Sociodemographic And Behavioural Information
Information on sociodemographic and behavioural risk factors was collected through face-to-face interviews using an interviewer-administered questionnaire. Information was collected on age, sex, ethnicity, educational status, marital status, occupation type, history of raised blood pressure and DM, alcohol consumption, and smoking habits. The commonly used classification for ethnicity in Nepal has six categories: Dalit Disadvantaged Janajatis Disadvantaged non Dalit Terai Caste Groups Religious Minorities Relatively advantaged Janajatis and Upper Caste Groups .
Data on part of physical measurements, blood pressure measurement and biochemical measurement were done using respective equipment and procedures, and the detail including the information on quality control has been explained elsewhere. Participants were defined as having DM if they had raised fasting glucose or raised PP blood glucose level , or if the participants were on anti-diabetic medication at the time of the study whereas the key definition of the terms raised blood pressure, body mass index , tobacco use and alcohol consumption has been explained in the report published previously.
Who Gets Diabetes What Are The Risk Factors
Factors that increase your risk differ depending on the type of diabetes you ultimately develop.
Risk factors for Type 1 diabetes include:
- Having a family history of Type 1 diabetes.
- Injury to the pancreas .
- Presence of autoantibodies .
- Physical stress .
- Exposure to illnesses caused by viruses.
Risk factors for prediabetes and Type 2 diabetes include:
- Family history of prediabetes or Type 2 diabetes.
- Being African-American, Hispanic, Native American, Asian-American race or Pacific Islander.
- Being overweight.
Risk factors for gestational diabetes include:
- Family history of prediabetes or Type 2 diabetes.
- Being African-American, Hispanic, Native American or Asian-American.
- Being overweight before your pregnancy.
- Being over 25 years of age.
Risk Factors For Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops when a person is pregnant.
Most women with gestational diabetes will not have had any diabetes before. Gestational diabetes resolves after the birth of the baby.
Once a woman has had gestational diabetes, the chances are that it will return in future pregnancies. Also, having had gestational diabetes, the individuals risk of developing type 2 diabetes increases sevenfold.
Risk factors for gestational diabetes are much the same as other kinds of diabetes. These include:
- a family or personal history of diabetes
- prediabetes
There is no cure for diabetes at present. However, a person can reverse diabetes or see it go into remission.
A return to normal blood glucose levels for at least 1 year without using medication suggests that diabetes is in remission.
Early diagnosis and proper treatment can help prevent or delay diabetes-induced difficulties. Knowing the risk factors can help people to identify and manage diabetes before it causes problems.
While a person cannot avoid some risk factors, such as age and race, they can take steps to reduce the damage of others, including high blood pressure, excess body weight, and a poor diet.
Controlling these risk factors can go a long way towards of diabetes or the possibility of developing it.
These steps include:
Recommended Reading: How To Get Rid Of Diabetes Stomach Fat
What Are The Symptoms Of Type 2 Diabetes
Symptoms of Type 2 diabetes tend to develop slowly over time. They can include:
- Urinary tract infections and bladder infections.
Rarely, Type 2 diabetes leads to a condition called diabetic ketoacidosis . DKA is a life-threatening condition that causes your blood to become acidic. People with Type 1 diabetes are more likely to have DKA.
How Is Type 2 Diabetes Diagnosed
The following blood tests help your healthcare provider diagnose diabetes:
- Fasting plasma glucose test: checks your blood glucose level. This test is best done in the office in the morning after an eight hour fast .
- Random plasma glucose test: This lab test can be done any time without the need to fast.
- Glycolated hemoglobin testing measures your average blood sugar levels over three months.
- Oral glucose tolerance testing checks your blood sugar levels before and after you drink a sugary beverage. The test evaluates how your body handles glucose.
| Type of test |
|---|
Don’t Miss: What Is The Best Meal Replacement For Diabetics
How Do I Check My Blood Glucose Level Why Is This Important
Checking your blood glucose level is important because the results help guide decisions about what to eat, your physical activity and any needed medication and insulin adjustments or additions.
The most common way to check your blood glucose level is with a blood glucose meter. With this test, you prick the side of your finger, apply the drop of blood to a test strip, insert the strip into the meter and the meter will show your glucose level at that moment in time. Your healthcare provider will tell you how often youll need to check your glucose level.
Diabetes Treatment & Care
Diabetes is a prevalent disease, every individual needs unique care. We embolden people with diabetes and their families to learn as much as possible about the latest medical approaches, as well as the salubrious lifestyle. Good communication with a team of experts can avail you feel in control and respond to transmuting needs.
The major goal of treating diabetes is to control blood sugar levels within the normal range.
Type 1 Diabetes Treatment:
- Weight reduction,
- Type 2 diabetes diet, and exercise
- Oral medications are prescribed when these quantifications fail to control the elevated blood sugars of type 2 diabetes.
If oral medications become fail to treatment then insulin is initiated.
Read Also: Number Of Grams Of Sugar Per Day For Diabetic
How Does Diabetes Lead To Amputation
Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to poor blood flow . Without oxygen and nutrients , you are more prone to the development of cuts and sores that can lead to infections that cant fully heal. Areas of your body that are farthest away from your heart are more likely to experience the effects of poor blood flow. So areas of your body like your toes, feet, legs and fingers are more likely to be amputated if infection develops and healing is poor.
Study Design Period And Sample Size
A study was a community-based cross-sectional conducted from January, 1 to February 15, 2019. The source population of the study was all adult population above 18 years in Hawassa Zuria woreda who are living in the area for more than six months. And, the study population was adult population aged above 18 years living within eligible households in randomly selected Kebeles in Hawassa zuria Woreda. The sample size was calculated by a single population proportion formula bearing in mind a 6.5% prevalence of DM from the previous study,7 3% desired precision, 95% confidence interval , and a design effect of 2. Accordingly, the smallest sample size intended was found to be 519.
Recommended Reading: Where Are Insulin Pumps Placed
How Often Do I Need To See My Primary Diabetes Healthcare Professional
In general, if you are being treated with insulin shots, you should see your doctor at least every three to four months. If you are treated with pills or are managing diabetes through diet, you should be seen at least every four to six months. More frequent visits may be needed if your blood sugar is not controlled or if complications of diabetes are worsening.
What Is Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a disease where your body cant use energy from food properly. Your pancreas produces insulin to help your cells use glucose . But over time your pancreas makes less insulin and the cells resist the insulin. This causes too much sugar to build up in your blood. High blood sugar levels from Type 2 diabetes can lead to serious health problems including heart disease, stroke or death.
Also Check: How To Count Carbs For Type 1 Diabetes
Can Diabetes Be Cured Or Reversed
Although these seem like simple questions, the answers are not so simple. Depending on the type of your diabetes and its specific cause, it may or may not be possible to reverse your diabetes. Successfully reversing diabetes is more commonly called achieving remission.
Type 1 diabetes is an immune system disease with some genetic component. This type of diabetes cant be reversed with traditional treatments. You need lifelong insulin to survive. Providing insulin through an artificial pancreas is the most advanced way of keeping glucose within a tight range at all times most closely mimicking the body. The closest thing toward a cure for Type 1 is a pancreas transplant or a pancreas islet transplant. Transplant candidates must meet strict criteria to be eligible. Its not an option for everyone and it requires taking immunosuppressant medications for life and dealing with the side effects of these drugs.
Its possible to reverse prediabetes and Type 2 diabetes with a lot of effort and motivation. Youd have to reverse all your risk factors for disease. To do this means a combination of losing weight, exercising regularly and eating healthy . These efforts should also lower your cholesterol numbers and blood pressure to within their normal range. Bariatric surgery has been shown to achieve remission in some people with Type 2 diabetes. This is a significant surgery that has its own risks and complications.
What Types Of Healthcare Professionals Might Be Part Of My Diabetes Treatment Team
Most people with diabetes see their primary healthcare provider first. Your provider might refer you to an endocrinologist/pediatric endocrinologist, a physician who specializes in diabetes care. Other members of your healthcare team may include an ophthalmologist , nephrologist , cardiologist , podiatrist , neurologist , gastroenterologist , registered dietician, nurse practitioners/physician assistants, diabetes educator, pharmacist, personal trainer, social worker, mental health professional, transplant team and others.
Don’t Miss: Can You Swim With An Insulin Pump
When Should I Call My Doctor
If you havent been diagnosed with diabetes, you should see your healthcare provider if you have any symptoms of diabetes. If you already have been diagnosed with diabetes, you should contact your provider if your blood glucose levels are outside of your target range, if current symptoms worsen or if you develop any new symptoms.
How Should I Manage Sick Days
People with diabetes need to monitor their health especially carefully if they get sick. Illnesses as common as a cold or the flu can be dangerous if they interfere with your food intake, insulin delivery, and blood sugar levels. Make a sick day plan with your healthcare provider so you know how often to check your blood sugar and what medications to take.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Type 1 diabetes is a disease that prevents your pancreas from making enough insulin. It causes glucose to build up in your blood. High blood glucose levels can lead to serious health problems, including nerve damage, heart disease or stroke. People with Type 1 diabetes need to monitor their blood glucose levels closely and take insulin regularly.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 07/07/2021.
References
Recommended Reading: What Does Insulin Do To Blood Sugar
What Should My Blood Glucose Level Be
Ask your healthcare team what your blood glucose level should be. They may have a specific target range for you. In general, though, most people try to keep their blood glucose levels at these targets:
- Before a meal: between 80 and 130 mg/dL.
- About two hours after the start of a meal: less than 180 mg/dL.
Can Diabetes Cause Headaches Or Dizziness
Yes, its possible to develop headaches or dizziness if your blood glucose level is too low usually below 70 mg/dL. This condition is called hypoglycemia. You can read about the other symptoms hypoglycemia causes in this article.Hypoglycemia is common in people with Type 1 diabetes and can happen in some people with Type 2 diabetes who take insulin or medications such as sulfonylureas.
You May Like: Pathophysiology Of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
Does Eating Sugary Foods Cause Diabetes
Sugar itself doesn’t directly cause diabetes. Eating foods high in sugar content can lead to weight gain, which is a risk factor for developing diabetes. Eating more sugar than recommended American Heart Association recommends no more than six teaspoons a day for women and nine teaspoons for men leads to all kinds of health harms in addition to weight gain.
These health harms are all risk factors for the development of diabetes or can worsen complications. Weight gain can:
- Raise blood pressure, cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
- Increase your risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Cause fat buildup in your liver.
- Cause tooth decay.
How Do I Take Insulin
You can take insulin in one of the following ways:
- Injection:Injectable insulin uses a vial and syringe. With each injection, you use a syringe to get the correct dose of insulin out of the vial. Insulin can be injected into the fatty tissue of your belly, upper arm, thigh or buttocks. Injections are usually the least expensive way to take insulin.
- Pen: Insulin pens are similar to injections, but the pen is pre-filled with insulin. The disposable pen needles are usually more convenient than shots. They can also be a good option for people with low vision.
- Pump:Insulin pumps are devices that deliver insulin continuously and on demand. They mimic the way your pancreas would naturally release insulin. Pumps deliver insulin through a tiny catheter that goes in your belly or another fleshy area of your body.
Your healthcare provider may recommend three to four doses of insulin each day. Long-acting insulin usually works best when taken at about the same time every day. Take rapid-acting insulin within 15 minutes before a meal. This ensures its ready to work when glucose from food enters your blood.
You May Like: How Can A Diabetic Wound Heal Faster
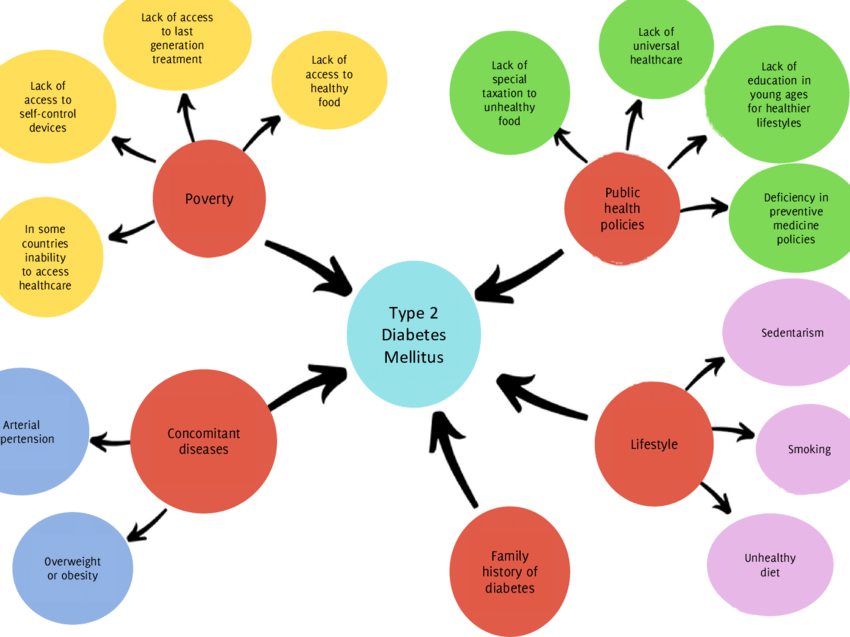
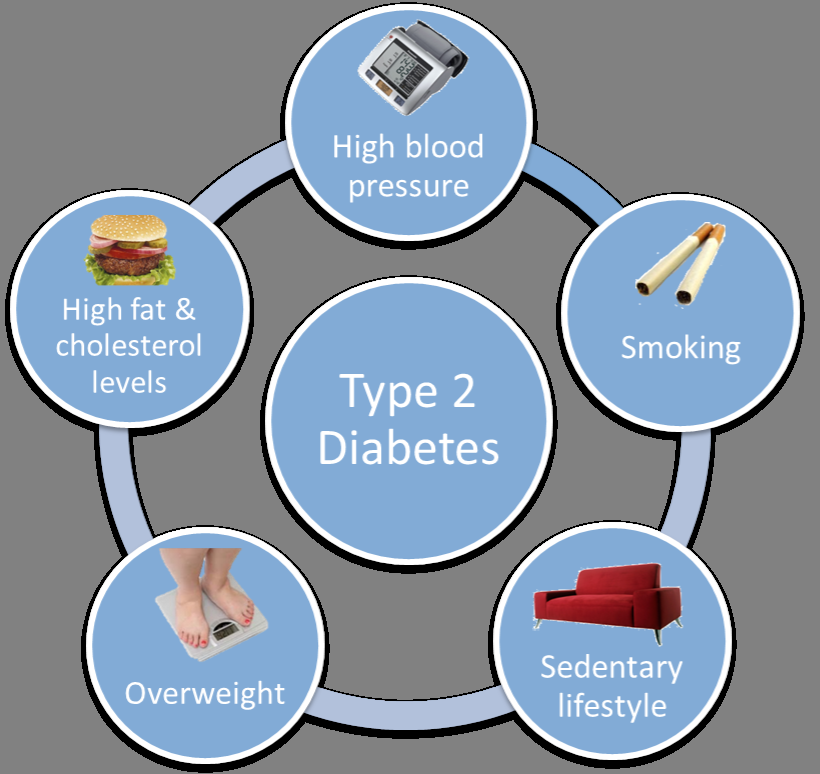
Risk Factors For Type 2 Diabetes
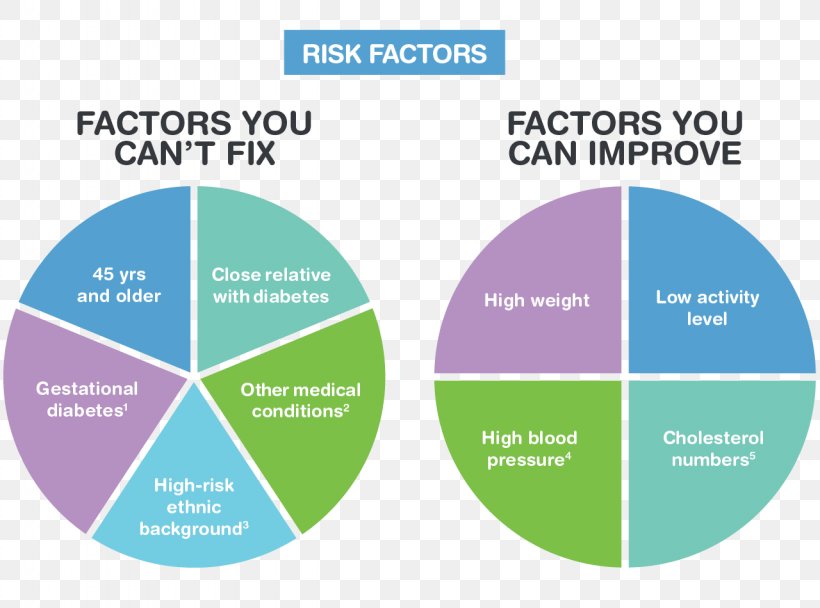
You can have type 2 diabetes without any obvious warning signs or symptoms. If you think you might be at risk for developing diabetes, don’t ignore these risk factors. The earlier you’re diagnosed, the sooner you can take action to stay wellnow and in the future.
Some diabetes risk factors can be managed or reduced, while other factors may be beyond your control. For example, you have a greater risk of developing type 2 diabetes if you are over the age of 40 or if you have a parent, brother, or sister with diabetes. Your ethnic background is also a factor: being of African, Arab, Asian, Hispanic, Indigenous, or South Asian descent can increase your risk of living with type 2 diabetes.
Having any of the following conditions increases your chances of developing diabetes:
- high blood pressure
- high levels of cholesterol or other fats in the blood
- a high BMIor are overweight
- prediabetes (impaired glucose tolerance or impaired fasting glucose
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
- psychiatric disorders
- obstructive sleep apnea
- darkened patches of skin called acanthosis nigricans
Lastly, if you have been prescribed a glucocorticoid medication by a doctor, you will also have an increased risk.
How Is Gestational Diabetes Managed
If youre diagnosed with gestational diabetes, you may need more frequent checkups during your pregnancy. Your healthcare provider will check your blood sugar levels regularly. You may need to monitor your blood sugar at home with a tool called a glucose meter.
Some women need medication to manage gestational diabetes. But most women can keep their blood sugar levels under control with diet and exercise.
Read Also: Diabetes Kidney Failure Life Expectancy
How Is Diabetes Managed
Diabetes affects your whole body. To best manage diabetes, youll need to take steps to keep your risk factors under control and within the normal range, including:
- Keep your blood glucose levels as near to normal as possible by following a diet plan, taking prescribed medication and increasing your activity level.
- Maintain your blood cholesterol and triglyceride levels as near the normal ranges as possible.
- Control your blood pressure. Your blood pressure should not be over 140/90 mmHg.
You hold the keys to managing your diabetes by:
- Planning what you eat and following a healthy meal plan. Follow a Mediterranean diet or Dash diet. These diets are high in nutrition and fiber and low in fats and calories. See a registered dietitian for help understanding nutrition and meal planning.
- Exercising regularly. Try to exercise at least 30 minutes most days of the week. Walk, swim or find some activity you enjoy.
- Losing weight if you are overweight. Work with your healthcare team to develop a weight-loss plan.
- Taking medication and insulin, if prescribed, and closely following recommendations on how and when to take it.
- Quitting smoking .
You have a lot of control on a day-to-day basis in managing your diabetes!
Can Prediabetes Type 2 Diabetes And Gestational Diabetes Be Prevented
Although diabetes risk factors like family history and race cant be changed, there are other risk factors that you do have some control over. Adopting some of the healthy lifestyle habits listed below can improve these modifiable risk factors and help to decrease your chances of getting diabetes:
- Eat a healthy diet, such as the Mediterranean or Dash diet. Keep a food diary and calorie count of everything you eat. Cutting 250 calories per day can help you lose ½ pound per week.
- Get physically active. Aim for 30 minutes a day at least five days a week. Start slow and work up to this amount or break up these minutes into more doable 10 minute segments. Walking is great exercise.
- Lose weight if you are overweight. Dont lose weight if you are pregnant, but check with your obstetrician about healthy weight gain during your pregnancy.
- Lower your stress. Learn relaxation techniques, deep breathing exercises, mindful meditation, yoga and other helpful strategies.
- Limit alcohol intake. Men should drink no more than two alcoholic beverages a day women should drink no more than one.
- Get an adequate amount of sleep .
- Take medications to manage existing risk factors for heart disease or to reduce the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes as directed by your healthcare provider.
- If you think you have symptoms of prediabetes, see your provider.
Also Check: What Foods Should A Diabetic Eat To Lose Weight