Can Symptoms Appear Suddenly
In people with type 1 diabetes, the onset of symptoms can be very sudden, while in type 2 diabetes, they tend to come about more gradually, and sometimes there are no signs at all.
Symptoms sometimes occur after a viral illness. In some cases, a person may reach the point of diabetic ketoacidosis before a type 1 diagnosis is made. DKA occurs when blood glucose is dangerously high and the body can’t get nutrients into the cells because of the absence of insulin. The body then breaks down muscle and fat for energy, causing an accumulation of ketones in the blood and urine. Symptoms of DKA include a fruity odor on the breath, heavy, taxed breathing and vomiting. If left untreated, DKA can result in stupor, unconsciousness, and even death.
People who have symptomsof type 1 or of DKAshould contact their health care provider immediately for an accurate diagnosis. Keep in mind that these symptoms could signal other problems, too.
Some people with type 1 have a “honeymoon” period, a brief remission of symptoms while the pancreas is still secreting some insulin. The honeymoon phase usually occurs after someone has started taking insulin. A honeymoon can last as little as a week or even up to a year. But its important to know that the absence of symptoms doesn’t mean the diabetes is gone. The pancreas will eventually be unable to secrete insulin, and, if untreated, the symptoms will return.
Other Type 1 Diabetes Treatments
Less-common type 1 diabetes treatments include:
- Artificial pancreas A cutting-edge device that combines an insulin pump, a CGM, and a dosing algorithm, says Dutta. The algorithm decides based on the CGM reading and the average over the last five minutes, to tell the pump, You dose X number of units of insulin, and it goes up and down depending on your glucose levels. Medtronics MiniMed 670G and 770G hybrid closed-loop systems, and Tandem Diabetes Cares closed-loop Control-IQ are FDA-approved artificial pancreases, he says.
- Jet injection Instead of a needle, an injector with an insulin cartridge delivers insulin beneath the skin via a jet of air, as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration describes.
- Inhaled insulin A rapid-acting inhaled insulin that you take at the beginning of each meal by breathing in powder through the mouth using an inhaler, according to the ADA. It is sold under the brand name Afrezza .
- Pramlintide This medication is taken with mealtime insulin and slows the movement of food through the stomach to keep blood sugar from spiking after a meal, according to MedlinePlus.
How Does My Diet Affect Diabetes
A healthy diet is an important part of managing Type 1 diabetes. The right foods can help keep your blood pressure and blood glucose in check. Healthy meal planning for people without Type 1 diabetes is similar to healthy meal planning for people with Type 1 diabetes:
- Avoid foods with added sugar, sodium and trans fats.
- Eat a balance of proteins, carbohydrates and healthy fats.
- Read nutrition labels to select foods with more fiber and less sugar.
- Skip the highly processed foods found in cans or packages.
In addition, it’s important for people with Type 1 diabetes to understand how foods with carbohydrates impact their blood sugar levels and how much insulin to take for various amounts of carbs. Work with your healthcare team to figure out the best plan for you.
You May Like: Does Insurance Cover Cgm For Type 2 Diabetes
Healthy Eating And Exercise
What you eat and how much exercise you do affects your blood glucose levels. The more you eat and the less you exercise, the higher your blood-glucose levels will be and the more insulin you will need. Learning how to fine-tune your insulin doses with different meal sizes and activity levels is part of managing type 1 diabetes.
To help give you more even blood glucose levels:
- Eat breakfast, lunch and dinner at regular times of the day, with snacks in between as advised by your dietitian or nurse.
- Eat healthy, balanced meals with a range of carbohydrates, fats and protein. See heart healthy eating
- Choose high fibre carbohydrates, eg, wholegrain breads , high-fibre breakfast cereals, legumes, fruit and vegetables and those with a low glycaemic index . Carbohydrate foods with a low GI are digested more slowly.
- Exercise regularly.
How Do You Manage Type 1 Diabetes
Living with T1D is a full-time balancing act requiring constant attention to avoid acute, life-threatening hypoglycemia or the long-term damage done by hyperglycemia . Blood sugar levels must be monitored either with finger pricks or a continuous glucose monitor. Insulin doses must then be carefully calculated based upon activity and stress levels, food intake, illness, and additional factors. These calculations are rarely perfect resulting in a tremendous emotional and mental burden for both patients and caregivers.
You May Like: How Does Diabetes Cause Heart Disease
How Is Gestational Diabetes Diagnosed
Gestational diabetes is regularly diagnosed by measuring blood glucose levels. There are different ways to test for diabetes. Your healthcare provider can identify which test is best for you.
Did You Know?
Gestational diabetes develops during pregnancy, affecting four per cent of all pregnant women.You can help manage gestational diabetes by eating well and exercising regularly.
Treatments For Type 1 Diabetes
Although there is currently no known cure for type 1 diabetes, several effective treatments are available, helping people to manage the disease and live a full life. Your doctor can help you manage Type 1 diabetes so you can assume life normally. You may need an insulin shot every day to manage blood levels and provide the energy the body needs.
Your doctor may also recommend checking your blood sugar levels regularly. This helps ensure that youre keeping it as close to the target level as possible to avoid complications.
Managing diabetes is similar to managing any healthy lifestyle by eating healthy foods, getting adequate physical activity, and controlling both cholesterol and blood pressure.
Read Also: Financial Help With Diabetic Supplies
Type 1 Vs Type 2 Diabetes
There are two main types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2. They have similar symptoms and over time, they can lead to many of the same complications. However, they are very different diseases.
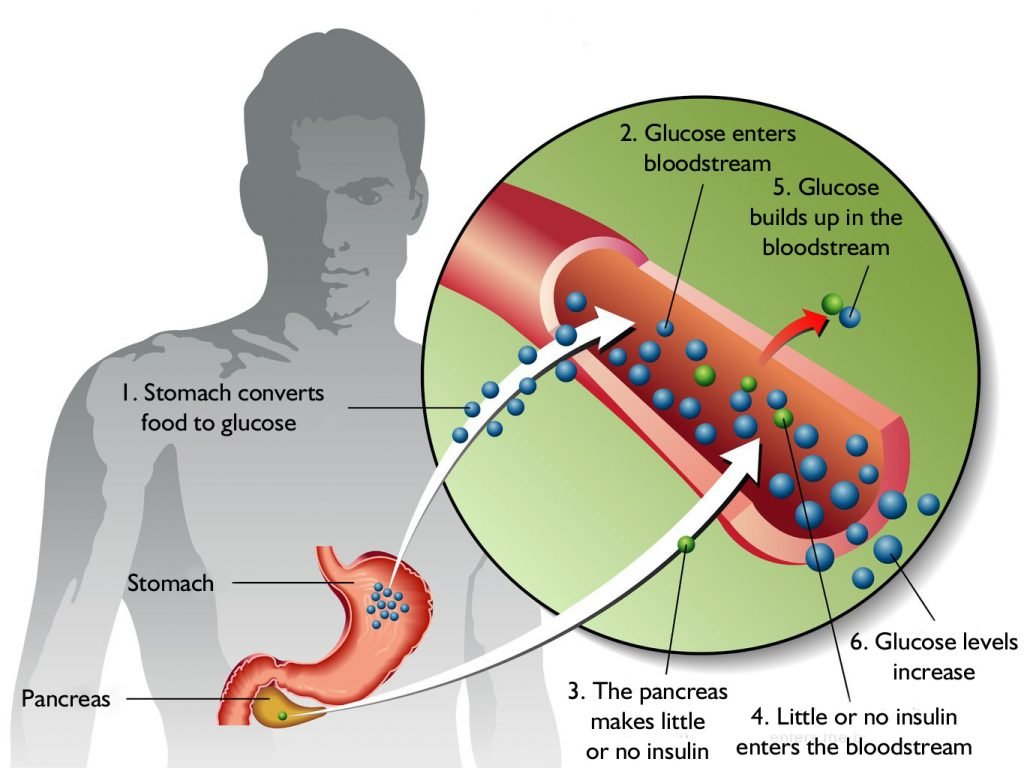
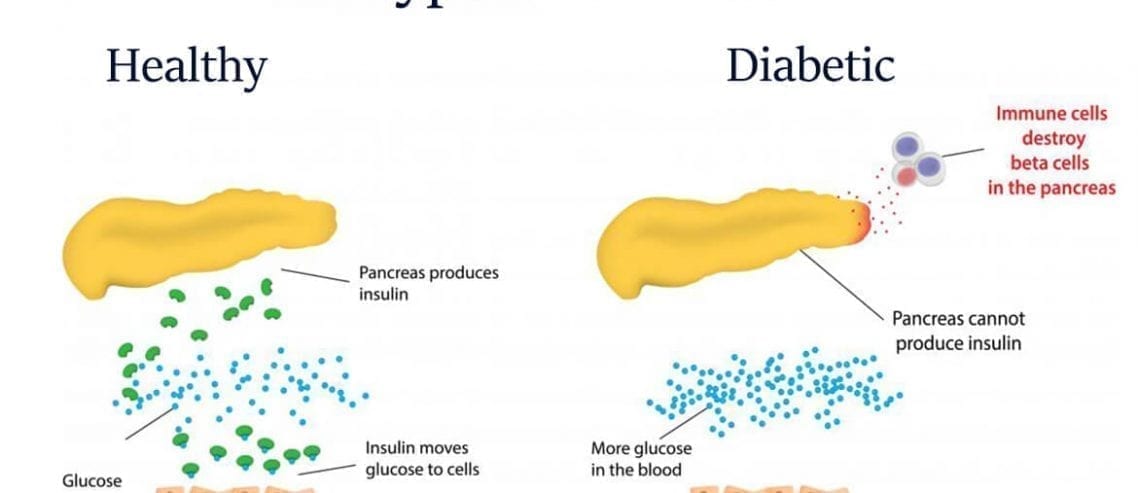
Type 1 diabetes is the result of a persons body not producing insulin on its own. Taking insulin is necessary for survival, to move glucose from the bloodstream into the bodys cells.
For people with type 2 diabetes, the cells have stopped responding well to insulin. The body struggles to move glucose from the blood into the cells, despite having adequate levels of the hormone. Eventually, their bodies may stop making adequate insulin entirely.
Type 1 diabetes develops very quickly and symptoms are obvious. For people with type 2 diabetes, the condition can develop over many years. In fact, a person with type 2 diabetes may not know they have it until they have a complication.
The two types of diabetes are caused by different things. They also have unique risk factors.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring Treatment
Another device that measures glucose is termed a continuous glucose monitoring system . This system consists of a tiny sensor under the skin to check blood sugar levels. It sends the information to a device that records an average glucose value every five minutes for several days, depending on the sensor design. CGM is now accepted for long term use in some people with models that turn off insulin infusion when sugars start to drop. Some devices alert you if the blood glucose level falls outside of preset range.
Don’t Miss: Gestational Diabetes Test At Home
Favorite Orgs For Essential Diabetes Info
JDRF
This nonprofit is among the most prominent in the United States focused specifically on type 1 diabetes research and advocacy. Its offerings are vast, with chapters nationwide, and they include a wealth of resources in English and Spanish to help you navigate life with the disease. You can also get matched with outreach volunteers who have a close personal connection to type 1 diabetes, and they can help you cope. They can also help you learn how to use their clinical trials matching tool. And because insulin therapy can be so expensive, they also provide a guide to navigating health insurance, and information on other ways to afford your medication.
American Diabetes Association
The largest organization in the United States focusing on all types of diabetes, it is a treasure trove of information about the disease, in part because of its prominent role in the research world through a professional society that hosts yearly conferences its highly respected, peer-reviewed journals and a key role setting standards of diabetes care in the United States. They advocate for legislation to make insulin more affordable, and host InsulinHelp.org, a guide to information about drug manufacturers patient assistance programs.
Complications Of Untreated Type 1 Diabetes
- kidney damage
- increased likelihood of infections such as thrush and also more serious infections
- damage to the eyes
- poor blood circulation in the legs and feet, potentially leading to lower limb amputation
- damage to the nerves of the feet
- much higher risk of heart disease and stroke
- sexual impotence.
Read Also: Type 1 Diabetes Symptoms In Adults
Do I Have Other Treatment Options For My Type 1 Diabetes
The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases has played an important role in developing artificial pancreas technology. An artificial pancreas replaces manual blood glucose testing and the use of insulin shots. A single system monitors blood glucose levels around the clock and provides insulin or a combination of insulin and glucagon automatically. The system can also be monitored remotely, for example by parents or medical staff.
In 2016, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved a type of artificial pancreas system called a hybrid closed-loop system. This system tests your glucose level every 5 minutes throughout the day and night through a continuous glucose monitor, and automatically gives you the right amount of basal insulin, a long-acting insulin, through a separate insulin pump. You still need to manually adjust the amount of insulin the pump delivers at mealtimes and when you need a correction dose. You also will need to test your blood with a glucose meter several times a day. Talk with your health care provider about whether this system might be right for you.
The illustration below shows the parts of a type of artificial pancreas system.
Starting in late 2016 and early 2017, the NIDDK has funded several important studies on different types of artificial pancreas devices to better help people with type 1 diabetes manage their disease. The devices may also help people with type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes.
For Those Diagnosed With Diabetes You Can Reduce The Risk Of Complications:
- Monitor blood glucose levels with appropriate testing and an A1C blood test every three months to measure the average amount of sugar in your blood
- If you smoke, it’s never too late to quit
- Be physically active
- Examine feet and skin every day
- Have an eye exam at least once a year
- Have a kidney function test at least once a year
- Visit your healthcare provider regularly
Recommended Reading: How To Test For Diabetes Without Taking Blood
Type 1 Diabetes Treatment
People who have type 1 diabetes can live long, healthy lives. Youâll need to keep a close eye on your blood sugar levels. Your doctor will give you a range that the numbers should stay within. Adjust your insulin, food, and activities as necessary.
Everyone with type 1 diabetes needs to use insulin shots to control their blood sugar.
When your doctor talks about insulin, theyâll mention three main things:
- “Onset” is how long it takes to reach your bloodstream and begin lowering your blood sugar.
- “Peak time” is when insulin is doing the most work in terms of lowering your blood sugar.
- “Duration” is how long it keeps working after onset.
Several types of insulin are available.
- Rapid-acting starts to work in about 15 minutes. It peaks about 1 hour after you take it and continues to work for 2 to 4 hours.
- Regular or short-acting gets to work in about 30 minutes. It peaks between 2 and 3 hours and keeps working for 3 to 6 hours.
- Intermediate-acting wonât get into your bloodstream for 2 to 4 hours after your shot. It peaks from 4 to 12 hours and works for 12 to 18 hours.
- Long-acting takes several hours to get into your system and lasts about 24 hours.
Your doctor may start you out with two injections a day of two types of insulin. Later, you might need more shots.
Southern Cross Medical Library
The purpose of the Southern Cross Medical Library is to provide information of a general nature to help you better understand certain medical conditions. Always seek specific medical advice for treatment appropriate to you. This information is not intended to relate specifically to insurance or healthcare services provided by Southern Cross. For more articles go to the Medical Library index page.
Read Also: Just Found Out I Have Diabetes
What Is Type 1 Diabetes
People of all ages can develop type 1 diabetes.
If you have type 1 diabetes, your pancreas doesnt make insulin or makes very little insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps blood sugar enter the cells in your body where it can be used for energy. Without insulin, blood sugar cant get into cells and builds up in the bloodstream. High blood sugar is damaging to the body and causes many of the symptoms and complications of diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in children, teens, and young adults, but it can develop at any age.
Type 1 diabetes is less common than type 2approximately 5-10% of people with diabetes have type 1. Currently, no one knows how to prevent type 1 diabetes, but it can be managed by following your doctors recommendations for living a healthy lifestyle, managing your blood sugar, getting regular health checkups, and getting diabetes self-management education and support.
Try To Lose Weight If You Are Overweight Or Obese
Excess weight is also a risk factor for heart and blood vessel disease. Getting to a perfect weight is often unrealistic. However, if you are overweight, losing some weight will help.
Some of these lifestyle issues may not seem to be relevant at first to young children who are diagnosed as having diabetes. However, as children grow, a healthy lifestyle should be greatly encouraged for the long-term benefits. See the separate leaflet called Cardiovascular Disease .
You May Like: Diabetic Recipes For Picky Eaters
Favorite Online Support Networks
Beyond Type 1
A frequent partner with JDRF, Beyond Type 1 is a social-media-savvy nonprofit focused on advocacy and insulin affordability. Join their social platform by connecting through Facebook or Apple, among other providers. Or, visit their GetInsulin.org guide for information about affording the medication and help devising an action plan to get it.
College Diabetes Network
This peer-support-focused nonprofit is focused on forging connections between and among students in high school and college with type 1 diabetes. Get advice for navigating care through the transition between high school and college, read blog posts written by college students, or find a college chapter to join.
Favorite Type 1 Diabetes Apps
Glooko
Many glucose monitoring devices have their own apps for receiving and analyzing your diabetes data but Glooko allows you to sync that data with their platform to help you understand how food, activity, and medication affect your glucose levels. The list of compatible devices is a long one, and you can also sync it with popular activity apps such as Runkeeper, Strava, Apple Health, and Fitbit. View your glucose trends, use a barcode scanner to add foods to your log, set medication reminders, and more. It has 4.7 stars in the Apple Store and also 4.0 stars in GooglePlay.
Many people use this popular apps free fitness log and interactive food diary in order to keep track of how many calories they are taking in and burning off each day. But if you upgrade to the premium monthly plan of $9.99, you can also track your carb intake and search for low-carb recipes. When you choose an activity or food, the nutrients attached are automatically added to your daily tracker. Download it in the Apple Store or .
Additional reporting by Joseph Bennington-Castro.
Recommended Reading: Best Low Carb Diet For Diabetics
Blood Glucose And Ketone Monitoring
Optimal diabetic control requires frequent self-monitoring of blood glucose levels as this allows for timely adjustments in insulin doses. People with type 1 diabetes learn how to self-monitor their blood glucose levels using a pocket-sized blood glucose meter and adjust their insulin doses accordingly. Depending on whether daily insulin injections or an insulin pump is used, blood glucose levels will likely need to be checked at least four times a day. Careful monitoring is the only way to ensure that blood glucose levels remain within the target range. Blood glucose testing involves using a lancing device to prick the skin to draw a drop of blood, which is placed on a test strip. The test strip is then inserted into a blood glucose meter, which provides a blood glucose level reading. Blood ketone meters, which measure blood ketone levels, and work in a similar way to blood glucose devices, are available to test for ketoacidosis.
What Is The Long
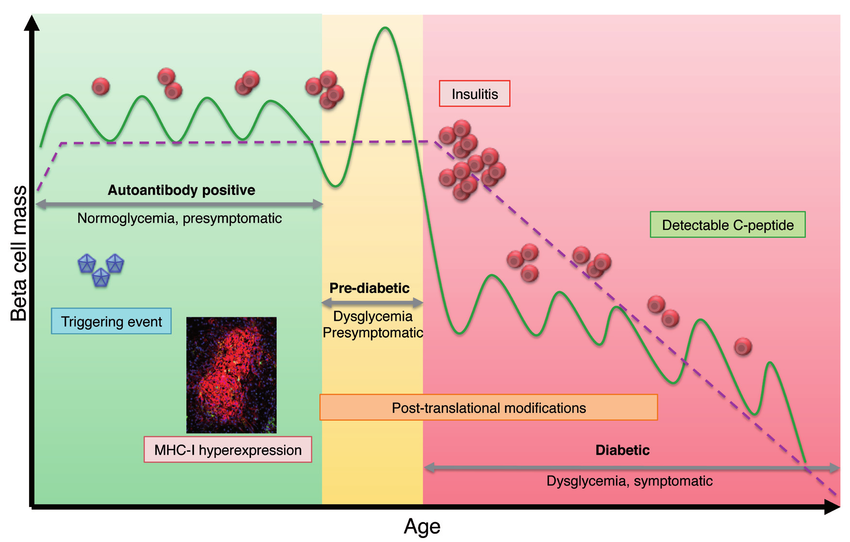
Over a period of many years, high glucose levels can cause damage to the eyes, kidneys, and nerves.
Lifelong insulin treatment is essential for people with type 1 diabetes. Maintaining healthy glucose levels over the long term greatly reduces your childs risk of developing diabetes complications later in life. Your diabetes team will teach you how to balance insulin, food, and exercise to maintain safe and healthy blood glucose levels.
You May Like: Is Dark Chocolate Good For Type 2 Diabetes