Learn More About Treatment Approaches> >
Large studies of people with Type 2 diabetes have shown that only about 30% of people taking two oral medicines have an HbA1c level of less than 7% after three years. Insulin is usually recommended as the initial therapy for diabetes if a persons HbA1c level at diagnosis is greater than 10% or if someones fasting blood glucose level is consistently above 250 mg/dl.
Studies have shown that many doctors wait until someones HbA1c level is higher than 9% to start insulin therapy, which often results in months or years of high blood glucose and an increased risk of developing complications later on. One unfortunate reality is that many busy medical practices are not set up to address the needs of people who take insulin. Starting insulin requires education and easy access to health-care providers who are knowledgeable about insulin therapy, including diabetes nurse educators, pharmacists, and doctors.
Do You Have Insulin Resistance
How do you find out if youre insulin resistant? No one test will tell you, but if you have high blood sugar levels, high triglycerides , high LDL cholesterol, and low HDL cholesterol, your health care provider may determine you have insulin resistance.
Important note: Type 1 diabetes is different its thought to be caused by an autoimmune reaction . People with type 1 diabetes dont make enough insulin and need to take it to survive.
When To Introduce More Complex Insulin Regimens
In some patients, fasting blood glucose concentrations may be quite acceptable and yet HbA1c remains significantly elevated. In this situation, a second dose of insulin is needed, usually given in the morning before breakfast. A small starting dose of medium-acting insulin in the order of 6-12 units would be reasonable.
Other patients who are at the more insulin-deficient end of the type 2 diabetes spectrum may be better starting on a twice-daily insulin regimen. The insulin sparing effects of oral hypoglycaemic drugs would still be present in this situation.
Also Check: Long Acting Insulin Side Effects
Why Insulin Can Become Necessary For A Person With Type 2 Diabetes
Starting insulin treatment should not be seen as a setback.
People with type 2 diabetes may require insulin when their meal plan, weight loss, exercise and antidiabetic drugs do not achieve targeted blood glucose levels.
Diabetes is a progressive disease and the body may require insulin injections to compensate for declining insulin production by the pancreas. That is why starting insulin treatment should never be seen as a failure.
Starting insulin treatment should never be seen as a failure.
Treatment with insulin may be added to an antidiabetic medication or completely replace it. Regardless of the treatment, lifestyle habits are essential to managing diabetes.
Many people are reluctant to inject insulin for various reasons:
- Fear of pain or needles
- Guilt
- Impression that this is the last resort
- Fear of hypoglycemic attacks
- Fear of weight gain
- Memories of loved one who had to take insulin
If this is the case, do not hesitate to discuss your concerns with a health care professional. Some of your fears may be due to false beliefs. Learning more about todays insulin treatment will probably allay your fears. For many people, insulin is an effective way to achieve good blood-sugar control, which can prevent or delay certain diabetes complications over the long term.
How To Prevent High Blood Sugar
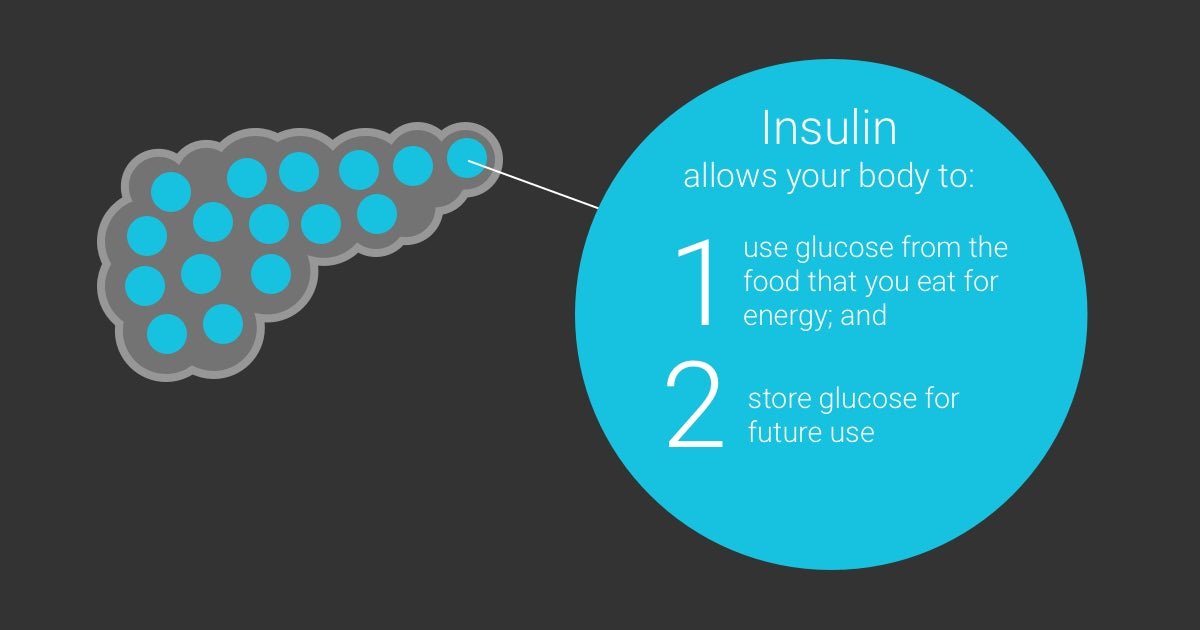
The best way to treat high blood sugar is to prevent it from happening in the first place. Not only does this help to avoid a potential emergency, but it also reduces the likelihood of experiencing diabetic complications. Patients with diabetes can prevent high blood sugar by taking some of the following measures:
Recommended Reading: Why Does Blood Sugar Go Up At Night
Recommended Reading: Non Insulin Injections For Type 2 Diabetes
Other Options For The Initiation Of Insulin Therapy
The recent Treating to Target in type 2 Diabetes study compared the introduction of basal insulin at bedtime to insulin initiation with either biphasic insulin twice daily or prandial insulin before meals . The biphasic and prandial insulin regimens provided better glycemic control than once-daily basal insulin but at the expense of increased risks of hypoglycemia and weight gain. Although biphasic insulin reduced A1C levels to the same extent as prandial insulin, the latter regimen was associated with the most hypoglycemic episodes and the highest weight gain . Therefore, and considering that to date there is no clinical trial evidence supporting the specific lowering of postprandial glucose levels when aiming to lower cardiovascular risk in type 2 diabetes, initiation with prandial insulin is generally not a first-choice approach when starting insulin in type 2 diabetic patients. This was confirmed by a recently reported direct comparison of once-daily insulin glargine versus thrice-daily insulin lispro in insulin-naive patients . Finally, also regarding feasibility in clinical practice and patients’ acceptance, three injections per day is the least attractive option for initiation of insulin therapy.
Ideal Blood Sugar Levels
A range of factors, including insulin resistance, diabetes, and an unbalanced diet, can cause blood sugar levels to spike or plummet.
The standard measurement units for blood sugar levels are milligrams per deciliter . Ideal blood sugar ranges are as follows:
| Timing |
Insulin and glucagon do not take immediate effect, particularly in people whose blood sugar levels are extremely high or low.
Read Also: Best Way To Eat For Diabetes
What Is Different About Insulin Lispro
Insulin lispro is a new type of insulin. It starts working sooner than other insulin types. It also reaches peak activity faster and goes away sooner. Insulin lispro helps keep your blood sugar level from going too high after you eat. To keep your blood sugar level steady, your doctor will probably prescribe either a longer-acting insulin or another drug for you to take each day in addition to the insulin lispro.
If you need to mix insulin lispro with a longer-acting insulin, it’s best that you mix insulin lispro only with Humulin U or Humulin N, which are brand names for certain longer-acting insulins. Insulin lispro should always be drawn into the syringe first. This will keep the longer-acting insulin from getting into the insulin lispro bottle.
Types of insulin
Each type of insulin works at a different speed and lasts for a different length of time.
-
Quick-acting, such as insulin lispro , begins to work very quickly and lasts for 3 to 4 hours.
-
Short-acting, such as Regular insulin, starts working within 30 minutes and lasts about 5 to 8 hours.
-
Intermediate-acting, such as NPH or Lente insulin, starts working in 1 to 3 hours and lasts 16 to 24 hours.
-
Long-acting, such as Ultralente insulin, doesn’t start to work for 4 to 6 hours, but lasts 24 to 28 hours.
-
NPH and Regular insulin mixture, two types of insulin mixed together in 1 bottle, starts working in 30 minutes and lasts 16 to 24 hours.
When To Start Insulin In Gestational Diabetes
In gestational diabetes , sometimes the medicine form of insulin is required to help control blood sugar. A frequently asked question, when to start it? Normally, insulin is produced by a gland behind the stomach called pancreas. But this hormone doesnt work as well as usual if you have GD, a kind of diabetes that only occurs during pregnancy. And high blood sugar can carry some pregnancy complications.
Don’t Miss: What’s The Treatment For Type 2 Diabetes
Total Daily Insulin Requirement:
= 500 ÷ TDI = 1unit insulin/ 12 g CHO
This example above assumes that you have a constant response to insulin throughout the day. In reality, individual insulin sensitivity varies. Someone who is resistant in the morning, but sensitive at mid-day, will need to adjust the insulin-to-carbohydrate ratio at different meal times. In such a case, the background insulin dose would still be approximately 20 units however, the breakfast insulin-to-carbohydrate ratio might be breakfast 1:8 grams, lunch 1:15 grams and dinner 1:12 grams.
The insulin to carbohydrate ratio may vary during the day.
Know The Signs Of Hypoglycaemia
Hypoglycaemia or low blood glucose occurs when your blood glucose level is less than 4 mmol/l, or where symptoms of hypoglycaemia are experienced at a level close to this. Hypoglycaemia can happen quickly so its a good idea for you and your whnau to know what symptoms to look out for, such as:
- blurred vision
- pale, sweaty skin
- irritability.
Its a good idea to carry something sugary with you in case your blood glucose levels start getting low. Jellybeans are a good, quick source of sugar. Read more about hypoglycemia.
Recommended Reading: Why Are Insulin Prices So High
Initiating Appropriate Insulin Therapy
The American College of Endocrinology and the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists recommend initiation of insulin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes and an initial A1C level greater than 9 percent, or if the diabetes is uncontrolled despite optimal oral glycemic therapy. 11 Insulin may be used alone or in combination with oral medications, such as metformin . This recommendation is based on expert opinion, and not on the results of randomized controlled trials comparing different approaches in patients with an initial A1C level greater than 9 percent.
In the U.K. Prospective Diabetes Study, early intensive glucose control starting with a sulfonylurea, then metformin, then insulin was associated with a 25 percent reduction in microvascular complications and a 12 percent risk reduction in any diabetes-related end point, but was not associated with a reduction in all-cause mortality. 5 A subgroup of patients randomized to intensive therapy with metformin alone had a 36 percent reduction in all-cause mortality. 12 This supports current ADA guidelines that recommend using metformin as first-line pharmacologic therapy however, additional therapies need to be added if diabetes is not controlled with metformin alone.
Do I Need To Monitor My Blood Sugar Level

Yes. Monitoring and controlling your blood sugar is key to preventing the complications of diabetes. If you dont already monitor your blood sugar level, you will need to learn how. Checking your blood sugar involves pricking your finger to get a small drop of blood that you put on a test strip. You can read the results yourself or insert the strip into a machine called an electronic glucose meter. The results will tell you whether your blood sugar is in a healthy range. Your doctor will give you additional information about monitoring your blood sugar.
Also Check: Does Insulin Cause Erectile Dysfunction
Why You May Need To Take Insulin
What impacts your need for insulin differs from person-to-person, Dr. Levy says. So, its important to understand what places you at-risk for diabetes complications. The higher your risk, the more you may potentially need to include insulin in your treatment plan. These risk factors include:
But if you dont fall into one of these risk groups, there may be ways that you can avoid taking insulin with certain lifestyle modifications.
Insulin And Type 1 Diabetes
In type 1 diabetes, the body produces insufficient insulin to regulate blood glucose levels.
Without the presence of insulin, many of the bodys cells cannot take glucose from the blood and therefore the body uses other sources of energy.
Ketones are produced by the liver as an alternative source of energy, however, high levels of the ketones can lead to a dangerous condition called ketoacidosis.
People with type 1 diabetes will need to inject insulin to compensate for their bodys lack of insulin.
Read Also: Type 1 2 3 Diabetes
What To Do With The Oral Drugs
The patient is asked to remain on all the oral hypoglycaemic drugs that they are currently taking. The only exceptions are:
- if the patient is taking supra-maximal doses of any of the oral drugs, they are reduced to what is recommended in the product information
- if the patient is suffering from the gastrointestinal adverse effects of metformin, it is reduced to a dose which is tolerated
- if the patient is taking three oral hypoglycaemic drugs including acarbose, the acarbose is stopped as its adverse effects usually outweigh its advantage.
Although the oral drugs have ‘failed’ in the situation of ‘secondary failure’, they are still exerting considerable hypoglycaemic effects. Clinical studies have shown that if either the sulfonylurea or metformin are stopped altogether, then each needs to be replaced by an extra 20-30 units of daily insulin. In other words, the insulin dosage would need to exceed about 60 units a day before improvement in glycaemic control could occur. This would require a more aggressive insulin regimen and titration, making the process of starting insulin much more difficult. If a thiazolidinedione has been used, this could be continued initially at least, as it may also contribute an insulin sparing effect.
Insulin Sensitivity And Your Dose
You may hear your healthcare professional talk about insulin sensitivity. This is how well your body is using insulin to get your blood sugar levels down. People with high sensitivity need less insulin than those with low sensitivity.
Your healthcare professional can test you for insulin sensitivity, and this will help them decide what dose of insulin you will need, and if insulin of you need it at all.
You May Like: Are Brussel Sprouts Good For Diabetics
What Is A Disability
In 1990, Congress passed the ADA, which protects employees from being discriminated against because of their disability. That means an employer cannot discriminate against a qualified individual based on their disability. That particular disability should not be a reason for an individual to be fired. It should not keep them any advancement in the workplace or from getting equal pay. Job benefits cannot be denied to a disabled employee, nor should tests be created that screen out otherwise qualified but disabled individuals.
In 2008, changes were made to the ADA that emphasized that diabetes would always be considered a disability under the Americans with Disabilities Act.
How To Titrate Insulin Dosage And Monitor Progress
A major feature of this regimen is that insulin is added to existing treatment. Glycaemic control should therefore improve immediately and for practical purposes, should not deteriorate. This means that the dose of insulin can be increased relatively slowly, minimising the risk of hypoglycaemia. As described originally, the regimen2 increased the insulin dosage by 4 units a day if the fasting blood glucose exceeded 8 mmol/L on three consecutive days and by 2 units a day if it exceeded 6 mmol/L. We tend to do it slightly slower and adjust insulin dosage according to these glucose thresholds every 1-2 weeks. The slower pace helps to gain the patient’s confidence and reduces the risk of hypoglycaemia. This titration regimen is of course not ‘cast in stone’ and there are ongoing trials that are exploring the best options.
After 2-3 months, the patient is likely to be on about 30 units of insulin each day and maximum oral drug therapy. Measuring the HbA1c concentration after this interval helps to quantify the new level of glycaemic control and further increases in insulin dosage can be made accordingly. There is generally a reduction in HbA1c of about 2% and an increase in body weight of several kilograms. If these changes are not evident, one should consider the possibility that the patient has not been taking the insulin regularly or someone unfamiliar with the regimen has reduced or stopped one or more of the oral hypoglycaemic drugs.
You May Like: What Are The Symptoms Of A Diabetic Foot
Using Insulin With Oral Medications
Many oral medications are safe and effective when combined with insulin therapy. To maximize benefit without causing significant adverse effects, it is important to consider the mechanism of action for different therapies.
Insulin sensitizers have been proven safe and effective when combined with insulin therapy. 36,37 Metformin is usually continued indefinitely after the patient starts insulin therapy because it reduces cardiovascular risk in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes.12 Metformin combined with insulin is also associated with decreased weight gain, a lower insulin dosage, and less hypoglycemia compared with insulin alone. 38 Thiazolidinediones improve insulin sensitivity but may increase weight gain, fluid retention, and risk of congestive heart failure when combined with insulin.36 Thiazolidinediones also have not been shown to reduce macrovascular complications or all-cause mortality.
Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors delay absorption of carbohydrates in the gastrointestinal tract to decrease postprandial hyperglycemia. These medications are safe and effective when combined with insulin.39
Read the full article.
- Get immediate access, anytime, anywhere.
- Choose a single article, issue, or full-access subscription.
- Earn up to 6 CME credits per issue.
Throwing Away Your Needles And Lancets
Sharps bins and needle clippers are the safest way of disposing of your insulin needles and your lancets. A needle clipper removes the needle from your insulin pen, and is useful when youre out and about. How you get rid of your sharps bin depends on where you live. Your healthcare team should have information to help you get rid of your bin.
Don’t Miss: Financial Help With Diabetic Supplies
Take Insulin As Prescribed
People who have type 1 diabetes must take insulin as part of their treatment. Because their bodies can’t make insulin anymore, they need to get the right amount to keep their blood sugar levels in a healthy range.
The only way to get insulin into the body now is by injection with a needle or with an insulin pump. If someone tried to take insulin as a pill, the acids and digestive juices in the stomach and intestines would break down the medicine, and it wouldn’t work.
Different kinds of insulin are used for different purposes. The types of insulin you use and the number of shots you take each day will depend on what’s best for you and your daily schedule.
As you grow and change, the amount of insulin you will need to take can change. Getting insulin injections today is nearly painless, thanks to smaller needles. Insulin pumps cut down on the number of injections needed.
Your diabetes health care team will teach you how and when to give yourself insulin shots.
page 2