How Does Diabetes Affect The Body
There are two main types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2.
Both types of diabetes are chronic diseases that affect the way your body regulates blood sugar, or glucose. Glucose is the fuel that feeds your bodys cells, but to enter your cells it needs a key. Insulin is that key.
People with type 1 diabetes dont produce insulin. You can think of it as not having a key.
People with type 2 diabetes dont respond to insulin as well as they should and later in the disease often dont make enough insulin. You can think of it as having a broken key.
People with type 1 and type 2 diabetes may also experience irritability, mood changes, and unintentional weight loss.
People with type 1 and type 2 diabetes may also have numbness and tingling in their hands or feet. Good glucose management significantly reduces the risk of developing numbness and tingling in someone with type 1 diabetes, according to the American Diabetes Association .
Although many of the symptoms of type 1 and type 2 diabetes are similar, they present in very different ways.
Many people with type 2 diabetes wont have symptoms for many years, and their symptoms often develop slowly over the course of time. Some people with type 2 diabetes have no symptoms at all and dont discover they have the condition until complications arise.
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes may have similar names, but theyre different diseases with unique causes.
How Are They Alike
Both types of diabetes greatly increase a person’s risk for a range of serious complications. Although monitoring and managing the disease can prevent complications, diabetes remains the leading cause of blindness and kidney failure. It also continues to be a critical risk factor for heart disease, stroke, and foot or leg amputations.
Current as of: July 28, 2021
What Problems Can Happen With Type 2 Diabetes
Sometimes, kids and teens with type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance, or obesity might develop thick, dark, velvet-like skin around the neck, armpits, groin, between fingers and toes, or on elbows and knees a cosmetic skin condition called acanthosis nigricans. This skin darkening can lighten over time with improvement in insulin resistance.
Polycystic ovary syndrome in girls is also often associated with insulin resistance. This hormone problem can make the ovaries become enlarged and develop cysts . Girls with PCOS might have irregular periods, might stop having periods, and may have excess facial and body hair growth. It also can cause fertility problems.
People with insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes are also more likely to develop hypertension or abnormal levels of blood fats . When these problems cluster together, its called metabolic syndrome. People with metabolic syndrome are at risk for heart disease, stroke, and other health problems.
Diabetes also can cause heart disease and stroke, as well as other long-term complications, including eye problems, kidney disease, nerve damage, and gum disease. While these problems dont usually show up in kids or teens whove had type 2 diabetes for only a few years, they can affect them in adulthood, particularly if their diabetes isnt well controlled.
p
You May Like: Low Blood Sugar With Type 2 Diabetes
Type 1 Vs Type 2 Diabetes Causes
Type 1 diabetes Type 2 diabetes An autoimmune disease where the body attacks the beta cells in the pancreas, stopping or reducing insulin production. Cells dont respond correctly to insulin as a result of insulin resistance. The pancreas will keep producing more insulin, but it will not effectively regulate blood sugar.
We Know Some People Get Confused Between Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes And Were Often Asked About The Differences Between Them

Although type 1 and type 2 diabetes both have stuff in common, there are lots of differences. Like what causes them, who they affect, and how you should manage them. There are other types of diabetes like gestational and MODY. But this page is mainly about the differences between type 1 and type 2.
For a start, type 1 affects 8% of everyone with diabetes. While type 2 diabetes affects about 90%.
Lots of people get confused between type 1 and type 2 diabetes. This can mean you have to explain that what works for one type doesn’t work for the other, and that there are different causes.
The main thing to remember is that both are as serious as each other. Having high blood glucose levels can lead to serious health complications, no matter whether you have type 1 or type 2 diabetes. So if you have either condition, you need to take the right steps to manage it.
Recommended Reading: Type 2 Diabetes Skin Problems
What Was Our Selection Criteria For The 3 Best Diabetes Programs
Can Symptoms Appear Suddenly
In people with type 1 diabetes, the onset of symptoms can be very sudden, while in type 2 diabetes, they tend to come about more gradually, and sometimes there are no signs at all.
Symptoms sometimes occur after a viral illness. In some cases, a person may reach the point of diabetic ketoacidosis before a type 1 diagnosis is made. DKA occurs when blood glucose is dangerously high and the body cant get nutrients into the cells because of the absence of insulin. The body then breaks down muscle and fat for energy, causing an accumulation of ketones in the blood and urine. Symptoms of DKA include a fruity odor on the breath, heavy, taxed breathing and vomiting. If left untreated, DKA can result in stupor, unconsciousness, and even death.
People who have symptomsof type 1 or of DKAshould contact their health care provider immediately for an accurate diagnosis. Keep in mind that these symptoms could signal other problems, too.
Some people with type 1 have a honeymoon period, a brief remission of symptoms while the pancreas is still secreting some insulin. The honeymoon phase usually occurs after someone has started taking insulin. A honeymoon can last as little as a week or even up to a year. But its important to know that the absence of symptoms doesnt mean the diabetes is gone. The pancreas will eventually be unable to secrete insulin, and, if untreated, the symptoms will return.
Also Check: What Foods Help Produce Insulin
There Are A Few Ways To Treat Type 1 Diabetes:
- Monitor your blood sugar. Living with diabetes means getting familiar with healthy blood sugar levels and checking yours regularly. Depending on your health care providers specific recommendation, you might need to check it four to ten times daily. Youll use a small blood sugar meter called a glucometer to measure glucose levels in a pin-prick of blood on a disposable test strip. Another option is to have a continuous glucose monitor, which automatically measures your blood sugar every few minutes using a sensor inserted underneath the skin.
- Take insulin. Because your body doesnt produce it on its own, youll have to get it another way. There are a few methods for taking insulin, including regular injections or a wearable insulin pump, which delivers small, steady doses of fast-acting insulin throughout the day through a thin tube. Though its certainly not the most convenient lifestyle, it often becomes second nature for people living with type 1 diabetes.
- Maintain a balanced diet. You dont have to be extremely restrictive, but carbohydrates are the foods youll want to watch, making sure to eat them consistently but not go overboard. If youre taking a fixed amount of insulin, keeping your carbohydrate intake consistent to match is important.
- Exercise. Staying active is always an important component of health, but for people with type 1 diabetes, it can help keep blood sugar levels in check and cause your body to use the insulin more efficiently.
Can Type 1 And Type 2 Of Diabetes Be Prevented
Diabetes is a complicated condition and although it is possible to regulate the same by adopting a healthy diet, a balanced lifestyle, and other important aspects, preventing either type 1 or type 2 is not a very common thing. Having said that, you can delay or postpone the onset of type 2 diabetes by adopting healthy measures.
You May Like: Type 2 Diabetes Support Groups Online
Risk Factors For Type 2 Diabetes
Four of the main risk factors for developing type 2 diabetes are:
- age being over the age of 40
- genetics having a close relative with the condition, such as a parent, brother or sister
- weight being overweight or obese
- ethnicity being of south Asian, Chinese, African-Caribbean or black African origin, even if you were born in the UK
Are The Same Tests Used To Diagnose Both Types
A fasting blood sugar measurement can be used to diagnose any type of diabetes. This test measures the level of sugar in the bloodstream in the morning before eating breakfast. Normal fasting plasma glucose levels are less than 100 milligrams per deciliter . Fasting plasma glucose levels of more than 126 mg/dl on two or more tests on different days indicate diabetes. A random blood glucose test can also be used to diagnose diabetes. A blood glucose level of 200 mg/dl or higher indicates diabetes.
Another test that is often used is a blood test to measure levels of glycated hemoglobin . This test provides a measure of the average levels of blood glucose over the past 3 months. Other names for the A1C test are HbA1C and glycosylated hemoglobin test.
Tests to identify the abnormal antibodies produced by the immune system are used to diagnose type 1 diabetes. Some of the antibodies seen in type 1 diabetes include anti-islet cell antibodies, anti-insulin antibodies and anti-glutamic decarboxylase antibodies.
Type 1 treatment: Insulin is the treatment of choice for type 1 diabetes, because the body responds appropriately to insulin and the problem is a lack of insulin production by the pancreas.
Recommended Reading: Diabetes Test App For Android
What Are The Complications Of Diabetes
“Whether it’s type 1 or type 2,” Drinsic says, “the big picture for diabetes is all about preventing complications,” which are mostly related to nerve and blood vessel damage. For example, if you have either type of diabetes, you have twice the risk of heart attack or heart disease as compared with someone without the disease. Other complications include eye problems, kidney disease, foot infections, skin infections, stroke, high blood pressure, cognitive decline, and high cholesterol.
Rick Factors: Who Is Affected
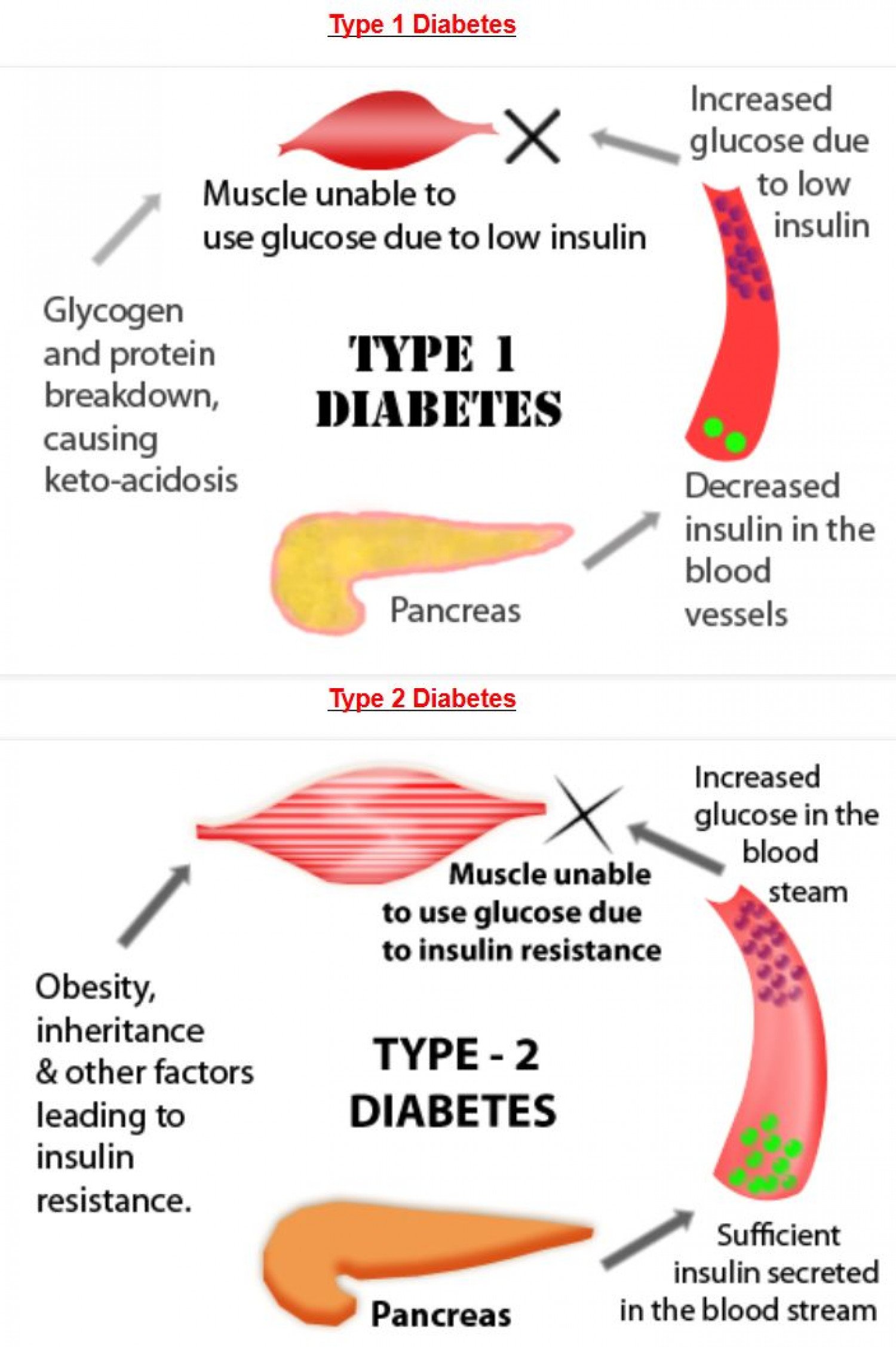
Only about 5% to 10% of diagnosed diabetes cases are type 1. The disease is usually diagnosed in children and young adults, although it can technically strike at any age. Scientists do not know yet exactly what causes type 1 diabetes but suspect the disease involves a combination of genetic, environmental, and autoimmune factors.
An overweight person who does not exercise, is over 30, and/or has close relatives who have type 2 diabetes, runs a very high risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Higher-risk ethnic groups include African Americans, Latinos and Hispanics, Native Americans, Alaskan Natives, Asians, and those with Pacific Islander American heritage.
People are more likely to get diabetes if they smoke, have high blood pressure or cholesterol, or, in women, if they had gestational diabetes or gave birth to a baby who weighed more than 9 pounds. A free diabetes risk test is provided by Diabetes.org and only takes a few minutes to complete.
You May Like: How Can Diabetes Be Managed
Peace Of Mind With Life Line Screening
At Life Line Screening, we have years of experience helping people prevent major medical issues with vital early detection services, including A1C screenings. In fact, screenings are our specialty. We partner with community centers to help people get quick, easy access to the screenings they want to stay on top of their health. No lengthy doctors visits, no complicated insurance to deal with, just convenient screenings for health-conscious people conducted by trained professionals.
Learn more or schedule a screening today at lifelinescreening.com or give us a call at . Wed love to help.
Type 2 Diabetes Risk Factors:
Your risk of developing type 2 diabetes is higher if your diet is high in carbs and fat but low in fiber, if youre not very physically active and/or if you have high blood pressure. High alcohol consumption and age are also risk factors. Though genes do play a role in the likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes, it can be prevented with the right lifestyle choices, unlike type 1.
Dont Miss: Does Medicare Cover Diabetic Testing Supplies
Don’t Miss: Type One Diabetes Side Effects
Is Type 1 Diabetes Worse Than Type 2 Diabetes
The way we think about type 1 and type 2 diabetes has changed dramatically over the past 20 to 30 years. Both types and their associated risk factors can be treated successfully today. Having type 1 diabetes is no longer considered to be a death sentence. There are so many approved treatment options, including fast- and long-acting insulin analogs, pumps, pens, and continuous glucose monitors. It is now possible to reduce swings in blood sugar levels and get the A1c to goal while reducing episodes of hypoglycemia. Type 2 diabetes is now considered an extremely serious condition associated with a very high rate of heart disease. In fact, it is estimated that four out of five people with type 2 diabetes will die from cardiovascular disease — and not the eye, kidney, and nerve disease that we commonly associate with diabetes complications. This content originally appeared in the Taking Control of Your Diabetes newsletter on tcoyd.org.Continue reading > >
What Causes Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes develops when the pancreas makes less insulin than the body needs, and the body cells stop responding to insulin. They dont take in sugar as they should. Sugar builds up in your blood. When cells dont respond to insulin, this is called insulin resistance. It’s usually caused by:
- Lifestyle factors, including obesity and a lack of exercise.
- Genetics, or abnormal genes, that prevent cells from working as they should.
Recommended Reading: Best Cold Medicine For Diabetes
What Is Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus, also called diabetes, is a term for several conditions involving how your body turns food into energy.
When you eat a carbohydrate, your body turns it into a sugar called glucose and sends that to your bloodstream. Your pancreas releases insulin, a hormone that helps move glucose from your blood into your cells, which use it for energy.
When you have diabetes and donât get treatment, your body doesnât use insulin like it should. Too much glucose stays in your blood, a condition usually called high blood sugar. This can cause health problems that may be serious or even life-threatening.
Thereâs no cure for diabetes. But with treatment and lifestyle changes, you can live a long, healthy life.
Diabetes comes in different forms, depending on the cause.
Type 1 Vs Type 2 Diabetes: Whats The Difference
Type 2 diabetes is not the same as Type 1 diabetes. In Type 1 diabetes, your pancreas doesnt make any insulin. In Type 2, your pancreas doesnt make enough insulin, and the insulin it is making doesnt always work as it should. Both types are forms of diabetes mellitus, meaning they lead to hyperglycemia .
Type 2 diabetes usually affects older adults, though its becoming more common in children. Type 1 diabetes usually develops in children or young adults, but people of any age can get it.
Read Also: Can You Get A Tummy Tuck If You Have Diabetes
Treating High Blood Glucose
Hyperglycaemia can occur when your blood glucose levels become too high. It can happen for several reasons, such as eating too much, being unwell or not taking enough insulin.
If you develop hyperglycaemia, you may need to adjust your diet or your insulin dose to keep your glucose levels normal. Your diabetes care team can advise you about the best way to do this.
If hyperglycaemia isn’t treated, it can lead to a condition called diabetic ketoacidosis, where the body begins to break down fats for energy instead of glucose, resulting in a build-up of ketones in your blood.
Diabetic ketoacidosis is very serious and, if not addressed quickly, it can lead to unconsciousness and, eventually, death.
The signs of diabetic ketoacidosis include:
- frequently passing urine
Read more about the symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis
Your healthcare team will educate you on how to decrease your risk of ketoacidosis by testing your own blood for ketones using blood ketone sticks if you’re unwell.
If you develop diabetic ketoacidosis, you’ll need urgent hospital treatment. You’ll be given insulin directly into a vein . You may also need other fluids given by a drip if you’re dehydrated, including salt solution and potassium.
Symptoms Of Type 1 Vs Type 2 Diabetes
Symptoms of Type 1 diabetes include increased thirst and urination, constant hunger, weight loss, blurred vision and extreme tiredness.
Type 2 symptoms appear gradually and are more subtle than those seen with type 1. This makes catching the onset of type 2 diabetes harder to recognize for early treatment. Symptoms include unexpected weight loss, blurred vision, feeling tired or sick more frequently, more frequent urination . Higher levels of thirst, frequent infections and slower healing of cuts and scrapes.
Don’t Miss: How To Tell If Your Child Has Type 1 Diabetes