How To Prevent High Blood Glucose Levels
type 1 diabetes ideas can help keep your glucose
- Follow your diabetes meal plan. If that you take insulin or oral diabetes medications, its significant that you be steady about the amount and timing of your meals and bites. The food you eat should be in balance with the insulin working in your body.
- Monitor your glucose. Depending upon your treatment plan, you may check and record your glucose level many times each week or several times each day. Careful monitoring is the best way to ensure that your glucose level remains within your objective reach. Note when your glucose readings are above or underneath your objective reach.
- Taking of your medications as prescribed by your doctor.
- Change your medicine if you change your physical activity. The change relies upon the glucose test results and on the type and length of the activity.
- Encountering emotional stress, for example, financial loss or working environment challenges
How To Calculate Your A1c
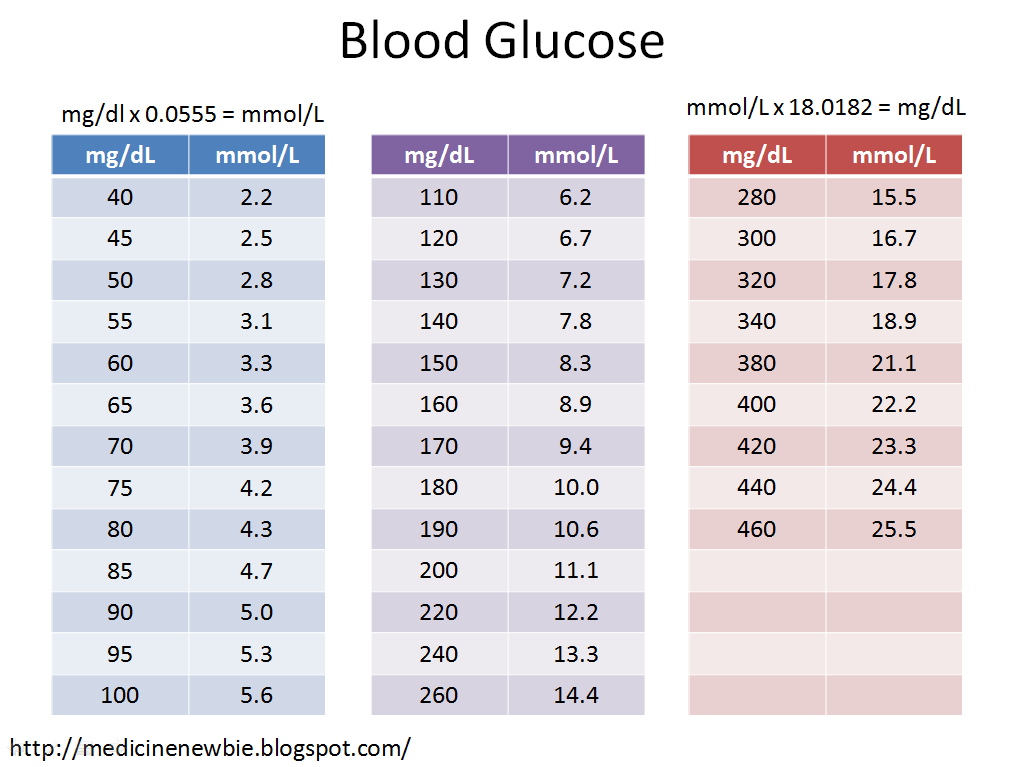
The Hemoglobin A1c test is a blood test used to measure the average blood glucose concentration in your body in the past 1-3 months. For diabetics, this is the standard way of determining how well the diabetes is controlled. An A1c of less than 7% is considered good. Getting the test every 3 months is usually enough. But sometimes you may want to just estimate your A1c level based on the data from your regular self-tests. The formula below could help in this case. Accuracy, of course, could vary depending on how often and when you check your blood sugar. I found it pretty accurate last time I used it. My calculation was off only by 0.1%. This is the same formula GlucoseTracker uses in the app’s dashboard. Glucose in mg/dL: A1c = / 28.7 Glucose in mmol/L: A1c = / 1.59 So, for example, if your average blood glucose level in the past 3 months is 130 mg/dL , your estimated A1c is 6.15%. There are also cheaper devices you can buy that will allow you to do the actual A1c tests yourself, like this one. If you need to do these tests more often, say every month, then it could save you money in the long run as lab tests could get expensive. It may not be as accurate as the lab tests, but my guess is it’s probably good enough.Continue reading > >
Why Do We Use Blood Glucose Metres
Blood glucose monitoring is used to measure and display the amount of glucose in the blood. Blood glucose can frequently fluctuate for multiple reasons such as exercise, food, medications and stress.
Therefore, being able to monitor glucose levels with the convenience of a portable and instantaneous pinprick test allows for the prevention of complications that can arise when blood glucose levels are not stable.
Read Also: Losing Hair On Legs Diabetes
What Should I Aim For
Effective management of diabetes is all about aiming for a careful balance between the foods you eat, how active you are and the medication you take for your diabetes. Because this is a delicate balance, it can be quite difficult to achieve the best possible blood glucose management all the time.
The ranges will vary depending on the individual and an individuals circumstances. While it is important to keep your blood glucose levels as close to the target range of target range between 4 to 6 mmol/L as possible to prevent complications, it is equally important to check with your doctor or Credentialled Diabetes Educator for the range of blood glucose levels that are right and safe for you. Therefore the following information should be treated only as a general guide.
Why Would I Need This Test
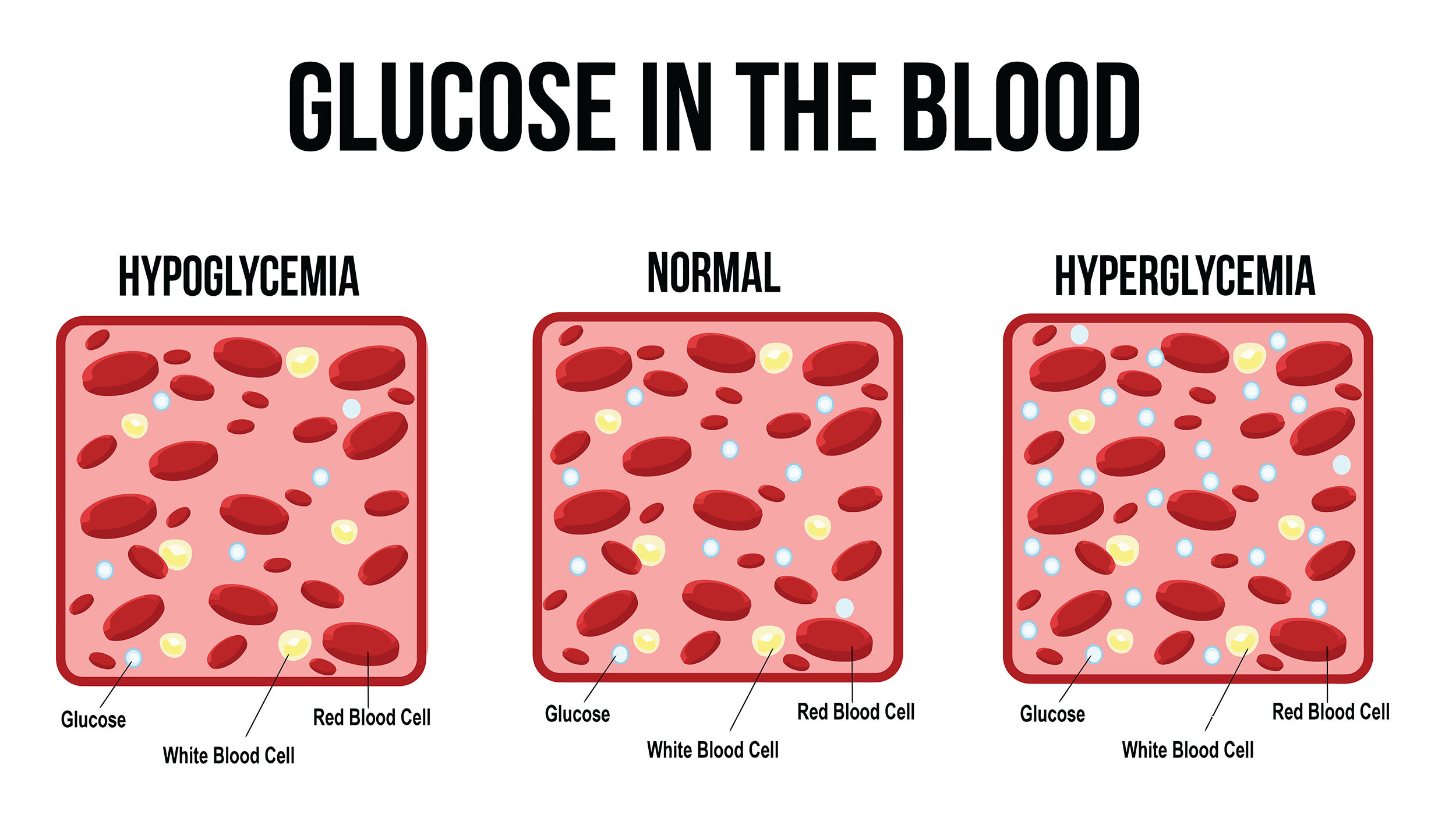
You might need this test if you are at risk of developing diabetes, or if you have had any symptoms or test results suggesting diabetes.
The standard blood glucose tests measure your blood sugar level at a particular time. The OGTT measures how you respond to glucose.
Pregnant women can develop a particular type of diabetes called gestational diabetes, and will be asked to have an OGTT around 24 to 28 weeks of pregnancy. Gestational diabetes usually goes away after the baby is born.
Don’t Miss: How Does An Insulin Pump Attach
Are Some Canadians At Higher Risk For Elevated Blood Sugar Levels Than Others
You may have a higher risk for elevated blood sugars and type 2 diabetes if you:
- Are 40 or years of age or older
- Have a close relative with diabetes
- Are of African, Arab, Asian, Hispanic, Indigenous or South Asian descent
- Are overweight
- Have been diagnosed with prediabetes
Some medical conditions can also increase your risk of type 2 diabetes, such as:
- High blood pressure or cholesterol levels
- Polycystic ovary syndrome
- Psychiatric disorders
- Sleep apnea
Time Lag For Interstitial Fluid
Glucose in the blood takes time to make its way to the interstitial fluid so there may be a lag in time. After a meal, a rise in blood glucose is induced by glucose uptake in the intestines.
However, this is not accompanied by a rise in interstitial fluid glucose simultaneously because there is a reported time lag of around 5 to 25 minutes.
This time lag can be explained by the gradient in glucose which increases in the blood, differing depending on the type and quantity of carbohydrates in a given meal. With a high glucose load and rapidly absorbable carbohydrates , there is a steeper increase in blood glucose.
Some studies suggest that if patients use the interstitial fluid glucose value 60 minutes after starting a meal, it may not correlate with the blood glucose value, which would be significantly higher if measured.
Unlike blood glucose, changes in interstitial fluid are subject to sensitive dynamics of muscle metabolism. Muscle metabolism is the amount of energy required by the cells in the muscles.
For example, more energy/glucose will be required by the cells in times of exercise.
According to the officially approved guidelines set by regulatory authorities, CGM readings should not be used to determine insulin doses for those with diabetes as CGM readings often do not correspond exactly to self-monitoring of blood glucose measurement results taken at the same time, especially during fast changes in blood glucose.
You May Like: Where Do You Give Insulin Injections
What Are Blood Sugar Targets
A blood sugar target is the range you try to reach as much as possible. These are typical targets:
- Before a meal: 80 to 130 mg/dL.
- Two hours after the start of a meal: Less than 180 mg/dL.
Your blood sugar targets may be different depending on your age, any additional health problems you have, and other factors. Be sure to talk to your health care team about which targets are best for you.
Work With Your Health Care Team
Most people with diabetes get health care from a primary care professional. Primary care professionals include internists, family physicians, and pediatricians. Sometimes physician assistants and nurses with extra training, called nurse practitioners, provide primary care. You also will need to see other care professionals from time to time. A team of health care professionals can help you improve your diabetes self-care. Remember, you are the most important member of your health care team.
Besides a primary care professional, your health care team may include
- an endocrinologist for more specialized diabetes care
- a registered dietitian, also called a nutritionist
- a nurse
You May Like: How To Take Diabetes Test
What Is Blood Sugar
Blood sugar or blood glucose is the glucose present in the bloodstream of animals. Its primary function is to enter the metabolizing cells of the body to be used as a source of energy. That is glucose takes part in the cellular respiration, producing approximately 38 ATPs per molecule. However, animals are typically heterotrophs, and hence, they do not produce glucose inside their body. Therefore, dietary carbohydrates serve as the main source of glucose in the animal body. In this process, the digestive system is responsible for the breakdown of the carbohydrates in the diet into glucose and other minor types of monosaccharides.
Figure 1: Idealized Curves of Human Blood Glucose and Insulin Concentrations During the Course of a Day Containing Three Meals
What If The Blood Glucose Check Result Doesnt Sound Right
If youre not convinced that a result is correct, heres a suggested check list:
- Have the strips expired?
- Is the meter too hot or too cold?
- Is the calibration code correct?
- Is the battery low or flat?
All meters will give a different result with a different drop of blood. As long as there is not a big difference there is not usually cause for concern.
The accuracy of all meters can be checked with meter-specific liquid drops called control solutions. If you are concerned, you can arrange to have your meter checked with a control solution. Your Credentialled Diabetes Educator or pharmacist can help you with this.
Also Check: Free Insulin For Diabetics Without Insurance
What Is Blood Glucose Monitoring
People use blood glucose monitoring to regularly test glucose levels in the blood.
It is an essential part of effective diabetes control. Many people with diabetes must check several times each day to plan for activities and meals, as well as scheduling doses of medication or insulin.
A person can test their blood glucose levels with a glucometer. They usually come with lancets, or tiny needles, as well as test strips and a logbook to record results.
Are There Different Recommendations For Blood Sugar Levels In Other Countries
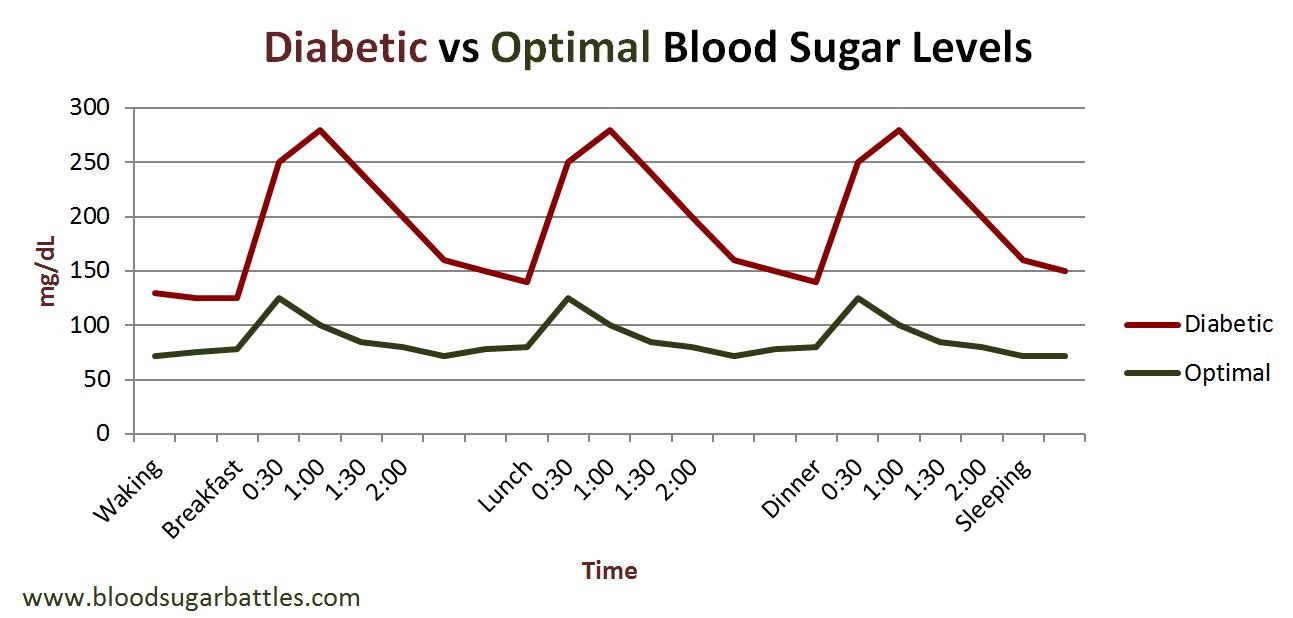
The recommended blood sugar level ranges in countries around the world are very similar. However, there are two different units of measurement that are used when referring to blood sugars, depending on where you live: millimoles per litre and milligrams per decilitre .
The mmol/L measurement is used here in Canada, as well as England, Australia and China, while mg/dL is used in such countries as the United States, France, Japan, Israel and India.
To convert mmol/L to mg/dl, simply multiply by 18. For example, a blood sugar level of 5.0 mmol/L would mean a level of 90 mg/dL .
Here are blood sugar recommendations from some countries other than Canada:
| Country | |
| 80 to 130 mg/dL | Less than 180 mg/dL |
Also Check: Robitussin Cough Syrup For Diabetics
What Causes Blood Sugar To Be High
Many things can cause high blood sugar , including being sick, being stressed, eating more than planned, and not giving yourself enough insulin. Over time, high blood sugar can lead to long-term, serious health problems. Symptoms of high blood sugar include:
- Feeling very tired.
- Having blurry vision.
- Needing to urinate more often.
If you get sick, your blood sugar can be hard to manage. You may not be able to eat or drink as much as usual, which can affect blood sugar levels. If youre ill and your blood sugar is 240 mg/dL or above, use an over-the-counter ketone test kit to check your urine for ketones and call your doctor if your ketones are high. High ketones can be an early sign of diabetic ketoacidosis, which is a medical emergency and needs to be treated immediately.
What Are Normal Blood Sugar Levels In Healthy Individuals
Blood sugar levels can either be normal, high, or low, depending on how much glucose someone has in their bloodstream. Glucose is a simple sugar thats present in the bloodstream at all times. Blood glucose levels can be measured at any time, for example, when someone fasts , before they eat, or after theyve eaten. A normal blood glucose level for adults, without diabetes, who havent eaten for at least eight hours is less than 100 mg/dL. A normal blood glucose level for adults, without diabetes, two hours after eating, is 90 to 110 mg/dL.
Many factors affect blood sugar levels throughout the day:
- Type of food consumed, how much, and when
- Physical activity
- Menstrual periods
- Alcohol
An ideal blood sugar level for anyone without diabetes or prediabetes, regardless of age, in the morning should be less than 100 mg/dL. Remember, blood sugar levels can fluctuate throughout the day as a result of the factors previously mentioned.
You May Like: Type 1 Diabetes And Premature Ejaculation
What Is Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Continuous glucose monitoring is another way to check your glucose levels. Most CGM systems use a tiny sensor that you insert under your skin. The sensor measures glucose levels in the fluids between your bodys cells every few minutes and can show changes in your glucose level throughout the day and night. If the CGM system shows that your glucose is too high or too low, you should check your glucose with a blood glucose meter before making any changes to your eating plan, physical activity, or medicines. A CGM system is especially useful for people who use insulin and have problems with low blood glucose.
What Causes Low Blood Sugar
Low blood sugar has many causes, including missing a meal, taking too much insulin, taking other diabetes medicines, exercising more than normal, and drinking alcohol. Blood sugar below 70 mg/dL is considered low.
Signs of low blood sugar are different for everyone. Common symptoms include:
- Shaking.
- Dizziness.
- Hunger.
Know what your individual symptoms are so you can catch low blood sugar early and treat it. If you think you may have low blood sugar, check it even if you dont have symptoms. Low blood sugar can be dangerous and should be treated as soon as possible.
Recommended Reading: Life Insurance For Diabetics Type 2
Target Blood Sugar Levels For Children And Adolescents With Diabetes
Age 6-12 Bedtime 100-180
Kids aged 6 to 12 should have blood sugar levels that range between 80 to 180 mg/dL over the course of a day. Blood sugar levels go up after eating a meal because the body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which is then distributed throughout the bloodstream. Other macronutrientsprotein and fatturn into glucose as well, but at a slower rate. Many people learn how to use these factors to their advantage. For example, if a childs sugar is trending low, a bedtime snack that includes something with protein and fat, like chocolate milk or peanut butter, will help raise blood sugar levels and help keep blood sugar levels steady through the night.
| Bedtime | 100-140 |
When you wake up in the morning, your fasting blood sugar is generally at its lowest because you havent consumed food for about eight hours. However, many people experience an increase in blood sugar levels in the early morning hours. If youre an adult and struggling with glucose control, your healthcare provider can help you develop a treatment plan to manage your blood sugar better.
Blood glucose levels outside the ranges listed above are categorized as either high or low blood sugar. For example, according to this chart, blood sugar levels are considered high if theyre over 130 mg/dL before a meal or 180 mg/dL within one to two hours after a meal. Many people wont start to experience symptoms from high blood sugar until their levels are at 250 mg/dL or higher. .
What Is The Difference Between Blood Sugar And Urine Sugar
Glucose is a normal component of blood. The normal blood glucose levels are:- Fasting blood glucose level: 70-110 mg/dl Postprandial blood glucose level: up to 140 mg/dl But glucose is not a normal component of urine. Under normal physiological conditions, when blood glucose level is within normal limits, the urine does not contain any glucose. However, under pathologic conditions like diabetes mellitus, when blood sugar level crosses renal threshold , the blood glucose appears in urine. This condition is called glycosuria or glucosuria.Continue reading > >
Also Check: Tooth Removal For Diabetic Patient
Accuracy Of Cgm Vs Glucometer
The most common metric used to assess performance and accuracy of a monitoring system is by looking at the Mean Absolute Relative Difference . MARD is the average of all absolute errors between the device and the matched lab reference values. When compared against the lab reference values, both Glucometer and CGM have some margin of error. According to a 2014 study, a MARD between 10 – 12% is accurate enough to give us insights on the patterns of hypo and hyperglycemia events over time, to help in making decisions about carbohydrate intake, changes in medication/insulin dosage and to avoid such events in the future.
Factors That Affect Blood Glucose Levels
Also Check: What Is A Fast Acting Insulin
How Can I Treat Low Blood Sugar
If youve had low blood sugar without feeling or noticing symptoms , you may need to check your blood sugar more often to see if its low and treat it. Driving with low blood sugar can be dangerous, so be sure to check your blood sugar before you get behind the wheel.
Carry supplies for treating low blood sugar with you. If you feel shaky, sweaty, or very hungry or have other symptoms, check your blood sugar. Even if you dont have symptoms but think you may have low blood sugar, check it. If your blood sugar is lower than 70 mg/dL, do one of the following immediately:
- Take four glucose tablets.
- Drink four ounces of fruit juice.
- Drink four ounces of regular soda, not diet soda.
- Eat four pieces of hard candy.
Wait for 15 minutes and then check your blood sugar again. Do one of the above treatments again until your blood sugar is 70 mg/dL or above and eat a snack if your next meal is an hour or more away. If you have problems with low blood sugar, ask your doctor if your treatment plan needs to be changed.