Hashimotos Fasting And Keto
I believe there is a way to reverse Hash! I feel so much better on keto and IF than any treatment over the past three years. Have you had any patients reversing Hashi with this program?
Thank you so much for all your work for all of us,Martha
Answer: I dont see Hashimotos very frequently so dont have much experience. Fasting and low carb diets usually drop insulin so are effective for diseases of excessive insulin such as obesity, type 2 diabetes and PCOS. However, it may also have a smaller effect on inflammation so it may certainly benefit Hashimotos as well, but there are no studies to prove this, and I have only limited clinical experience with Hashimotos.
Dr. Jason Fung
- Women’s questions introduction 01:36 In this video series, you can find expert views on some of your top questions about low-carb and women’s health.
- MEMBERS ONLY
- Is low carb bad for gut bacteria? 02:14 Can a low-carb diet be potentially harmful to your gut microbiome?
- MEMBERS ONLY
- Is saturated fat bad? 07:29 Low carb is great. But could the saturated fat clog your arteries and kill you? Top low-carb doctors answer this question.
- MEMBERS ONLY
Why They Happen And How To Try And Reduce Them If You Live With Type 1 Diabetes
Living with type 1 diabetes requires you to regularly check your blood sugar levels before you eat. However, we may not always consider what happens to our sugar levels immediately after we eat where it is very normal for people who dont have diabetes, let alone those who do, to temporarily have high sugar levels. Given that having high sugar levels can give you symptoms like thirst, tiredness and needing to go to the toilet a lot, learning about ways to try and reduce spikes in your sugar levels after meals may make a difference to your overall health and wellbeing.
What Happens In The Body When The Glucose Level Rises
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
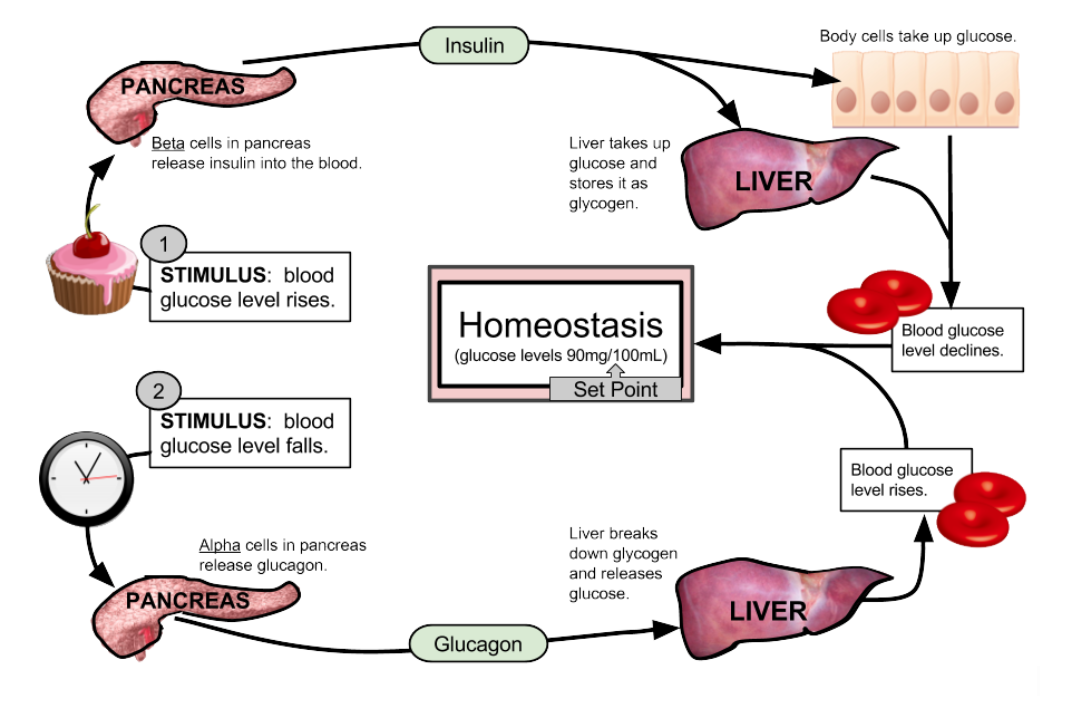
When the level of glucose in the blood rises, insulin is produced. This substance helps glucose to move from the blood to the muscle tissue. When insulin performs this important role, its level drops sharply to normal.
You May Like: One Touch Ultra Glucose Meter
The Blood Sugar Level Regulation Mechanism
When you eat rice, bread, or any other typical food high in carbohydrates, it is digested by the stomach and small intestine, where it is absorbed into the blood as glucose. Figure 1 shows how it is absorbed into the body.
When glucose enters the bloodstream, insulin facilitates its uptake into the body’s cells. When an excess of glucose is ingested, insulin over secretion occurs. Insulin increases the biosynthesis of fat and suppresses its breakdown. Thus, it becomes easier for fat to accumulate in body tissues.
Blood sugar level will not drop if the sugar in the blood is not properly processed due to, for example, too little insulin being secreted, or resistance to the action of insulin. If blood sugar levels have not decreased several hours after eating on a regular basis, this indicates a susceptibility to diabetes. To avoid this and stay healthy, we should eat types of foods that will not cause a sudden, extreme rise in blood sugar levels.
What is BMI?
What is a healthy blood sugar level
- Fasting blood sugar level 99mg/dL
- Postprandial blood sugar level 7.8mmol/L
Exercise And Blood Sugar
Exercise can have a big effect on your blood sugar levels because blood sugar is used for energy. When you use your muscles, your cells absorb sugar from the blood for energy.
Depending on the intensity or duration of exercise, physical activity can help lower your blood sugar for many hours after you stop moving.
If you exercise regularly, the cells in your body may be more sensitive to insulin. This will help keep blood sugar levels within normal ranges.
Don’t Miss: Does Aloe Vera Help Diabetes
What Is Diabetic Ketoacidosis
When the body doesn’t have enough insulin, glucose stays in the blood and can’t get into the body’s cells to be used for energy. This can happen, for example, when someone skips doses of insulin or when the need for insulin suddenly increases and the doses are not adjusted.
When the body can’t use glucose for fuel, it starts to use fat. When this happens, chemicals called ketones are released into the blood. Some of these ketones, like extra glucose, pass out of the body through the urine.
High levels of ketones in the blood can be a problem because they cause the blood to become acidic. Too much acid in the blood throws off the body’s chemical balance and causes the symptoms listed below. In people with diabetes, this problem is called diabetic , or DKA. DKA is a very serious condition that can lead to coma or death if it’s not treated. The good news, though, is that it’s preventable and can be treated.
DKA happens more often in people with type 1 diabetes, but can sometimes also happen to those with type 2 diabetes.
What Happens To Your Blood Sugar When You Drink Alcohol
Most people don’t think about their blood sugar when they have a few drinks at Happy Hour. Instead, they may be more concerned about their blood alcohol concentration and being pulled over for a DUI while driving home. But even if you have a designated driver, those drinks can still be dangerous. It all depends on how they impact your blood sugar levels.
Blood sugar is your body’s main energy source and is supplied by the foods and beverages you consume. When you eat food or drink something containing carbohydrates and calories, your blood sugar typically rises. But when you drink alcohol, your blood sugar could either rise or drop. It depends on what you’re drinking, how much, and how your individual body reacts to the alcoholic beverage.
Recommended Reading: Healthy Snacks For Diabetic Kids
Moderate To Severe High Blood Sugar
You may have moderate to severe symptoms if your blood sugar levels are consistently high. These symptoms include:
- Blurred vision.
- Flushed, hot, dry skin.
- Restlessness, drowsiness, or difficulty waking up.
People with type 1 diabetes and some people with type 2 diabetes produce little or no insulin. These people may also have:
- Rapid, deep breathing.
- A fast heart rate and a weak pulse.
- A strong, fruity breath odor.
- Loss of appetite, belly pain, and/or vomiting.
If your blood sugar levels continue to rise, you may:
- Become confused and sluggish.
- Pass out if your blood sugar levels are very high.
Current as of: April 13, 2022
Author: Healthwise Staff
Medical Review:E. Gregory Thompson MD – Internal Medicine& Adam Husney MD – Family Medicine& Rhonda O’Brien MS, RD, CDE – Certified Diabetes Educator
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Healthwise, Incorporated, disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use. Learn how we develop our content.
To learn more about Healthwise, visit Healthwise.org.
About High Blood Sugar
Normal blood sugar measures 70 to 99 milligrams per deciliter after fasting, or less than 140 milligrams per deciliter two hours after eating. High blood sugar occurs when your body either doesn’t make enough insulin or can’t properly use the insulin it does make, and is most often associated with diabetes. A fasting blood sugar of 126 milligrams per deciliter or a random blood sugar reading of 200 milligrams per deciliter indicates high blood sugar. Frequent urination, increased thirst, weight loss or fatigue are signs that your blood sugar levels may be high. If left uncontrolled, high blood sugar leads to ketoacidosis, also referred to as a diabetic coma, which is when your body breaks down fat into ketones for fuel and the ketones build up in the blood.
Read Also: How Much Is A Vial Of Insulin
Planning For Sick Days
Your body releases stress hormones when you are sick, which can cause hyperglycemia. Keep taking your insulin and other diabetes medications, even if you are throwing up. If you have ketones and your blood sugar is above 240 mg/dL, call your doctor. They might also want you to call if:
- You have diarrhea that lasts more than 6 hours
- You are throwing up
- You have a high fever or trouble breathing
- You feel very sleepy or confused
Continue checking your blood sugar levels and keep track of the results.
What Is The Dawn Phenomenon
Dr. Parilo explains that its a natural surge of hormones produced by your body growth hormone, cortisol, adrenaline, and others typically between 2 and 8 a.m.
People without diabetes can handle this extra hormonal activity. But if you have diabetes, dawn phenomenon can suppress production of the hormone insulin, which is essential for controlling blood sugar. Insulin enables sugar, or glucose, to enter cells to fuel the body.
Dr. Parilo explains how the dawn phenomenon affects someone with diabetes.
Click play to watch the video or read video transcript.
How can the dawn phenomenon affect someone with diabetes?
The effects of dawn phenomenon typically go unnoticed. As far as the way an individual feels, the real feeling is of frustration because an individual’s trying to do the right thing in taking their medicines and eating appropriately. Many times, a patient will say, “I didn’t eat anything this morning and I noticed my blood sugar escalating.” We have to check closely, do questions, try and figure out … Is it something that you’re doing? A stressful event? Is it unaccounted for carbohydrates like creamer in coffee? Is it a healthy meal, but yet a meal that has carbohydrates and you’re not really accounting for that, so the blood sugar’s escalating? Are your medicines wearing out and you actually just need a change of how or when you’re using your medicines? Or, is this dawn phenomenon?
Recommended Reading: Medipeds 8 Pair Diabetic Crew Socks With Non Binding Top
How Do I Detect Spikes In My Sugar Levels
The exact timing of blood sugar spikes can vary from person to person and meal to meal. However, on average, the post-meal peaks tend to be about one hour and 15 minutes after starting a meal.
The best way to measure post-meal patterns is by using a continuous glucose monitor or Flash monitors. These devices can give you a clear view, including graphs, of what happens with the glucose levels after meals without the need for finger pricking . You can ask your diabetes health team if they are available for you as they are not available to everybody.
If you are not using a CGM, then please speak to your healthcare team about the best way to do this for you with finger prick testing.
How do I know it is a spike?
There is no universal answer or specific guidelines on when a sugar level is too high after meals. However, if post-meal readings are consistently above your target range , then you should discuss whether it would be beneficial for you to address these spikes and how to do this, with your healthcare team .
If you are reviewing your post-breakfast sugar levels, you should also be aware of changes in your hormones in the morning, which cause increases in sugar levels . This Digibete video may help.
Some ways to reduce blood sugar spikes after meals
1. Choose low glycaemic index foods
When blood sugar levels are low or hypoglycaemic we need high glycaemic index foods , such as dextrose tablets or juice, that are absorbed quickly to raise our levels and to treat the hypo.
Insulin And Blood Sugar

Insulin is an important hormone that helps regulate your blood sugar levels. The pancreas makes insulin. It helps control your blood sugar levels by assisting the cells that absorb sugar from the bloodstream.
If you have type 1 diabetes, your body doesnt make insulin. This means you have to inject insulin every day.
If diet and exercise arent enough to manage blood sugar, those with type 2 diabetes may be prescribed medications to help keep blood sugar levels within target ranges.
If you have type 2 diabetes, your body produces insulin, but may not use it properly or produce enough of it. Your cells dont respond to insulin, so more sugar keeps circulating in the blood.
Exercise can help the cells respond better and be more sensitive to insulin. The proper diet can also help you avoid spikes in blood sugar. This can help keep your pancreas functioning well since high blood sugar levels decrease pancreatic function.
Also Check: Diabetes 2 What Is It
Can Sleep Raise Or Lower Glucose Levels
Although it sounds contradictory, sleep can both raise and lower glucose levels. Our bodies experience a cycle of changes every daycalled a circadian rhythmwhich naturally raises blood sugar levels at night and when a person sleeps. These natural blood sugar elevations are not a cause for concern.
Restorative sleep might also lower unhealthy blood sugar levels by promoting healthy systems. levels. Even partial sleep deprivation over one night increases insulin resistance, which can in turn increase blood sugar levels. As a result, a lack of sleep has been associated with diabetes, a blood sugar disorder.
More research is needed to better understand the connection between sleep and blood sugar. So far, the following factors have been found to influence the relationship between sleep and blood sugar levels:
- Inflammatory markers IL-6 and TNF-alpha are increased by sleep deprivation and can cause insulin resistance, which impacts glucose
What Happens If Your Blood Sugar Gets Too High With Diabetes
If you have diabetes and your blood sugar is too high, your cells cant function correctly, and youll start to feel uncomfortably sick.
The cells in your body need glucose, more commonly known as sugar, to survive and function. Our diets contain many sources of glucose, but it cant reach our bodies cells without the help of insulin, a hormone secreted by the pancreas.
Insulin is responsible for transporting glucose to your cells. When your body doesnt have enough insulin or it is not active enough, both symptoms of diabetes, the sugar remains in the blood without reaching cells. Thats why diabetes and high blood sugar often go hand in hand.
What Causes High Blood Sugar?
Sugar accumulates in the blood either when there is not enough insulin to transport it or when the insulin that is available is not active.
Type 1 diabetes patients are incapable of making the insulin necessary to transport glucose to the cells.
Type 2 diabetes patients are insulin resistant. They often, but not always, have the insulin required by the body, but the insulin is ineffective.
Patients with diabetes are more prone to high blood sugar levels if they:
- Miss taking diabetes medication or insulin
- Eat too much food
Read Also: Reverse Type 2 Diabetes Quickly
What To Do If Your Blood Sugar Is Over 400
If you have diabetes, it’s very important to keep your blood sugar, or glucose, levels within a healthy range.
Video of the Day
Here’s why: If your glucose levels dip too low, you can experience symptoms of hypoglycemia, which include shakiness, a rapid heartbeat and lightheadedness.
And if your blood sugar levels swing too high , you could experience not just long-term health complications, but short-term problems like diabetic ketoacidosis , a serious condition that could possibly be fatal.
Find out what happens when your blood sugar levels are too high, as well as potential outcomes when they rise above 400 milligrams per deciliter .
Warning
If your blood sugar is over 400 , seek medical attention immediately, according to the Mayo Clinic.
How Can High Blood Sugar Levels In The Morning Be Controlled
Once you and your doctor determine how your blood sugar levels are behaving at night, he or she can advise you about the changes you need to make to better control them. Options that your doctor may discuss depend on the cause of the morning high blood sugars.
For dawn phenomenon:
- Changing the timing or type of your diabetes medications
- Eating a lighter breakfast
- Increasing your morning dose of diabetes medication
- If you take insulin, switching to an insulin pump and programming it to release additional insulin in the morning
For Somogyi effect:
- Diabetes Forecast. Why Is My Blood Glucose So High in the Morning? Accessed 8/8/2018.
- American Diabetes Association. Somogyi effect, also called rebound hyperglycemia Accessed 8/8/2018.
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. Dawn Phenomenon. Accessed 8/8/2018.
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services.Policy
Don’t Miss: Does One High A1c Mean Diabetes
What Is Insulin Resistance
Excess of insulin in the blood leads to an increase in fat deposits and weight gain. This glucose is stored in the form of fat, instead of giving you energy for life.
With insulin resistance, this substance is no longer able to transport glucose to muscle cells, and then there is a sharp appetite – more than usual. It seems that a person is undernourished, but it is not.
In addition, glucose, not penetrating into cells, but remaining in the blood, does not give the body sufficient vital energy. And then a paradoxical situation arises: there is a lot of glucose in the blood, but you still want to eat brutally. And you eat: it’s very difficult to fight with hunger. So, you get better.
In this case, glucose with an excess of fat cells, and the amount of fat in the body increases. But the cells demand “fuel” again and again. They receive it, divide and grow. Here whence at women at insensitivity to an insulin appears superfluous weight. Even though you minimize the calories in your menu.