The Goal Of This Nursing Care Plan For Diabetes
The goal for any nursing plan is it bring more beneficial changes in a patients life in terms of numerous healings. The healings which are monitored through a complete Nursing Care Plan such as this are spiritual, psychological, social, and, most importantly the physical ones. The target is to examine all the improvements coming on health in different forms as you care for someone with diabetes.
Nursing Care Plan For Diabetes Mellitus
The most important aspect of a Nursing Care Plan for Diabetes is its consistency. The plan must be written in a consistent format and should address the needs of the patient. The nursing staff must be well-informed about diabetes to provide quality care. The plan should outline a patients goals, identify any risks, and ensure that the patient receives a balanced diet. Patients with diabetes should be encouraged to engage in exercise so that their weight is maintained. The plan should also include assessments for skin problems, slow-healing wounds, and foot pain.
The nursing care plan should address the need to monitor blood glucose levels in the patient. This is an essential component of the plan because elevated blood sugar levels are associated with a greater risk of mortality. It is also crucial to encourage self-monitoring of blood glucose, daily foot checks, and regular eye exams. To further prevent complications, nurses should encourage patients to quit smoking. It is also important to seek patient consent to administer certain medicines.
Please wait while flipbook is loading. For more related info, FAQs and issues please refer to DearFlip WordPress Flipbook Plugin Help documentation.
Please wait while flipbook is loading. For more related info, FAQs and issues please refer to DearFlip WordPress Flipbook Plugin Help documentation.
How Can Gestational Diabetes Affect My Baby
Gestational diabetes can cause an increased risk of developing congenital health problems, such as a heart defect, or breathing difficulties.
Your baby may also be born with a high birth weight. This can make labour difficult, and you may need to have a caesarean section.
Once born, your baby’s blood glucose level may be lower than usual, and will need to be monitored. They are also more likely to develop jaundice.
Read Also: What Does Type 1 Diabetes Do
Risk Reduction And Mitigation
Safety is a major concern for all residents of long-term care facilities regardless of their diabetes status. However, residents with diabetes have special safety needs related to medication management , prevention of hypoglycemia and excessive hyperglycemia, fall prevention, foot care, and transitions of care. Care transitions can be diverse and involve admission to and discharge from the long-term care facility, as well as transfers to and from acute-care facilities when necessary.
Protein In Diabetes Management
Recommendations
-
For individuals with diabetes and normal renal function, there is insufficient evidence to suggest that usual protein intake should be modified.
-
In individuals with type 2 diabetes, ingested protein can increase insulin response without increasing plasma glucose concentrations. Therefore, protein should not be used to treat acute or prevent nighttime hypoglycemia.
-
High-protein diets are not recommended as a method for weight loss at this time. The long-term effects of protein intake > 20% of calories on diabetes management and its complications are unknown. Although such diets may produce short-term weight loss and improved glycemia, it has not been established that these benefits are maintained long term.
The Dietary Reference Intakesâ acceptable macronutrient distribution range for protein is 10â35% of energy intake, with 15% being the average adult intake in the U.S. and Canada . The RDA is 0.8 g good-quality protein · kg body wtâ1 · dayâ1 . Good-quality protein sources are defined as having high PDCAAS scores and provide all nine indispensable amino acids. Examples are meat, poultry, fish, eggs, milk, cheese, and soy. Sources not in the âgoodâ category include cereals, grains, nuts, and vegetables. In meal planning, protein intake should be greater than 0.8 g · kgâ1 · dayâ1 to account for mixed protein quality in foods.
Dietary protein and its relationships to hypoglycemia and nephropathy are addressed in later sections.
Don’t Miss: Best Protein Powder For Type 2 Diabetes
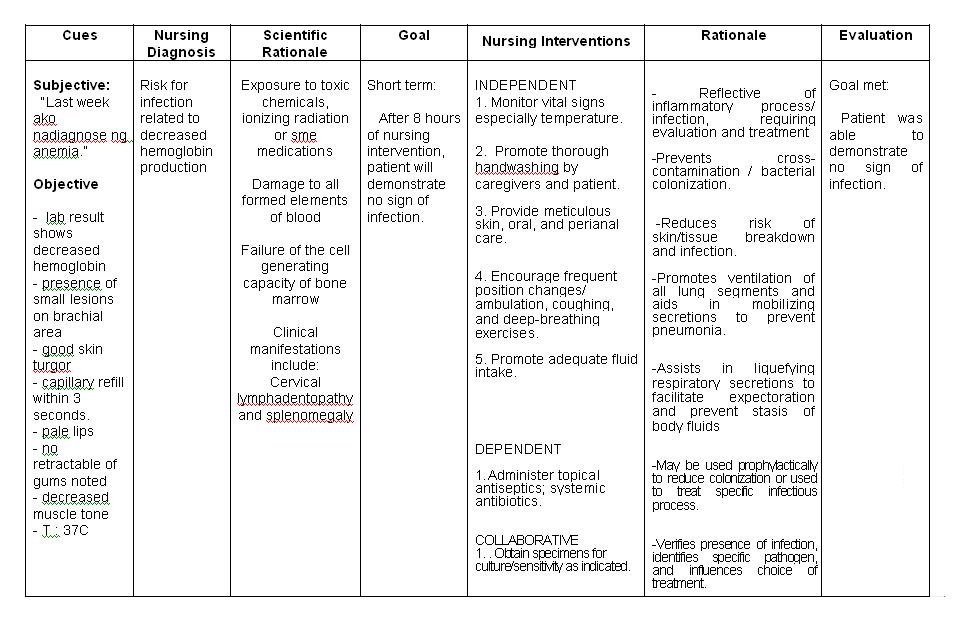
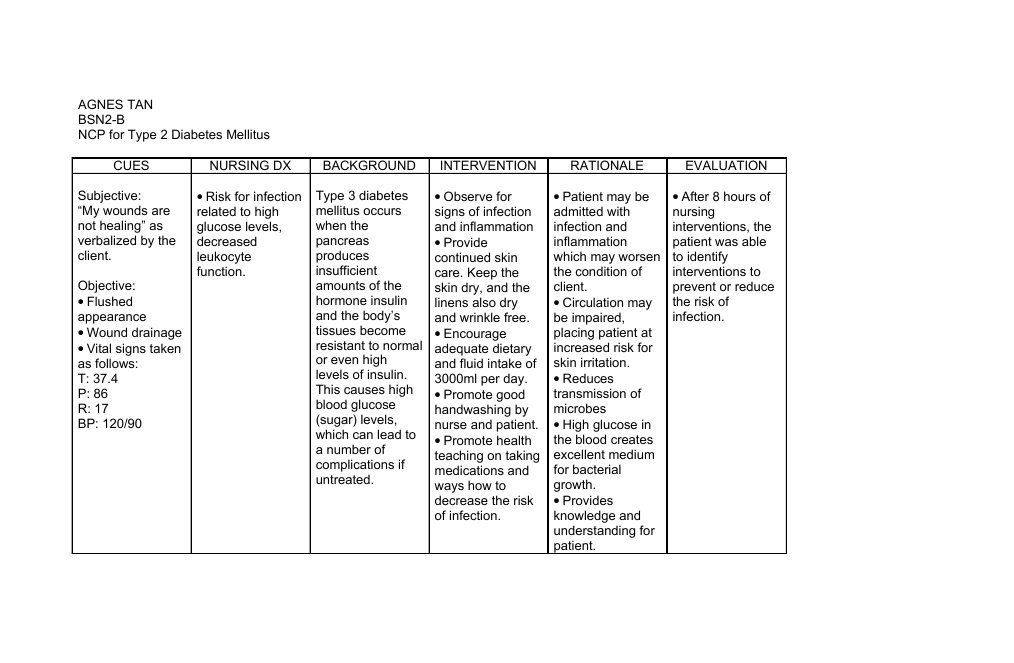
Risk For Deficient Or Imbalanced Fluid Volume
When blood sugars rise, the body attempts to remove that excess sugar by increasing the release of fluid through excessive urination and thirst. The increase may cause the body to become dehydrated and have electrolyte imbalances. When choosing a diagnosis, you may select either deficient or imbalanced fluid volume depending on your patients situation.
Nursing Care Plan For Diabetes 9
Risk for Impaired Skin Integrity
Nursing Diagnosis: Risk for Impaired Skin Integrity related to neuropathy and decreased sensation and circulation caused by peripheral neuropathy and arterial obstruction secondary to diabetes mellitus.
Desired Outcome: The patient will demonstrate ways to properly care for the feet and the patient will maintain an intact skin on the legs and feet while still admitted to the hospital.
Also Check: What’s The Treatment For Type 2 Diabetes
Nurse Diabetes Case Management Interventions And Blood Glucose Control: Results Of A Meta
Nurse diabetes case management interventions and blood glucose control: Results of a meta-analysis Author links open overlay panel GarryWelcha Get rights and content We conducted a meta-analysis of studies reporting diabetes case management interventions to examine the impact of case management on blood glucose control . Databases used for the search included Medline, PubMed, Cochrane EPOC, Cumulative Index to Nursing & Allied Health Literature database guide , and PsychInfo. A composite estimate of effect size was calculated using a random effects model and subgroup analyses were conducted. Twenty-nine salient studies involving 9397 patients had sufficient data for analysis. Mean patient age was 63.2 years, 49% were male, and ethnicity/race was 54% White. Type 2 diabetes was the focus in 91% of studies. Results showed a large overall effect size favoring case management intervention over controls or baseline values on HbA1c . This corresponds to a mean HbA1c reduction of 0.89 . Subgroup analyses showed clinical setting, team composition, and baseline HbA1c were important predictors of effect size, but not diabetes self-management education which was poorly described or absent in most diabetes case management interventions examined. Nurse-led case management provides an effective clinical strategy for poorly controlled diabetes based on a meta-analysis of clinical trials focusing on blood glucose control.Continue reading > >
How To Use This Nursing Plan For Diabetic Patients
A treatment program is formed that seeks recovery and emphasis on changes and interventions that can be implemented promptly to the patient.
It involves a process of changes that are needed in making diabetes-related conditions quite better for the patients. The person who provides nursing care should keep track of all the caring planning processes in the patients care.
I encourage people who provide self-care for their diabetes to use this Nursing Care Plan as well.
Read Also: Salty Taste In Mouth Diabetes
Implication Of The Study
Self-management of diabetic patients could be achieved through effective nursing intervention. The availability of a well-designed educational package administered steps wisely to diabetic patients will foster standardized and effective knowledge based nursing intervention that will improve self-management among this population. This may also encourage further studies on factors that may enable effective nursing intervention on self management of diabetic patients.
Risk For Unstable Blood Glucose Level
Related to
- Recognize factors leading to glucose instability and DKA.
- Verbalize understanding of body and energy needs.
- Verbalize plan to modify factors to prevent or minimize complications.
Nursing intervention
Monitor blood glucose before meals and at bedtime.
Rationale
This monitors the effectiveness of blood glucose control at times when the patients glucose is not increased by digestion of food.
Nursing intervention
Assess for changes in mentality, apprehension, erratic behavior, tremors, slurred speech, staggering gait, and seizure activity. Treat hypoglycemia as prescribed.
Rationale
These are signs of hypoglycemia. Patients with hypoglycemia may experience vasodilation and decreased myocardial contractility, which decreases cerebral circulation and impairs cognition.
Nursing intervention
Administer basal, prandial, and correction insulin doses as prescribed.
Rationale
Encourage and teach the patient to perform regular home blood glucose monitoring.
Rationale
Donât Miss: Number Of Grams Of Sugar Per Day For Diabetic
Read Also: Diabetic Desserts Without Artificial Sweeteners
What Is A Nursing Care Plan For Type 2 Diabetes
This is a plan, guide, and a checklist to help you provide proper care for an individual or family with type 2 diabetes. This nursing plan is explicitly allotted to diabetic patients.
The nursing plan merely focuses on methods proven to work with proper comprehensive treatment tactics offered to patients at hospitals and nursing home facilities, which can be used at individual and family levels.
The care plan involves diagnosis, monitoring, and planning the management that detains on effective recovery from type 2 diabetes through regular sugar monitoring, diets, exercises, and timely medications .
Blood Sugar Blood Pressure And Rehabilitation Effect Before And After Nursing
The levels of FPG, 2h PG, SBP, DBP, and rehabilitation effect of the two groups of patients before and after nursing were shown in Figures 3, 4.
Figure 3 Comparison of blood glucose and blood pressure before and after nursing .
Figure 4 Comparison of rehabilitation effects between the two groups of patients .
As illustrated in Figures 3, 4, after nursing, the levels of FPG, 2h PG, SBP, and DBP in the two groups of patients were significantly decreased, and those in group B were much lower than group A . Similarly, the rehabilitation effect of patients in group B was significantly better than that in group A, and the difference was statistically significant .
Read Also: Cold Medicine For Diabetics With High Blood Pressure
Your Diabetes Care Plan
The annual diabetes review is an ideal time to have your care planning review. Care planning is a process that should be available to all people with diabetes. It:
- allows you to be more involved in decisions about how your diabetes is managed
- gives you a say in every aspect of the care you get
- helps you to work towards goals that are personal to you
- helps you to work in partnership with your diabetes team.
The care planning appointment is a chance to talk about the results of your annual diabetes checks with your healthcare professional, talk about your experiences and discuss how you feel, set goals, and create an action plan to help you manage your diabetes.
Your healthcare professional can help you to understand the results of your diabetes checks, provide you with information and advice, talk about different options for example, different types of medication available to you and refer or signpost you to support in your local area.
A care plan is a written document of all these discussions, goals and actions.
The short film below will help you to understand what care planning is, and how you can get more involved in your diabetes care.
You May Like: What Is Considered Low Blood Sugar For Type 2 Diabetes
Goals Of Mnt That Apply To Individuals With Diabetes
) Achieve and maintain
Blood glucose levels in the normal range or as close to normal as is safely possible
A lipid and lipoprotein profile that reduces the risk for vascular disease
Blood pressure levels in the normal range or as close to normal as is safely possible
) To prevent, or at least slow, the rate of development of the chronic complications of diabetes by modifying nutrient intake and lifestyle
) To address individual nutrition needs, taking into account personal and cultural preferences and willingness to change
) To maintain the pleasure of eating by only limiting food choices when indicated by scientific evidence
Recommended Reading: The Effects Of Diabetes On Your Body
Physical Activity And Exercise
Physical activity is one of the most effective methods for preventing and treating T2DM because obesity is a factor in the development of insulin resistance in T2DM. Physical activity involves any muscular movement that requires energy.
Exercise is activity that is planned with the intention to improve health. Exercise has been called the closest thing there is to a magic bullet when it comes to preventing T2DM. In fact, exercise may be superior to medications for health-related benefits in individuals with T2DM, but an estimated 50% of individuals do not participate in regular exercise.
Healthcare providers may not have time to emphasize the importance of exercise, and exercise is often considered useful, rather than essential. T2DM has been dubbed the stealth epidemic because of its insidious onset. Exercise could be considered the stealth solution to T2DM because of the many benefits that it confers, some of which are immediately apparent. Exercise prescriptions are currently considered essential for individuals with T2DM. Nurses have a key role in educating individuals with T2DM of the significant benefits that result from exercise and warning of the hazardous consequences of T2DM.
Nursing Care Plan For Diabetes 6
Nursing Diagnosis: Risk for Disturbed Sensory Perception
Desired Outcome: The patient will recognize any changes in sensory perception and effectively cope with them.
| Nursing Interventions for Diabetes | Rationales |
| Assess vital signs and perform an initial head-to-toe assessment, particularly checking visual acuity, presence of tingling or numbness in the extremities, and response to pain stimuli. | Retinopathy and peripheral neuropathy are some of the complications of diabetes. |
| Educate the patient for the need to monitor and report any visual disturbances or other sensory changes. | To facilitate early detection and management of disturbed sensory perception. |
| Create a daily routine for the patient, as consistent as possible. | To keep the patient in touch with reality and maintain safety. |
| Monitor blood sugar levels regularly. | Uncontrolled levels of blood glucose may lead to serious complications such as neuropathy and retinopathy. |
Also Check: How Much Sugar Can A Type 2 Diabetic Have
Signs And Symptoms Of Hyperglycemia
Signs and symptoms to be aware of that can potentially indicate hyperglycemia include: frequent urination, increased thirst, blurred vision, fatigue, and headaches. If hyperglycemia is left untreated symptoms can progress and the patient may then develop fruity-smelling breath, nausea and vomiting, shortness of breath, weakness, confusion, or coma. This can become a medical emergency and therefore should be monitored closely and appropriate treatment administered if blood glucose levels are elevated.
Nursing Care Plan For Diabetes 2
Nursing Diagnosis: Imbalanced Nutrition: Less than Body Requirements related to insulin deficiency, as evidenced by unexplained weight loss, increased urinary output, dilute urine, high blood glucose levels, fatigue, and weakness
Desired Outcome: The patient will be able to achieve a weight within his/her normal BMI range, demonstrating healthy eating patterns and choices.
| Nursing Interventions for Diabetes | Rationale |
| Explain to the patient the relationship between diabetes and unexplained weight loss. | To help the patient understand why unexplained weight loss is one of the signs of diabetes. |
| Create a daily weight chart and a food and fluid chart. Discuss with the patient the short term and long-term goals of weight loss. | To effectively monitory the patients daily nutritional intake and progress in weight loss goals. |
| Help the patient to select appropriate dietary choices to follow a high fiber, low fat diet. | Low fat, and high fiber foods are ideal for diabetic patients. |
| Refer the patient to the dietitian. | To provide a more specialized care for the patient in terms of nutrition and diet in relation to newly diagnoses diabetes. |
Also Check: Type 2 Diabetes Would Be Considered An
Causes Of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is caused mainly by two interconnected problems:
- Insulin resistance develops in muscle, fat, and liver cells. These cells do not consume enough sugar because they do not generally interact with insulin.
- The pancreas cannot produce adequate insulin to keep blood sugar levels under normal levels.
It is unclear why this happens, but being overweight and inactive are significant contributors.
Treatment And Management Of Cvd Risk
Recommendations
-
Target A1C is as close to normal as possible without significant hypoglycemia.
-
For patients with diabetes at risk for CVD, diets high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and nuts may reduce the risk.
-
For patients with diabetes and symptomatic heart failure, dietary sodium intake of < 2,000 mg/day may reduce symptoms.
-
In normotensive and hypertensive individuals, a reduced sodium intake with a diet high in fruits, vegetables, and low-fat dairy products lowers blood pressure.
-
In most individuals, a modest amount of weight loss beneficially affects blood pressure.
In the EDIC study, the follow-up of the DCCT , intensive treatment of type 1 diabetic subjects during the DCCT study period improved glycemic control and significantly reduced the risk of the combined end point of cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, and stroke . Adjustment for A1C explained most of the treatment effect. The risk reductions obtained with improved glycemia exceeded those that have been demonstrated for other interventions such as cholesterol and blood pressure reductions. Observational data from the UKPDS suggest that CVD risk in type 2 diabetes is also proportionate to the level of A1C elevation .
Also Check: What Eye Problems Does Diabetes Cause
Explaining The Importance Of Exercise
The fourth intervention is to explain the role of exercise in controlling type 2 diabetes mellitus. Exercise intervention is considered a cornerstone. It improves glycemic control significantly in patients with type 2 diabetes. Considering the significant relationship between blood glucose content and the risk of cardiovascular disease and premature death, such a decline in blood glucose content would lead to a reduction in the risk of microvascular and macrovascular disease and premature death.
The rationale behind this intervention is insulin absorption increases in a body part that is exercised, which alters the insulins absorption. Exercising with others ensures that assistance is available should hypoglycemia occur. Proper timing of exercise, monitoring blood glucose, and adjusting food or insulin decreases the risk of exercise induced hypoglycemia. In the event of a severe reaction, a semiconscious or unconscious client may require glucagon. Exercise is one of the major factors in controlling type 2 diabetes mellitus so encouraging the patient to avoid a sedentary lifestyle is very important.