiologyPopulation Research and Policy ReviewJournal of General Internal Medicine PLoS MedicineJournal of Racial and Ethnic Health Disparities
Taking the ADAs 60-Second Type 2 Diabetes Risk Test can help you determine whether youre at a higher risk for diabetes based on a number of factors, including your race or ethnicity.
Can Diabetes Kill You
Yes, its possible that if diabetes remains undiagnosed and uncontrolled it can cause devastating harm to your body. Diabetes can cause heart attack, heart failure, stroke, kidney failure and coma. These complications can lead to your death. Cardiovascular disease in particular is the leading cause of death in adults with diabetes.
Also Check: Type 1 Diabetes Emergency Kit
Prognosis In Intensive Therapy
In the UKPDS, more than 5000 patients with type 2 diabetes were followed up for up to 15 years. Those in the intensely treated group had a significantly lower rate of progression of microvascular complications than did patients receiving standard care. Rates of macrovascular disease were not altered except in the metformin-monotherapy arm in obese individuals, in which the risk of myocardial infarction was significantly decreased.
In the 10-year follow-up to the UKPDS, patients in the previously intensively treated group demonstrated a continued reduction in microvascular and all-cause mortality, as well as in cardiovascular events, despite early loss of differences in glycated hemoglobin levels between the intensive-therapy and conventional-therapy groups. The total follow-up was 20 years, half while in the study and half after the study ended.
Other, shorter studies, such as Action in Diabetes and Vascular Disease: Preterax and Diamicron Modified Release Controlled Evaluation and the Veterans Affairs Diabetes Trial , showed no improvement in cardiovascular disease and death with tight control .
A British study indicated that the HbA1c level achieved 3 months after the initial diagnosis of type 2 diabetes mellitus predicts subsequent mortality. In other words, according to the report, aggressive lowering of glucose after diagnosis bodes well for long-term survival.
Checking Your Blood Sugar Levels
Checking your blood sugar levels is an important part of managing your diabetes, so well take you through how to check them and what your readings mean.
And weve also got more information about what happens your blood sugar levels get too low, called a hypo, or too high, called a hyper, so that youre aware of the signs and symptoms to look out for.
You May Like: What Is A Good Diet For Type 2 Diabetes
How Are Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes Diagnosed
The primary test used to diagnose both type 1 and type 2 diabetes is known as the A1C, or glycated hemoglobin, test.
This blood test determines your average blood sugar level for the past 2 to 3 months. Your doctor may draw your blood or give you a small finger prick.
The higher your blood sugar levels have been over the past few months, the higher your A1C level will be. Test results are expressed as a percentage. An A1C level of 6.5 percent or higher indicates diabetes.
The A1C test isnt accurate for people with sickle cell anemia or the sickle cell trait. If you have this condition or trait, then your doctor will have to use a different test.
How Is Type 2 Diabetes Diagnosed
If your doctor suspects you have diabetes, you will probably need to have a blood test to assess your glucose level. It is important for diabetes to be diagnosed early, whether its type 1 or type 2 diabetes. That way, it can be better controlled and complications can be avoided or minimised.
During a test, blood is taken from a vein and sent to a pathology lab. The tests that can be done include:
- a fasting blood glucose test fasting is required for at least 8 hours, which may mean not eating or drinking overnight
- an oral glucose tolerance test after fasting for 8 hours, you have a blood glucose test, then you drink a sugary drink and then have another blood test done 1 and then 2 hours later
- HbA1c this blood test shows your average blood glucose levels over a period of time it does not involve fasting beforehand
Watch the first video below to learn why its important to detect undiagnosed type 2 diabetes. The second video tells you all about the HbA1c test.
Video provided by Lab Tests Online
Read Also: Healthy Breakfast Bars For Diabetics
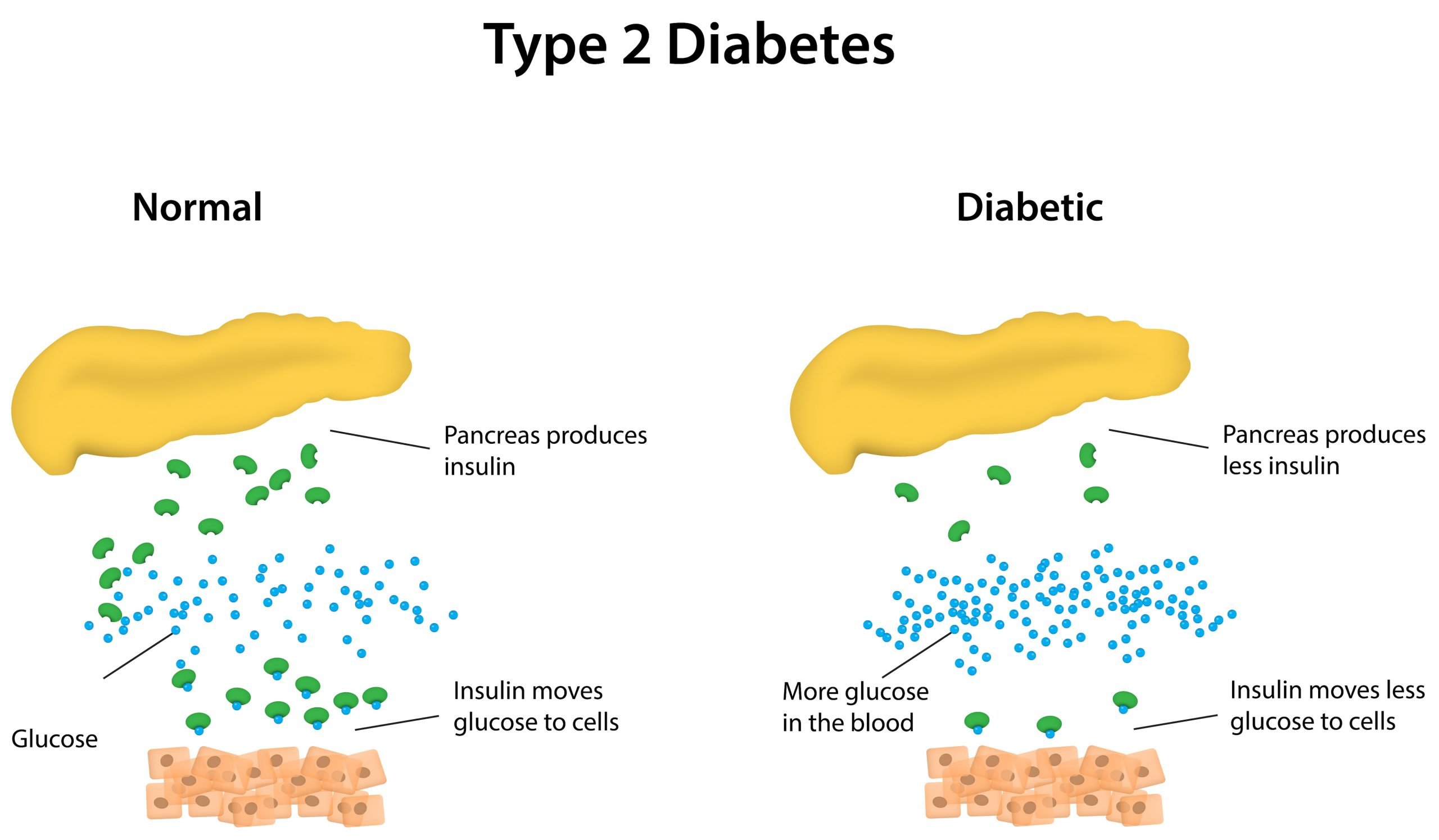
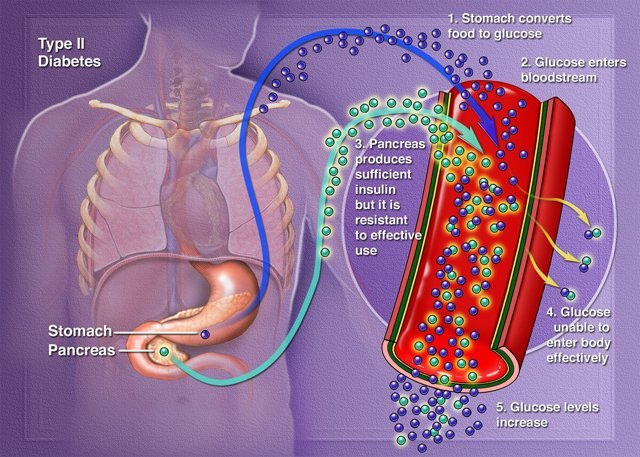
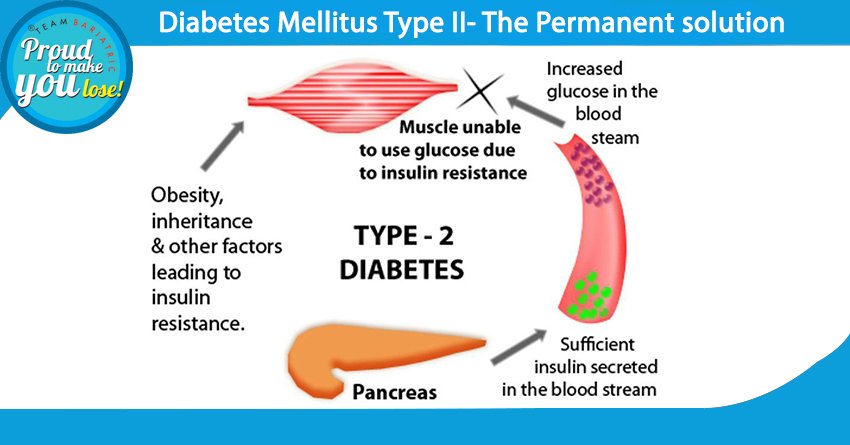
Causes Of Type 2 Diabetes
Your pancreas makes a hormone called insulin. It helps your cells turn glucose, a type of sugar, from the food you eat into energy. People with type 2 diabetes make insulin, but their cells don’t use it as well as they should.
At first, your pancreas makes more insulin to try to get glucose into your cells. But eventually, it can’t keep up, and the glucose builds up in your blood instead.
Usually, a combination of things causes type 2 diabetes. They might include:
What Should I Expect If I Have Been Diagnosed With Diabetes
If you have diabetes, the most important thing you can do is keep your blood glucose level within the target range recommended by your healthcare provider. In general, these targets are:
- Before a meal: between 80 and 130 mg/dL.
- About two hours after the start of a meal: less than 180 mg/dL.
You will need to closely follow a treatment plan, which will likely include following a customized diet plan, exercising 30 minutes five times a week, quitting smoking, limiting alcohol and getting seven to nine hours of sleep a night. Always take your medications and insulin as instructed by your provider.
Don’t Miss: How To Administer Insulin Pen
How Are Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes Treated
Theres no cure for type 1 diabetes. People with type 1 diabetes dont produce insulin, so it must be regularly injected into the body.
Some people take injections into soft tissue, such as the stomach, arm, or buttocks, several times per day. Other people use insulin pumps. Insulin pumps supply a steady amount of insulin into the body through a small tube.
Blood sugar testing is an essential part of managing type 1 diabetes, because levels can go up and down quickly.
Type 2 diabetes can be managed and even reversed with diet and exercise alone, but many people need extra support. If lifestyle changes arent enough, your doctor may prescribe medications that help your body use insulin more effectively.
Monitoring your blood sugar is an essential part of type 2 diabetes management too. Its the only way to know if youre meeting your target levels.
Your doctor may recommend testing your blood sugar occasionally or more frequently. If your blood sugar levels are high, your doctor may recommend insulin injections.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
The diagnosis and management of type 2 diabetes mellitus are with an interprofessional team. These patients need an appropriate referral to the ophthalmologist, nephrologist, cardiologist, and vascular surgeon. Also, patients need to be educated about lifestyle changes that can help lower blood glucose. All obese patients should be encouraged to lose weight, exercise, and eat a healthy diet. The primary care provider and the diabetic nurse must encourage all people with diabetes to stop smoking and abstain from drinking alcohol. The complications of diabetes mellitus are limb and life-threatening and seriously diminish the quality of life.
Don’t Miss: How To Treat Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 Diabetes Risk Factors
Certain things make it more likely that youâll get type 2 diabetes. The more of these that apply to you, the higher your chances of getting it are. Some things are related to who you are:
- Age. 45 or older
- Family. A parent, sister, or brother with diabetes
- Ethnicity. African American, Alaska Native, Native American, Asian American, Hispanic or Latino, or Pacific Islander American
Risk factors related to your health and medical history include:
- Prediabetes
- Sleeping too little or too much
Which Specialties Of Doctors Treat Type 2 Diabetes
Adult and pediatric endocrinologists, specialists in treating hormone imbalances and disorders of the endocrine system, are experts in helping patients with diabetes manage their disease. People with the disease also may seek care from a number of primary care providers including family or internal medicine practitioners, naturopathic doctors, or nurse practitioners. When complications arise, these patients often consult other specialists, including neurologists, gastroenterologists, ophthalmologists, acupuncturists, surgeons, and cardiologists. Nutritionists, integrative and functional medicine doctors, and physical activity experts such as personal trainers are also important members of a diabetes treatment team. It is important to interview new health care professionals about their experience, expertise, and credentials to make sure they are well qualified to help you.
You May Like: How To Care For Someone With Diabetes
When Should I Call My Doctor
If you havent been diagnosed with diabetes, you should see your healthcare provider if you have any symptoms of diabetes. If you already have been diagnosed with diabetes, you should contact your provider if your blood glucose levels are outside of your target range, if current symptoms worsen or if you develop any new symptoms.
Pearls And Other Issues
- T1DM is characterized by the autoimmune destruction of pancreatic beta cells in the majority.
- T2DM is caused due to duel defects in insulin resistance and insulin secretion.
- Gestational diabetes is associated with maternal as well as fetal complications.
- Exercise and a healthy diet are beneficial in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Read Also: Protein Shake For Diabetic Patients
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Pathophysiologic Perspective
- Department of Medicine, Duke University, Durham, NC, United States
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus is characterized by chronically elevated blood glucose and elevated blood insulin . When the blood glucose concentration is 100 milligrams/deciliter the bloodstream of an average adult contains about 510 grams of glucose. Carbohydrate-restricted diets have been used effectively to treat obesity and T2DM for over 100 years, and their effectiveness may simply be due to lowering the dietary contribution to glucose and insulin levels, which then leads to improvements in hyperglycemia and hyperinsulinemia. Treatments for T2DM that lead to improvements in glycemic control and reductions in blood insulin levels are sensible based on this pathophysiologic perspective. In this article, a pathophysiological argument for using carbohydrate restriction to treat T2DM will be made.
When To Call A Professional
If you have diabetes, see your doctor regularly.
People with high blood sugar levels have a higher risk of dehydration. Contact your doctor immediately if you develop vomiting or diarrhea and are not able to drink enough fluids.
Monitor your blood sugar as advised by your health care team. Report any significant deviations in blood sugar levels.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Best Treatment For Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 Diabetes Prevention
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can help you lower your risk of diabetes.
- Lose weight. Dropping just 7% to 10% of your weight can cut your risk of type 2 diabetes in half.
- Get active. Thirty minutes of brisk walking a day will cut your risk by almost a third.
- Eat right. Avoid highly processed carbs, sugary drinks, and trans and saturated fats. Limit red and processed meats.
- Quit smoking. Work with your doctor to keep from gaining weight after you quit, so you don’t create one problem by solving another.
Who Gets Diabetes What Are The Risk Factors
Factors that increase your risk differ depending on the type of diabetes you ultimately develop.
Risk factors for Type 1 diabetes include:
- Having a family history of Type 1 diabetes.
- Injury to the pancreas .
- Presence of autoantibodies .
- Physical stress .
- Exposure to illnesses caused by viruses.
Risk factors for prediabetes and Type 2 diabetes include:
- Family history of prediabetes or Type 2 diabetes.
- Being African-American, Hispanic, Native American, Asian-American race or Pacific Islander.
- Being overweight.
Risk factors for gestational diabetes include:
- Family history of prediabetes or Type 2 diabetes.
- Being African-American, Hispanic, Native American or Asian-American.
- Being overweight before your pregnancy.
- Being over 25 years of age.
Don’t Miss: What Diet Plan Is Best For Type 2 Diabetes
How Is Diabetes Treated
Treatments for diabetes depend on your type of diabetes, how well controlled your blood glucose level is and your other existing health conditions.
- Type 1 diabetes: If you have this type, you must take insulin every day. Your pancreas no longer makes insulin.
- Type 2 diabetes: If you have this type, your treatments can include medications , insulin and lifestyle changes such as losing weight, making healthy food choices and being more physically active.
- Prediabetes: If you have prediabetes, the goal is to keep you from progressing to diabetes. Treatments are focused on treatable risk factors, such as losing weight by eating a healthy diet and exercising . Many of the strategies used to prevent diabetes are the same as those recommended to treat diabetes .
- Gestational diabetes: If you have this type and your glucose level is not too high, your initial treatment might be modifying your diet and getting regular exercise. If the target goal is still not met or your glucose level is very high, your healthcare team may start medication or insulin.
Oral medications and insulin work in one of these ways to treat your diabetes:
- Stimulates your pancreas to make and release more insulin.
- Slows down the release of glucose from your liver .
- Blocks the breakdown of carbohydrates in your stomach or intestines so that your tissues are more sensitive to insulin.
- Helps rid your body of glucose through increased urination.
How Does Diabetes Affect Your Heart Eyes Feet Nerves And Kidneys
Blood vessels are located throughout our bodys tissues and organs. They surround our bodys cells, providing a transfer of oxygen, nutrients and other substances, using blood as the exchange vehicle. In simple terms, diabetes doesnt allow glucose to get into cells and it damages blood vessels in/near these organs and those that nourish nerves. If organs, nerves and tissues cant get the essentials they need to properly function, they can begin to fail.Proper function means that your hearts blood vessels, including arteries, are not damaged . In your kidneys, this means that waste products can be filtered out of your blood. In your eyes, this means that the blood vessels in your retina remain intact. In your feet and nerves, this means that nerves are nourished and that theres blood flow to your feet. Diabetes causes damage that prevents proper function.
You May Like: Type 2 Diabetes Level Range
Can Type 2 Diabetes Be Cured
Type 2 diabetes cannot be cured, but people with the condition may be able to manage their type 2 diabetes through lifestyle changes and, if needed, diabetes medications to control blood sugar levels.
Its also emerging that some people who are overweight or obese can put their type 2 diabetes into remission by losing a substantial amount of weight, especially early in their diagnosis. Their blood sugar measurements return to healthy levels below the diabetes range. Its not a permanent solution, and diabetes could come back, so it needs to be maintained. However, many people were still in remission 2 years later. This should only be tried under the supervision of your doctor.