Signs Of Type 2 Diabetes In Aging Adults
By Debbie Waddell 9 am on January 29, 2019
Type 2 diabetes is a common disease thousands of seniors are diagnosed with every year. Luckily, most older adults can completely reverse this condition as long as they catch the early warning signs and make extensive lifestyle changes. Heres a closer look at five of the most common symptoms of type 2 diabetes and a few steps seniors can take to avoid this pervasive disease.
Symptoms Of Type 2 Diabetes Older Adults May Experience
By Debbie Waddell 9 am on December 25, 2018
Diabetes is a life-altering metabolic disease that can result in a wide array of health complications. Luckily, diabetes can often be controlled or completely reversed as long as its diagnosed early on and sweeping changes are made to the diet. Here are five of the most common symptoms of type 2 diabetes and a few steps seniors can take to control their insulin levels.
When Type 1 Diabetes Strikes Older Adults
Teresa Fieldsell* had no idea anything was wrong with her health until one day last April, when she found herself unable to catch her breath while out for a walk. Things felt not right, she says, and suspecting she might have COVID, she went to the emergency department of her local hospital.
Throughout her life, Teresa kept physically fit, ate a healthy diet, and maintained a runners trim physique. Now in her 60s, she runs several miles a week, rows, and spins.
So when an emergency medicine physician suggested she might have type 2 diabetes, because her glucose levels had spiked, it didnt make sense to her. Although type 2 diabetes is due to a combination of defective insulin secretion and the bodys inability to appropriately respond to insulin, it is often associated with obesity and a sedentary lifestyle.
In the ED, the physicians discovered her symptoms were a result of a dangerously high blood glucose level425far above numbers considered normal . With her sugar levels that high, Teresa was at risk of coma or death.
She was admitted to the hospital to bring her blood sugar to normal levels, diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, and sent home with prescriptions for short- and long-acting insulin and a handout of instructions.
Nobody talked to me about, What does this mean? What do I eat? What happens next? None of that, she says.
Also Check: What Is The Best Glucose Meter For Diabetes
Signs Of Undiagnosed Diabetes
There are various symptoms to watch out for that could indicate you have diabetes. While the symptoms can be the same for type 1 and type 2 diabetes, symptoms often show up more rapidly and severely in people who have type 1.
The symptoms to look for include:
- Feeling tired
- Frequent infections
- Slow-healing sores
Again, diabetes in older adults tends to be type 2, so you may only notice mild symptoms at first. There are times when there might not be any symptoms, as well. If you do experience any of those, you should discuss it with your doctor immediately. The sooner you are diagnosed with the condition the better.
Cognitive Dysfunction And Depression

There is evidence that type 2 diabetes is associated with cognitive dysfunctions. Older diabetic patients have higher risk to develop mild cognitive impairment , all-cause dementia and Alzheimer’s disease . Specific mechanisms underlying this association are still unclear however, main factors involved are vascular dysfunction, high blood pressure, hyperglycemia, hypoglycemic events, insulin resistance, and neuroinflammation . Furthermore, depressive and apathic symptoms frequently co-exist with diabetes , and some studies have found that combination of diabetes and depression may express a toxic effect on the brain, increasing the risk for dementia . In light of this, the American Diabetes Association recommends for subjects over 65 years old a neuro-psychological screening at the initial visit and annually to early detect mild cognitive impairment and depression, by using some specific test , and minimizing hypoglycemic events to reduce the risk of MCI .
Also Check: Insulin Pump For Type 2 Diabetes
What Is The Ndss
The National Diabetes Services Scheme is an Australian Government initiative to help people with diabetes to manage their condition. Anyone who has been diagnosed with diabetes who holds a Medicare or Veterans Affairs card is eligible for the NDSS.
The NDSS can help older Australians living with diabetes to understand the health system and manage their diabetes.
The NDSS has a helpline and a website . The NDSS is run by Diabetes Australia.
It also allows people to access subsidised products such as testing strips and insulin pens.
Diabetes In Older People
Diabetes is a serious disease, and it affects many older adults. People get diabetes when their blood glucose, also called blood sugar, is too high. The good news is that you can take steps to delay or prevent type 2 diabetes, which is the most common form of the disease to develop in older adults. If you already have diabetes, there are steps you can take to manage the condition and prevent diabetes-related health problems.
You May Like: How To Get Diabetic Shoes Through Medicare
Talk With A Senior Living Advisor
Our advisors help 300,000 families each year find the right senior care for their loved ones.
For example, a resident who independently manages, stores, and administers their insulin and medication may not incur any diabetes care costs, Leistner says.
On the other hand, more hands-on assistance from the community, such as developing a special diet or monitoring blood sugar levels, may incur a higher cost.
Understanding the communitys cost method is important as the needs of the resident may change over time, Leistner says.
Be sure to ask about pricing and payment plans when determining your loved ones care level, and ask the following questions:
- What will my loved ones diabetes care cost?
- Does providing a special diet add to the cost? How much?
- Does glucose monitoring incur a cost?
- How will the cost change if my loved ones level of care increases?
Symptoms Of Type 1 Diabetes In Seniors
Though uncommon, type 1 diabetes is sometimes diagnosed in adults over age 40 and even into their 50s and 60s. With that said, knowing the warning signs can help you manage the condition and potentially avoid complications down the road.
Symptoms of type 1 diabetes in seniors may include:
- Frequent urination or incontinence
- Blurred vision
- Changes in mood or behavior
Type 1 diabetes can lead to myriad health issues in aging adults, which mostly has to do with the effects of trying to manage blood sugar. Over time, altering glucose levels can damage various organs, ultimately creating ailments throughout the body and making a person more susceptible to certain diseases. This includes hypoglycemia, heart disease, and kidney disease, as well as nerve and eye damage.
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia, which is different from hyperglycemia, means someone has exceedingly low blood sugar levels. Those with type 1 diabetes may be susceptible to developing the condition, which is particularly concerning in seniors, as even brief episodes can lead to fainting, falling, comas, or seizures.
Heart Disease
Adults over 65 are already substantially more likely than the younger population to develop heart disease, which poses an increased risk for strokes, heart attacks, and coronary artery disease. Sadly, seniors with type 1 diabetes often have an even greater chance of suffering from one of these cardiovascular conditions.
Kidney Disease
Nerve Damage
Eye Damage
Recommended Reading: Urine Test For Diabetes Type 2
Comorbidities And Geriatric Syndromes
Diabetes is associated with increased risk of multiple coexisting medical conditions in older adults. In addition to the classic cardiovascular and microvascular diseases, a group of conditions termed geriatric syndromes, described below, also occur at higher frequency in older adults with diabetes and may affect self-care abilities and health outcomes including quality of life .
Cognitive dysfunction.
Alzheimers-type and multi-infarct dementia are approximately twice as likely to occur in those with diabetes compared with age-matched nondiabetic control subjects . The presentation of cognitive dysfunction can vary from subtle executive dysfunction to overt dementia and memory loss. In the ACCORD trial, for which referred participants were felt to be capable of adhering to a very complex protocol, 20% of those in the ancillary trial of cognition were found to have undiagnosed cognitive dysfunction at baseline . In this trial, neither intensive glycemic control nor blood pressure control to a target SBP < 120 mmHg was shown to prevent a decline in brain function . Cross-sectional studies have shown an association between hyperglycemia and cognitive dysfunction . Hypoglycemia is linked to cognitive dysfunction in a bidirectional fashion: cognitive impairment increases the subsequent risk of hypoglycemia , and a history of severe hypoglycemia is linked to the incidence of dementia .
Functional impairment.
Falls and fractures.
Polypharmacy.
Depression.
Itching And Yeast Infections
Excess sugar in the blood and urine provides food for yeast, which can lead to infection. Yeast infections tend to occur on warm, moist areas of the skin, such as the mouth, genital areas, and armpits.
The affected areas are usually itchy, but a person may also experience burning, redness, and soreness.
Don’t Miss: Cauliflower Pizza Crust For Diabetics
Wounds That Wont Heal
For a wound to heal, blood must circulate through the area to clear away the damaged cells. Blood also triggers the production of vital proteins and growth factors. If the nearby veins are damaged, it could take weeks for a wound to heal, which is why many seniors with diabetes have lingering wounds on their feet, calves, and thighs. Seniors with diabetes must carefully clean and dress their wounds as often as possible to prevent infections.
Understanding Diabetes In Seniors: The Causes Symptoms And Treatments
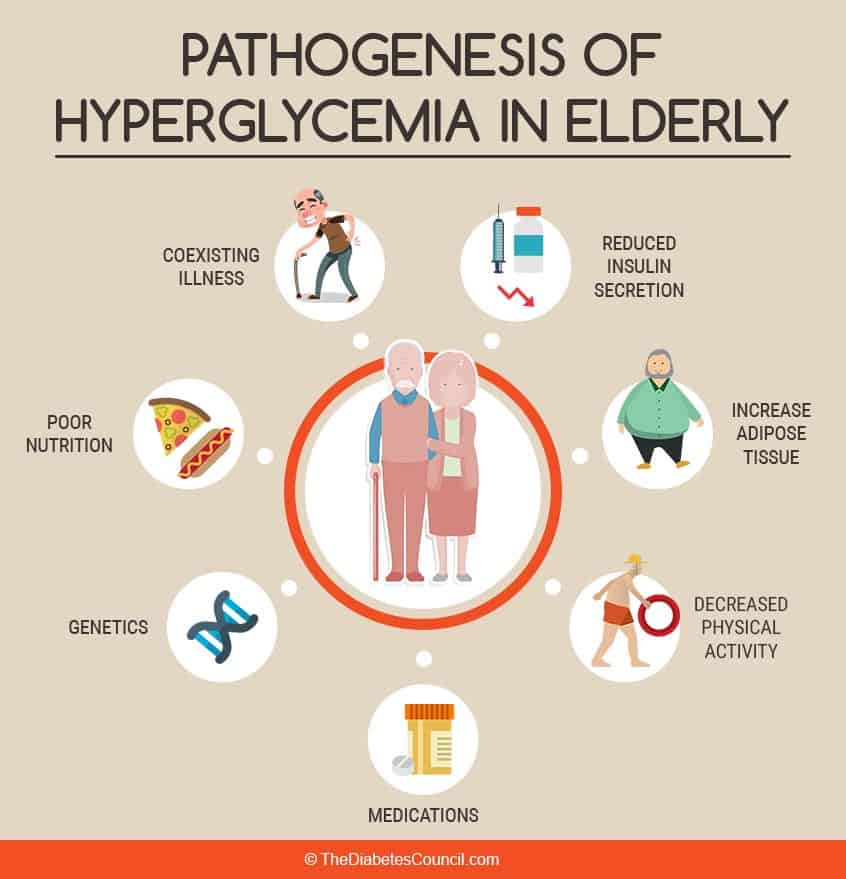
Diabetes is a serious disease that affects many seniors. Diabetes occurs when blood sugar levels are too high. Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder that affects the bodys ability to regulate the blood glucose level, and how the body utilizes glucose for repair, energy, and growth. Diabetes affects the bodys ability to produce and use insulin, which is a hormone that converts glucose to energy. As of 2021, the number of Americans afflicted with diabetes is set to grow, due to an increase in sedentary lifestyle and obesity. This guide aims to explain diabetes and the possible treatments for it.
You May Like: What Is Considered Low Blood Sugar For Type 2 Diabetes
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Tracking blood sugar levels is an important part of managing diabetes. Blood-sugar levels can become too high when diabetes is not properly controlled. High levels can cause complications such as circulation problems, heart disease, and kidney disease. Sometimes, a patients insulin or diabetes pills push levels too low, causing tiredness, shakiness, dizziness, anxiety, and irritability. According to the American Diabetes Associations guide to health living for those 55 and up, even seizures are possible.
Your loved ones care team will determine if the resident is able to monitor their own blood sugar levels and administer insulin as needed or, if not, how levels will be monitored and kept stable. Each community will have policies for monitoring and stabilizing residents blood-sugar levels and for administering and tracking medications. These policies are often dependent on state regulations and a communitys clinical capabilities.
For example, most assisted living facilities will provide help with taking medications. Some states require a third-party home health service to monitor levels and give insulin, but most communities provide this service through nurses or medical technicians.
Your loved ones care plan should clearly state who will monitor blood sugar levels, who will administer necessary medications including insulin, and the role of the residents physician.
When assessing how a community develops diabetes care plans, ask these questions:
Dementia & Alzheimers Disease
These are also linked to both aging and diabetes. High blood sugar can affect many organs, including your brain. Over time, Alzheimerâs disease can impact your memory, ability to learn, reason, use good judgment, and do your normal daily tasks. Doctors still have a lot to learn about the connection, but the best way to reduce your odds of getting it is to keep your diabetes under control.
Show Sources
Don’t Miss: What Is An Omnipod Insulin Pump
Blood Glucose Targets In The Elderly
Generally, blood glucose targets in the elderly are the same as other adults with diabetes:
- A1C: less than 7.0%
- Fasting blood glucose : 4.0 to 7.0 mmol/L
- Blood glucose two hours after eating a meal: 5.0 to 10.0 mmol/L
However, in elderly people who are described as frail, their blood glucose targets are different from the general population with diabetes. Frail elderly people are described as those who suffer from three or more of the following conditions:
In the frail elderly, blood glucose levels two hours before eating a meal are a better gauge of diabetes control than A1C or post-meal blood glucose levels. The recommended fasting blood glucose for the frail elderly is 5.0 to 12.0 mmol/L.
For more information about blood glucose, click here.
How Communities Ensure Proper Management Of Diabetes In Long
Most senior living communities are experienced in managing diabetes in the elderly. After all, one in four people over the age of 60 has diabetes, according to the American Diabetes Association. The American Geriatric Society recommends that communities provide an individualized care plan that considers the seniors life expectancy, cognitive status, functional status, and social support.
To determine the level of care your loved one needs, the communitys health care team will use an evaluation tool to assess your seniors health, the severity of their diabetes, and how much care they will need. A higher assessment score indicates the need for a more intensive diabetic care plan. For example, in some communities, a Level 1 care plan encompasses basic needs, such as help with activities of daily living . As the levels of needed care increase, the plan becomes more intensive and specialized.
As you evaluate communities for a loved one, ask the communitys health care team how they will work with you and your loved one to create a diabetes management plan. A well-rounded plan should be based on your seniors lifestyle, preferences, health goals, and any other existing health conditions.
Ask specific questions to the nurse leader or executive director about how the community nurses and clinical team will met the needs of you or your loved one living with diabetes, Leistner says. Here are some initial questions to ask:
You May Like: Life Insurance For Diabetics Type 2
Type 2 Diabetes In Seniors
As the most common type of diabetes, type 2 accounts for roughly 90% of cases. That said, its also more preventable and treatable than type 1, especially if its caught in the prediabetic stage.
Around 10 million seniors in the United States have type 2 diabetes, which occurs when the body doesnt use insulin properly. When the condition is diagnosed later in life, its most often a result of obesity. In an attempt to process high levels of sugar in the blood, the pancreas generates an excess of the hormone, but over time, people develop a buildup of glucose in their bloodstream.
Diabetes And Older Adults
As the general population continues to age, the number of adults 65 years or older affected by diabetes is also increasing. An estimated 33% of adults aged 65 or older have diabetes. This population is more at risk of developing diabetes-related complications like hypoglycemia , kidney failure, and heart disease than younger people living with diabetes.
There is new and emerging information to improve the understanding and treatment for diabetes in older adults. Special considerations should be addressed to support overall health and quality of life. Older adults often have one or more co-existing conditions like cognitive impairment, cardiovascular disease, and others that impact diabetes education and management.
The relevant therapies for glycemic control, hyperlipidemia, and hypertension are important in older people.
The treatment of diabetes in adults 65 years and older should be based on an assessment of your overall health and other medical conditions. Medication regimens should be simplified in adults 65 years to improve adherence and prevent treatment-related complications. Glycemic targets should be a shared decision between you and your healthcare team and tailored to each individual.
General Health Assessments:
- Screening for cognitive impairment and dementia
- Frailty & Physical Exam
Diabetes- Specific Assessments:
- Diabetes Self-Management and Training
- Supporting at home needs
- Family or community support
- Access to proper medications and food
Also Check: Does Water And Baking Soda Help Diabetes
Why Are Seniors At Elevated Risk For Diabetes
About 25 percent of adults 65 and older live with diabetes. Those who have type 2 diabetes are more likely to be hospitalized or die from complications of the disease.
Older adults with diabetes are also more likely to experience mobility issues and cardiovascular complications. Heres what you should know about diabetes for yourself or a loved one.
Sudden Changes To Energy Levels

Some seniors with diabetes have sporadic bursts of energy followed by overwhelming lethargy. These fluctuations usually take place when the body cant properly balance insulin levels after consuming sugar or carbohydrates. Sticking to a healthy diet filled with fiber, protein, and complex carbohydrates is one of the best ways for seniors with diabetes to stay energized throughout the day.
Seniors with mobility limitations or health conditions may find it difficult to prepare meals on their own, which can result in not getting proper nutrition. Living with a serious health condition can make it challenging for seniors to age in place. However, they can maintain a higher quality of life with the help of professional live-in care. Roseville seniors can benefit from assistance with meal prep, bathing, transportation to the doctors office, medication reminders, and much more.
Don’t Miss: Blood Testing Meters For Diabetes
Symptoms Of Prediabetes In Aging Adults
By 9 am on March 4, 2021
Identifying prediabetes in seniors is important for preventing it from progressing to type 2 diabetes. In the early stages, prediabetes can mimic other disorders and have mild symptoms that are easy to overlook. Being aware of the following symptoms of prediabetes allows family caregivers to take prompt action to protect their senior loved ones health.