How Age Affects A T1d Diagnosis
There are some side effects in the overall health of a person with T1D that present themselves in time. Diabetic eye disease and kidney, nerve or circulation damage can appear in people who have had T1D for 15 years or more. With proper maintenance and routine checkups, these effects can often be limited or avoided altogether.
Fasting Plasma Glucose Test:
As the name suggests, this test is conducted when you are in a fasting state, meaning that you have not eaten for a minimum of 8 hours. A fasting plasma glucose test is thus usually conducted in the morning before breakfast.
The blood is either taken by pricking your fingertip and placing it on a strip attached to the glucometer, or a technician takes the blood from a vein in your arm. An FPG test tells you how much sugar is in your blood at the time of checking.
According to Mayo Clinic, these values suggest what stage of diabetes you are at:
| FPG status | Amount of sugar in mg/dL | Amount of sugar in mmol/L |
| Normal | ||
| 7.0 or higher |
However, researchers suggest that if your FPG is below 100 but in the range of 91-99 mg/dL, you are at risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Testing For Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
If diabetes is confirmed by the results of a blood test the type of diabetes you have is usually determined by factors like weight , age at diagnosis, family history and how quickly any symptoms came on.
The test results can also indicate if you are at risk of developing type 2 diabetes even if you dont have it now.
If youre being tested for type 1 diabetes then further blood tests can check your blood ketone levels. Following this you may be sent to hospital for further assessment.
Also Check: When You Have Type 2 Diabetes
The Role Of Glucose Testing
There are several different reasons a doctor may recommend glucose testing for you. These include screening, diagnosis, and monitoring.
Screening
Screening means using tests to find health problems before those problems cause any symptoms or signs that you or your doctor might notice.
If you are over 40, overweight or obese, or have a heightened risk of developing diabetes, your doctor may order one or more screening glucose tests to find prediabetes or diabetes. People with prediabetes have glucose levels that are higher than normal but not high enough to be diagnosed with diabetes.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is the use of tests and procedures to determine what underlying health condition might be causing noticeable signs and symptoms.
If you have symptoms of diabetes, high blood sugar, or low blood sugar, your doctor may order glucose testing for you. Glucose testing may be accompanied by other blood or urine tests to make an accurate diagnosis.
Monitoring
If you have been diagnosed with diabetes or prediabetes, your doctor may want you to track your blood glucose levels with an at-home glucose testing or monitoring device. Your doctor may also recommend periodic laboratory testing during check-ups to learn how your condition is being managed.
Fasting Plasma Glucose Test
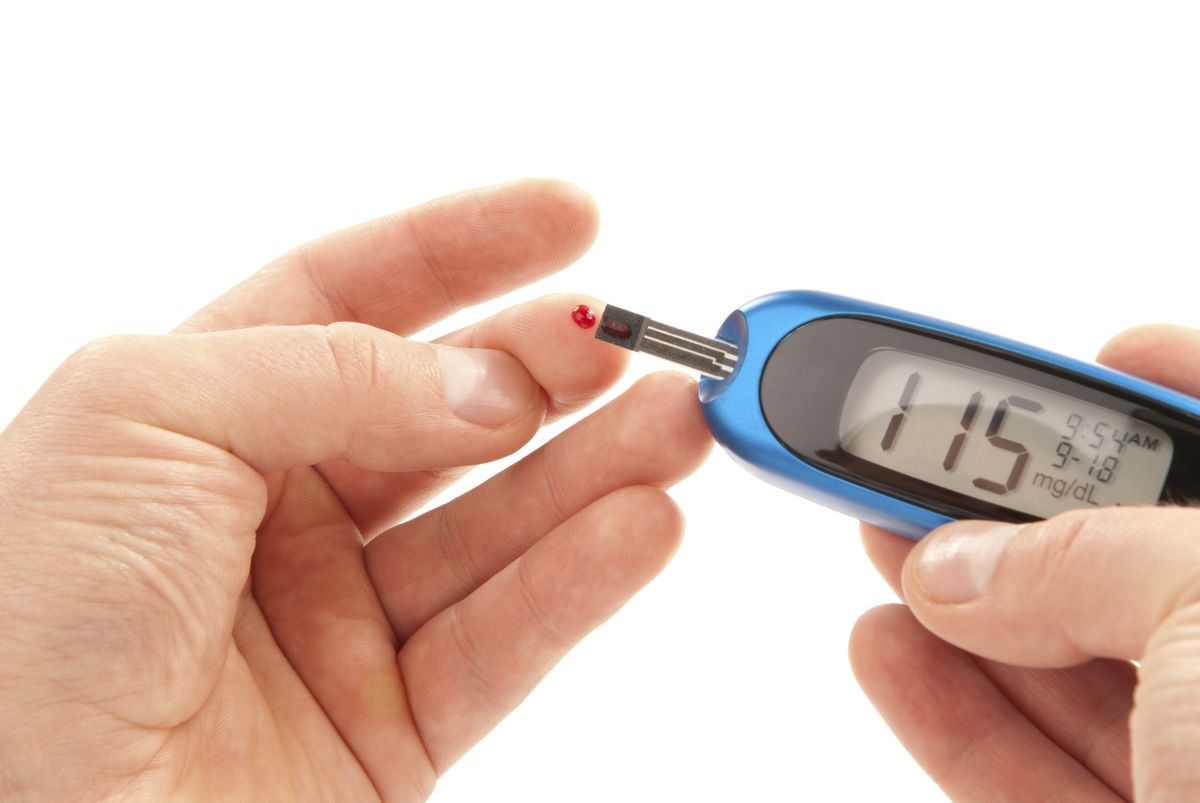
The FPG is most reliable when done in the morning. Results and their meaning are shown in table 1. If your fasting glucose level is 100 to 125 mg/dL, you have a form of prediabetes called impaired fasting glucose , meaning that you are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes but do not have it yet. A level of 126 mg/dL or above, confirmed by repeating the test on another day, means that you have diabetes.
Table 1. Fasting Plasma Glucose Test
| Plasma Glucose Result |
*Confirmed by repeating the test on a different day.
Also Check: When Is Insulin Needed For Type 2 Diabetes
What Is The A1c Test
The A1C test is a blood test that provides information about your average levels of blood glucose, also called blood sugar, over the past 3 months. The A1C test can be used to diagnose type 2 diabetes and prediabetes.1 The A1C test is also the primary test used for diabetes management.
The A1C test is sometimes called the hemoglobin A1C, HbA1c, glycated hemoglobin, or glycohemoglobin test. Hemoglobin is the part of a red blood cell that carries oxygen to the cells. Glucose attaches to or binds with hemoglobin in your blood cells, and the A1C test is based on this attachment of glucose to hemoglobin.
The higher the glucose level in your bloodstream, the more glucose will attach to the hemoglobin. The A1C test measures the amount of hemoglobin with attached glucose and reflects your average blood glucose levels over the past 3 months.
The A1C test result is reported as a percentage. The higher the percentage, the higher your blood glucose levels have been. A normal A1C level is below 5.7 percent.
Maintain A Healthy Weight
Eating a balanced diet and exercising can help you lose or maintain weight. Ask your doctor what a healthy weight is for you.
Work with them to determine how many calories you should be eating. If you need to lose weight, ask them how much weight you should be losing per week to stay healthy.
Crash diets and extreme workout plans may make for entertaining television, but they arent realistic for long-term maintenance. Theyre often unhealthy as well.
Also Check: Type 1 Diabetes Symptoms In Adults
What Should My Blood Glucose Level Be
Ask your healthcare team what your blood glucose level should be. They may have a specific target range for you. In general, though, most people try to keep their blood glucose levels at these targets:
- Before a meal: between 80 and 130 mg/dL.
- About two hours after the start of a meal: less than 180 mg/dL.
Can Prediabetes Type 2 Diabetes And Gestational Diabetes Be Prevented
Although diabetes risk factors like family history and race cant be changed, there are other risk factors that you do have some control over. Adopting some of the healthy lifestyle habits listed below can improve these modifiable risk factors and help to decrease your chances of getting diabetes:
- Eat a healthy diet, such as the Mediterranean or Dash diet. Keep a food diary and calorie count of everything you eat. Cutting 250 calories per day can help you lose ½ pound per week.
- Get physically active. Aim for 30 minutes a day at least five days a week. Start slow and work up to this amount or break up these minutes into more doable 10 minute segments. Walking is great exercise.
- Lose weight if you are overweight. Dont lose weight if you are pregnant, but check with your obstetrician about healthy weight gain during your pregnancy.
- Lower your stress. Learn relaxation techniques, deep breathing exercises, mindful meditation, yoga and other helpful strategies.
- Limit alcohol intake. Men should drink no more than two alcoholic beverages a day women should drink no more than one.
- Get an adequate amount of sleep .
- Take medications to manage existing risk factors for heart disease or to reduce the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes as directed by your healthcare provider.
- If you think you have symptoms of prediabetes, see your provider.
Don’t Miss: Type 1 Diabetes Emergency Kit
Why So Many Tests Can’t Diabetes Be Diagnosed By An Elevated Blood Sugar Value Alone
Elevated fasting blood and urine glucose values are absolutely essential for the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus, but other screening tests provide additional information about the severity of the diabetes, any conditions that may be contributing to the diabetes, and any complications related to the diabetic state.
Because diabetes mellitus is usually diagnosed in middle-aged to older cats, your cat may have other unrelated conditions that need to be managed along with diabetes. The screening tests will usually alert your veterinarian to any such conditions.
Our Diabetes Panel Includes The Following:
Hemoglobin A1c / Glycohemoglobin – The Hemoglobin A1c test evaluates the average amount of glucose in the blood over the past 8-12 weeks.
Random Microalbumin, Urine Test – Healthy kidneys filter waste and toxins from the blood and hang on to the healthy components, including proteins such as albumin. Kidney damage can cause proteins to leak through the kidneys and exit the body via urine. Albumin is one of the first proteins to leak when the kidneys become damaged.
Comprehensive Metabolic Panel – This panel contains 14 different measurements that collectively provide a look at the overall health of your metabolism. This test is used as a broad screening tool to evaluate organ function and check for conditions such as diabetes, liver disease, and kidney disease. CMPs are commonly ordered as part of routine blood work or are recommended by doctors as part of an annual physical.
The 14 measurements in the CMP panel include:
In addition to the 14 measurements, the CMP test also includes the following calculations:
- Albumin/Globulin Ratio – The A/G ratio is calculated from measured total protein, measured albumin, and calculated globulin to help diagnose diseases.
- BUN/Creatinine Ratio – The ratio of BUN to creatinine is usually between 10:1 and 20:1. An increased ratio may be due to a condition that causes a decrease in the flow of blood to the kidneys.
Read Also: Pathophysiology Of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
Can Diabetes Cause Hearing Loss
Scientists dont have firm answers yet but there appears to be a correlation between hearing loss and diabetes. According to the American Diabetes Association, a recent study found that hearing loss was twice as common in people with diabetes versus those who didnt have diabetes. Also, the rate of hearing loss in people with prediabetes was 30% higher compared with those who had normal blood glucose levels. Scientists think diabetes damages the blood vessels in the inner ear, but more research is needed.
The Honeymoon Phase And Treatment

No matter how good A1C or blood-sugar tests are during the honeymoon phase, the disease is still present and killing beta cells. During this phase, physicians will help maintain blood-glucose management with low-dose insulin treatments. Eventually, the remaining healthy cells will die off and insulin dosages will need to be increased.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Rid Of Diabetes Type 1
Who Should Have A Diabetes Test
You should have a diabetes test if you are at a high risk of type 2 diabetes. An AUSDRISK score of 12 or more is considered high risk.
You may also be at high risk of diabetes if you:
- have had a heart attack or stroke
- have had gestational diabetes
- take medications to treat psychosis
You should have a diabetes test every year if you have pre-diabetes.
What Insulin Medications Are Approved To Treat Diabetes
There are many types of insulins for diabetes. If you need insulin, you healthcare team will discuss the different types and if they are to be combined with oral medications. To follow is a brief review of insulin types.
- Rapid-acting insulins: These insulins are taken 15 minutes before meals, they peak at one hour and work for another two to four hours. Examples include insulin glulisine , insulin lispro and insulin aspart .
- Short-acting insulins: These insulins take about 30 minutes to reach your bloodstream, reach their peak effects in two to three hours and last for three to six hours. An example is insulin regular .
- Intermediate-acting insulins: These insulins reach your bloodstream in two to four hours, peak in four to 12 hours and work for up to 18 hours. An example in NPH.
- Long-acting insulins: These insulins work to keep your blood sugar stable all day. Usually, these insulins last for about 18 hours. Examples include insulin glargine , insulin detemir and insulin degludec .
There are insulins that are a combination of different insulins. There are also insulins that are combined with a GLP-1 receptor agonist medication .
Recommended Reading: Does Viagra Work For Diabetics
How Does A Blood Test Determine If You Have Type 1 Diabetes
Answer:
Diagnosis of diabetes is arbitrary and the American Diabetes Association and WHO determine what the blood sugar cut-off levels will be However, type 1 diabetes in childhood is universally accompanied by symptoms and would almost never be diagnosed without them.
[Editors comment: See: Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes Guidelines.
Type 1A diabetes can be distinguished from type 1B or type 2 diabetes by measuring antibodies In type 1A, antibodies will be positive. In type 1B, insulin therapy may or may not be needed.
Friday, February 18, 2022 18:08:45 UTC
This internet site provides information of a general nature and is designed for educational purposes only. If you have any concerns about your own health or the health of your child, you should always consult with a physician or other health care professional.
This site is published by T-1 Today, Inc. , a 501c3 not-for-profit organization, which is responsible for its contents. By using this site, you agree to our Terms of Use, Legal Notice and Privacy Policy.
Children with Diabetes.com © 1995-2021 Children with Diabetes, Inc. | | All Rights Reserved.
Social
When Should I Call My Doctor
If you havent been diagnosed with diabetes, you should see your healthcare provider if you have any symptoms of diabetes. If you already have been diagnosed with diabetes, you should contact your provider if your blood glucose levels are outside of your target range, if current symptoms worsen or if you develop any new symptoms.
You May Like: When Is Insulin Prescribed For Type 2 Diabetes
Symptoms Diagnosis And Monitoring Of Diabetes
Nearly 33 million American adults have Type 2 diabetes and many dont know it. Type 1 diabetes often remains undiagnosed until symptoms become so severe that hospitalization is required.
Both of these facts speak to a larger truth: Left untreated, diabetes can cause many health complications. Thats why its crucial to know the warning signs and to see a healthcare professional regularly for routine wellness screenings.
Recommended Target Blood Glucose Level Ranges
The NICE recommended target blood glucose levels are stated below for adults with type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes and children with type 1 diabetes.
In addition, the International Diabetes Federations target ranges for people without diabetes is stated.
The table provides general guidance. An individual target set by your healthcare team is the one you should aim for.
| Target Levels |
|---|
*The non-diabetic figures are provided for information but are not part of NICE guidelines.
You May Like: Reversing Type 2 Diabetes With Ketogenic Diet
Are There Other Treatment Options For Diabetes
Yes. There are two types of transplantations that might be an option for a select number of patients who have Type 1 diabetes. A pancreas transplant is possible. However, getting an organ transplant requires taking immune-suppressing drugs for the rest of your life and dealing with the side effects of these drugs. However, if the transplant is successful, youll likely be able to stop taking insulin.
Another type of transplant is a pancreatic islet transplant. In this transplant, clusters of islet cells are transplanted from an organ donor into your pancreas to replace those that have been destroyed.
Another treatment under research for Type 1 diabetes is immunotherapy. Since Type 1 is an immune system disease, immunotherapy holds promise as a way to use medication to turn off the parts of the immune system that cause Type 1 disease.
Bariatric surgery is another treatment option thats an indirect treatment for diabetes. Bariatric surgery is an option if you have Type 2 diabetes, are obese and considered a good candidate for this type of surgery. Much improved blood glucose levels are seen in people who have lost a significant amount of weight.
Of course other medications are prescribed to treat any existing health problems that contribute to increasing your risk of developing diabetes. These conditions include high blood pressure, high cholesterol and other heart-related diseases.
Is There Anything Else I Need To Know About Diabetes Testing
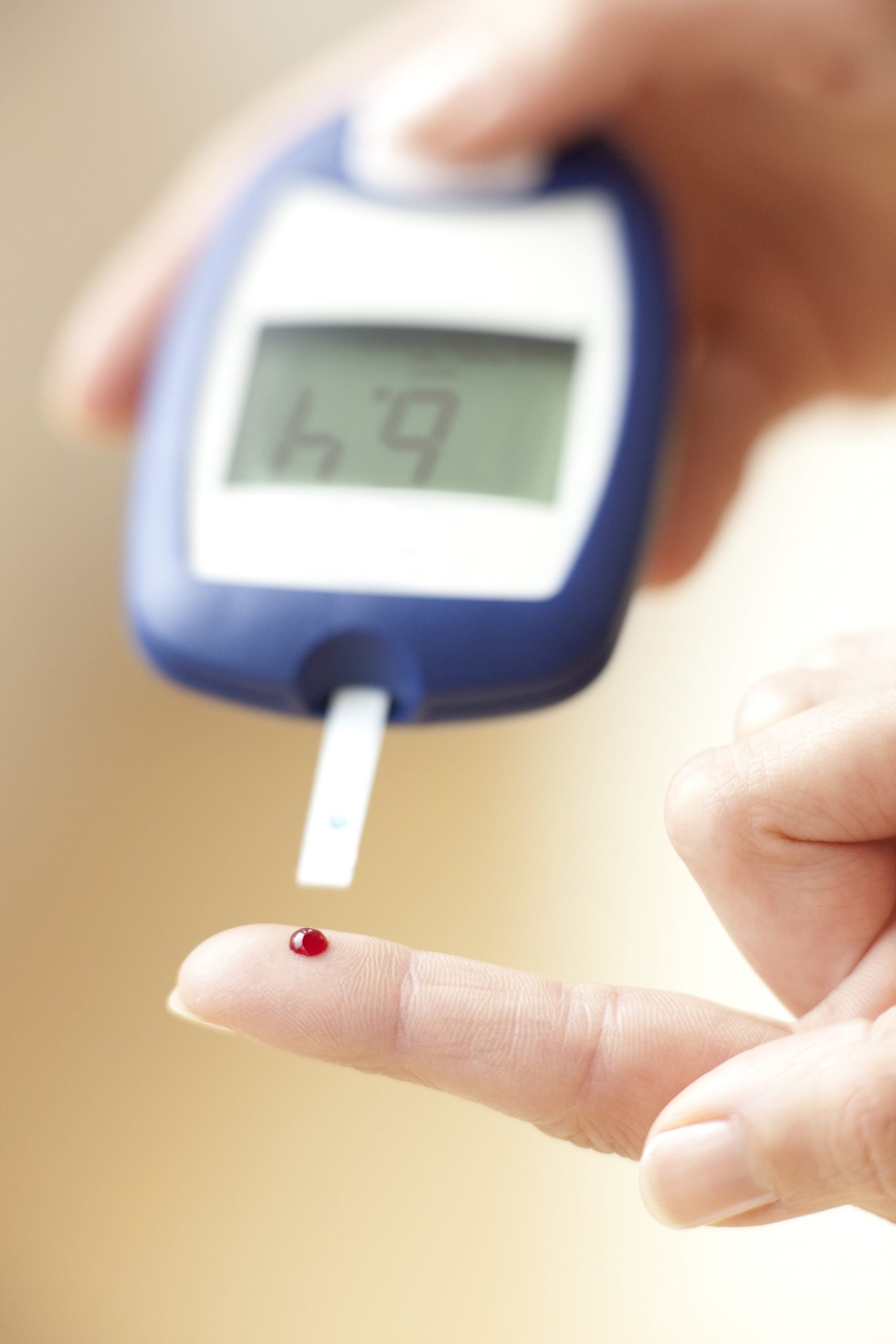
If you’ve been diagnosed with type 1 diabetes, you will need to monitor blood glucose levels daily, often several times a day. Your health care provider can recommend a kit you can use at home. Most kits include a lancet, a device that pricks your finger. You will use this to collect a drop of blood for testing. There are some newer kits available that don’t require pricking your finger. Some pregnant women with gestational diabetes may also need to monitor their glucose levels in this way.
People with type 2 diabetes will also have to check their blood sugar on a regular basis. If you have type 2 diabetes, talk to your provider about how often it should be checked.
People with type 2 diabetes may also need to have their insulin levels checked regularly. Insulin plays a key role in keeping glucose at the right levels. An insulin in blood test is done at a provider’s office.
Don’t Miss: Sure Comfort Insulin Syringes 30 Gauge
Where Can I Get Blood Work Done
There are different locations that offer laboratory services that include blood work. Most hospitals contain a laboratory that you can visit to get tests done. Some laboratories will have walk-in options. Others may require an appointment.
Additional locations for blood testing may include:
- Private laboratories. Hospitals may use private labs to offload some testing from their own laboratories, or in cases when a specialized test is needed. Often, health insurance plans will require you to use a specific laboratory that is in their network for the test to be covered.
- Point-of care. This describes situations when you may need to get a blood test wherever you are receiving medical care. In routine scenarios, this typically
Results may take anywhere from a few hours to a few days to become available. Heres an overview of how long some common tests may take:
- complete blood count : 24 hours
- basic metabolic panel: 24 hours
- complete metabolic panel: 24 to 72 hours
- lipid panel: 24 hours
Timing can depend on the specific lab where you get tested, and how many tests you get done at once. If you order multiple tests, you may not get the complete results until all of the tests are completed.
Sometimes a lab will only release results to your doctor, who reviews them and then releases them to you.