How To Take An Insulin Injection
When your healthcare provider or diabetes educator teaches you how to give yourself an insulin injection, they may have you give yourself an injection in order to observe your technique and provide support. Once you get home and its time to give yourself an injection, you can follow these steps as a reminder. If your healthcare provider has given you individualized instructions, always follow them.
In general, the following steps cover how to take an insulin injection:
Before you begin, wash your hands and gather supplies, including your insulin vial or pen, a new pen needle or syringe, an alcohol swab, sharps container, and a magnifier if needed.
How to inject insulin using an insulin pen:
How to inject insulin with a syringe:
A note about mixing insulin: Some people mix two types of insulin in one syringe. Mixing insulin in a syringe requires specific steps, and you will want to meet with your healthcare provider or diabetes educator to ensure that that you are accurate in dosing your insulin.
Storage and disposal tips:
Dispose of used pen or syringe needles safely so that no one gets an unwanted stick. Pick up a sharps container at the pharmacy, or make your own with a sturdy detergent container or similar plastic jug. Once the container is ¾ full, tape the top back on securely and contact your town to see if they have a sharps program for proper disposal. For more information on sharps disposal follow these guidelines from the FDA.
Best Practices In Injection Technique
A healthcare professional trained in injection techniques can teach you how to do it right
The following recommendations apply to people with diabetes being treated with insulin injections or GLP-1 analogues , dulaglutide , exenatide , exenatide sustained release and liraglutide ). They are based on the Recommendations for Best Practice in Injection Technique from the Forum for Injection Technique .
Lower Back Hips Or Buttocks
The final site for administering an insulin injection is the lower back or hip.
To administer an injection here, draw an imaginary line across the top of the buttocks between the hips.
Place the needle above this line but below the waist, about halfway between the spine and the side.
As with the upper arm, this site is very difficult to use for self-injection and may require another person for administration. When injecting into the buttocks, avoid the lower part.
The body absorbs insulin at different speeds from each of the sites. This information can be useful when planning insulin injections:
- Abdomen: Insulin enters the bloodstream most quickly after an abdominal injection.
- Upper arms: The body absorbs insulin with moderate speed but slower than an injection in the abdomen.
- Lower back and thighs: Insulin enters the bloodstream most slowly from these sites.
- Administer rapid-acting insulin into the abdomen right after a meal for the fastest results.
Inject long-acting and intermediate-acting insulin into the other sites, as rapid absorption would reduce the effectiveness of these types. Insulin works more efficiently over the entire time it needs to because of the slower absorption rate.
Exercise can increase the absorption rate of insulin. If planning a workout or physical activity, account for these when planning injections.
Wait to for at least 45 minutes after the injection to exercise a part of the body that is near the injection site.
Read Also: Do I Need Prescription For Insulin
Does Hypoglycemia Occur In Dogs
Hypoglycemia means low blood sugar. If the blood sugar falls below 40 mg/dl, it can be life threatening. Hypoglycemia generally occurs under two conditions:
“It is possible for the dog’s insulin requirements to suddenly change.”
Your veterinarian may have you offer an extra meal and recheck the glucose level within a short time after the dog eats.
The 4 Main Areas On The Body That Are Best To Give Insulin Shots Are The:
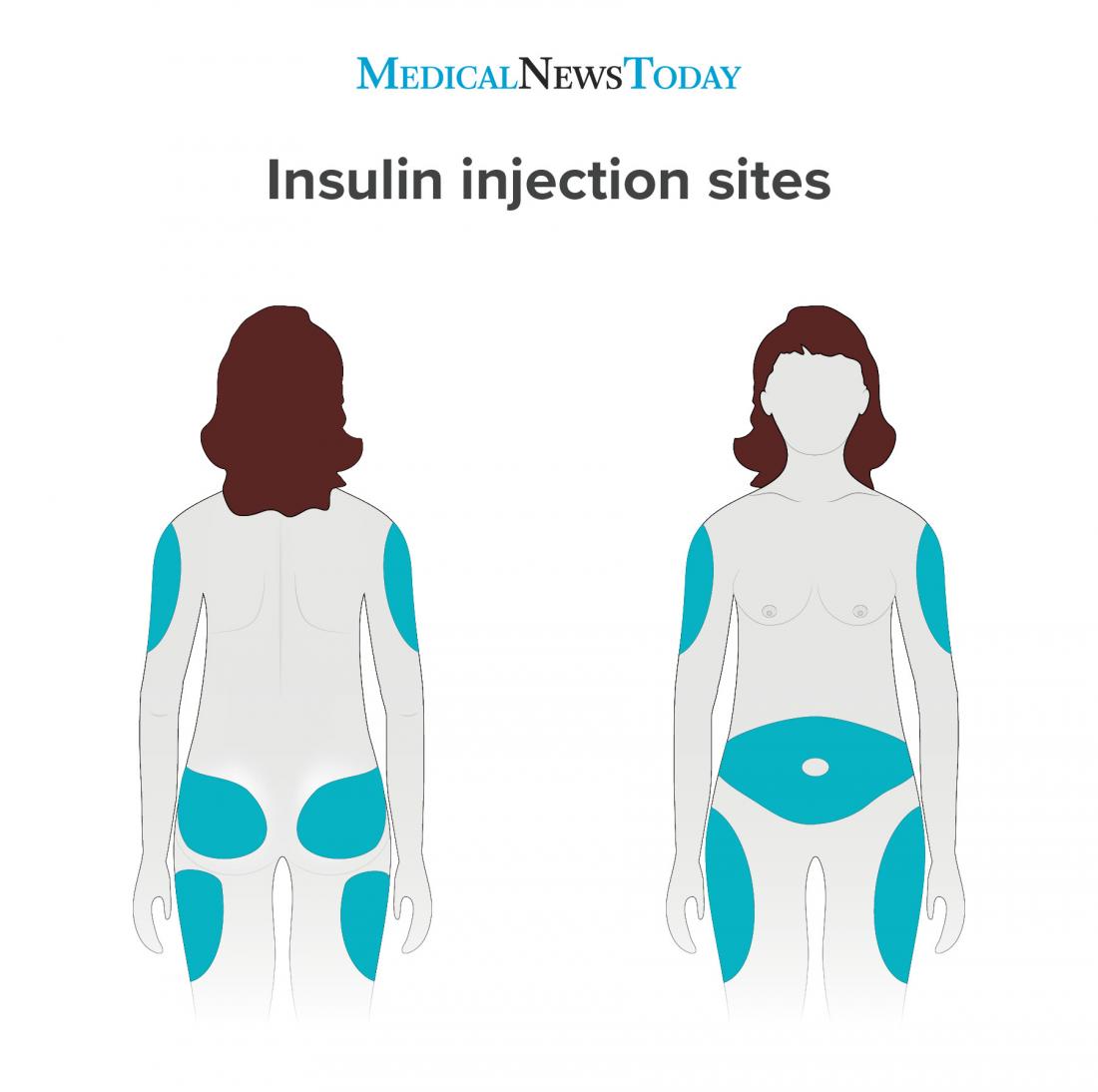
Do not give yourself insulin in the same spot each time. Use different spots in each area. Giving a shot in the same spot each time causes hard lumps in skin. Insulin will not absorb as well in hard lumps, and blood sugar can go too high.
Don’t Miss: Why Are Insulin Prices So High
Where On The Body Do I Inject With The Insulin Pen
Recommended injection sites include the abdomen, front and side of the thighs, upper and outer arms and buttocks. Do not inject near joints, the groin area, the navel, the middle of the abdomen, or scar tissue.
You will also need to rotate, or switch, your injection sites. If you use the same injection site over and over again, you may develop hardened areas under your skin that keep the insulin from working properly. Rotating your injection sites will make your injections easier, safer and more comfortable.
Follow these guidelines:
- Ask your healthcare provider which sites on your body you should use for injections.
- The injection site is about two inches of skin. Clean this area with an alcohol wipe in a circular motion.
- Move the site of each injection. Inject at least one-and-a-half inches away from the last spot where you injected.
- Try to inject in the same general area of your body at the same time each day.
- Keep a record of which injection sites you have used. Every time you give yourself an injection, write down the date, time and site.
Depending on which type of insulin you are taking, different parts of the body may absorb the insulin differently.
How Do I Give Myself An Injection
Don’t Miss: How Can An Ophthalmologist Help A Diabetic
Avoiding Injection Bruises And Lumps
Bruising can happen when you catch a tiny blood vessel under the skin where you have injected. It is quite normal for this to happen occasionally when you are injecting regularly and youre not doing anything wrong.
If you are concerned, you could make an appointment with your diabetes specialist nurse who will be able to do a review of your injection technique. In some cases, bleeding and bruising can be reduced by something as simple as using a different sized needle or changing your needle after each injection.
Some people notice hard lumps that can form if you inject in the same place too often. This might be lipohypertrophy , or could be something called cutaneous amyloidosis. These lumps can stop the insulin from working properly, so make sure you rotate where you inject and choose a different spot each time. If you notice any lumps, especially if they’re not going away, speak to your healthcare professional for more advice.
Other side effects from injecting a lot can be itching, rashes and other skin irritations. Changing where you inject helps with this too. You can also get treatments from your local pharmacy that can will help with the irritation.
Tips For Choosing Sites
Fast absorption of mealtime carbohydrates is typically important to reduce after meal blood sugars, therefore, unless instructed otherwise by your healthcare provider, or if you have an increased risk of low blood sugar or reactive hypoglycemia, it’s probably smart to inject your breakfast and lunch, and maybe dinner bolus doses into the abdomen. What is not advised is to inject your breakfast insulin in the abdomen one day and into the thigh the next day. If possible, be consistent within each site and rotate accordingly.
Long-acting or bedtime insulin could be injected into the thigh, buttocks, or upper arm so that the absorption can happen gradually, covering your insulin needs throughout the night.
Ultimately, what’s most important is that you have access to a site and are consistent. The choice is always yours.
Recommended Reading: Diabetes Injection Pen For Weight Loss
Infusion Set Insertion Locations
Locations for Inserting Infusion Sets
Shown here are the best body areas for infusion set insertion.
Note: Work with your healthcare professional to determine the sites that will work best for you.
Infusion Set Insertion Site Guidelines
Avoid inserting the infusion set:
- Into the 2-inch area around your belly button
- Where your body naturally bends a great deal
- In areas where clothing might cause irritation
- Where you have scarred or hardened tissue or stretch marks
Your infusion sites should be at least:
- 2 inches away from your sensor site
- 2 inches away from your belly button
- 3 inches away from the previous site
Monitoring Your Blood Glucose And Ketone Levels
If you have missed an injection, it is important that you monitor your blood glucose levels more regularly than usual over the next 24 hours to prevent blood glucose levels from going either too high or too low.
If you have type 1 diabetes , or have type 2 diabetes and produce very little of your own insulin, be prepared to test your blood or urine for ketones if your blood glucose levels rise above 15 mmol/l.
You May Like: Weekly Diet Plan For Type 2 Diabetes
When Should I Use An Insulin Pen
To determine when you should inject insulin, pay attention to the times you check your blood sugar, when you eat and what kind of insulin you are taking:
- Check your blood sugar no more than 30 minutes before you eat.
- If you take rapid-acting insulin before meals, inject the insulin when you sit down to eat.
- If you take regular insulin before meals, inject the insulin no more than 30 minutes before the meal.
- If you take intermediate- or long-acting insulin, inject the insulin at the same time each day.
There is no standard or typical dose of insulin. Your dose will be the amount of insulin that you need in order to keep your blood sugar in good control. Your doctor will prescribe an insulin dose that is right for you.
How Do I Draw Up One Kind Of Insulin

Recommended Reading: Type 1 Diabetes Symptoms In Adults
Select And Clean The Injection Site
Choose an injection site for your insulin shot.
Do not inject near joints, the groin area, navel, the middle of the abdomen, or near scars.
Clean the injection site in a circular motion with an alcohol wipe or a cotton ball dampened with rubbing alcohol. Leave the alcohol wipe or cotton ball nearby.
How To Give Insulin In The Stomach With An Insulin Pen Or Syringe
Injecting insulin into the stomach is easy, and the same method can be used whether you are using a syringe or an insulin pen.
Also Check: Bach Flower Remedies For Diabetes
Reasons To Avoid A Particular Site
If you develop lumps and bumps at injection sites, avoid the area of the bump for several months because that area will absorb insulin differently and this can affect your blood sugar levels.
In addition, avoid sites that you plan on exercising, as this can increase the risk of hypoglycemia due to increased absorption.
Lastly, avoid injecting into moles or scar tissue as these can also affect insulin absorption.
Do Tell Friends And Family That Youre Taking Insulin
Its a good idea to teach your friends, colleagues, and family members about insulin and its potential side effects. If you do end up taking too much insulin and having a hypoglycemic episode, they should know how to help.
If you become unconscious, a friend or family member can give you a shot of glucagon. Talk to your doctor about keeping a supply of glucagon on hand and learning when and how to use it.
Also Check: How To Treat Diabetic Sores
Prepare The Insulin And Syringe
- Remove the plastic cap from the insulin bottle.
- Roll the bottle of insulin between your hands two to three times to mix the insulin. Do not shake the bottle, as air bubbles can form and affect the amount of insulin withdrawn.
- Wipe off the rubber part on the top of the insulin bottle with an alcohol pad or cotton ball dampened with alcohol.
- Set the insulin bottle nearby on a flat surface.
- Remove the cap from the needle.
If you’ve been prescribed two types of insulin to be taken at once , skip to the instructions in the next section.
- Draw the required number of units of air into the syringe by pulling the plunger back. You need to draw the same amount of air into the syringe as insulin you need to inject. Always measure from the top of the plunger.
- Insert the needle into the rubber stopper of the insulin bottle. Push the plunger down to inject air into the bottle . Leave the needle in the bottle.
- Turn the bottle and syringe upside-down. Be sure the insulin covers the needle.
- Pull back on the plunger to the required number of units .
- Check the syringe for air bubbles. Air bubbles in the syringe will not harm you if they are injected, but they can reduce the amount of insulin in the syringe. To remove air bubbles, tap the syringe so the air bubbles rise to the top and push up on the plunger to remove the air bubbles. Recheck the dose and add more insulin to the syringe if necessary.
- Remove the needle from the insulin bottle. Carefully replace the cap on the needle.
When To Throw Away Your Insulin Pens
Youll use the same insulin pen over and over for a certain number of days. The number of days depends on the type of insulin pen youre using. The table below lists some common types of insulin pens and the number of days you can use each one. You can also read the instructions that come with your insulin pens.
| Insulin Type |
|---|
Whenever you start using a new insulin pen:
For example, if you start using a Lantus SoloStar insulin pen on January 1st, count ahead 28 days to January 28th. Write January 28 on a piece of paper tape and put the paper tape on the pen. Throw away the pen on January 28th, even if theres still insulin in it.
You can keep unused insulin pens in the refrigerator until the expiration date listed on the pen label. Once an insulin pen reaches the expiration date listed on the pen label, throw it away.
Also Check: What Do You Do If You Think You Have Diabetes