What Is A Normal Blood Sugar Level
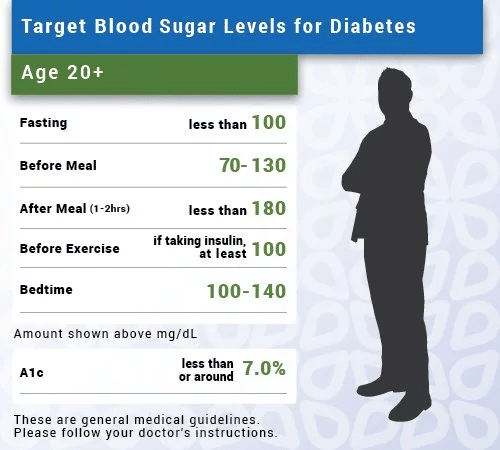
According to the American Diabetes Association, a normal fasting blood sugar is less than 100 mg/dL.
A fasting blood sugar reading of 100-125 mg/dL indicates prediabetes, and a reading above 125 indicates diabetes.
| Fasting Blood Sugar | |
| 100 mg/dl to 125 mg/dl | Prediabetes |
| 126 mg/dl or higher | Diabetes |
If you test your blood sugar two hours after eating or drinking something containing sugar instead , the numbers to look for are:
| Oral Glucose Tolerance Test | |
| 140 mg/dl to 199 mg/dl | Prediabetes |
You can learn more in the in-depth article: What Are Normal Blood Sugar Levels?
Causes Related To Lifestyle
Physical inactivity
Exercising prompts your body to burn more energy than usual, and, as a result, consume more glucose. Maintaining a low level of physical activity, on the other hand, means more glucose will remain in the bloodstream. This raises your overall blood glucose values in the process.
Exercise also makes our body more insulin sensitive, which means we will require less insulin for the rest of the day to control glucose levels.
Stress
Part of the bodyâs fight-or-flight response to stress is to produce additional glucose. Another facet of that response is an increase in the hormone cortisol. High cortisol can reduce the bodyâs sensitivity to insulin. As a result, blood glucose levels may also increase.
Poor sleep
A lack of quality sleep can inhibit how much insulin your body can release. It can also cause the production of cortisol, which makes it harder for insulin to work. When your bodyâs insulin cannot properly metabolize the glucose in your blood, the glucose remains there and your glucose levels rise.
How Are High Blood Sugar Levels Treated
Treating high blood sugar levels involves fixing what caused them in the first place. Your diabetes health care team will give you specific advice on how to keep your blood sugar levels in a healthy range. But here are some ways to manage the common causes of high blood sugar levels:
| Reason for High Blood Sugar Level | What to Do |
|---|---|
| Not getting enough insulin or other diabetes medicine |
|
| Not following the meal plan |
|
| Not getting enough exercise |
|
| Illness or stress |
|
| Use of other medicines that can increase blood sugar |
|
page 3
Also Check: Best Continuous Glucose Monitor For Non Diabetics
What Is Considered Low Blood Sugar
For the average person with diabetes, low blood sugar means anything under 80 mg/dL .
Very low blood sugars are any readings under 40 mg/dL. Anything under 40 mg/dL is considered extremely dangerous and potentially fatal.
A person is at a significantly higher risk of falling into a diabetic coma if they cannot get their blood sugar above 40 mg/dL for several hours.
If a person is experiencing a severe low, and they are unable to chew food or swallow liquids, they will require an emergency shot of Glucagon .
What Causes Blood Sugar To Be High
Many things can cause high blood sugar , including being sick, being stressed, eating more than planned, and not giving yourself enough insulin. Over time, high blood sugar can lead to long-term, serious health problems. Symptoms of high blood sugar include:
- Feeling very tired.
- Having blurry vision.
- Needing to urinate more often.
If you get sick, your blood sugar can be hard to manage. You may not be able to eat or drink as much as usual, which can affect blood sugar levels. If youre ill and your blood sugar is 240 mg/dL or above, use an over-the-counter ketone test kit to check your urine for ketones and call your doctor if your ketones are high. High ketones can be an early sign of diabetic ketoacidosis, which is a medical emergency and needs to be treated immediately.
Read Also: Salty Taste In Mouth Diabetes
How Can I Treat Low Blood Sugar
If youve had low blood sugar without feeling or noticing symptoms , you may need to check your blood sugar more often to see if its low and treat it. Driving with low blood sugar can be dangerous, so be sure to check your blood sugar before you get behind the wheel.
Carry supplies for treating low blood sugar with you. If you feel shaky, sweaty, or very hungry or have other symptoms, check your blood sugar. Even if you dont have symptoms but think you may have low blood sugar, check it. If your blood sugar is lower than 70 mg/dL, do one of the following immediately:
- Take four glucose tablets.
- Drink four ounces of fruit juice.
- Drink four ounces of regular soda, not diet soda.
- Eat four pieces of hard candy.
Wait for 15 minutes and then check your blood sugar again. Do one of the above treatments again until your blood sugar is 70 mg/dL or above and eat a snack if your next meal is an hour or more away. If you have problems with low blood sugar, ask your doctor if your treatment plan needs to be changed.
Factors That Contribute To Blood Sugar Range
The bodys level of blood glucose is controlled by , a hormone produced in the that helps your body absorb the sugar and use it in your cells. As your level of blood glucose rises, your pancreas produces more insulin to compensate. This helps keep your average blood glucose level within a safe range.
In diabetes, the body cant produce enough insulin or cant use the insulin properly . This means that your body cant compensate well for increases in blood glucose, which prevents your pancreas from stopping sharp spikes in blood glucose and increases the average blood glucose level over time.
Blood glucose spikes happen to everyone, especially after eating and drinking, but also after skipping breakfast, when youre dehydrated, and after you get a sunburn, among other triggers. They are especially dangerous for people with diabetes because their bodies cant , or even out, the spikes.
Also Check: What Is Too Low Of Blood Sugar
Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic Nonketotic Syndrome : When Hyperglycemia Becomes Severe For People With Type 2 Diabetes
Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic nonketotic syndrome is very rare, but you should be aware of it and know how to handle it if it occurs.
HHNS is when your blood glucose level goes way too highyou become extremely hyperglycemic. HHNS affects people with type 2 diabetes.
HHNS is most likely to occur when you’re sick, and elderly people are most likely to develop it.
It starts when your blood glucose level starts to climb: when that happens, your body will try to get rid of all the excess glucose through frequent urination. That dehydrates your body, and you’ll become very thirsty.
Unfortunately, when you’re sick, it’s sometimes more difficult to rehydrate your body. For example, it might be difficult to keep fluids down.
When you don’t rehydrate your body, the blood glucose level continues to climb, and it can eventually go so high that it could send you into a coma.
To avoid hyperosmolar hyperglycemic nonketotic syndrome, you should keep close watch on your blood glucose level when you’re sick .
Talk to your health care professional about having a sick-day plan to follow that will help you avoid HHNS.
You should also be able to quickly recognize the signs and symptoms of HHNS, which include:
-
Extremely high blood glucose level
Ketoacidosis: When Hyperglycemia Becomes Severe For People With Type 1 Diabetes
If you have type 1 diabetes, it is important to recognize and treat hyperglycemia because if left untreated it can lead to a dangerous condition called .
This happens because without glucose, the body’s cells must use ketones as a source of energy. Ketoacidosis develops when ketones build up in the blood. It can become serious and lead to diabetic coma or even death.
According to the American Diabetes Association, ketoacidosis affects people with type 1 diabetes, but it rarely affects people with type 2 diabetes.
Many symptoms of ketoacidosis are similar to hyperglycemia. The hallmarks of ketoacidosis are:
-
High level of ketones in the urine
-
Shortness of breath
-
Fruit-smelling breath
Additionally, stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, and confusion may accompany ketoacidosis. Immediate medical attention is highly recommended if you have any of these symptoms.
Some people with diabetes are instructed by their doctor to regularly test ketone levels. Ketone testing is performed two ways: using urine or using blood.
For a urine test, you dip a special type of test strip into your urine. For testing blood ketones, a special meter and test strips are used. The test is performed exactly like a blood glucose test.
If ketone testing is part of your self-monitoring of diabetes, your health care professional will provide you with other information including prevention.
Don’t Miss: What Is Insulin Good For
How Should You Treat Hypoglycaemia
The symptoms of low blood glucose include: weakness, dizziness or feeling light-headed, nervousness, sweating, pounding heartbeat, hunger and thirst, and confusion.
To tackle hypoglycaemia, follow the 15-15 rule: Have 15 grams of carbohydrate or fast-acting sugar, such as half a cup of regular fruit juice or 4 glucose tablets, to raise your blood glucose. Check your level after 15 minutes. If its still below 70 mg/dL , repeat the above step until your blood sugar reaches normal levels. Once your blood glucose is at least 70 mg/dL , have a snack or a meal to ensure it doesnt lower again.
Severely low blood sugarIf your hypoglycaemia is left untreated, or if your blood sugar level remains abnormally low and does not increase, you may pass out. In such cases, you need to be given emergency glucagon and require immediate medical attention.
The people around you, such as your family members, friends, or co-workers, should be taught how to administer glucagon in case of an emergency. They should also remember: NOT to give you insulin, as it will lower your blood sugar even more NOT to give you anything to eat or drink if you are unconscious, as it could cause you to choke.
Diagnosis And Monitoring Of Hyperglycaemia
Blood glucose levels can be tested and monitored in a variety of ways including:
- Random blood glucose test a blood test that checks the blood glucose level, regardless of when the person last ate
- Fasting blood glucose test the person fasts so that a baseline blood glucose level can be established by blood test. This is the most common way a diagnosis of diabetes is made
- Oral glucose tolerance test the person drinks a special preparation that contains glucose. A blood test is taken two hours later to check the blood glucose level
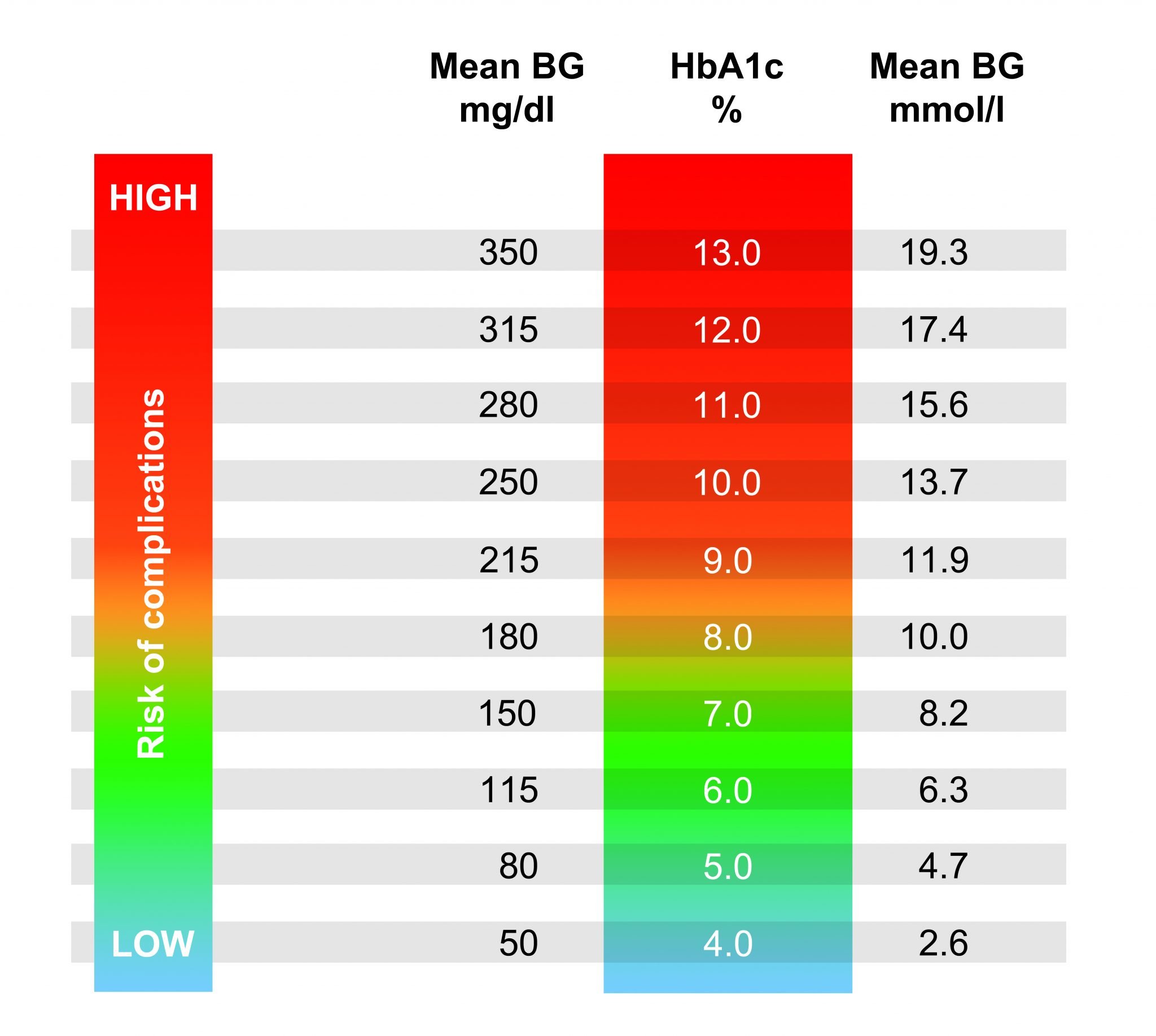
- Glycosylated haemoglobin test this test is a guide to the average level of blood glucose over the previous three months. The glycosylated haemoglobin test is typically used as a way to monitor the treatment of a person with diagnosed diabetes
- Home blood glucose monitoring test a person with diagnosed diabetes can test their blood glucose at home with a special kit. A drop of blood is placed on a strip of paper, which is then fed into a blood glucometer.
Don’t Miss: How Fast Can Blood Sugar Drop
Blood Sugar Level Charts For Those With Diabetes
Normal blood sugar levels, for those with diabetes, will vary depending on someones age and the time of day. For example, when fasting, blood sugar levels are often in the target goal range. The type of food eaten will impact blood sugar levels in different ways. A meal with a lot of carbohydrates will raise blood sugar quicker than a meal that contains carbohydrates, protein, and fat . Blood sugar will rise after a meal, but will start to return to normal levels in several hours.
Lets take a look at what blood sugar levels should be, in those with diabetes, based on their age.
What Are Blood Sugar Levels
Blood sugar levels, also known as blood glucose level, is the level of sugar/glucose present in the blood. Glucose is a simple version of sugar which comes from the food we eat. Therefore, the more food you consume with high sugar levels over a period of time, will typically increase your blood sugar level.
Glucose comes from the foods we eat and its sugar content. When a person consumes a food with high sugar content, that is turned into glucose. The glucose is then absorbed into the bloodstream with the support of insulin. This is then distributed between the bodys cells and used as energy.
Foods high in glucose include most carbohydrates and a handful of proteins and fats. Most foods contain glucose as it is simply a natural sugar that occurs in most dietary forms. However, it is carbohydrates that contain the most sugar and 100% of it turns into glucose, through the process mentioned above, once consumed. The concentration of glucose present in the blood will determine your blood sugar level.
Here is a quick video explaining Blood sugar levels chart :
Your blood sugar level can either be low, normal or high. Depending on what you eat and health conditions, it will vary from person to person. Here is a breakdown of how your blood sugar works and how low or high blood sugar levels happens:
Recommended Reading: How Much Sugar Diabetes Type 2
How Is Hyperglycaemia Treated
If you experience hyperglycaemia regularly, speak to your doctor or diabetes care team. You may need to change your treatment or lifestyle to keep your blood glucose levels within a healthy range.
You may be advised to:
- adjust the foods you eat eg, avoid foods such as cakes or sugary drinks
- drink plenty of sugar-free fluids to help keep you well hydrated
- exercise more often even gentle, regular exercise such as walking can lower your blood sugar level
- if you use insulin, adjust your dose your healthcare team can give you specific advice about how to do this.
You may also be advised to monitor your blood glucose level more closely or test your blood or urine for substances called ketones .
Low Blood Sugar Symptoms
Low blood sugar, also called hypoglycemia, is what happens when blood glucose levels drop too low. People who take insulin may have low blood sugar if they take too much insulin or mistime the insulin dose in relation to food, or if they exercise more than usual when there is fast-acting insulin on board .
Your healthcare provider will tell you when and how to check blood sugar, and when and how to treat low blood sugar. A low blood sugar is generally considered to be less than 70 mg/dL. A dangerously low blood sugar is below 54 mg/dL.
Low blood sugar can also be caused by many things including certain medications or combinations of medications, alcohol, endocrine disorders, eating disorders, and disorders of the liver, kidneys, or heart.
Here are some of the most common symptoms that someone with low blood sugar might experience:
- Lightheadedness
If your blood sugar is low you might start to feel some of the first signs of hypoglycemia like dizziness, lightheadedness, or sweating. The only way to know for sure if your blood sugar is low is to test it with a glucose meter or monitor it with a continuous glucose monitor such as the Dexcom G6.
If your blood sugar is low , a general rule of thumb is to consume 15 grams of fast-acting carbs to raise your blood sugar levels and avoid further symptoms, according to the American Diabetes Association . Your healthcare provider will give you a plan for what to do in case of low blood sugar that is specifically designed for you.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Chances Of Getting Diabetes
The Danger Of High Blood Sugar
Having a high blood sugar means there is too much sugar in the blood because the body is lacking in insulin. This can happen for many reasons, including not taking enough insulin exogenously, too little exercise, eating too much, or even stress, hormonal changes, or lack of sleep.
High blood sugar is dangerous, but its important to remember that high blood sugar is mostly dangerous over prolonged periods of time .
This means that, for the most part, your blood sugar at diagnosis will not cause long-term complications, and the spike you saw last week from eating an ice cream sundae wont impact you over the long term.
But chronic, prolonged high blood sugars will cause diabetes complications in most people.
For Adults With Type 1 And 2 Children With Type 2
What is considered a normal blood glucose level varies from person to person. Its affected by factors such as weight, age, activity level, and whether you have any health conditions. Your health care provider will generally account for all these factors to develop a target glucose level.
A broad baseline range is between 60 mg/dL and 130 mg/dL when fasting and up to 180 mg/dL 2 hours after you begin eating, or under 7% on an A1c test.
Results that are higher than the range are called , while results that are lower are called . The borders between extremes of the ranges are not precise, but they are useful markers for monitoring general trends.
Careful monitoring is especially important for people with type 1 diabetes, as they are at higher risk of both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia.Its also useful for reducing long-term damage to your body, because it helps you stay within the healthy range for as long as possible throughout the day. This is called your time in range, and health care providers generally aim for about 70%, which equals around 16 to 17 hours per day.
You May Like: Is Bio X4 Safe For Diabetics