How Common Is Low Blood Glucose
Low blood glucose is common among people with type 1 diabetes and among people with type 2 diabetes who take insulin or some other diabetes medicines. In a large global study of people with diabetes who take insulin, 4 in 5 people with type 1 diabetes and nearly half of those with type 2 diabetes reported a low blood sugar event at least once over a 4-week period.2
Severely low blood glucose, defined as when your blood glucose level drops so low you cant treat it yourself, is less common. Among U.S. adults with diabetes who take insulin or some diabetes medicines that help the pancreas release insulin into the blood, 2 in 100 may develop severely low blood glucose each year.3
The Effects Of Ageing On The Responses To Hypoglycemia
Despite the increasing incidence of type 2 diabetes in young people, this condition is primarily associated with advancing age. It is pertinent therefore to consider the specific effects of ageing on the responses to hypoglycemia before examining how type 2 diabetes affects these processes.
With increasing age, the symptoms of hypoglycemia may become less intense and the symptom profile is modified . In a small British study that compared responses to hypoglycemia in seven nondiabetic adults, aged 6580 years, with six younger people, aged 2449 years, the symptom scores were significantly lower in the older group autonomic and neuroglycopenic symptoms were affected equally. A Canadian study comparing symptom responses to hypoglycemia in 10 young and 9 older nondiabetic subjects implicated attenuation of autonomic activation as the cause of the diminished symptomatic response. A further study by the same group reported that symptomatic responses were similar in 10 elderly people with and 10 without type 2 diabetes, suggesting that the decreased symptom intensity observed in their first study was associated with increasing age, independent of any effects of diabetes.
What Causes Hypoglycemia In A Child
Hypoglycemia can be a condition by itself. Or it can be a complication of diabetes or other disorder. Its most often a problem in someone with diabetes. It occurs when theres too much insulin. This is also called an insulin reaction.
Causes in children with diabetes may include:
-
Too much insulin or oral diabetes medicine
-
The wrong kind of insulin
-
Incorrect blood-glucose readings
-
Tingling feelings around the mouth
-
Seizure
-
Nightmares and confusion on awakening
The symptoms of hypoglycemia can be like other health conditions. Make sure your child sees his or her healthcare provider for a diagnosis.
Read Also: Diabetes Test App For Android
How To Test Your Blood Sugar At Home
To perform a blood sugar test, you will need to prick your finger with a lancet . Youll put a small sample of blood from this onto a strip inserted into the blood glucose meter.
Before you test your blood sugar at home, its important to find out from your doctor what a healthy blood sugar range is for you. Your doctor will determine this range based on factors such as:
- the type of diabetes you have
- how long youve had diabetes
- your age
- whether you have any other chronic health conditions
If you dont have a blood sugar testing machine on hand and are experiencing signs or symptoms of low blood sugar with diabetes, your symptoms may be enough to diagnose low blood sugar.
What Causes Reactive Hypoglycemia
Reactive hypoglycemia comes from having too much insulin in your blood. It usually happens within a few hours after you eat. Other possible causes include:
- Having prediabetes or being more likely to have diabetes
Also Check: Safest Sugar Substitute For Diabetics
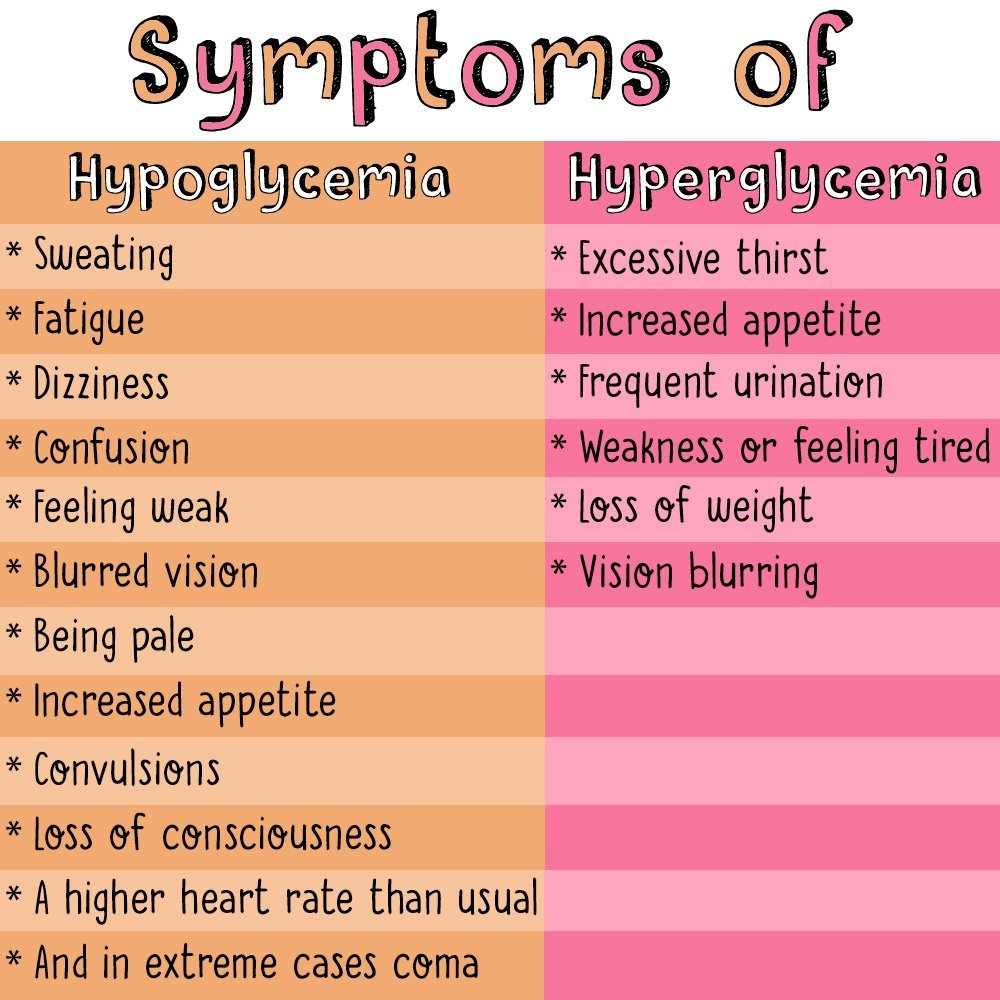
Whats The Difference Between Hyperglycemia And Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia is low blood sugar. Hyperglycemia, on the other hand, occurs when blood sugar levels are too high.
Hyperglycemia happens when you dont have enough insulin to handle the sugar. This can be because you:
- took too little insulin
- ate more than you planned
- exercised less than you thought you would
- are already feeling sick or stressed
Symptoms of hyperglycemia include thirst and frequent urination.
What Are The Common Reasons For Hypoglycemia In Diabetics
1)most common is injecting an excessive amount of insulin relative to your diet. for example you are fasting and you inject the same dose of insulin as you previously inject.
2)excessive physical activity and you injected the same amount of insulin as you use previously.
4)Infections.
1)keep your blood sugar levels optimal levels between 85-160mg/dl and Hba1c should be between 6-7.
2)avoid prolonged fast.
3)reduce your insulin dose if you are planning to have some aggressive physical activity.
4)avoid using sulfonylureas these are no longer recommended first-line drugs for diabetes .though they are cheap but they are notorious for causing hypoglycemia.
5)keep some sugary foods always in your reach there should be some dates, candies, glucose drinks, chocolates on your bedside. some times this hypoglycemia can be so sudden that you will be unable to call someone or get out of bed to get something for you. so it is always advised to have some of these items in your reach here is a list of common foods to correct your hypoglycemia rapidly:
6)should have a working glucometer in your house.
8)keep an eye on your kidney function tests.
Hope this article will help you and your loved ones in understanding some important causes of hypoglycemia and how to avoid this.
Don’t Miss: Diabetic Injection For Weight Loss
How To Treat A Low Blood Sugar Level Yourself
Follow these steps if your blood sugar level is less than 3.5mmol/L or you have hypo symptoms:
You do not usually need to get medical help once you’re feeling better if you only have a few hypos.
But tell your diabetes team if you keep having hypos or if you stop having symptoms when your blood sugar level is low.
What Causes Hypoglycemia In People Without Diabetes
Blood sugar spikes can often lead to crashes, where glucose dips too low. Here are common causes of hypoglycemia and how to avoid them.
8 min read
A basic tenet of metabolic health is that chronically elevated blood sugar has negative health consequences, including low energy, impaired brain function, and higher risk of diabetes and other chronic metabolic diseases. What you may not know: the flip side also has repercussions.
Some degree of fluctuation in blood sugar is totally normal. The amount of glucose circulating in your body rises and falls over the course of the day and its affected by factors such as food intake, exercise, stress, and sleep. Generally, glucose levels shouldpeak around an hour after a meal and be lowest after fasting overnight. However, blood sugar can sometimes dip too low for a few different reasons.
Recommended Reading: Managing Type 2 Diabetes For Dummies
Do Not Inject Insulin
If a person with diabetes is having symptoms so severe that they cannot treat themselves, such as losing consciousness, others should not inject them with insulin, as this will lower their blood glucose further.
Additionally, they should not give them food or fluids, as the person may choke.
People taking diabetes medication should work with their healthcare team to develop a management plan to prevent hypoglycemia.
Additionally, the following strategies may help avoid low blood sugar:
- checking blood glucose levels
- eating regular meals or snacks
- engaging in physical activity safely
Regularly monitoring blood glucose levels may also lower a personâs risk of developing complications from hypoglycemia.
What Is Hypoglycemia And Why Does It Happen
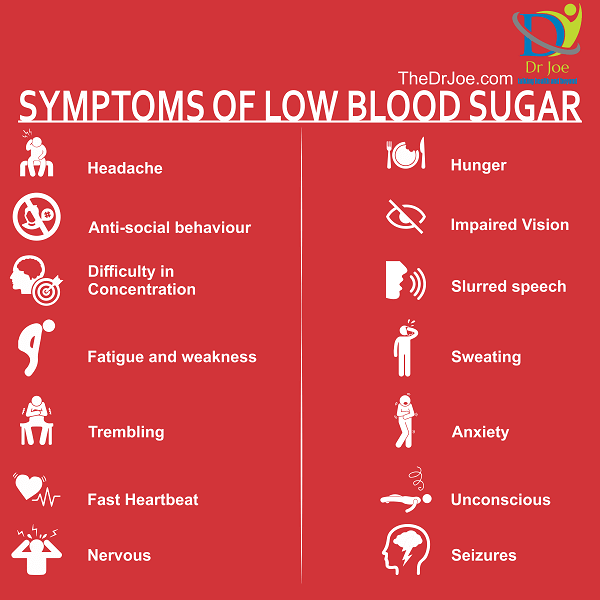
Hypoglycemia is the clinical term for what happens when blood sugar drops lower than normal for any amount of time. People who experience hypoglycemia often have symptoms including shakiness, sweating, and difficulty concentrating. Other problems includeblurred vision, confusion, and a fast heartbeat. If it happens while youre asleep , it may cause night sweats, nightmares, and interfere with sleep quality.
During a hypoglycemic episode, many symptoms arise when the brain doesnt get enough sugar. Without an adequate supply of glucose from the bloodstream, the brain triggers the release of norepinephrine and epinephrine , which may cause palpitations, tremors, and anxiety. It also triggers the release of acetylcholine, which can cause sweating and hunger. Symptoms like confusion, weakness, or blurry vision are direct results of the central nervous system being deprived of glucose.
One challenge in diagnosing hypoglycemia is that the associated symptoms could be due to an unrelated cause. Its a mistake to rely on symptoms alone, says Mary-Elizabeth Patti, MD, director of the Joslin Diabetes Center Hypoglycemia Clinic and Associate Professor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School. In the face of a nerve-wracking situation, for instance, hormones such as adrenaline may make your heart raceeven if they dont cause any major changes in blood sugar levels. Yet you might assume a quickening heartbeat means youre hypoglycemic.
You May Like: How To Control Pre Diabetic Condition
Hospitalized Patients With Hypoglycemia
At any given moment persons with diabetes constitute about 30 percent of hospitalized patients. Attitudes towards glycemic control during hospitalization have altered considerably in the last decades, changing from a strict approach with tight control to a more lenient approach with less tight control. For the majority of critically and non-critically ill patients, a target glucose range of 140-180 mg/dL is recommended. This change in recommendations is mostly based on observations that too much control often results in severe hypoglycemia and even endangers life, and thus, for diabetic patients, there is no improvement in morbidity or hospitalization parameters.
Does Everyone Have Symptoms From Hypoglycemia

Some people dont have symptoms or dont notice them. Healthcare providers call that situation hypoglycemia unawareness. People with such a challenge arent aware when they need to do something about their blood sugar. Theyre then more likely to have severe episodes and need medical help. People with hypoglycemia unawareness should check their blood sugar more often.
Don’t Miss: Is Insulin Used To Treat Type 2 Diabetes
When To Call 911
Your friend, relative, or coworker should call 911 for help if:
- You pass out and no glucagon is available
- You need a second dose of glucagon
- You had glucagon, but are still confused
- Your blood sugar stays too low 20 minutes after treatment or doesnt respond to your usual treatments
The emergency medical technicians can give you IV sugar . This raises your blood sugar level right away. You might need to stay in the hospital for a few hours.
NEVER be afraid to call 911 or ask someone to call 911 for you if you are concerned .
Other things to know about hypoglycemia:
It takes time for blood sugar to rise after eating, and its important to give your first treatment time to work. Use the table above to guide your treatment and timing instead of eating until you feel better, which will almost always lead to eating too much.
Hypoglycemia can be common with certain types of exercise. Managing blood sugar during and after physical activity is important and is something that a lot of people with T1D have questions about. JDRF has a number of resources available for people with T1D and their families, many of which can be found here.
What Is The Treatment For Hypoglycemia
The immediate treatment for hypoglycemia is to have the child eat sugar-containing foods/liquids or to give intravenous fluids. Specific treatment for hypoglycemia depends on the specific cause of the hypoglycemia and will be determined by your child’s doctor based on:
- Your child’s age, overall health and medical history
- Extent of the disorder
You May Like: Signs To Know If You Have Diabetes
What If Im Experiencing Hypoglycemic Episodes Even Though My Doctor Has Confirmed That I Dont Have Diabetes Or Prediabetes
If you have low blood sugar and dont have diabetes or , it can be a sign of another serious health issue such as a tumor, hormone deficiency, kidney disorder, anorexia, or other eating disorder, all of which can cause dangerously low blood sugar.
Anorexia has an extremely high mortality rate compared with other psychiatric disorders, according to the NIHs National Institute of Mental Health , and the cause of death can be hypoglycemia. So take your illness seriously and seek help if you suspect your eating disorder may be progressing to the point where it is causing you to faint or experience other signs and symptoms of dangerously low blood sugar. The National Eating Disorders Association has resources on how to identify the signs that you may have an eating disorder, a hotline for help, as well as easily accessible information on everything from how to know when you need help to how to find quality treatment options in your zip code.
People who are not diabetic don’t spontaneously have hypoglycemia for no reason, explains Dr. Christofides. Its often an indication of another underlying issue, such as a hormone deficiency or eating disorder, so its important to schedule an appointment with your doctor to determine the cause in order to prevent complications.
Common causes of hypoglycemia in people without diabetes include:
-
Pancreatic tumor
-
Hormone deficiencies
-
Anorexia and other eating disorders
How Can I Prevent Low Blood Sugar
Your best bet is to practice good diabetes management and learn to detect hypoglycemia so you can treat it earlybefore it gets worse.
Monitoring blood sugar, with either a meter or a CGM, is the tried and true method for preventing hypoglycemia. Studies consistently show that the more a person checks blood sugar, the lower his or her risk of hypoglycemia. This is because you can see when blood sugar levels are dropping and can treat it before it gets too low.
If you can, check often!
- Check before and after meals.
- Check before and after exercise .
- Check before bed.
- After intense exercise, also check in the middle of the night.
- Check more if things around you change such as, a new insulin routine, a different work schedule, an increase in physical activity, or travel across time zones.
You May Like: Is Diabetes 2 An Autoimmune Disease
Can Someone Without Diabetes Have Low Blood Sugar
If you don’t have diabetes, hypoglycemia can happen if your body can’t stabilize your blood sugar levels. It can also happen after meals if your body produces too much insulin. Hypoglycemia in people who don’t have diabetes is less common than hypoglycemia that occurs in people who have diabetes or related conditions.
Possible Causes Without Diabetes
Even if you dont have diabetes, you may experience low blood sugar. However, hypoglycemia is much less common in people without diabetes.
Some possible causes of low blood sugar in people who dont have diabetes are:
- certain medications, such as quinine
- some medical conditions, such as hepatitis and kidney disorders
- a tumor that produces excess insulin
- endocrine disorders, such as adrenal gland deficiency
You May Like: What Number Is Too High For Diabetes
A Low Blood Sugar Level And Driving
You may still be allowed to drive if you have diabetes or you’re at risk of a low blood sugar level for another reason, but you’ll need to do things to reduce the chance of this happening while you’re driving.
You also need to tell the Driver and Vehicle Licensing Agency and your car insurance company about your condition.
For more information, see:
Classification And Frequency Of Hypoglycemia In Diabetes
Hypoglycemia in diabetes has been defined as all episodes of abnormally low plasma glucose concentration that expose the individual to potential harm . It has been classified as the following:
Severe hypoglycemia. An event requiring assistance of another person to actively administer carbohydrate, glucagon, or other resuscitative actions.
Documented symptomatic hypoglycemia. An event during which typical symptoms of hypoglycemia are accompanied by a low measured plasma glucose concentration.
Asymptomatic hypoglycemia. An event not accompanied by typical symptoms of hypoglycemia but with a measured low plasma glucose concentration.
Probable symptomatic hypoglycemia. An event during which symptoms typical of hypoglycemia are not accompanied by a plasma glucose determination but that are presumed to be caused by a low plasma glucose concentration.
Relative hypoglycemia. An event during which the person with diabetes reports any of the typical symptoms of hypoglycemia and interprets those as indicative of hypoglycemia with a measured plasma glucose concentration that is not low.
Findings of differences in clinical associations with symptomatic and severe hypoglycemia suggest that hypoglycemic events that do or do not require the assistance of another person might be considered separately. They are related because an increase in the frequency of the former predicts the occurrence of the latter , but an episode of severe hypoglycemia is a clinical red flag that demands action.
Read Also: The Best Meal Replacement Shakes For Diabetics
What Happens In Diabetic Patients Then
In patients with long-standing diabetes, their alpha cells are burnt out and they are unable to produce enough glucagon under the period stress. As a result, their blood glucose keeps on falling and they have to take carbohydrate-rich food as soon as they feel symptoms of hypoglycemia. Otherwise, such low levels can prove fatal for them.