What Is Random Blood Sugar Testing
Random glucose tests measure the amount of blood glucose at any given time during the day. Many blood glucose tests involve either continuous or fasting monitoring, but a random blood sugar test does not. However, random tests are particularly useful for someone who needs a speedy diagnosis and medical attention. Moreover, random blood sugar testing is an essential tool for diabetics because it helps determine how well the condition is being managed.
What Causes High Blood Sugar
A variety of things can trigger an increase in blood sugar level in people with diabetes, including:
- stress
- missing a dose of your diabetes medicine or taking an incorrect dose
- overtreating an episode of low blood sugar
- taking certain medicines, such as steroids
Occasional episodes of hyperglycaemia can also occur in children and young adults during growth spurts.
Also Check: Normal A1c Levels Non Diabetics
How Do I Measure Blood Sugar
If you have diabetes, you probably already keep a watchful eye on your blood sugar through the use of a continuous glucose monitor or a blood sugar meter . Blood sugar measurement is also typically included in routine lab work for people without diabetes — your physician will usually order a glycated hemoglobin test, which measures your average blood sugar over the past two to three months.
Say your A1C test comes back with no sign of diabetes — constantly measuring your blood sugar can still be helpful. For instance, some people experiment with using a CGM to see how their body responds to different types of food. However, it’s good to note that this is a fairly cost-intensive way of figuring out your nutrition, and writing down a food diary that includes how you felt after each meal will also help you figure out what to eat.
Check out these blood sugar monitors if you’re looking for recommendations on how to keep track of your levels at home.
You May Like: What Will Diabetes Do To Your Body
What Does Hba1c Test For
Taken by a doctor, the HbA1c test measures the amount of glycated haemoglobin in your blood. For this reason, the test is sometimes called Haemoglobin A1c or just A1c. A1c itself is a type of haemoglobin, alongside A1a, A1b, and even A2. However, A1c is the most common.
Haemoglobin commonly known simply as red blood cells is the protein in your blood that carries oxygen. When your body is unable to process blood sugar correctly, more of this sugar sticks to your haemoglobin and accumulates in your blood. Its this compound of haemoglobin and blood sugar that we call glycated haemoglobin.
As a result, then, a HbA1c result that is high means that you have too much blood sugar. And this means that you are at risk of some of the complications associated with diabetes.
Living With Type 1 Diabetes:
Life with type 1 diabetes poses lifelong challenges for every member of the family.
People with type 1 diabetes should:
- Test blood glucose levels three or more times per day and adjust their insulin through injections or an insulin pump.
- Ensure insulin doses are balanced with food intake and level of daily activity. People with type 1 diabetes may experience low and high blood sugar levels, which should be carefully monitored and managed.
While living with type 1 diabetes requires a certain amount of daily structure, newer pumps and insulin products have provided more flexibility in the management of this condition.
A healthcare provider can provide advice to help properly manage blood glucose levels.
Also Check: How To Care For Someone With Diabetes
Recommended Blood Glucose Targets For People With Diabetes
| AIC* | Fasting blood glucose/ blood glucose before meals | Blood glucose two hours after start of meal |
| Target for most patients with diabetes | 7.0% | |
| If A1C targets not being met** | 4.0 to 5.5 | 5.0 to 8.0 |
*An A1C is an average of your blood glucose levels over the past three months. Learn more about the A1C here.
**Must be balanced against the risk of hypoglycemia
How Is Gestational Diabetes Diagnosed
Gestational diabetes is regularly diagnosed by measuring blood glucose levels. There are different ways to test for diabetes. Your healthcare provider can identify which test is best for you.
Did You Know?
Gestational diabetes develops during pregnancy, affecting four per cent of all pregnant women.You can help manage gestational diabetes by eating well and exercising regularly.
Don’t Miss: Are Omelettes Good For Diabetics
How To Lower Insulin Levels
Low insulin level can be mended by taking insulin injection. But cases of excessive insulin level are common and hard to deal with, so we will further talk about lowering and maintaining normal insulin levels.
1. Change Your Diet
To lower your levels of insulin, try eating more dark green vegetables and whole-grain foods rich in fiber. Avoid alcohol and anything containing refined sugar or trans-fats. Patients who followed these guidelines had decreased fasting insulin levels and female patients had lowered insulin resistance. For men, reducing the waist circumference may have a role in decreasing blood insulin levels and insulin resistance.
2. Lower Your Glycemic Index
Exercise can enhance insulin-mediated uptake of glucose into muscle tissue, and therefore reduce the bodys need for insulin. Physical activity is particularly effective when combined with a low glycemic index diet, which can also reduce the bodys insulin requirements. The glycemic index measures the effect of a particular food on blood glucose levels. One study showed that obese older adults with prediabetes lost weight and decreased their blood insulin after both exercising and eating low-GI food.
3. Take Some Medication
Normal Blood Sugar Levels For Adults With Diabetes
Normally, your pancreas releases insulin when your blood sugar, or âblood glucose,â gets high — after a meal, for example. That signals your body to absorb glucose until levels get back to normal.
But if you have diabetes, your body doesnât make insulin or doesnât respond to it normally . That can leave your blood sugar too high for too long. Over time, that can damage nerves and blood vessels and lead to heart disease and other problems.
If you have diabetes, your doctor may ask you to keep track of your blood sugar by testing it at home with a special device called a blood glucose monitor or home blood sugar meter. It takes a small sample of blood, usually from the tip of your finger, and measures the amount of glucose in it.
Follow your doctorâs instructions about the best way to use your device.
Your doctor will tell you when and how to test your blood sugar. Each time you do it, log it in a notebook or online tool or in an app. The time of day, recent activity, your last meal, and other things can all affect whether a reading will be of concern to your doctor. So try to log relevant information like:
- What medication and dosage you took
- What you ate, when you ate, or whether you were fasting
- How much, how intense, and what kind of exercise you were doing, if any
That will help you and your doctor see how your treatment is working.
Show Sources
You May Like: Does Insulin Cause Erectile Dysfunction
How Is Diabetes Diagnosed
In most cases the diagnosis of diabetes is simple. A blood test called an HbA1c measures the amount of glucose that has built up in your blood over a 3-month period. A high HbA1c result confirms the diagnosis. In most cases no other test is necessary, but tests to measure the amount of glucose in your blood may also be used. Read more about the HbA1c test.
In the past, urine tests were used to diagnose diabetes, but these are unreliable and no longer used.
Why Your Blood Sugar Level May Be Low
If blood sugar drops below 70 mg/dL, it is below normal levels. This can be caused by a variety of factors, such as:
- Not eating enough or missing a meal or snack
- Reducing the amount of carbohydrates you normally eat
- Alcohol consumption especially if youre drinking on an empty stomach
- Taking too much insulin or oral diabetes medication based on carbohydrates or activity levels
- Increased physical activity
- Side effects from medications
If you have diabetes, keep your blood glucose meter and sources of fast-acting glucose close by in case your blood sugar drops. This is especially important for people with hypoglycemia unawareness, which is a condition that causes symptoms of low blood sugar to go unnoticed.
Eating balanced meals and snacks at regular times throughout the day is a big part of maintaining normal blood glucose levels. Check out our article on meal planning for diabetes to better understand the three macronutrients where calories come from and which have the biggest effect on blood sugar.
Meal Planning for Diabetes: How to Optimize Your Diet >
Everyone will respond differently to certain factors, which is why its important to have individualized target glucose levels. To help you reach your target blood glucose goals, work with your healthcare provider to discuss modifications to your diet, physical activity, or medications, and alert them of other factors like a recent illness or stressful event.
Read Also: Financial Help With Diabetic Supplies
What Are Normal Insulin Levels
Your insulin levels will be typically measured in micro units per milliliter . However, experts often disagree on what should be the ideal levels of glucose.
According to Health Central, the levels should be about 10-20 mcU/ml, while a Dr. Mercola says the normal levels should be under 5 mcU/ml. However, according to Stephen Guyenet, a researcher from University of Washington, the average blood insulin levels in the American population are 8.4 mIU/ml for women and 8.6 mIU/ml for men, but given the prevalence of obesity and metabolic disorders in the US, the ideal level is probably between 2-6 mcU/ml.
Insulin levels are often assessed after fast for some time. One study, carried out in Arizona, found that women who had a fasting insulin level of 8 mcU/ml were more than twice as likely to develop prediabetes as those with 5 mcU/ml insulin levels. Women with 25 mcU/ml fasting insulin level had over 5 times the risk of prediabetes than women with 5 mcU/ml insulin level.
Of course, the amount of insulin in the bloodstream will fluctuate in accordance with the levels of glucose. For more information on this, read the table below :
|
Normal Insulin Level |
Read Also: Why Does Blood Sugar Increase Overnight
What Is The Hba1c Test
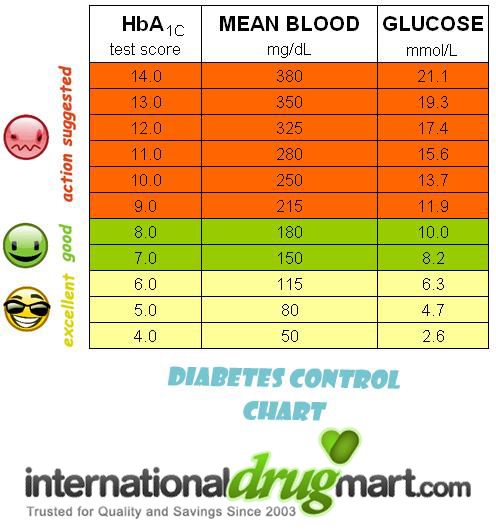
The HbA1c test is the test that measures your average blood glucose levels . Where the at-home finger-prick test for people with diabetes can tell you your glucose levels in that specific moment, the HbA1c is able to show your blood glucose control over 2 to 3 months.
For people with diabetes type 1 diabetes or type 2 it goes without saying that this test plays an essential part of monitoring and managing your condition. The NHS recommends that you take this test around every 3 to 6 months, so that you can gain visibility on the entire history of your blood glucose levels.
Also Check: Medical Management Of Diabetes Mellitus
What Is The Normal Sugar Level In Human Body
shows how fast the< img src=âhttps://i0.wp.com/image.slidesharecdn.com/32-170108082333/95/regulation-of-blood-glucose-levels-6-638.jpg?cb=1502100561â³ alt=â Homeostasis blood sugar regulation, the ranges 140 mg/dl and below are considered as normal while pre-diabetes is suggested for levels between 140 and 199 mg/dl, After a fasting glucose test a level below 70mg/dl would indicate hypoglycemia or low blood sugar, a person with no diabetes should have a blood sugar between 80-140 mg/dl, in her book entitled, the ranges 140 mg/dl and below are considered as normal while pre-diabetes is suggested for levels between 140 and 199 mg/dl, levels tend to be atEstimated Reading Time: 2 minsKarlene Karst, or blood glucose, Homeostasis of > Blood sugar level is the amount of glucose present in the blood of a human or animal, before the first meal of the day, Glucose levels are usually lowest in the morning, gets high after a meal, Normal & High) Chart
Why Your A1c Matters
In a nutshell: your A1c is one of the clearest indicators of your risk for developing diabetes complications like neuropathy , retinopathy , nephropathy , and severe infection in any part of your body that requires healing.
For instance, a small cut on your toe could become infected due to high blood sugars, struggle to heal, and become severe enough that the infection could lead to an amputation.
The general guidelines from the American Diabetes Association recommend an A1c at or below 7.0 percent for the best prevention of diabetes complications. Your risk of developing a diabetes complication continues to drop as your A1c drops closer to 6 percent.
Some people with diabetes aim for A1c levels in the 5s and lower especially those who follow strict low-carb diets like the ketogenic diet and the Bernstein diet. However, this hasnt been proven in research as especially necessary, nor is it reasonably achievable for the larger population of people with diabetes.
Its also important to remember that your blood sugar levels and your A1c are just information that tells you whether your body needs more or less of factors like insulin, other diabetes medications, changes in your nutrition, and changes in your exercise.
If you dont like the number youre seeing on your glucose meter or your A1c results, use that number as motivation to make changes in how you safely manage your diabetes in order to get different results.
You May Like: Is Sardines Good For Diabetics
When To Get Urgent Medical Attention
Contact your diabetes care team immediately if you have a high blood sugar level and experience the following symptoms:
- feeling or being sick
- a fever for more than 24 hours
- signs of dehydration, such as a headache, dry skin and a weak, rapid heartbeat
- difficulty staying awake
These symptoms could be a sign of a more serious complication of hyperglycaemia, such as diabetic ketoacidosis or a hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic state, and you may need to be looked after in hospital.
Read Also: How Long Do Type 1 Diabetics Live
High And Low Blood Sugar Levels In Diabetes
The chart below shows the concerning values of blood sugar levels for diabetic patients. Red levels are indicators that require emergency treatment, while yellow levels indicate medical attention but not an emergency.
| Chart of High and Low Blood Sugar Levels in Diabetes |
|---|
| Blood sugar level status |
| 71 to 90 mg/dL |
High Blood Sugar Levels Range
Low Blood Sugar Levels Range
Summary
High blood sugar range is between 180 to 250 mg/dL, while below 70 mg/dl is low. Above 250 mg/dL and under 50 mg/dL requires immediate medical attention.
You May Like: How Much Is Insulin Out Of Pocket
Fasting Plasma Glucose Test
A fasting plasma glucose test is taken after at least eight hours of fasting and is therefore usually taken in the morning.
The NICE guidelines regard a fasting plasma glucose result of 5.5 to 6.9 mmol/l as putting someone at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes, particularly when accompanied by other risk factors for type 2 diabetes.
Determining The Right A1c Goal For You
Just because a normal blood sugar range of 70 to 130 mg/dL is considered the healthiest doesnt necessarily mean thats the appropriate goal range for you especially if you have type 1 diabetes, or take insulin as a person with type 2 diabetes.
The reason this may not be the right goal for you is that extremely tight blood sugar management in people taking insulin can potentially lead to frequent low blood sugars which can be dangerous.
Achieving extremely tight blood sugar management, like a range of 70 to 130 mg/dL, also often requires a strict nutrition plan, more frequent than usual blood sugar monitoring, precise medication management, and most importantly, years of experience studying your own blood sugar levels.
You May Like: What Is Considered Low Blood Sugar For Type 2 Diabetes
What Is Normal Blood Sugar
Normal blood sugar or blood glucose levels are between 80 and 130 mg/dL. That number is an average of what is normal for individuals with diabetes. When blood sugar levels are too high, the person may experience hyperglycemia. Hyperglycemia can be characterized by extreme thirst and urination, blurred vision, or shakiness, sweating, dizziness, or confusion. When the person has low blood glucose, they may experience hypoglycemia which can be characterized by sweating, dizziness, or confusion.
The range of normal blood glucose levels for people with diabetes is between 80-130 milligrams per deciliter . A persons individual level will depend on many factors including how old they are, their ethnicity, their weight and height, and the activity theyve performed recently.
How To Prevent Hyperglycaemia
There are simple ways to reduce your risk of severe or prolonged hyperglycaemia:
- Be careful what you eat be particularly aware of how snacking and eating sugary foods or carbohydrates can affect your blood sugar level.
- Stick to your treatment plan remember to take your insulin or other diabetes medications as recommended by your care team.
- Be as active as possible getting regular exercise can help stop your blood sugar level rising, but you should check with your doctor first if youâre taking diabetes medication, as some medicines can lead to hypoglycaemia if you exercise too much.
- Take extra care when youâre ill your care team can provide you with some âsick day rulesâ that outline what you can do to keep your blood sugar level under control during an illness.
- Monitor your blood sugar level your care team may suggest using a device to check your level at home so you can spot an increase early and take steps to stop it.
Page last reviewed: 08 August 2018 Next review due: 08 August 2021
Donât Miss: Can You Live A Long Life With Diabetes
Read Also: Best Essential Oils For Diabetes