Age Insulin Resistance And Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a group of metabolic abnormalities of which central obesity and insulin resistance are believed to be the primary backgrounds. The diagnostic criteria for metabolic syndrome have been proposed by several organizations and associations, all of which are based on five parameters i.e. central obesity, high blood pressure, high fasting blood glucose levels, high TG levels and low levels of HDL-C. The pathogenesis of how central obesity causes insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome has been explained in many publications. Decreased insulin sensitivity, reduced muscle mass, and increased body fat mass, especially visceral fat that accompanies aging contribute to insulin resistance in the elderly. Aging process is also associated with reduced compensatory beta cell mass function of the pancreas and to insulin resistance as well as with decreased mitochondrial function that contributes to insulin resistance . A study by Gupta et al. showed that hepatic insulin resistant was related to body fat and its distribution, and hepatic insulin action could be preserved by caloric restriction in aging caloric restriction rat.
Who Is More Likely To Develop Type 2 Diabetes
You can develop type 2 diabetes at any age, even during childhood. However, type 2 diabetes occurs most often in middle-aged and older people. You are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes if you are age 45 or older, have a family history of diabetes, or are overweight or obese. Diabetes is more common in people who are African American, Hispanic/Latino, American Indian, Asian American, or Pacific Islander.
Physical inactivity and certain health problems such as high blood pressure affect your chances of developing type 2 diabetes. You are also more likely to develop type 2 diabetes if you have prediabetes or had gestational diabetes when you were pregnant. Learn more about risk factors for type 2 diabetes.
Who Gets Type 2 Diabetes
No one knows for sure what causes type 2 diabetes. But many kids who develop it have at least one parent with diabetes and a family history of the disease, so there seems to be a genetic risk.
Most people with type 2 diabetes are overweight. Excess fat makes it harder for the cells to respond to insulin, and not being physically active makes this even worse. Type 2 diabetes used to mostly affect adults, but now more and more U.S. kids and teens, especially those who are overweight, are developing the disease.
Also, kids in puberty are more likely to have it than younger kids, probably because of normal rises in hormone levels that can cause insulin resistance during this stage of fast growth and physical development.
p
Read Also: How Much Sugar Diabetes Type 2
We Need A Strategy Now
Although people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes have different journeys, including whether or not they experience symptoms, there is one issue that unites all people living with the disease. Canada has no strategy to address one of the most significant health-care crisis of our time.
With no dedicated support or action to tackle the diabetes epidemic, it means that, every 24 hours:
- more than 20 Canadians die of diabetes-related complications
- 480 more Canadians are diagnosed with this devastating disease
- 14 Canadians have a lower limb amputation
- our health care system spends $75 million treating diabetes
The Challenge Of Diabetes
There are about 60 million people with diabetes in the European Region, or about 10.3% of men and 9.6% of women aged 25 years and over.
Prevalence of diabetes is increasing among all ages in the European Region, mostly due to increases in overweight and obesity, unhealthy diet and physical inactivity.
Worldwide, high blood glucose kills about 3.4 million people annually. Almost 80% of these deaths occur in low- and middle-income countries, and almost half are people aged under 70 years. WHO projects diabetes deaths will double between 2005 and 2030.
Recommended Reading: Do I Need Prescription For Insulin
What Are The Symptoms Of Type 2 Diabetes In Children And Teens
Many of the signs of type 2 diabetes are the same in children as they are in adults. The ADA lists these as common symptoms:
- Feeling very hungry even if you are eating well
- Fatigue
Perez-Colon also looks for weight gain around the middle. In addition, she is watchful for acanthosis nigricans: a velvety darkening and thickening of the skin that usually happens around the neck and skin folds and which can be a sign of type 2 diabetes, according to the ADA. Research indicates that it is more common among Native American, Black, and Hispanic people in the United States.
A big tipoff for her that a child is at risk of obesity, and perhaps type 2 diabetes, comes from lifestyle. Most of the time they have a sedentary lifestyle and barely do physical activities. Diet-wise, they are drinking an increased amount of juice or sweetened drinks. They are not eating much in the way of fruit or vegetables. They are eating a lot of salty foods, such as chips. They may be eating very late at night, which can predispose you to putting on weight. And they eat large portions, getting seconds and sometimes even thirds.
RELATED: Losing Excess Fat in Young Adulthood Could Reduce Heart Risks of Childhood Obesity
The Big Picture: Monitoring Treatment
This relatively simple blood test can tell you a lot. The test results give you a picture of your average blood sugar level over the past two to three months. The higher the levels, the greater your risk of developing diabetes complications. Your doctor will tell you how often you need the A1C test, but usually youll have the test at least twice a year if youre meeting your treatment goals. If you’re not meeting your goals or you change treatments, you may need to get an A1C test more often.
Don’t Miss: Diabetes 2 Meal Plan For A Week
Managing Type 2 Diabetes
Many people with type 2 diabetes can manage their blood glucose levels with diet and exercise alone. Others may need diabetes pills or insulin injections, along with medicines to manage other conditions like high blood pressure and high cholesterol. Over time, a person with diabetes may need both lifestyle changes and medication.
Once youve been told you have diabetes, a health care team will work with you to create a diabetes management plan. Your plan will be based on your lifestyle, preferences, health goals, and other health conditions you have.
As part of your plan, your doctor may prescribe one or more medications. Other health care professionals may also be involved. For example, a diabetes educator may help you understand diabetes and provide support as you make lifestyle changes to manage your diabetes. A dietitian may help with meal planning. An exercise coach may help you become more physically active.
Who Is It For
If you are prediabetic or experience Type 2 Diabetes, as well as you observe that you do not get adequate high quality rest at night, Deep Sleep Diabetes Remedy program is more than likely the program for you. Kill 2 birds with one rock: boost your sleep as well as vitality and also reverse your diabetes with this program. type 2 diabetes age range
One More Thing I Found An Awesome Free Bonus For You!
Ive got great information! I found an internet site offering a pretty significant reward on the Deep Sleep Diabetes Remedy. You can save a minimum of $47 on these perks but you have to act now. To get the rewards for free, please click on the link below. Yet hurry, because the perk is only readily available for a limited time. type 2 diabetes age range
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Rid Of Diabetes By Losing Weight
How Can I Manage My Type 2 Diabetes
Managing your blood glucose, blood pressure, and cholesterol, and quitting smoking if you smoke, are important ways to manage your type 2 diabetes. Lifestyle changes that include planning healthy meals, limiting calories if you are overweight, and being physically active are also part of managing your diabetes. So is taking any prescribed medicines. Work with your health care team to create a diabetes care plan that works for you.
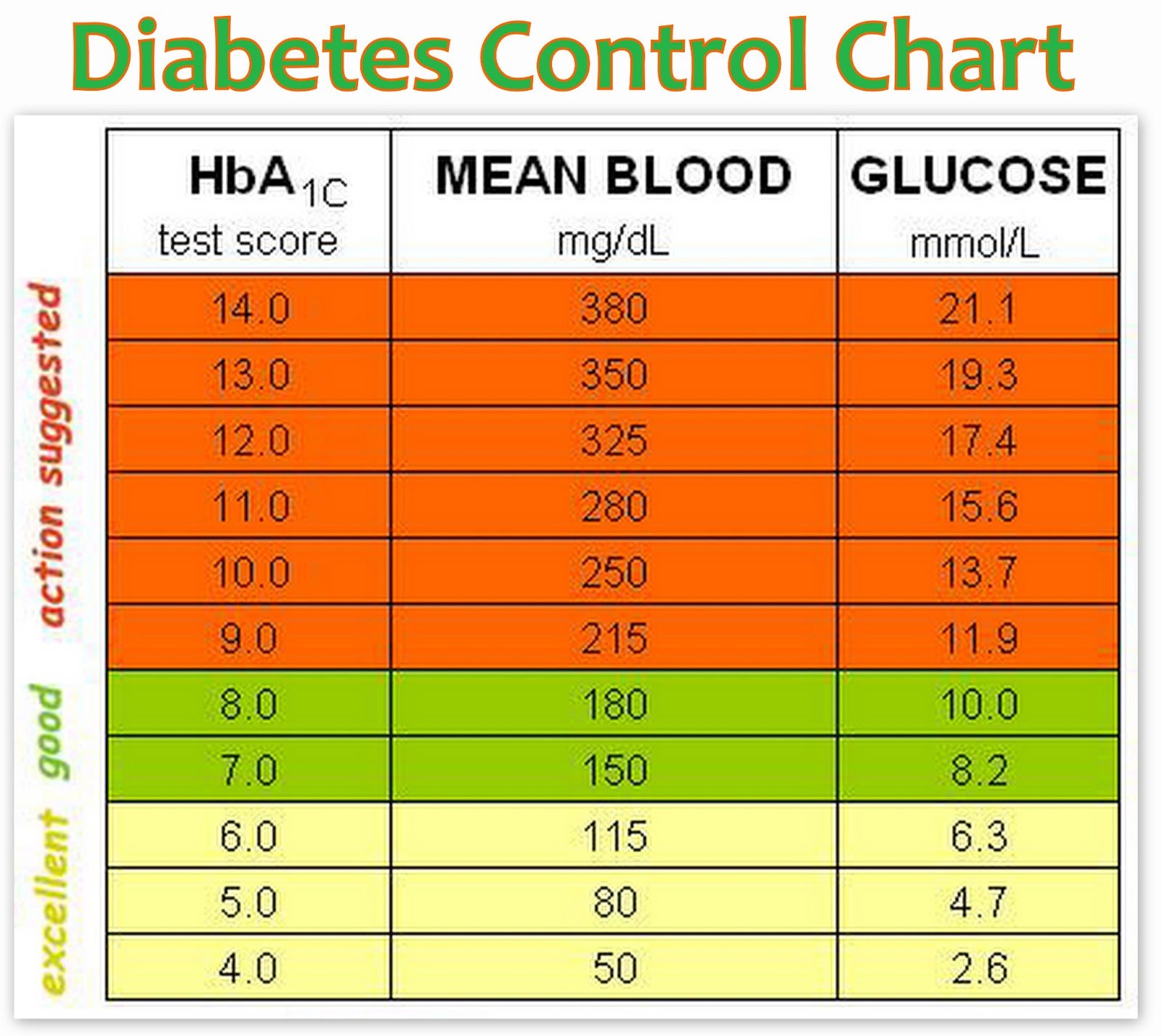
Recommended Target Blood Glucose Level Ranges
The NICE recommended target blood glucose levels are stated below for adults with type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes and children with type 1 diabetes.
In addition, the International Diabetes Federations target ranges for people without diabetes is stated.
The table provides general guidance. An individual target set by your healthcare team is the one you should aim for.
| Target Levels |
|---|
*The non-diabetic figures are provided for information but are not part of NICE guidelines.
Also Check: Can Diabetics Eat Activia Yogurt
Type 1 Vs Type 2 Diabetes: Whats The Difference
Type 2 diabetes is not the same as Type 1 diabetes. In Type 1 diabetes, your pancreas doesnt make any insulin. In Type 2, your pancreas doesnt make enough insulin, and the insulin it is making doesnt always work as it should. Both types are forms of diabetes mellitus, meaning they lead to hyperglycemia .
Type 2 diabetes usually affects older adults, though its becoming more common in children. Type 1 diabetes usually develops in children or young adults, but people of any age can get it.
The Health Risks Of Type 2 Diabetes

Diabetes is a lifelong condition. High blood glucose levels over a long period of time can cause:
- blindness
- reduced blood supply to the limbs, leading to amputation
- nerve damage
- erectile dysfunction and
- stroke.
Although there is no cure for diabetes, the condition can be managed by medication and/or insulin, and by making healthy lifestyle choices.
Don’t Miss: Number Of Grams Of Sugar Per Day For Diabetic
Prevention Of Diabetes In Older Adults
The ADA recommends that all overweight adults with risk factors and all adults > 45 years of age should be screened for prediabetes and diabetes in the clinical setting every 13 years . Although a great deal of evidence supports diabetes screening of younger adults, for older adults, consideration should be given to the heterogeneity within this population, which can affect treatment decisions . The benefits of screening depend on whether primary or secondary preventive interventions would be effective for the older patient, which in turn depends on issues such as life expectancy, anticipated timeframe of benefits, and aggressiveness of the intervention. For older adults who have a long life expectancy and are relatively healthy, it is reasonable to follow current general screening recommendations. For very old adults, those with multiple comorbidities, and those with a short life expectancy, it is best to focus intervention on preventing worsening of their conditions and complications and to be cognizant of complications that could further impair patients functional status or quality of life.
Background Characteristics Of The Sample
Responses were received from 2866 respondents . The response rate was highest in the oldest age group , lower in the middle age group and lowest in the youngest age group . The mean age of respondents in the study sample was 63years , 56% were male, and 41% had a higher professional education, meaning college, polytechnic or university education. The mean duration of diabetes was 8years , and the majority used oral diabetes medication only. Moreover, for the majority municipal primary healthcare centres were the main provider of diabetes care. Of respondents, 84% had been for over 2years, and 95% at least for 1year, in care at their current primary care centre.
In the sample, 13% were 2754years, 38.7% were 5564, and 48.3% 6575years. In the youngest age group , 70% had been diagnosed with T2D at the age45years. In the other age groups, as well, there were persons with early onset diabetes: 11% of the middle age group, and 4% of the oldest age group.
Read Also: How Much Do Diabetic Test Strips Sell For
What’s New In The Treatment Of Type 2 Diabetes
Doctors and researchers are developing new equipment and treatments to help kids deal with the special problems of growing up with diabetes.
Some kids and teens already use new devices that make blood glucose testing and insulin injections easier and more effective. One of these is the insulin pump, a mechanical device that can be programmed to deliver insulin more like the pancreas does.
Researchers are also testing ways to stop diabetes before it starts. For example, scientists are studying whether diabetes can be prevented in those who may have inherited an increased risk for the disease.
What Are The Complications Of Type 2 Diabetes In Youth
When youth under age 20 develop type 2 diabetes, complications arise at an accelerated pace, according to a September 2016 report in the ADAs journal Diabetes Care. Furthermore, the risk of death is twofold higher for those who develop type 2 diabetes under 20 than it is for the general population under 20, according to a 2018 study.
Many of the complications are similar to those seen in adults. According to the ADA, complications of diabetes include:
- Diabetic neuropathy
- High cholesterol
- Stroke
Perez-Colon has seen these complications in her own young patients. She stresses that good blood sugar management can help children avoid complications down the road.
And while Perez-Colon says there isnt yet enough data to know how a COVID-19 infection can affect a child or teen with type 2 diabetes, she notes that having an infection can cause the body to release hormones that raise your blood sugar another reason for being vigilant about blood sugar management. Adults with type 2 diabetes are certainly at risk for serious COVID-19 illness, according to the CDC.
RELATED: What People With Diabetes Must Know About COVID-19
Also Check: Type 2 Diabetes Need Insulin
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes
Symptoms, treatment, and complications from type 2 diabetes may vary from person to person. The following information will help you learn more about this disease and provide you with helpful tools, assessments and resources.
-
If left untreated or improperly managed, diabetes can lead to a variety of life-threatening complications.
Best Approach To Pharmacotherapy In Older Adults
Older adults with diabetes differ from their younger-adult counterparts in terms of glycemic goals and management of other cardiovascular risk factors. They also often have comorbidities and geriatric syndromes that interfere with self-care. It is crucial for providers to be aware of these differences to allow for proper assessment and to develop pharmacotherapeutic strategies that are adapted to unique challenges.
Lifestyle modification is important as the starting point for all patients with diabetes, including older adults. Although very restrictive diets are not recommended for older adults, counseling to avoid large carbohydrate loads at any one meal can reduce glucose excursions without unnecessary dietary restriction. Exercise is also important for all ages. It is important to consider patients physical abilities when developing an exercise plan. For example, older adults who are not very active and at risk of falls should be encouraged to walk for 510 minutes, two to three times per day, inside the house. The exercise program can be increased gradually as tolerated.
Don’t Miss: How Can I Check If I Have Diabetes
Diabetes In Older Adults: A Growing Population With Special Challenges
The population of elderly patients with diabetes is rapidly growing, with significant impact on population health and economics . Currently in the United States, older adults make up > 25% of the total population with diabetes . Even if the diabetes incidence rates were to level off, the prevalence of diabetes will double in the next 20 years as the population ages .
What Is Diabetes
Our bodies turn a lot of the food we eat into sugar, called glucose, which gives us energy. To use glucose as energy, our body needs insulin, a hormone that helps glucose get into our cells. If you have diabetes, your body may not make enough insulin, may not use insulin in the right way, or both. That can cause too much glucose to stay in the blood, which can cause health problems over time. Your family doctor may refer you to a doctor who specializes in taking care of people with diabetes, called an endocrinologist. Often, your family doctor will work directly with you to manage your diabetes.
You May Like: Young Living Oils For Diabetes
What You Can Do
Type 2 diabetes doesnât have to be a normal part of aging.
Some risk factors for the disease are things you canât change. They include if your mother had gestational diabetes during their pregnancy, if diabetes runs in your family, and if youâre African American, Asian American, Native American, or Latino.
But healthy habits can go a long ways to prevent diabetes, keep it under control, and even reverse it. Steps you can take include:
- Lose extra weight, especially if you carry a lot of belly fat.
- Move your body. Aim for at least 30 minutes of physical activity like walking every day, 5 days a week.
- Eat healthy. Cut back on sugar, salt, processed packaged foods, and saturated fats from meats. Load up on dark leafy vegetables, fresh fruit, whole grains, and lean protein.
- If you smoke, quit.
Show Sources
CDC: âNational Diabetes Statistics Report 2020,â âPrevent Type 2 Diabetes in Kids,â âPrevalence of Diagnosed Diabetes in Adults by Diabetes Type â United States, 2016.â
MedlinePlus: âDiabetes Type 2.â
The New England Journal of Medicine: âIncidence Trends of Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes among Youths, 2002â2012.â
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. âRisk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes.â
Diabetes Care: âAn Inverse Relationship Between Age of Type 2 Diabetes Onset and Complication Risk and Mortality: The Impact of Youth-Onset Type 2 Diabetes,â âDiabetes and Aging: Unique Considerations and Goals of Care.â