Types Of Insulin Treatments
All types of insulin produce the same effect. They are used to mimic the natural increases and decreases of insulin levels in the body during the day. The makeup of different types of insulin affects how fast and how long they work.
The type of insulin youll be prescribed will vary depending on things like:
- how long it takes your body to absorb insulin
- how long insulin stays active in your system
| Insulin type | ||
|---|---|---|
| varied peaks | 10 to 16 hours | Taken twice a day, commonly 10 to 30 minutes before breakfast and dinner. This type is a combination of intermediate- and short-acting insulin. |
Talk with a doctor about the right insulin for you and your lifestyle.
Insulin Synthesis And Secretion
Insulin is a small protein, with a molecular weight of about 6000 Daltons. It is composed of two chains held together by disulfide bonds. The figure to the right shows a molecular model of bovine insulin, with the A chain colored blue and the larger B chain green. You can get a better appreciation for the structure of insulin by manipulating such a model yourself.
The amino acid sequence is highly conserved among vertebrates, and insulin from one mammal almost certainly is biologically active in another. Even today, many diabetic patients are treated with insulin extracted from pig pancreas.
Biosynthesis of Insulin
Insulin is synthesized in significant quantities only in beta cells in the pancreas. The insulin mRNA is translated as a single chain precursor called preproinsulin, and removal of its signal peptide during insertion into the endoplasmic reticulum generates proinsulin.
Proinsulin consists of three domains: an amino-terminal B chain, a carboxy-terminal A chain and a connecting peptide in the middle known as the C peptide. Within the endoplasmic reticulum, proinsulin is exposed to several specific endopeptidases which excise the C peptide, thereby generating the mature form of insulin. Insulin and free C peptide are packaged in the Golgi into secretory granules which accumulate in the cytoplasm.
Control of Insulin Secretion
Advanced and Supplemental Topics
What Causes Someone To Be Prescribed Insulin
If your body doesnt make insulin or doesnt make enough, you are eventually diagnosed with type 1 diabetes. It used to be called juvenile diabetes, but new estimates show that as many as half of people with type 1 diabetes are not diagnosed until adulthood. On the other hand, if your body doesnt use insulin properly, you have type 2 diabetes.
While people with type 1 diabetes need to take insulin to survive, many people with type 2 are able to stave off insulin use or even avoid it altogether by exercising, losing weight, adapting healthier eating habits, or using other prescription medications.
You May Like: Do You Give Insulin If Blood Sugar Is Low
Cell Isolation By Centrifugation
Cell isolation is the first step in down streaming of the insulin made by transformed E. coli cells. This process is also referred to as cell harvesting because the proinsulin inclusion bodies are harvested using both filtration and centrifugation. Since E. coli has the highest density of all the components in the growth medium, the bacterial cells settle to the bottom after centrifugation at 7500 x g for 10 minutes. Then the supernatant is discarded and the dense mixture left behind is further processed since it contains a higher concentration of bacterial cells40.
Produced In The Pancreas
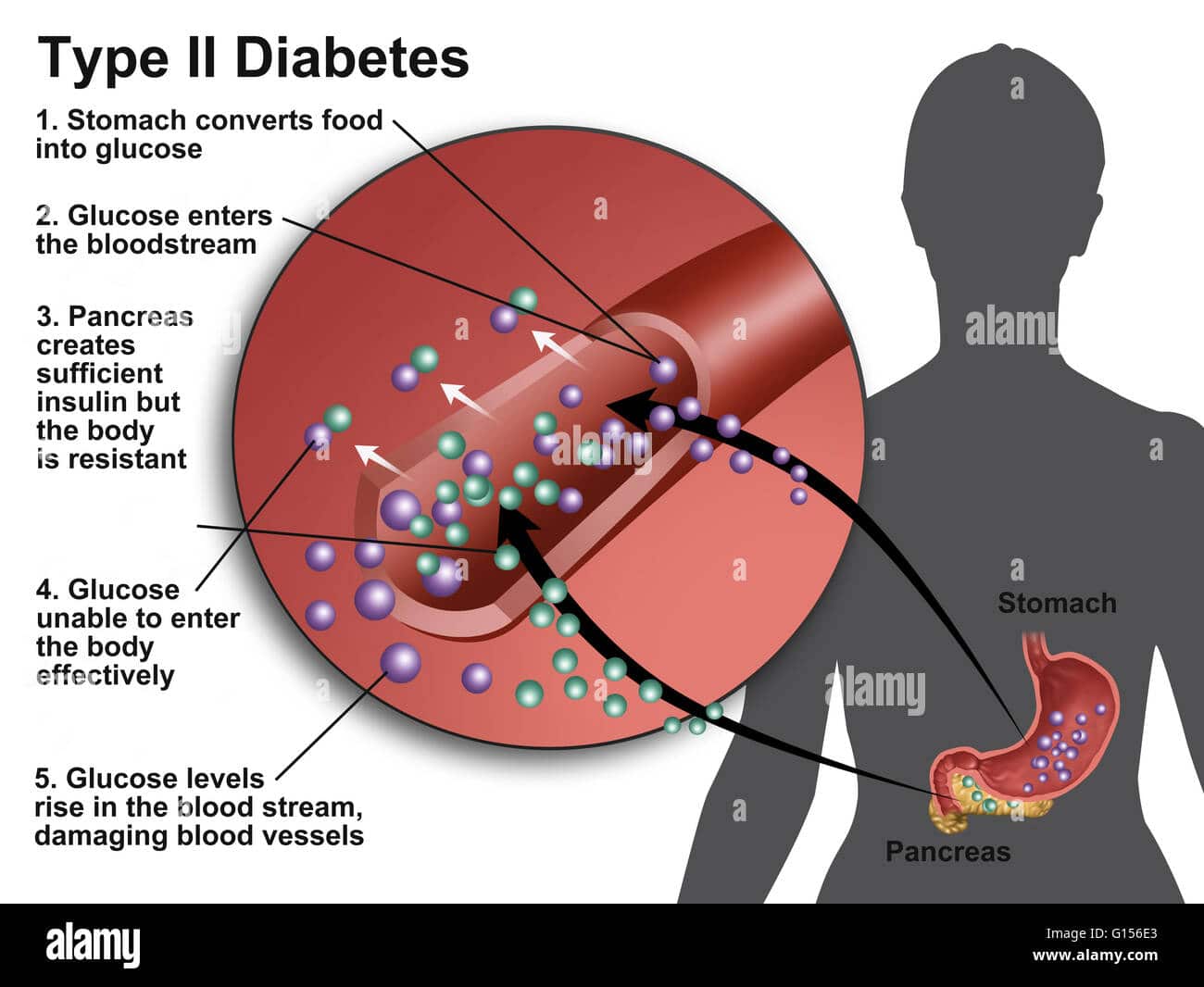
When you eat, food travels to your stomach and small intestines, where its broken down into nutrients that include glucose. The nutrients are absorbed and distributed via your bloodstream.
The pancreas is a gland located behind your stomach that performs an essential role in the digestion process. It creates enzymes that break down the fat, starches, and sugar in the food. It also secretes insulin and other hormones into your bloodstream.
Insulin is created in the beta cells of the pancreas. Beta cells comprise about 75% of pancreatic hormone cells.
Other hormones produced by the pancreas are:
- glucagon, which alerts your liver to raise your blood sugar if it gets too low
- gastrin, which stimulates the production of gastric acid in your stomach
- amylin, which helps control your appetite
Read Also: Blood Sugar Monitoring For Type 2 Diabetes
How Does Diabetes Lead To Amputation
Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to poor blood flow . Without oxygen and nutrients , you are more prone to the development of cuts and sores that can lead to infections that cant fully heal. Areas of your body that are farthest away from your heart are more likely to experience the effects of poor blood flow. So areas of your body like your toes, feet, legs and fingers are more likely to be amputated if infection develops and healing is poor.
How Is Insulin Controlled
The main actions that insulin has are to allow glucose to enter cells to be used as energy and to maintain the amount of glucose found in the bloodstream within normal levels. The release of insulin is tightly regulated in healthy people in order to balance food intake and the metabolic needs of the body. This is a complex process and other hormones found in the gut and pancreas also contribute to this blood glucose regulation. When we eat food, glucose is absorbed from our gut into the bloodstream, raising blood glucose levels. This rise in blood glucose causes insulin to be released from the pancreas so glucose can move inside the cells and be used. As glucose moves inside the cells, the amount of glucose in the bloodstream returns to normal and insulin release slows down. Proteins in food and other hormones produced by the gut in response to food also stimulate insulin release. Hormones released in times of acute stress, such as adrenaline, stop the release of insulin, leading to higher blood glucose levels to help cope with the stressful event.
Insulin works in tandem with glucagon, another hormone produced by the pancreas. While insulin’s role is to lower blood sugar levels if needed, glucagon’s role is to raise blood sugar levels if they fall too low. Using this system, the body ensures that the blood glucose levels remain within set limits, which allows the body to function properly.
Don’t Miss: Symptoms Of Diabetes In Seniors
Solubilization Of Inclusion Bodies
After the separation of inclusion bodies, proinsulin is in an insoluble form and therefore must be solubilized. This is accomplished through the addition of denaturing agents such as urea or guanidium hydrochloric acid, which will release the fusion proteins. This process is followed by the addition of either -mercaptoethanol or DTT, which are reducing agents, to break the disulfide bonds present within the proinsulin fusion proteins.
In the traditional proinsulin procedure, after solubilization, a cleavage step for the preparation of proinsulin is performed. This step can also be performed later in the processing. It involves adding cyanogen bromide and 70% formic acid to cleave the peptide linker between proinsulin and its fusion protein partner43.
The History Of A Wonderful Thing We Call Insulin
Since the dawn of time, we have searched for ways to make life easier for us. The modern age has given us some amazing technological advanceswhat we would do without the internet, our iPhones or high-speed travel?
For many people, surviving life without these things sounds rough. However, if you have diabetes, no doubt youre also a big fan of one particular 20th-century discovery: insulin.
Before insulin was discovered in 1921, people with diabetes didnt live for long there wasnt much doctors could do for them. The most effective treatment was to put patients with diabetes on very strict diets with minimal carbohydrate intake. This could buy patients a few extra years but couldnt save them. Harsh diets sometimes even caused patients to die of starvation.
So how did this wonderful breakthrough blossom? Lets travel back a little more than 100 years ago.
In 1889, two German researchers, Oskar Minkowski and Joseph von Mering, found that when the pancreas gland was removed from dogs, the animals developed symptoms of diabetes and died soon afterward. This led to the idea that the pancreas was the site where pancreatic substances were produced.
Later experimenters narrowed this search to the islets of Langerhans . In 1910, Sir Edward Albert Sharpey-Shafer suggested only one chemical was missing from the pancreas in people with diabetes. He decided to call this chemical insulin, which comes for the Latin word insula, meaning island.
Last reviewed: August 31, 2020
Also Check: Nature Made Diabetes Health Pack Side Effects
How Insulin Is Made
Insulin is produced by the pancreas, a gland-like organ nestled in the curve of the duodenum , just behind the stomach. The pancreas functions both as an exocrine gland and an endocrine gland.
The exocrine function of the pancreas is to help with digestion. The endocrine function of the pancreas is to produce insulin and another hormone called glucagon that helps regulate blood sugar. The pancreatic cells that produce glucagon are called alpha cells.
Insulin is produced by specialized beta cells in the pancreas, which are clustered into groups called islets of Langerhans, or islets for short. A healthy adult pancreas has approximately one million islets, composing about 5% of the entire organ.
Role Of Stem Cells In The Treatment Of Diabetes
Stem cells are specialized cells that eventually develop into the tissues and organs of the body. Throughout its life, the body relies on stem cells to repair damaged tissues and cells that are lost regularly, as they can self-renew and differentiate. Embryonic stem cells , mesenchymal stem cells , and induced pluripotent stem cells have all been developed into insulin-producing cells 2, 97.
You May Like: What Level Of Sugar Is Considered Diabetic
Working With Human Insulin
- 1 The insulin gene is a protein consisting of two separate chains of amino acids, an A above a B chain, that are held together with bonds. Amino acids are the basic units that build all proteins. The insulin A chain consists of 21 amino acids and the B chain has 30.
- 2 Before becoming an active insulin protein, insulin is first produced as preproinsulin. This is one single long protein chain with the A and B chains not yet separated, a section in the middle linking the chains together and a signal sequence at one end telling the protein when to start secreting outside the cell. After preproinsulin, the chain evolves into proinsulin, still a single chain but without the signaling sequence. Then comes the active protein insulin, the protein without the section linking the A and B chains. At each step, the protein needs specific enzymes to produce the next form of insulin.
What Problems Can Happen With Type 2 Diabetes
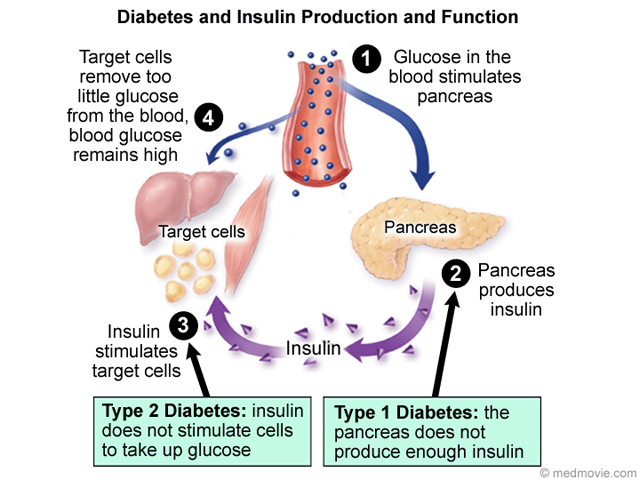
Not having the right amount of sugar in the blood can lead to:
- hyperglycemia.This is when blood sugars are too high. Someone with hyperglycemia may be extra thirsty and pee more than usual. If high blood sugars arent treated, they can get very sick and have health issues later in life, like heart and kidney problems.
- diabetic ketoacidosis . This serious condition needs treatment right away. When theres not enough insulin in the body to let the glucose into the cells, the body starts to break down fat instead of sugar. Symptoms of DKA can include nausea, vomiting, belly pain, fast breathing, and in severe cases, unconsciousness. DKA happens more often in people with type 1 diabetes, but it can sometimes happen to those with type 2 diabetes.
- hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state . Like DKA, this is a serious condition that needs treatment right away. People with HHS have severe dehydration and very high blood sugars.
- hypoglycemia. This is when blood sugars are too low. It can sometimes happen when people with type 2 diabetes are treated with insulin. If a person with diabetes gets more insulin than they need, their blood sugar level can drop too low. Symptoms can include headache, weakness, shakiness, anxiety, and sweating.
Read Also: When Do You Check Your Blood Sugar
Inclusion Body Separation By Centrifugation
After the E. coli have been lysed, the inclusion bodies need to be isolated from the cell debris. For this purpose, centrifugation can be used for reverse osmosis. Since the proinsulin inclusion bodies are dense, they will sink to the bottom. However, the speed of centrifugation must be higher than before, since the inclusion bodies have a lower density than the intact bacterial cells. After centrifugation, the supernatant is discarded while proinsulin and some impurities remain in the tube37.
Regulations Are Keeping Insulin Expensive
Insulin is known as a biologic drug, meaning that it is produced by a living organism instead of a chemical reaction. This can be prove to be more inconsistent than the chemical synthesis of non-biologic drugs.
The process of bringing that drug onto the market can cost up to $250 million, but no company will be able to pay that amount if it cant get a patent to regain the investment, as Medical Express reports.
To make matters more complicated, insulin requires more than one patent. All the inventions it makes use of, such as test pens and other devices, which help patients better manage their diabetes, require their own patents.
Read Also: What Happens When Your Blood Sugar Rises
The Pancreas And Type 1 Diabetes
In type 1 diabetes , the beta cells that produce insulin are attacked by the bodys immune system.
As more beta cells get killed off, the pancreas struggles to produce enough insulin to keep blood sugar levels down and the symptoms of diabetes begin to appear.
Research has shown that whilst many beta cells are killed off, the body can continue to produce very small amounts of insulin even after decades have passed.
Insulin And Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is characterised by the body not responding effectively to insulin. This is termed insulin resistance. As a result the body is less able to take up glucose from the blood. In the earlier stages of type 2 diabetes, the body responds by producing more insulin than it would normally need to.
If type 2 diabetes develops over a number of years, the extra demands on the pancreas to produce insulin can lead to a loss of insulin producing cells as they wear out.
Depending on their level of insulin resistance, people with type 2 diabetes may also need to take insulin injections to manage their blood sugar levels.
Recommended Reading: Blood Sugar Levels After Meals For Diabetics
Evolution And Species Distribution
Insulin may have originated more than a billion years ago. The molecular origins of insulin go at least as far back as the simplest unicellular eukaryotes. Apart from animals, insulin-like proteins are also known to exist in the Fungi and Protista kingdoms.
Insulin is produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets in most vertebrates and by the Brockmann body in some teleost fish.Cone snailsConus geographus and Conus tulipa, venomous sea snails that hunt small fish, use modified forms of insulin in their venom cocktails. The insulin toxin, closer in structure to fishes’ than to snails’ native insulin, slows down the prey fishes by lowering their blood glucose levels.
How Is Type 2 Diabetes Diagnosed
Doctors may check for diabetes if a person has symptoms or risk factors, like being overweight and having acanthosis. Different kinds of blood tests can check for diabetes, including:
- HbA1c. This test shows a person’s average blood sugar levels over the past few months. Its also called a glycosylated hemoglobin or hemoglobin A1c test. HbA1c of 6.5% or higher means the person may have diabetes.
- fasting glucose. To get this test, a person first stops eating for at least 8 hours. A blood sugar reading of 126 mg/dL or higher means they might have diabetes.
- random glucose. This test can be taken at any time. A blood sugar level of 200 mg/dL or higher means a person may have diabetes.
- glucose tolerance test. To get this test, a person first stops eating or drinking for at least 8 hours. Then, they drink a sugary liquid and their blood sugar is checked 1 and 2 hours later. A blood sugar of 200mg/dL or higher at 2 hours means they might have diabetes.
The doctor uses the results from one or more of these tests to tell if the person has diabetes. The doctor can order other tests to find out if it is type 1 diabetes or type 2 diabetes.
Read Also: What Are Nursing Interventions For Type 2 Diabetes
How Is Diabetes Treated
Treatments for diabetes depend on your type of diabetes, how well controlled your blood glucose level is and your other existing health conditions.
- Type 1 diabetes: If you have this type, you must take insulin every day. Your pancreas no longer makes insulin.
- Type 2 diabetes: If you have this type, your treatments can include medications , insulin and lifestyle changes such as losing weight, making healthy food choices and being more physically active.
- Prediabetes: If you have prediabetes, the goal is to keep you from progressing to diabetes. Treatments are focused on treatable risk factors, such as losing weight by eating a healthy diet and exercising . Many of the strategies used to prevent diabetes are the same as those recommended to treat diabetes .
- Gestational diabetes: If you have this type and your glucose level is not too high, your initial treatment might be modifying your diet and getting regular exercise. If the target goal is still not met or your glucose level is very high, your healthcare team may start medication or insulin.
Oral medications and insulin work in one of these ways to treat your diabetes:
- Stimulates your pancreas to make and release more insulin.
- Slows down the release of glucose from your liver .
- Blocks the breakdown of carbohydrates in your stomach or intestines so that your tissues are more sensitive to insulin.
- Helps rid your body of glucose through increased urination.