What Is The Best Time To Take Metformin
Standard metformin is taken two or three times per day. Be sure to take it with meals to reduce the stomach and bowel side effects that can occur most people take metformin with breakfast and dinner.
Extended-release metformin is taken once a day and should be taken at night, with dinner. This can help to treat high glucose levels overnight.
Will My Dose Go Up Or Down
Your doctor will check your blood sugar levels regularly and may change your dose of metformin if necessary.
When you first start taking metformin standard-release tablets, you’ll be advised to increase the dose slowly. This reduces the chances of getting side effects.
For example:
- one 500mg tablet with or after breakfast for at least 1 week, then
- one 500mg tablet with or after breakfast and your evening meal for at least 1 week, then
- one 500mg tablet with or after breakfast, lunch and your evening meal
If you find you cannot tolerate the side effects of standard-release metformin, your doctor may suggest switching to slow-release tablets.
Metformin Use In Childhood And Adolescence
Type 2 diabetes mellitus has dramatically increased in children and adolescents worldwide to the extent that has been labeled an epidemic . Before 1990, it was a rare condition in the pediatric population by 1999, the incidence varied from 8% to 45%, depending on geographic location, and was disproportionally represented among minority groups . There are few studies of metformin use in the pediatric population. Most of them are of short duration and heterogeneous designs.
The beneficial role of metformin in young patients with type 2 diabetes has been demonstrated in a randomized, controlled trial which showed a significant decrease in fasting blood glucose, HbA1c, weight, and total cholesterol. The most frequently reported adverse events were abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea/vomiting, and headaches. There were no cases of clinical hypoglycemia, lactic acidosis, or clinically significant changes in physical examinations . When compared to glimepiride , metformin lowered HbA1c to < 7%, similar to glimepiride, but was associated with significantly less weight gain. A total of 42.4% and 48.1% of subjects in the glimepiride and metformin groups, respectively, in the intent-to-treat population achieved A1C levels of < 7.0% at week 24 .
You May Like: Insulin Pills For Type 1 Diabetes
Metformin Interactions: What Should I Avoid While Taking Metformin
When taken at the same time, some drugs may interfere with metformin. Make sure your healthcare team is aware of any medications that you take before you start on metformin, especially certain types of diuretics and antibiotics. Remember, insulin and insulin releasing medications can increase your risk of hypoglycemia, so it is particularly important to carefully monitor your glucose levels.
You should also avoid drinking excessive amounts of alcohol while taking metformin aim for no more than one glass per day for women, and two per day for men. Alcohol can contribute to lactic acidosis.
How Should This Medicine Be Used
Metformin comes as a liquid, a tablet, and an extended-release tablet to take by mouth. The liquid is usually taken with meals one or two times a day. The regular tablet is usually taken with meals two or three times a day. The extended-release tablet is usually taken once daily with the evening meal. To help you remember to take metformin, take it around the same time every day. Follow the directions on your prescription label carefully, and ask your doctor or pharmacist to explain any part you do not understand. Take metformin exactly as directed. Do not take more or less of it or take it more often than prescribed by your doctor.
Swallow metformin extended-release tablets whole do not split, chew, or crush them.
Your doctor may start you on a low dose of metformin and gradually increase your dose not more often than once every 1â2 weeks. You will need to monitor your blood sugar carefully so your doctor will be able to tell how well metformin is working.
Metformin controls diabetes but does not cure it. Continue to take metformin even if you feel well. Do not stop taking metformin without talking to your doctor.
Ask your pharmacist or doctor for a copy of the manufacturer’s information for the patient.
Also Check: Can Diabetics Eat Activia Yogurt
Can I Drink Alcohol While Taking Metformin
While you can drink whilst taking Metformin, it is advisable that you drink no more than 2 units a day.
Avoid binge drinking or drinking in excess of the recommended weekly limit of 14 units.
Drinking alcohol increases the risk of low blood sugar levels . It also increased your risk of lactic acidosis.
How To Take Metformin
Metformin is only available by prescription. It comes in a tablet, extended-release tablet, or oral solution, and is usually taken twice a day at breakfast and at dinner. Some patients may be instructed to take metformin three times a day, one with each meal. Take Metformin with a meal to help decrease the likelihood of an upset stomach.
The Mayo Clinic states that when it comes to taking the extended-release metformin tablet, you should take it with a full glass of water and make sure not to crush, break, or chew it. Also, be aware that part of the extended-release tablet may pass in your stool and this is considered normal and not an issue of concern. The extended-release tablet is generally taken once a day in the morning.
Also recommended is to take the brand of metformin that your doctor prescribes since other brands of metformin may not work the same.
Recommended Reading: Medtronic Vs Tandem Insulin Pump
When To Take Metformin
Metformin usually takes a few days to perhaps a week to develop its full effect. In that time and even after its good to decide a time that works best for you.
From a healthcare professionals point of view, most recommend that you take metformin during suppertime. Or with your evening meal atleast. This is to avoid side effects like nausea/vomiting. However, some have found that they actually benefit more when taking metformin at bedtime instead. This is because when they wake up the following morning, their blood sugar levels are even lower. This option may work for those who struggle with morning hyperglycemia .
My Doctor Wants Me To Take Metformin But Im Concerned About Side Effects What Are The Most Common Side Effects
The most common side effect of metformin is gastrointestinal: diarrhea, bloating, gas, and abdominal discomfort. This occurs in a small percentage of patients and it generally goes away within 2 weeks as the body adjusts to the medication.
Other side effects include: risk of vitamin B12 deficiency and lactic acidosis .
You May Like: What To Do If You Think Your Diabetic
Signs Metformin Is Not Working
If your blood sugar is elevated due to a large meal or because of a stressful day, you don’t need to be alarmed. However, if you notice a pattern of high blood sugars it may mean that you need a change in your treatment plan. Elevated blood sugar levels for several days without explanation can be a sign that your metformin is no longer working or that your dose needs to be changed.
Type 2 diabetes is a progressive disease and, in some people, maintenance of blood sugar control with one drug is often possible for only a few years. After that time, you may need additional medicine.
Your blood sugars can also be impacted by:
- Diet
- Hormones
- Illness
Perhaps you have been taking metformin for a while but haven’t improved your diet or you stopped exercising. These changes can impact your blood sugar, so it’s important to always work on any behavioral or lifestyle changes that can improve them.
If it is unclear why your blood sugar is elevated, collaborate with your healthcare provider and meet with a certified diabetes care and education specialist who can help with your specific needs.
What Are Warnings And Precautions For Metformin
Warnings
Metformin has moderate interactions with at least 74 different drugs.
Keep out of reach of children. In case of overdose, get medical help or contact a Poison Control Center immediately.
Contraindications
Contraindication includes hypersensitivity, chronicheart failure, metabolic acidosis with or without coma, diabetic ketoacidosis , severe renal disease, abnormal creatinine clearance resulting from shock, , or myocardial infarction and lactation.
Effects of Drug Abuse
There are no effects of drug abuse from the use of metformin.
Short-Term Effects
There are no short-term effects from the use of metformin.
Long-Term Effects
There are no long-term effects from the use of metformin.
Cautions
Use with caution in patients with congestive heart failure, fever, trauma, surgery, the elderly, renal impairment, or hepatic impairment.
Instruct patients to avoid heavy alcohol use.
Suspend therapy prior to any type of surgery.
Rare, but serious, lactic acidosis can occur due to accumulation.
Possible increased risk of cardiovascular mortality.
May cause ovulation in anovulatory and premenopausal polycystic ovary syndrome patients.
It may be necessary to discontinue therapy with metformin and administer insulin if patient is exposed to stress .
Ethanol may potentiate metformin’s effect on lactate metabolism.
May impair vitamin B12 or calcium intake/absorption monitor B12serum concentrations periodically with long-term therapy.
Iodinated contrast imaging procedures.
Recommended Reading: How I Reversed My Diabetes
How And When To Take It
Take metformin tablets with or after a meal to reduce the side effects. Swallow your metformin tablets whole with water. Do not chew them.
Metformin tablets come in different strengths. Your doctor will tell you how many tablets to take a day.
When you first start taking metformin, you’ll be advised to increase the dose slowly. This reduces the chances of getting side effects.
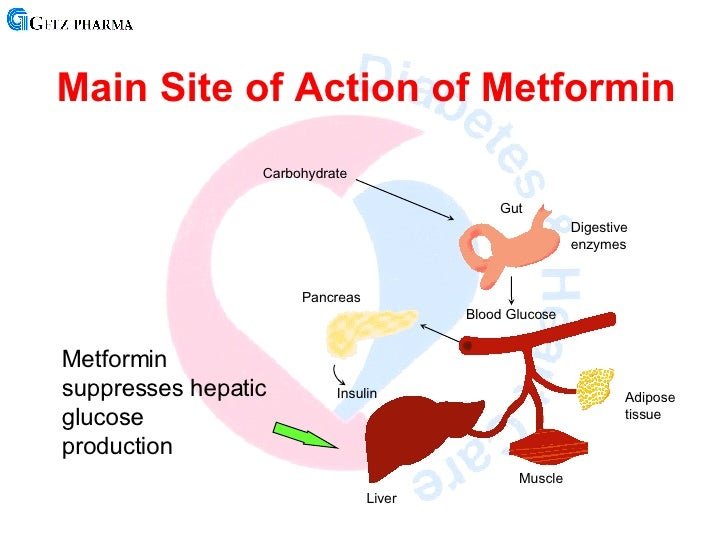
How Does Metformin Help Treat Type 2 Diabetes
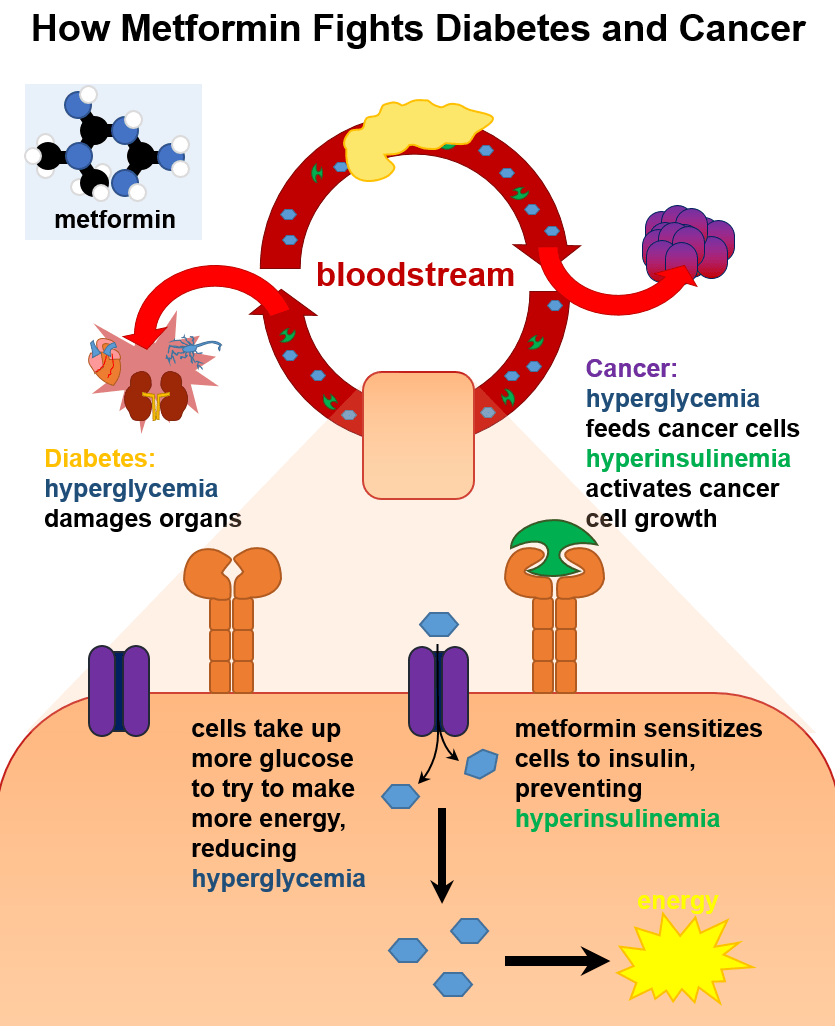
Metformin is a prescription medication that is used to treat type 2 diabetes. It helps to control blood sugar by decreasing the amount of sugar that is produced in the liver, increasing the sensitivity of insulin receptors and limiting the amount of sugar that is absorbed by the body from food. It may be combined with other treatments like insulin. This medication is used in conjunction with exercise and diet.
Don’t Miss: What Do You Do If You Think You Have Diabetes
Sign Up For The Better Registry
References
- Livingstone, R., Boyle, J.G., Petrie, J.R., et al. . A new perspective on metformin therapy in type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia, 60, 15941600.
- Meng, H., Zhang, A., Liang, Y., Hao, J., Zhang, X., Lu, J. . Effect of metformin on glycaemic control in patients with type 1 diabetes: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews, 34. doi:10.1002/dmrr.2983
Metformin For Type 1 Diabetes
Metformin is not formally approved for use in type 1 diabetes, but its sometimes prescribed off-label, especially for patients with obesity or overweight, or those that have issues with insulin resistance.
Many doctors have assumed that metformin would enhance glucose control in patients with type 1 for the same reasons that it works in patients with type 2. Clinical evidence, however, has been mixed, with some trials showing good results and others indicating no benefit for glycemic management. The drug may result in modest improvements in LDL-cholesterol, weight, and kidney function.
Don’t Miss: What Foods Help Produce Insulin
Metformin In The Management Of Adult Diabetic Patients
Current guidelines from the American Diabetes Association/European Association for the Study of Diabetes and the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists/American College of Endocrinology recommend early initiation of metformin as a first-line drug for monotherapy and combination therapy for patients with T2DM. This recommendation is based primarily on metformins glucose-lowering effects, relatively low cost, and generally low level of side effects, including the absence of weight gain .
Metformins first-line position was strengthened by the United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study observation that the metformin-treated group had risk reductions of 32% for any diabetes-related endpoint, 42% for diabetes-related death , and 36% for all-cause mortality compared with the control group. The UKPDS demonstrated that metformin is as effective as sulfonylurea in controlling blood glucose levels of obese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus . Metformin has been also been shown to be effective in normal weight patients .
Effects On Thyroid Function
Metformin decreases serum levels of thyrotropin to subnormal levels in hypothyroid patients that use levothyroxin on a regular basis . A significant decrease in TSH without reciprocal changes in any thyroid function parameter in diabetic patients had also been reported but only in hypothyroid subjects, not in euthyroid ones .
The mechanism of the drop in TSH is unclear at this time. Some of the proposed explanations for this effect are enhanced inhibitory modulation of thyroid hormones on central TSH secretion, improved thyroid reserve in patients with hypothyroidism , changes in the affinity or the number of thyroid hormone receptors, increased dopaminergic tone, or induced constituent activation of the TSH receptor .
Recommended Reading: When Is Insulin Needed For Type 2 Diabetes
Managing Metformin Side Effects
Some side effects go away on their own over time. There are a few ways you can ease or avoid problems:
- Ask to start at a low dose. This makes it easier for your body to adjust to the medicine.
- Take metformin with food. Itâs OK to take the medicine on an empty stomach, but having it with a meal makes it easier to handle.
- Ask about the extended-release form of metformin. Youâll take it once a day rather than twice. Because it doesnât release the drug in one burst, side effects are often milder. In one study, just 10% of people who took the extended-release form had diarrhea, compared with 53% of those who took the standard formula. Just 7% had nausea, compared with 26%. And fewer than 1% of those on extended-release metformin had to stop taking it because of side effects.
When Will I See Results
Metformin does not necessarily lead to an overnight improvement in blood sugar levels. It may take a week or two to notice improvement, and several months to experience the peak of action.
Continue to check your blood sugar as prescribed by your healthcare provider and log your results. This way, you can provide your healthcare provider valuable information regarding how your metformin dose is working for you, and they will be much better equipped to adjust your dosage in the future.
Recommended Reading: Does Chromium Picolinate Help With Diabetes
How Does Metformin Work For Prediabetes And Insulin Resistance
It is now being reported that many doctors have started to prescribe metformin for prediabetes or those with suspected insulin resistance.
Both conditions, prediabetes and insulin resistance, can be treated with metformin effectively but it is important to treat the cause instead of simply the symptoms. Thats why changing dietary patterns, adopting more physical activity throughout the day, targeting stress levels and treating any hormonal imbalances naturally should be made a priority first.
Should I Expect Immediate Results From Metformin
Results vary from person to person, but will probably take a minimum of a few days to a week to see changes. Most often people will need to gradually increase the dosage over time before they start seeing numbers come down. If you dont see any difference in a month it probably isnt having much of an effect.
Read Also: Cost Of Tandem Insulin Pump
Metformin Indications For Management Of Obesity Insulin Resistance And Non
Insulin resistance in obese children and adolescents should be appropriately and aggressively addressed once it is linked to known cardiovascular risks such as IGT, T2DM, dyslipidemia, and hypertension . Non-alcoholic fatty disease, a frequent cause of chronic liver disease in obese adults, is also associated with a higher risk of developing diabetes and of progression to fibrosis and cirrhosis with an increased relative risk of cardiovascular events or death . The true prevalence of NAFLD in children is underestimated. The prevalence of steatosis in obese children was estimated to be 38% in a large retrospective autopsy study .
Currently, the best supported therapy for NAFLD is gradual weight loss through exercise and nutritional support . Metformin is associated with short-term weight loss, improvement of insulin sensitivity, and decreased visceral fat . A reduction in ALT, GGT, and fatty liver incidence and severity has also been described with metformin use .
Metformin may not be as effective as behavioral interventions in reducing BMI and when compared with drugs that are licensed for obesity, its effects are moderate .
Risks Or Side Effects Of Taking Metformin
If you are taking the drug for the effective management of diabetes, you should be aware of the risks and side effects which the drug might cause. Following are the associated risks:
Given the risks associated with taking Metformin, an expert advice is a must before going for the medicine.
We hope that the above post has been helpful in educating you about Metformin and how the drug is used for combatting diabetes. However, a word of precaution needs to be mentioned here: the drug may not be meant for all types of patients and as such, you need to be extremely cautious while taking it and any type of side-effect felt should immediately be communicated to the doctor who might have prescribed Metformin. In the case of regular side-effects, you need to stop the dosage at the earliest possible time!!
Also Check: What Is Good For Diabetic Dry Skin
Diabetes : What Is Metformin
Metformin is so popular because it is inexpensive and can reduce the glucose level and A1C the most compared with other diabetes medications, says Dr. Griebeler.
RELATED: How to Treat Diabetes From the Inside Out
Metformin is generally part of a diabetes-maintenance plan, and it works in conjunction with a healthy diet and exercise routine. Its usually taken twice a day with meals and can take anywhere from one week to two months to see blood sugar improvements, according to the Mayo Clinic.