When To Get Urgent Medical Attention
Contact your diabetes care team immediately if you have a high blood sugar level and experience the following symptoms:
- feeling or being sick
- a fever for more than 24 hours
- signs of dehydration, such as a headache, dry skin and a weak, rapid heartbeat
- difficulty staying awake
These symptoms could be a sign of a more serious complication of hyperglycaemia, such as diabetic ketoacidosis or a hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic state, and you may need to be looked after in hospital.
Low Blood Glucose During Sleep
Your blood glucose level can drop while you sleep and stay low for several hours, causing serious problems.7 Symptoms of low blood glucose while you sleep can include
- crying out or having nightmares
- sweating enough to make your pajamas or sheets damp
- feeling tired, irritable, or confused after waking up
Although you may not wake up or notice any symptoms, low blood glucose can interfere with your sleep, which may affect your quality of life, mood, and ability to work. Having low blood glucose during sleep can also make you less likely to notice and respond to symptoms of low blood glucose during the day.
Now That Youre Checking Your Blood Glucose What Do The Numbers Mean
Depending on your diabetes treatment plan, your doctor or diabetes educator may advise you to check once a week, once a day or up to 10 times a day . But what does it mean when you see a 67, 101 or 350 on your meter? And what is a normal blood sugar, anyway? Great questions! After all, if you dont know what the numbers on your meter mean, its hard to know how youre doing.
The American Diabetes Association provides guidelines for blood glucose goals for people with diabetes, and the goals vary depending on when youre checking your glucose:
Fasting and before meals: 80130 mg/dl
Postprandial : Less than 180 mg/dl
By the way, these guidelines are for non-pregnant adults with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Children, adolescents and pregnant women may have different goals.
Your blood glucose goals may be different, however. If youre younger, have had diabetes for a shorter amount of time or are not taking any medicine for your diabetes, your glucose goals might be a little tighter, or lower. Likewise, your blood glucose goals may be higher than what ADA recommends if youre older, have diabetes complications, or dont get symptoms when your blood glucose is low.
Bottom line: talk with your health-care provider about the following:
When to check your blood glucose How often to check your blood glucose What your blood glucose goals are
Don’t Miss: Symptoms Of Low Blood Sugar In Type 2 Diabetes
Official Fasting Blood Sugar Ada Recommendation For Someone With Diabetes
The American Diabetes Association recommends a fasting blood sugar target of 80 to 130 mg/dl for most nonpregnant adults with diabetes. However, the fasting blood sugar target may need to be individualized for certain people based on such factors as duration of diabetes, age and life expectancy, cognitive status, other health conditions, cardiovascular complications, and hypoglycemia unawareness. Its important that people with diabetes discuss their target blood sugar goals with their healthcare provider.
What Should I Do After I Check My Blood Glucose
Write the blood glucose number in a log book or on a log sheet , and:
- Include all of your blood glucose numbers.
- Write a comment if there is a reason the blood glucose is above or below target.
- Take your blood glucose meter with you when you are away from home.
- Know your blood glucose numbers when you call the clinic or the doctor.
- Bring your blood glucose meter and blood glucose records to all your appointments.
- Bring a list of any questions that you may have.
Don’t Miss: Development Of Type 2 Diabetes
Normal Blood Sugar Ranges In Healthy Non
For a person without any type of diabetes, blood sugar levels are generally between 70 to 130 mg/dL depending on the time of day and the last time they ate a meal. Newer theories about non-diabetic blood sugar levels have included post-meal blood sugar levels as high as 140 mg/dL.
Here are the normal blood sugar ranges for a person without diabetes according to the American Diabetes Association:
- Fasting blood sugar : under 100 mg/dL
- 1 hour after a meal: 90 to 130 mg/dL
- 2 hours after a meal: 90 to 110 mg/dL
- 5 or more hours after eating: 70 to 90 mg/dL
What Is Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes occurs when the body no longer produces enough insulin, or has difficulty using the insulin it produces, causing sugar to build up in the blood.
Over time, this damages blood vessels and nerves and can result in severe complications including: blindness, heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, nerve damage, amputation, and erectile dysfunction.
Adopting a healthier lifestyle can help prevent or control type 2 diabetes, and can significantly reduce your risk of heart disease, and stroke. It can also contribute to your overall well-being and quality of life.
Did You Know?
Nine out of ten Canadians with diabetes have type 2 diabetes. Seniors represent almost 45 per cent of the total number of people with the disease, and this number is expected to rise as Canada’s population continues to age.
Also Check: What Can People With Type 2 Diabetes Eat
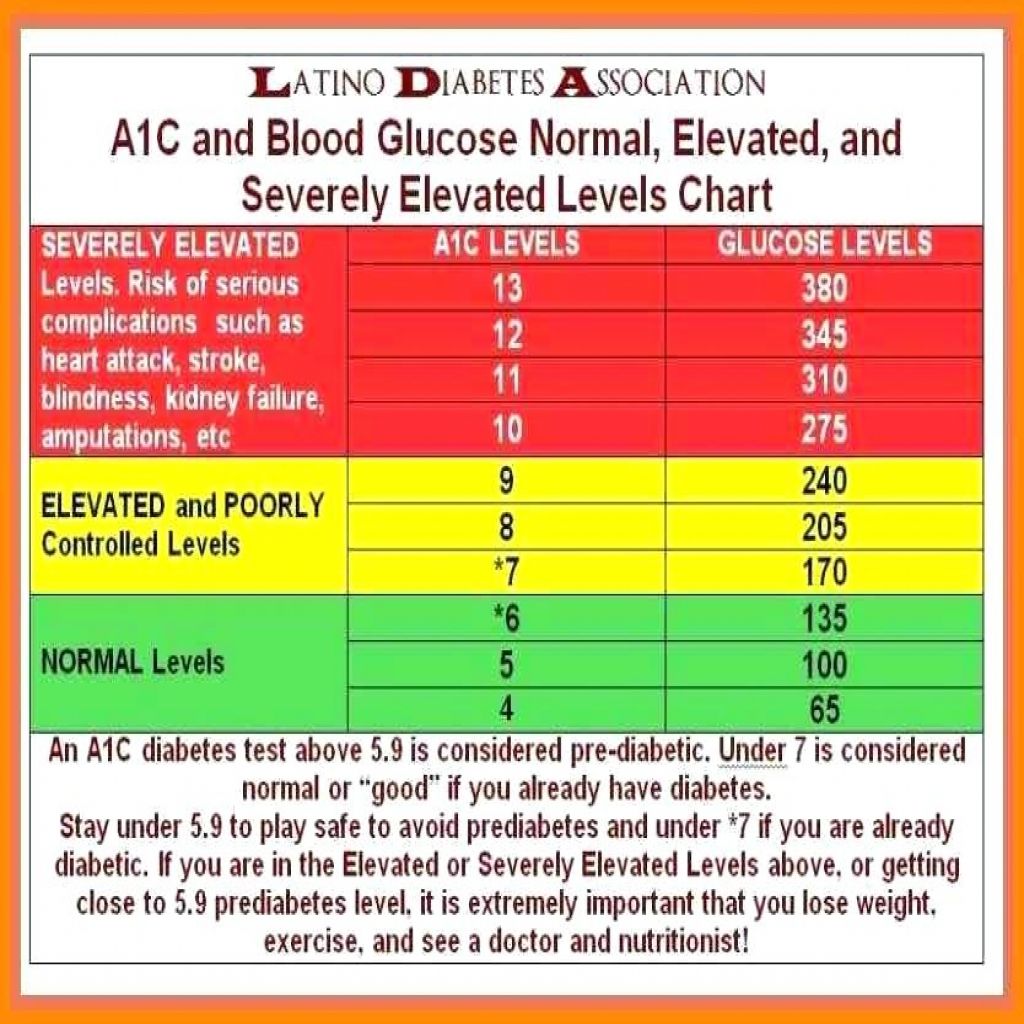
What Is Hemoglobin A1c
Hemoglobin A1C is a lab test. It indicates an average blood glucose reading for the last 90 days. It is done when you find out you have diabetes, and every 3 months after that at clinic visits. A person without diabetes has a Hemoglobin A1C of less than 5.6%.
|
Target Hgb A1C is 7.5% for all children and adults with diabetes. |
The chart below shows the Hemoglobin A1C result compared with the blood glucose number.
Are High Blood Glucose Levels Dangerous
- Sometimes, your blood glucose levels may be high and you may not understand why.
- If you have type 1 diabetes and your blood glucose levels are high, or if you are sick, itâs important to check for ketones in your blood or urine. If you have ketones or are unwell, itâs important to seek medical attention.
- Long-term diabetes-related complications can occur if blood glucose levels are above the target range over a long period of time. If your blood glucose levels are high on a regular basis, ask your doctor or diabetes health professionals for advice.
Read Also: Protein Shake For Diabetic Patients
Normal Blood Sugar Levels In Healthy Individuals
Blood glucose levels, also known as blood sugar levels, can be normal, high, or low. The blood sugar levels are generally measured after 8 hours of eating.
A normal blood sugar range for a healthy adult after 8 hours of fasting is > 70 mg/dL. and < 100 mg/dL.
While a normal blood sugar level in a healthy person after 2 hours of eating is between 90 to 100 mg/dL.
Blood glucose levels change throughout the day. Major factors affecting for such change in the blood glucose levels are as follows:
Summary
Blood Glucose Target Levels
Blood glucose is checked using fingerprick monitoring. Blood glucose targets are individual to each person, and you should agree your own target levels with your diabetes care team. The target blood glucose ranges in Table 1 below are indicated as a guide only.
Table 1: Target blood glucose ranges
*National Institute of Clinical Excellence 2015
** Diabetes UK Council of Health Care Professionals 2015
You May Like: Are Omelettes Good For Diabetics
Fasting Vs Nonfasting Blood Sugar
Fasting blood sugar is a test that measures blood sugar and is used to determine if an individual has diabetes. When a person takes this test, they are not to eat or drink for at least eight hours prior to the test. The results determine whether or not a person is prediabetic or diabetic.
The results are measured in milligrams per deciliter or mg/dL. The following results indicate whether or not a person is prediabetic or diabetic:
- Normal: Less than 100 mg/dL
- Prediabetes: 100 mg/dL to 125 mg/dL
- Diabetes: 126 mg/dL or higher
To test nonfasting blood sugar, an A1C test is administered to determine the average blood sugar level of an individual over a period of two to three months. There is no need to fast prior to taking this test. The following results indicate whether or not a person is prediabetic or diabetic:
- Normal: 5.7%
- Diabetes: 6.5%
What Affects Blood Sugar Levels

While many things affect blood sugar levels, these are the major factors:
People without diabetes usually dont think about their blood sugar because their pancreas is always working to keep it in a healthy range. People with type 1 diabetes must check their blood sugar several times a day using a glucometer , which measures a small drop of blood from a finger:
- If blood sugar is too low, they need a source of fast-acting glucose .
- If blood sugar is too high, they need insulin.
Read Also: What Do You Do If You Think You Have Diabetes
Blood Sugar Target Levels For Nonpregnant Adults With Diabetes
From the 2017 American Diabetes Association Standards of Care, the following chart shows current targets for blood sugars for nonpregnant adult patients with diabetes:
Summary of Glycemic Recommendations for Adults with Diabetes
| A1C < 7.0% |
| Preprandial capillary plasma glucose 80130 mg/dL* |
| Peak postprandial capillary plasma glucose < 180 mg/dL* |
| *More or less stringent glycemic goals may be appropriate for individual patients. Goals should be individualized |
| **based on duration of diabetes, age/life expectancy, comorbid conditions, known CVD or advancedmicrovascular complications, hypoglycemia unawareness, and individual patient considerations.Postprandial glucose may be targeted |
Blood sugar target levels for nonpregnant adults with diabetes coincide with A1C less than 7
An A1C less than 7 percent is the guideline for adults with diabetes, and the target ranges of 80-130 mg/dl fasting or pre-meal, and 80-180 mg/dl after meals corresponds with an A1C of less than 7 percent.
I suggest you read the following articles:
These values represent what research has shown to be the optimal blood sugar targets for nonpregnant adults to avoid complications of diabetes in the long term. Less than 70 mg/dl is considered a low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia, and the newest guideline consider that you want to catch a low blood sugar before it occurs.
Why Your Blood Sugar Level May Be High
Based on the ADA guidelines above, if your blood sugar is above 180 mg/dL two hours after a meal, it is considered above the normal range. What might cause your glucose or blood sugar to rise? Consider the following factors:
- Consuming more carbohydrates or a larger meal than usual
- Not taking enough insulin or oral diabetes medication based on carbohydrates or activity levels
- Reduced physical activity
- Side effects from medications like steroids or antipsychotics
Don’t Miss: Type 2 Diabetes Dry Mouth
Blood Sugar Levels For Adults With Diabetes
Each time you test your blood sugar, log it in a notebook or online tool or with an app. Note the date, time, results, and any recent activities: What medication and dosage you took What you ate How much and what kind of exercise you were doing That will help you and your doctor see how your treatment is working. Well-managed diabetes can delay or prevent complications that affect your eyes, kidneys, and nerves. Diabetes doubles your risk for heart disease and stroke, too. Fortunately, controlling your blood sugar will also make these problems less likely. Tight blood sugar control, however, means a greater chance of low blood sugar levels, so your doctor may suggest higher targets.Continue reading > >
Measure Your Waist Circumference
The risk of developing type 2 diabetes is higher if fat is stored around the abdomen . BMI assessments do not take into account where fat is stored. Men with a waist circumference of 102 cm or more and women with a waist circumference of 88 cm or more are at higher risk. Measure after breathing out . This is not the same as the waist size on your pants.
You May Like: Can You Get Rid Of Diabetes Type 1
Why Test My Blood Glucose
Blood testing is the best way to stay in control of your diabetes because it tells you what is happening at any particular moment. It can help determine if you are at risk of a hypoglycaemic episode or a hyperglycaemic episode . You should never change any long-term medication you are taking in response to a one-off high or low reading. You should first try to work out if there is a pattern before making any changes and always talk to your diabetes care team first.
What Is Diabetic Ketoacidosis
If you think you may have low blood sugar, check it even if you dont have symptoms.
When too many ketones are produced too fast, they can build up in your body and cause diabetic ketoacidosis, or DKA. DKA is very serious and can cause a coma or even death. Common symptoms of DKA include:
- Fast, deep breathing.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Stomach pain.
If you think you may have DKA, test your urine for ketones. Follow the test kit directions, checking the color of the test strip against the color chart in the kit to see your ketone level. If your ketones are high, . DKA requires treatment in a hospital.
DKA happens most in people with type 1 diabetes and is sometimes the first sign of type 1 in people who havent yet been diagnosed. People with type 2 diabetes can also develop DKA, but its less common.
Read Also: How Does Diabetes Lead To Renal Failure
Hemoglobin A1c Levels In Children And Adolescents With Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract Hemoglobin A1c was measured as an indicator of glucose control in 180 children and adolescents with diabetes mellitus who received two daily injections of insulin as part of a highly structured treatment program. A total of 426 HbA1c determinations was made in the group of 180 patients. HbA1c values were elevated in most patients despite the aggressive treatment. The HbA1c level was very elevated at diagnosis, fell to near normal after 60-90 days of insulin therapy, increased gradually, and reached a plateau after approximately 4 yr duration . Mean insulin dose paralleled both HbA1c and duration of diabetes. The relationship between endogenous insulin secretion and glucose control was examined in those patients with diabetes for longer than 5 yr. Patients were separated into three groups based on HbA1c levels: those with HbA1c less than 9% , between 9 and 11% , and greater than 11% . Serum C-peptide and glucose concentrations were measured 2 h after a standard breakfast in those patients in the low and high HbA1c groups . C-peptide was detectable in all patients and the mean C-peptide levels did not differ significantly in the two groups, although postprandial glucose concentrations were significantly lower in the low HbA1c group .Continue reading > >
What Are Normal Blood Sugar Levels

April 19, 2018 by Diabetes Care
When you or someone you care for is diagnosed with diabetes, a three-worded phrase quickly becomes part of everyday conversation: that is, blood sugar levels or blood glucose levels.
Blood glucose is the amount of glucose in a persons blood at a given time. An individual with diabetes can gain valuable information by knowing how their levels compare with targeted healthy blood sugar levels at various times in the day.
Lets start by clarifying the generally agreed upon blood glucose targets.
Diabetes Canadas 2018 Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Prevention and Management of Diabetes in Canada is a guide issued to healthcare professionals to help direct an agreed standard of diabetes care in Canada. The chart below shows the recommendations for blood glucose levels for most people with diabetes.
Don’t Miss: Does Insulin Cause Erectile Dysfunction
High Blood Sugar Symptoms
Hyperglycemia is the medical term for high blood sugar. Hyperglycemia happens when the body doesnt have enough insulin or when it cant use insulin correctly. Many things can cause high blood glucose levels like Type 1 diabetes, Type 2 diabetes, stress, illness, or the dawn phenomenon. If you have hyperglycemia or suspect you may have it, talking with a healthcare provider is always a good idea. A doctor can help you determine whats causing your high blood sugar levels and lower it to a healthy range.
Here are some of the most common symptoms that may indicate hyperglycemia:
- Fatigue
- Vision loss
You should seek immediate medical attention if your blood sugar reaches 400 mg/dL or higher.
When patients experience any of these accompanied by elevated blood sugar levels, diabetic patients are advised to go directly to the ER to avoid diabetes-induced coma, says Vikram Tarugu, MD, a gastroenterologist and the CEO of Detox of South Florida. Patients who have elevated blood sugar may also present with frothy, ketone-like smelling breath.
Here are some lifestyle changes and medical treatments that can help treat hyperglycemia: