Possible Health Effects Of Insulin
When biological matter such as insulin, both animal and biosynthetic, are introduced into the human body, the body may recognize it as foreign and begin manufacturing antibodies to fight it. In some cases, this process results in a person having to take more insulin to manage his/her diabetes.
In the past few years, a small number of people have reported difficulty managing their diabetes with human biosynthetic insulins. They reported having hypoglycemia without clearly recognizable symptoms, and wide and sudden swings in blood glucose levels. The reasons for these difficulties are unclear.
A review of the major clinical studies on insulin showed that the safety and effectiveness of human biosynthetic insulin and animal-sourced insulin are comparable. In addition, the number and types of adverse reactions reported with both types of insulins were similar, based on the number of patients using each product. In fact, adverse reactions such as hypoglycemia , may occur while taking either type of insulin.
Hypoglycemia can occur regardless of what type of insulin you take and can cause fatigue, sweating, heart palpitations, disturbed behaviour, hunger, loss of consciousness, or in extreme circumstances even death and can occur without recognizable symptoms. It may be brought on:
Should I Start Using Insulin For My Diabetes Recent Study Shows The Details
In 1991, the World Health Organization and the IDF created World Diabetes Day, to be observed every 14th of November, in commemoration of the birthday of Sir Frederick Banting, who co-discovered life-saving insulin alongside Charles Best, back in 1921. The observance is an annual campaign to raise awareness on diabetes as an escalating global threat, affecting millions of people worldwide.
One of the main goals of celebrating WDD is to keep highlighting diabetes as an issue of concern that public stakeholders should pay attention to until, of course, such a time that diabetes is well-managed worldwide. Until then, coordinated and concerted efforts to confront diabetes are conducted yearly to emphasize that we should all, as a community, respond to the fight against diabetes.
The theme for 2021 to 2023 is Access to Diabetes Care If Not Now, When? As in previous years, this event will serve to promote awareness about the importance of increasing access to diabetes care to improve diabetes management, prevent complications, and improve the quality of life of people living with diabetes around the world. Because truly, if we dont act now against diabetes, then when?
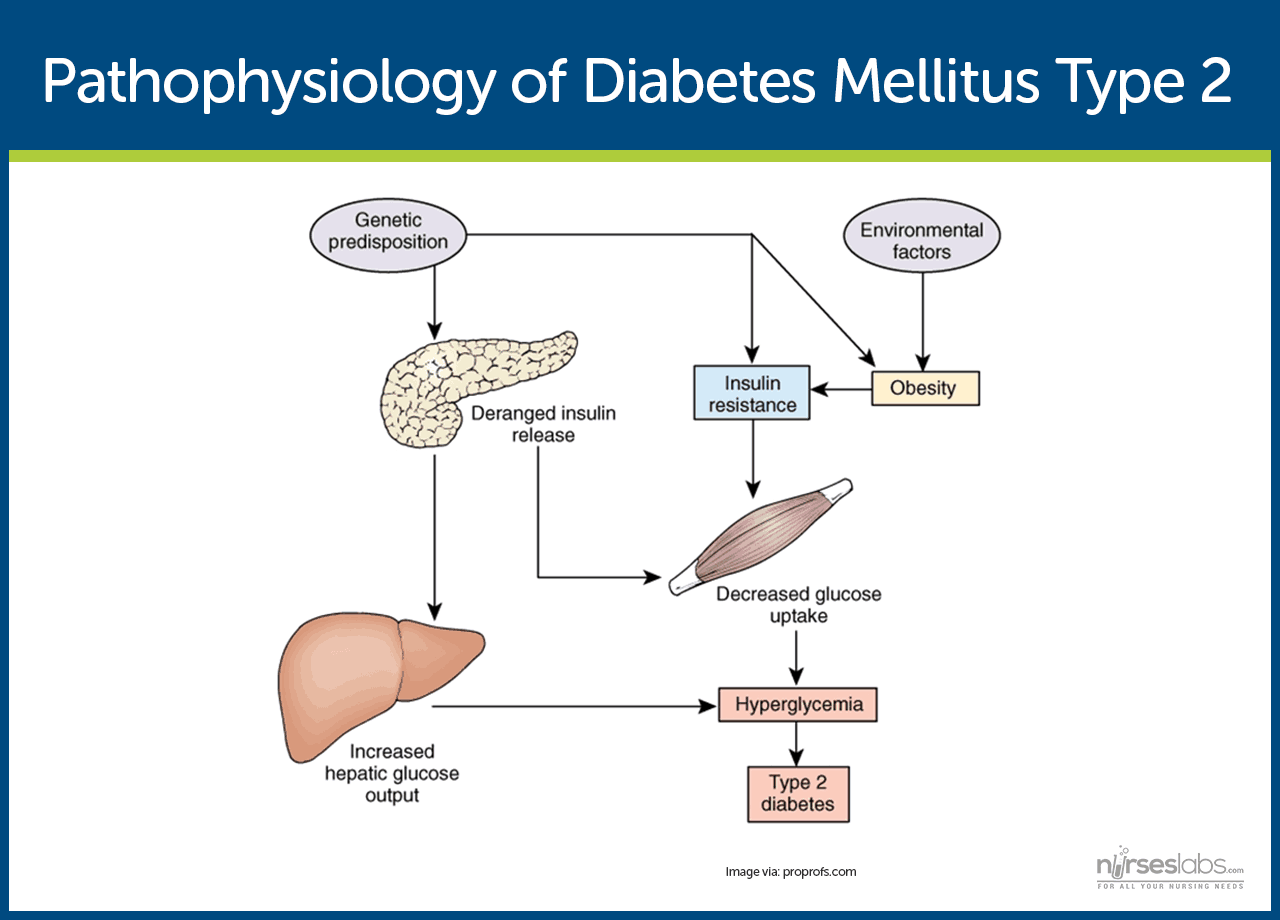
Diabetes and insulin
Real-world data gives real evidence
A key aspect of diabetes care and treatment is the use of insulin drugs. Diabetes complications can be prevented by understanding the role insulin plays in managing your blood sugar.
Promising results from insulin drug
ADVT.
Characteristics Of Insulin Action
There are three characteristics that define how insulin medication function:
Insulin is prescribed by matching the characteristics of a particular insulin with the individual needs of the patient. Some people are on only one kind of insulin, while others take a combination of insulin medication to customize good glucose control.
Also Check: Is 6.2 A1c Diabetes
What Will Insulin Be Like In The Future
Pharmaceutical companies are working on very long-acting versions of insulin that could last for a week. There is also an ultra-fast version of insulin under development that will act in less than 15 minutes.
Another group of researchers is looking at glucose responsive insulin , which would react to the needs of your body in real time. It would have nanosensors bound to the insulin so that when insulin is needed, it releases, and when it isnt, it stops, according to Dr. Hirsch.
What Should I Know About Storage And Disposal Of This Medication
Store unopened vials of human insulin, unopened disposable dosing devices and unopened human insulin pens in the refrigerator. Do not freeze human insulin and do not use human insulin that has been frozen. Opened vials of human insulin should be stored in the refrigerator but may also be stored at room temperature, in a cool place that is away from heat and direct sunlight. Store opened human insulin pens and opened dosing devices at room temperature. Check the manufacturer’s information to find out how long you may keep your pen or dosing device after the first use.
Unneeded medications should be disposed of in special ways to ensure that pets, children, and other people cannot consume them. However, you should not flush this medication down the toilet. Instead, the best way to dispose of your medication is through a medicine take-back program. Talk to your pharmacist or contact your local garbage/recycling department to learn about take-back programs in your community. See the FDA’s Safe Disposal of Medicines website for more information if you do not have access to a take-back program.
It is important to keep all medication out of sight and reach of children as many containers are not child-resistant and young children can open them easily. To protect young children from poisoning, always lock safety caps and immediately place the medication in a safe location â one that is up and away and out of their sight and reach.
Read Also: Diabetic Supply Companies That Accept Medicaid
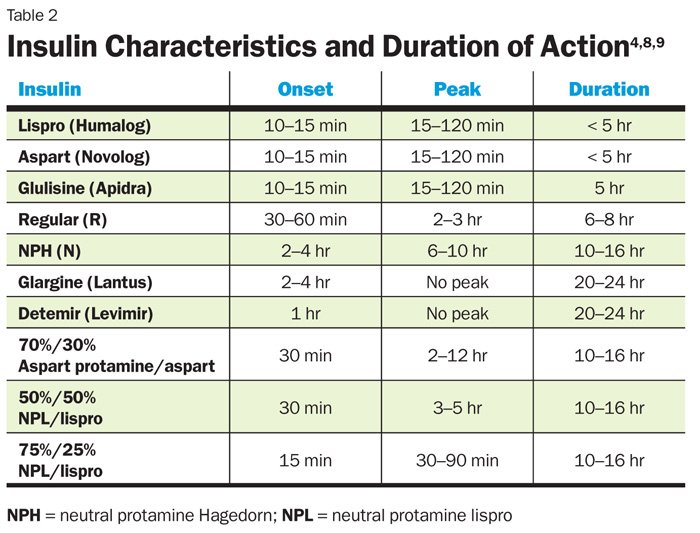
What Are The Different Types Of Insulin
The American Diabetes Association characterizes insulin by how fast it works. But everyones body is different. If you have diabetes, you should expect deviations in the amount of time any medication takes to reach your bloodstream. Here are a few useful terms related to how fast and how long insulin acts in your body:
- Onset is defined as the length of time before insulin hits your bloodstream and begins to lower blood glucose.
- Peak is the time during which insulin is at its maximum effectiveness at lowering your blood glucose levels.
- Duration is the length of time insulin continues to lower your blood glucose levels.
These are the five main types of insulin that doctors prescribe:
What Are Warnings And Precautions The Diabetes Drug Insulin
- Insulin should not be used if low blood sugar is present.
- Any adjustment of insulin, whether to a different brand, type, strength, or method of administration, must be made under medical supervision.
- Injury, illness, surgery, pregnancy, and changes in activity level can affect blood sugar levels, which might require an adjustment in insulin dose.
- Patients should inform medical providers of previous medical history before using insulin, especially adrenal/pituitary gland problems, infections, kidney or liver disease, thyroid issues, and nerve problems such as tingling or numbness.
- Patients should advise medical providers if they are pregnant.
- Alcohol can increase the risk of developing low blood sugar.
- Children and the elderly may be more sensitive to insulin.
- Discard open vials of insulin after 28 days.
- Do not use insulin after its expiration date.
Recommended Reading: What Eye Problems Does Diabetes Cause
What Other Drugs Interact With Insulin Nph
If your medical doctor is using this medicine to treat your pain, your doctor or pharmacist may already be aware of any possible drug interactions and may be monitoring you for them. Do not start, stop, or change the dosage of any medicine before checking with your doctor, health care provider, or pharmacist first
- Insulin NPH has severe interactions with the following drug:
- pramlintide
This information does not contain all possible interactions or adverse effects. Visit the RxList Drug Interaction Checker for any drug interactions. Therefore, before using this drug, tell your doctor or pharmacist of all the drugs you use. Keep a list of all your medications with you, and share the list with your doctor and pharmacist. Check with your physician if you have health questions or concerns.
How Do You Inject Insulin
When injecting insulin, always make sure youre giving yourself the correct insulin type and dosage according to your prescription. Injecting too much insulin can lead to low blood sugar and can turn into a medical emergency quickly . Also, never mix or dilute insulin unless your doctor tells you to, and never use expired insulin.
Your doctor or pharmacist can explain how to properly inject insulin. But here is an overview of the steps you should follow if you are using a vial and a syringerather than an insulin pento inject your insulin:
First, gather these supplies:
Soap and water or hand sanitizer
Alcohol wipes
Sharps container
Wash your hands with soap and water or clean them with hand sanitizer.
Gently roll the insulin vial between your hands to mix. Never shake a vial of insulin.
Wipe the top of the insulin vial with an alcohol wipe.
Remove the cap of your insulin needle and pull back the plunger of the syringe to match the marking of your insulin dose.
Push the needle into the top of the insulin vial and then push the plunger down.
Turn the vial upside down with the needle still inside.
Now, slowly pull the plunger down to the desired dosage again.
Check the syringe for bubbles. If you see bubbles, tap the side of the syringe to float the bubbles to the tip. Next, gently push the plunger to get the bubbles out of the syringe. Do this step while the vial is still upside down with the syringe inside. Repeat until all bubbles are removed.
Also Check: Lantus Insulin Patient Assistance Program
Can I Have A Negative Reaction To Insulin
One complication facing people with diabetes who use insulin is the potential for severe hypoglycemia, also known as insulin shock, which involves using too much insulin and causing your blood sugar to drop extremely low. This can cause coma, seizures, and heart attacks, says Dr. Powers. It requires treatment in a hospital but thankfully is highly treatable once you are there.
What Are The 6 Different Types Of Insulin
If you need insulin, your doctor will recommend a specific type depending on your lifestyle, the type of diabetes you have, and your blood sugar levels at different times of the day. You may need more insulin coverage at mealtimes, overnight, or throughout the entire day. Currently, there are 5 types of injectable insulins and 1 inhaled insulin.
Types of insulin and how they work in your body
| How long it takes to start working | How long it lasts |
|---|---|
| Inhaled insulin |
Also Check: Why Are Insulin Prices So High
What Are The Side Effects Of Insulin
One of the most common side effects of insulin is hypoglycemia .
Symptoms include a headache, sweating, trembling, anxiety, confusion, irritability, rapid breathing, or a fast heartbeat. People with hypoglycemia may also faint and severe hypoglycemia that is left untreated may be fatal.
Hypoglycemia is relatively common because insulin requirements can vary depending on the food you eat, exercise you do, and how well you are. Hyperglycemia from too low an insulin dose can also occasionally occur.
Other common side effects include:
- swelling, itching, redness or lumps around the injection site
- weight gain
- electrolyte disturbances
- blurred vision .
Insulin analogues are less likely to cause weight gain or low night-time blood sugar levels than standard human insulins.
How Does Insulin Work
Immediately following a meal, food that is eaten, particularly carbohydrates, quickly breaks down into a specific type of sugar called glucose that is absorbed into the bloodstream. This rapid rise in blood glucose causes insulin to be released from the pancreas. The insulin allows cells in the body, such as muscle cells, to absorb the glucose to use as a source of energy. Insulin has other effects, but mainly it controls how the body utilizes glucose.
In people with diabetes, if the body does not produce enough insulin or does not use it efficiently, blood glucose levels increase and the cells go without the glucose they need to function properly. If blood glucose levels remain too high over time, a state known as hyperglycemia, this may increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other health problems.
To overcome the problems associated with high blood glucose levels, people with Type 1 diabetes require insulin by injection or by using an insulin pump. Those with Type 2 diabetes may respond to lifestyle changes to reduce high blood glucose levels, such as diet and exercise, or they may require pills, insulin, or a combination of medicines.
- Gestational diabetes
Recommended Reading: Can Someone With Type 1 Diabetes Join The Military
Other Drugs For Type 1 Diabetes
The following drugs, non-insulin injectables, are also common for people treating type 1 diabetes:
- Amylin analogs: Pramlintide mimics another hormone, amylin, that plays a role in glucose regulation.
- Glucagon can reverse blood sugar levels when they fall too low as a result of insulin treatment.
Insulin can also help manage high blood glucose levels in type 2 diabetes, but doctors typically prescribe it only when other treatments have not had the desired effect.
Women with type 2 diabetes who become pregnant may also use it to reduce the effects of the condition on the fetus.
In people with high blood glucose levels in spite of applying lifestyle measures to bring them down, doctors can prescribe non-insulin drugs to lower blood glucose. These drugs are listed below.
Many of the drugs have a combination of effects. If a person needs two or more treatments to manage glucose levels, insulin treatment may be necessary.
Why Is This Medication Prescribed
Human insulin is used to control blood sugar in people who have type 1 diabetes or in people who have type 2 diabetes that cannot be controlled with oral medications alone. Human insulin is in a class of medications called hormones. Human insulin is used to take the place of insulin that is normally produced by the body. It works by helping move sugar from the blood into other body tissues where it is used for energy. It also stops the liver from producing more sugar. All of the types of insulin that are available work in this way. The types of insulin differ only in how quickly they begin to work and how long they continue to control blood sugar.
Over time, people who have diabetes and high blood sugar can develop serious or life-threatening complications, including heart disease, stroke, kidney problems, nerve damage, and eye problems. Using medication, making lifestyle changes , and regularly checking your blood sugar may help to manage your diabetes and improve your health. This therapy may also decrease your chances of having a heart attack, stroke, or other diabetes-related complications such as kidney failure, nerve damage , eye problems, including changes or loss of vision, or gum disease. Your doctor and other healthcare providers will talk to you about the best way to manage your diabetes.
Recommended Reading: What Is Diabetic Retinopathy With Macular Edema
Glimepiride Glyburide Glipizide Gliclazide
These are drugs that stimulate the release of insulin from the beta cells of the pancreas. First generation sulfonylureas are rarely used. However, the second generation sulfonylureas like glimepiride, glyburide , glipizide, and gliclazide are widely used for the management of diabetes mellitus. There are other insulin secretagogues like repaglinide and nateglinide.
These drugs, its actions, side effects and contraindications are discussed in detail under Sulfonylurea Drug Information.
Some Side Effects Can Be Serious If You Experience Any Of The Following Symptoms Call Your Doctor Immediately:
- rash and/or itching over the whole body
- shortness of breath
- large weight gain in a short period of time
- swelling of the arms, hands, feet, ankles, or lower legs
If you experience a serious side effect, you or your doctor may send a report to the Food and Drug Administration’s MedWatch Adverse Event Reporting program online or by phone .
Recommended Reading: Is Keto Diet Safe For Type 1 Diabetes
How Do I Take It
Many people get insulin into their blood using a needle and syringe, a cartridge system, or pre-filled pen systems.
The place on the body where you give yourself the shot may matter. You’ll absorb insulin the most evenly when you inject it into your belly. The next best places to inject it are your arms, thighs, and buttocks. Make it a habit to inject insulin at the same general area of your body, but change up the exact injection spot. This helps lessen scarring under the skin.
Inhaled insulin, insulin pumps, and a quick-acting insulin device are also available.
Factors That Speed Insulin Absorption
Variation in insulin absorption can cause changes in blood glucose levels. Insulin absorption is increased by:
- injecting into an exercised area such as the thighs or arms
- high temperatures due to a hot shower, bath, hot water bottle, spa or sauna
- massaging the area around the injection site
- injecting into muscle this causes the insulin to be absorbed more quickly and could cause blood glucose levels to drop too low.
Don’t Miss: Ginger For Diabetes Type 2
How Is Insulin Administered
Insulin is most commonly administered subcutaneously and there are three main delivery methods:
- Insulin Pens: these hold a replaceable cartridge of insulin and use a replaceable needle to puncture the skin and deliver the insulin subcutaneously
- Insulin pumps: these are small computerized devices that deliver a continuous supply of insulin under the skin. They are also known as continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion devices
- Via a syringe and needle using a vial of insulin.
So far, nobody has successfully made an oral insulin tablet that delivers an effective dose of insulin. The problem is that insulin degrades in the stomach and intestine before it even has a chance to get absorbed into the blood stream. In hospital, insulin may be administered directly into a vein or into a muscle under certain circumstances.