What Are The Drawbacks
Using an insulin pump isnt always the best option for everyone. Lets take a closer look at some of the drawbacks of this device.
An insulin pump and daily injections are both effective methods of controlling your blood sugar levels. Whats most important is that you monitor your blood sugar carefully and follow your doctors instructions for managing your diabetes.
Its very important that you spend time with a diabetes educator or your doctor to learn how to use your insulin pump properly.
Before you start using an insulin pump, its important that you know how to:
Most pumps contain a bolus dose calculator. This helps you calculate how much extra insulin you may need based on your daily carbohydrate intake.
Some pumps also offer an extended bolus option. This allows you to administer the dose over 2 to 3 hours. This option can help prevent hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar. Hypoglycemia is a potentially dangerous condition.
You must change the insulin in the pump according to the manufacturers recommendations. For example, rapid-acting insulin formulations such as lispro and aspart must be replaced every 144 hours or every 6 days, according to a 2019 study. Glulisine, on the other hand, should be replaced every 48 hours.
Remember that insulin pumps cannot do everything to manage your diabetes. You play the most important role in managing your care, including:
- checking your blood sugar regularly
Pros And Cons Of Insulin Pumps
Insulin pumps have some pros and cons. One pro is that they help you calculate your insulin doses and make it easier to take bolus doses of insulin.
Additionally, the pumps that integrate with a continuous glucose monitor make it easier to manage glucose levels, says Isaacs.
However, there are also some disadvantages of insulin pumps. These include:
- The risk of a serious complication called diabetic ketoacidosis if you get disconnected from the pump. Diabetic ketoacidosis occurs when your body produces ketones, or a type of blood acid, after not making enough insulin. It can be fatal if left untreated.
- You must wear the device constantly. Ask your doctor how long you can safely disconnect from your pump, and make sure to check your blood sugar regularly if you must disconnect it.
- You have to refill the pump with insulin regularly.
- You should have extra supplies handy in case of a pump failure.
- There’s a risk of infection if the infusion set is left in for too long and not changed.
Advantages Of An Insulin Pump
- Youâll need fewer needle sticks. A pump requires one shot every few days when you change your infusion set.
- A pump is more accurate than shots, helping you better manage blood sugar levels.
- Youâll have fewer blood sugar lows, which is important if you often have hypoglycemia.
- It may improve your A1c levels.
- Dosing for meals and snacks is easier.
- Itâs easier to plan for exercise.
- Itâs easier to bolus.
- It helps manage early morning high blood sugar, also called the âdawn phenomenon.â
One thing to keep in mind: Youâll always need to have regular injectable insulin on hand in case the pump stops working.
Read Also: Diabetic Strips 4 Cash Phone Number
Choosing And Using An Insulin Pump Infusion Set
When a person uses an insulin pump to control his diabetes, one of the decisions he has to make is what model of infusion set to use. Pumps are often an excellent choice for people who use insulin and seek tight control of their diabetes but need some flexibility in their diabetes regimen.
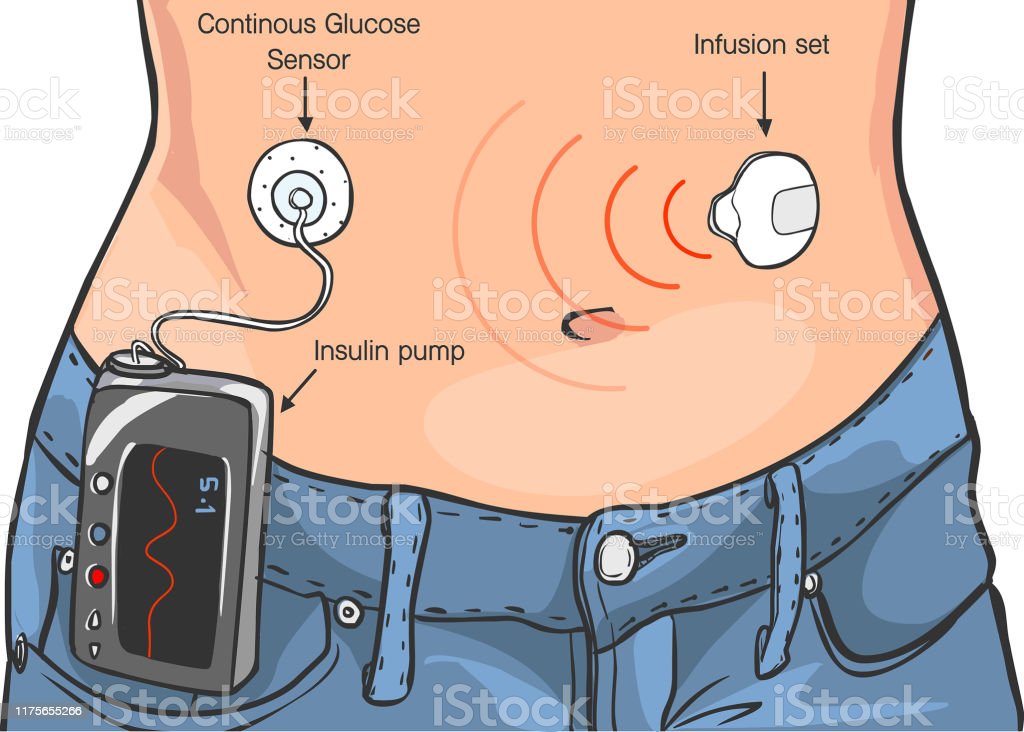
Most insulin pumps require the use of an infusion set to deliver insulin from the pump to the user. An infusion set consists of a length of thin plastic tubing, a very thin stainless steel or Teflon cannula that is inserted just under the skin, and a plastic connector that joins tubing and cannula together. The connector is generally mounted on an adhesive patch that is stuck to the skin at the insertion site to help keep the cannula in place. The connector allows a person to disconnect from his pump temporarily without removing the infusion set.
Insulin infusion sets come in a variety of styles to suit individuals unique needs and preferences. In addition to having either a Teflon or steel cannula, infusion sets may be designed to have the cannula inserted straight into the subcutaneous tissue or at an angle. Some cannulas can only be inserted manually, while others can be inserted either manually or with an insertion device. All infusion sets offer a variety of tubing lengths.
Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion
Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion can give a better quality of life .
There has been a systematic review of 11 studies of at least 10 weeks duration, comparing soluble insulin with the analogues lispro and, in one case, aspart in pumps . The analogue produced a small, significant improvement in HbA1c. There were no differences in hypoglycemia. Ketosis, hyperglycemia, and clogging were not common.
In 132 patients with type 2 diabetes using insulin randomly assigned to continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion or multiple daily injections of insulin aspart and NPH insulin) for 16 weeks, after 8 weeks training to establish optimal dosages there were more episodes of hyperglycemia with multiple daily injections. HbA1c was identical. Most of the patients who expressed a view wanted to stay on the pump.
In 40 patients aged 425 years with type 1 diabetes who were given continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion for 6 months the number of episodes of hypoglycemia was reduced by a half . There were two episodes of diabetic ketoacidosis. In 10 patients lipohypertrophy developed at the insertion site and three patients had signs of skin redness, which improved with local antibiotic treatment.
Sujoy Ghosh MD DM MRCP MRCPS, Andrew Collier BSc MD FRCP, in, 2012
Read Also: Is Chocolate Milk Good For Diabetics
Where Do I Attach The Needle For My Insulin Pump
Most people choose the abdomen for insulin delivery. This area is convenient to use and gives a reliable, uniform absorption of insulin. How you insert the insulin needle will be different for different brands of infusion sets. With some infusion sets, you use a needle to insert a catheter and then remove the needle, leaving the soft catheter under your skin. With other sets, you insert a short needle. Pumps are easy to remove temporarily because, after clamping the tubing, you can leave the infusion set in place. You reattach only the pump. Some infusion sets even have a quick-release feature. Continue Learning about Insulin Pumps Videos Important: This content reflects information from various individuals and organizations and may offer alternative or opposing points of view. It should not be used for medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. As always, you should consult with your healthcare provider about your specific health needs.Continue reading > >
Sensor Augmented Pump Therapy
The development of CGM systems in the early 2000s was followed by the advent of the sensor augmented pump , which combines a CGM and insulin pump in one system. A CGM device consists of three components: 1) a thin, flexible sensor, which is inserted into the subcutaneous tissue and continuously measures glucose levels in the interstitial fluid, 2) a transmitter that sends the sensor glucose data to a receiver, and 3) a receiver, which displays the glucose values. In an SAP system, the insulin pump pairs to a CGM system and acts as the receiver, displaying CGM sensor glucose data on the pumps home screen and thus allowing users easy access to the sensor glucose information. SAP systems have shown a greater reduction in A1C after 12 months when compared to MDI therapy . The STAR 3 study, a randomized controlled trial involving 82 children and adolescents, found that participants using SAP therapy were more likely to meet glycemic targets than those using MDI, and SAP users had reduced glycemic variability after 12 months . Those wearing the sensor more consistently in the SAP group were more likely to meet glycemic targets, suggesting that easy access to CGM data on the pump helps individuals respond more readily to high and low glucose values, thus reducing glucose variability .
Read Also: Can Diabetes Cause Swollen Lymph Nodes
Why Should I Use An Insulin Pump
The choice to use an insulin pump instead of injections usually comes down to personal preference. However, you may want to consider an insulin pump if:
- You have frequent low blood sugar reactions.
- You have a condition called gastroparesis, which causes a delay in your stomach’s ability to absorb food.
- You are planning to get pregnant.
- You want to use the pump’s bolus calculator functions to set up insulin doses.
About 25% of people with type 1 diabetes use an insulin pump. Some people switch between injections and pump use. For instance, children may use an insulin pump during the school year but not in the summer.
You can use an insulin pump to give your body insulin, but you still need to check your blood sugar level. By checking your blood sugar regularly, you can make sure that the pump and the infusion are working correctly.
How Is An Insulin Pump Worn
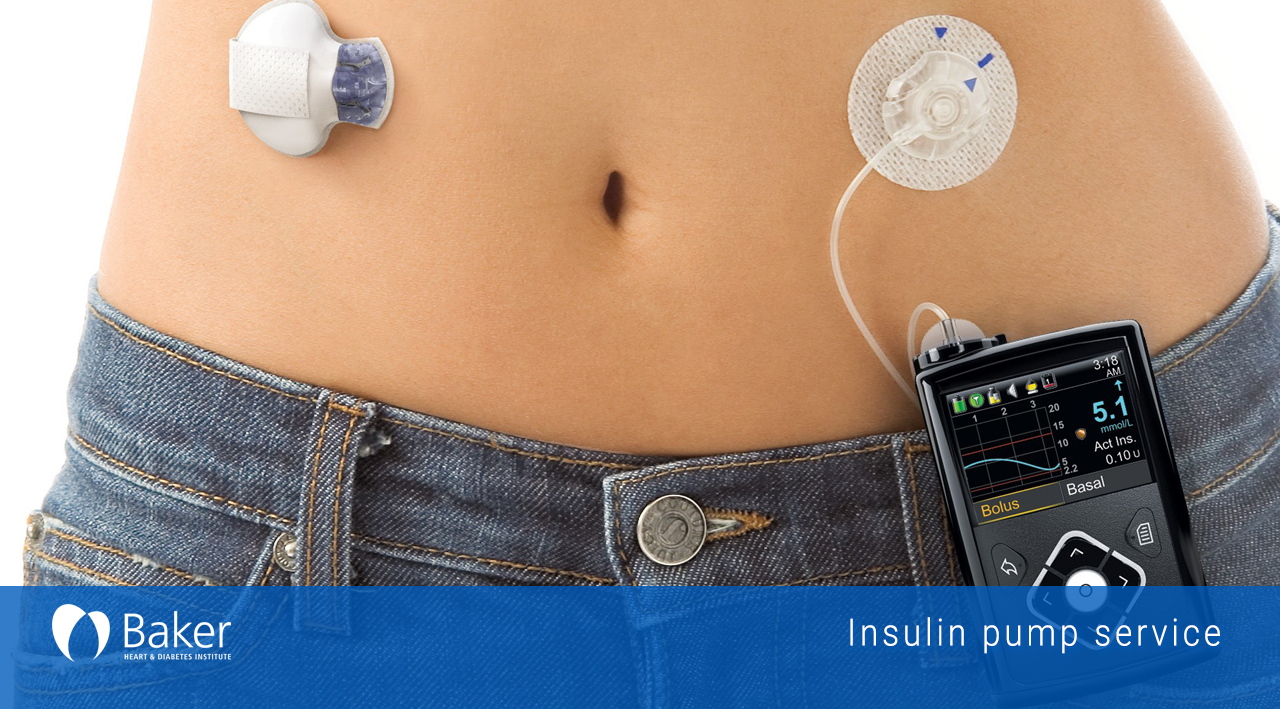
Insulin pumps are connected to the body via the infusion set. The small needle or plastic cannula sits under your skin through the day whilst the infusion set is held in place by an adhesive that is similar to the sticky backing of a plaster.
The infusion set can usually be placed in the same sites on the body as are used for injections. The infusion set can usually be left in for two to three days. After this you must insert a new infusion set into a different place on your body. It is important to rotate sites, just as you should do with standard insulin injections.
The pump itself can be safely and discretely attached in lots of different ways, such as to a belt or the waist of trousers, held in pockets or in pouches attached to your thigh or upper arm.
Don’t Miss: What Is A Good Low Carb Diet For Diabetics
Hyperglycemia And Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Studies have also shown improved glycemic control in patients using insulin pumps compared with patients using multiple daily insulin injections. Another study showed that the incidence of DKA is equivalent for pump users and patients on MDIs. In particular, nocturnal and predawn glycemic control is improved on insulin pump therapy, as hour-by-hour preprogrammed basal rate changes facilitated by the pump help counteract prebreakfast blood glucose increases that are not easily addressed with injection therapy.
However, hyperglycemia and DKA can occur with insulin pump use, whether due to user error in programming or to device malfunction. Studies show that device problems leading to hyperglycemia include diminished insulin delivery due to a depleted or malpositioned battery, occlusion or crimping of the cannula, disruption of the infusion set , or complete pump failure. DKA in particular occurs more frequently early after starting insulin pump use, suggesting that acclimation to the device has a learning curve.
Finally, continuous use of the same infusion set for an extended period increases the risk of cannula occlusion and changes the physiochemical environment at the delivery site, altering the rate of insulin absorption and increasing the risk of hyperglycemia, as well as other problems described below. One study has found that there was a slow but steady increase in average daily serum glucose concentrations as patients wore an infusion set continuously beyond 3 days.
What Is The Best Injection Site For Insulin
The best injection site for insulin is the abdomen. Injecting insulin on the stomach will ensure the insulin reaches your bloodstream quickly since there is no fatty tissue in that area to slow down absorption. You can also inject insulin in your thigh or buttocks, but these areas of the body may not absorb as quickly as the stomach or arm. However, injecting insulin in these areas can give you a sense of comfort since you’ll be able to see the needle before it goes into your skin. If you feel more comfortable with a particular site, then stick with that one. It’s important to inject into all areas of your body, but be aware that injections in some sites may require more force and pressure than others.
Recommended Reading: Is Propel Water Good For Diabetics
What Happens While Using An Insulin Pump
An insulin pump delivers insulin in one of two ways:
- Small, continuous insulin doses .
- Surges of insulin near mealtimes .
While using an insulin pump, you still need to check your blood sugar levels. Most people check blood sugar at least four times a day. Or you may use a continuous glucose monitor.
The pump uses information you enter about your food intake and blood sugar levels to calculate how much bolus insulin you need. The pump then recommends a bolus dose to you and waits for your approval before delivering. In addition, some pumps automatically adjust basal doses based on glucose levels from a continuous glucose monitor.
Tips For Using Insulin Pump Therapy
If used properly, insulin pumps and their related components are reliable and safe. But as with any technology, problems can sometimes occur. It’s important to be aware of potential problems and what to do if they arise, to maintain blood sugar levels and avoid side effects.
Tips for proper insulin pump therapy include:
- Watch for cannulas becoming kinked, or leakage in the reservoir or the infusion sets. Kinked cannulas and insulin leaks can lead to interruption of insulin flow, blockages, or mechanical failures.
- Check your pump for damage, such as a cracked display or jammed buttons.
- Make sure your battery is working, check the battery indicator and replace the battery as needed. Check for a loose or damaged battery cap to avoid unexpected power loss.
- Don’t expose your pump to water if it is not waterproof. Also avoid exposing the internal casing to water by changing the battery only in a dry area and making sure that the battery cover is not worn out or missing.
- Understand your personal settings. Be sure to adjust the program to account for changes in activity or diet.
- Change the infusion set according to the instructions for the infusion set you are using and the recommendations of your doctor or health care team.
- Pay attention to device alerts, such as beeps or vibrations. Make sure the volume is set high enough so that you can hear it.
Also Check: Symptoms Of High Blood Sugar Levels In Type 2 Diabetes
Tip From The Trenches
For both of our boys , the bum was the only body part that worked very well for infusion sites. This is/was true for us through the preschool, elementary years and into early adolescence. The only snag in using bum sites is that its possible to pull out an infusion set when little hands are pulling pants up and down particularly, for very young children, during the early stages of independent toileting. At 3 years old, our son pulled out more than one set going to the bathroom, and I hate to admit that I pulled out a few myself. These instances were, however, relatively rare, and the possibility exists for sites on any body part. And with practice, both my son and I learned to reduce the risk. ~Michelle
Insulin Pump Therapy For Type 2 Diabetes
Insulin pump therapy was originally developed for use in type 1 diabetes. However, it may also benefit those with type 2 diabetes who require insulin therapy . Several studies have demonstrated improved glycemic control for individuals with suboptimally controlled type 2 diabetes treated with multiple oral diabetes medications or an MDI insulin regimen who discontinue all oral medications other than metformin and initiate insulin pump therapy. These studies have reported a reduction in A1C of 1.0% or more with lower total daily insulin requirements, reduced risk of hypoglycemia, and higher treatment satisfaction compared to MDI . These benefits were obtained using relatively simple insulin dosing regimens. Participants required only one or two basal rates, and use of the bolus calculator to determine bolus doses was not associated with reduction in A1C . This result suggests that individuals with type 2 diabetes may not require the complex pump features that are beneficial for the management of type 1 diabetes and that cited barriers to conventional insulin pump therapy for individuals with type 2 diabetes, such as extensive educational requirements and high cost compared to MDI, could be reduced with simpler devices .
Clinical studies using these novel patch pumps for type 2 diabetes management have demonstrated improve glycemic control, high patient satisfaction, reduced barriers to insulin pump treatment, and cost savings when compared to MDI therapy .
Also Check: Is Cassava Flour Good For Diabetics
Medtronic Minimed 630g System
For an integrated CGM
This model from Medtronic comes with an optional CGM so a person can also monitor their blood sugar levels using the same device. It is also compatible with the Contour Next Link 2.4 blood glucose meter.
Medtronic claims that this system makes a person four times more likely to reach their target A1C level, which is their average blood glucose level over about 3 months.
Other stand out features include:
- alarms if a person goes below their preset glucose levels the device will stop issuing insulin if a person does not respond
- a bolus calculator, which automatically calculates doses and tells a person if they set them too close together
- predictive alerts
- compatible app for smartphones, which displays all readings and allows for notifications and alarms
- suitable for those with type 1 or type 2 diabetes
Many insurance companies cover the Omnipod Dash. It is also available through pharmacies with a prescription.