Guidelines And Glycemic Targets
Hypoglycemia in the treatment of diabetes is addressed throughout the ADAs guideline, Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes2018, particularly in three of its chapters: 6, Establishing the Glycemic Target 11, Older Adults and 14, Diabetes Care in the Hospital.5
The A1C threshold for prediabetes is 5.7% and that for diabetes is 6.5% both of these are risk factors for cardiovascular disease. The most common A1C goal is < 7% for most patients with cognizance to avoid hypoglycemia. However, A1C goals are determined on a patient-by-patient basis those at higher risk for hypoglycemia and its negative consequences should have a considerably relaxed A1C goal in order to avoid hypoglycemia. This is because evidence to date has established the break-even point for benefit-versus-risk balance in this range, mostly based on patient-specific risk factors for hypoglycemia and its consequences, including CV events. Several recent clinical trials have demonstrated improved CV outcomes with drugs in certain drug classes that typically carry a low risk of hypoglycemia however, these data do not support lower-than-currently-recommended glycemic targets.6
Overdose Of Diabetes Medication
A common cause of hypoglycaemia is taking too much insulin for your current needs. Insulin is a medication that helps control your blood glucose levels. It’s commonly used to treat type 1 diabetes and is also recommended for some people with type 2 diabetes.
A fall in blood glucose levels can also occur after taking too much oral hypoglycaemia medication, such as sulphonylurea, which causes a release of insulin. This medication is often used to lower blood glucose levels in people with type 2 diabetes.
Treating An Episode Of Hypoglycaemia
The immediate treatment for hypoglycaemia is to have some sugary food or drink to end the attack.
For example, this could be:
- a glass of fruit juice or non-diet soft drink
- between three and five dextrose tablets
- a handful of sweets
At first you should avoid fatty foods and drinks, such as chocolate and milk, because they don’t usually contain as much sugar and the sugar they do contain may be absorbed more slowly.
After having something sugary, you should have a longer-acting carbohydrate food, such as a few biscuits, a cereal bar, a piece of fruit or a sandwich.
It will usually take around 15 minutes to recover from a mild episode of hypoglycaemia. If you have a blood glucose meter, measure your blood sugar again after 15 to 20 minutes. If it’s still too low , you should have some more sugary food or a drink before testing your levels again in another 15 to 20 minutes.
When treating someone else with hypoglycaemia, if the above treatment isn’t effective, you may be able to help them by applying glucose gel to the inside of their cheeks, and gently massaging the outside of their cheeks.
It may take 10 to 15 minutes before they feel better. This shouldn’t be done if the person is drowsy or unconscious because of the risk of choking.
Don’t Miss: Treatment Of Type 1 Diabetes In Child
How Do You Treat Hypoglycemia
Its important to know that treatment of hypoglycemia depends on the severity of the low blood sugar reading. It also depends on if person having hypoglycemia is alert. If you can, seek help from a family member, friend, or a doctor for treating hypoglycemia.
If your meter shows that your blood sugar is low, its recommended that you eat or drink about 15g of fast acting sugars. Each of the following are recommended ways to treat a low blood sugar :
- Chew 4 glucose tablets
- Drink 4 ounces of fruit juice
- Drink 4 ounces of regular soda, not diet soda or
- Chew 4 pieces of hard candy
After taking one of these treatments, wait for 15 minutes, then check your blood sugar again. Repeat these steps until your blood sugar is 3.9 mmol/L70 mg/dL or above. After your blood sugar gets back up to 3.9 mmol/L70 mg/dL or more, eat a snack if your next meal is 1 hour or more away.
If you experience low blood sugars often, its a good idea to always check your blood sugar before driving. Treat and make sure it is in a safe range before getting behind the wheel.
Nighttime Low Blood Sugar
While low blood sugar can happen at any time during the day, some people may experience low blood sugar while they sleep. Reasons this may happen include:
- Having an active day.
- Being physically active close to bedtime.
- Taking too much insulin.
- Drinking alcohol at night.
Eating regular meals and not skipping them can help you avoid nighttime low blood sugar. Eating when you drink alcohol can also help. If you think youre at risk for low blood sugar overnight, have a snack before bed.
You may wake up when you have low blood sugar, but you shouldnt rely on that. A continuous glucose monitor can alert you with an alarm if your blood sugar gets low while youre sleeping.
You May Like: How To Treat Diabetes Without Insulin
How To Treat Someone Who’s Unconscious Or Very Sleepy
Follow these steps:
They may need to go to hospital if they’re being sick , or their blood sugar level drops again.
Tell your diabetes care team if you ever have a severe hypo that caused you to lose consciousness.
After You Have Low Blood Sugar
If your low blood sugar was mild , you can return to your normal activities once your blood sugar is back in its target range.
After you have low blood sugar, your early symptoms for low blood sugar are less noticeable for 48 to 72 hours. Be sure to check your blood sugar more often to keep it from getting too low again, especially before eating, physical activity, or driving a car.
If you used glucagon because of a severe low , immediately call your doctor for emergency medical treatment. If you have had lows several times close together , you should also tell you doctor. They may want to change your diabetes plan.
You May Like: What Is Stage 2 Diabetes
Do Not Inject Insulin
If a person with diabetes is having symptoms so severe that they cannot treat themselves, such as losing consciousness, others should not inject them with insulin, as this will lower their blood glucose further.
Additionally, they should not give them food or fluids, as the person may choke.
People taking diabetes medication should work with their healthcare team to develop a management plan to prevent hypoglycemia.
Additionally, the following strategies may help avoid low blood sugar:
- checking blood glucose levels
- eating regular meals or snacks
- engaging in physical activity safely
Regularly monitoring blood glucose levels may also lower a personâs risk of developing complications from hypoglycemia.
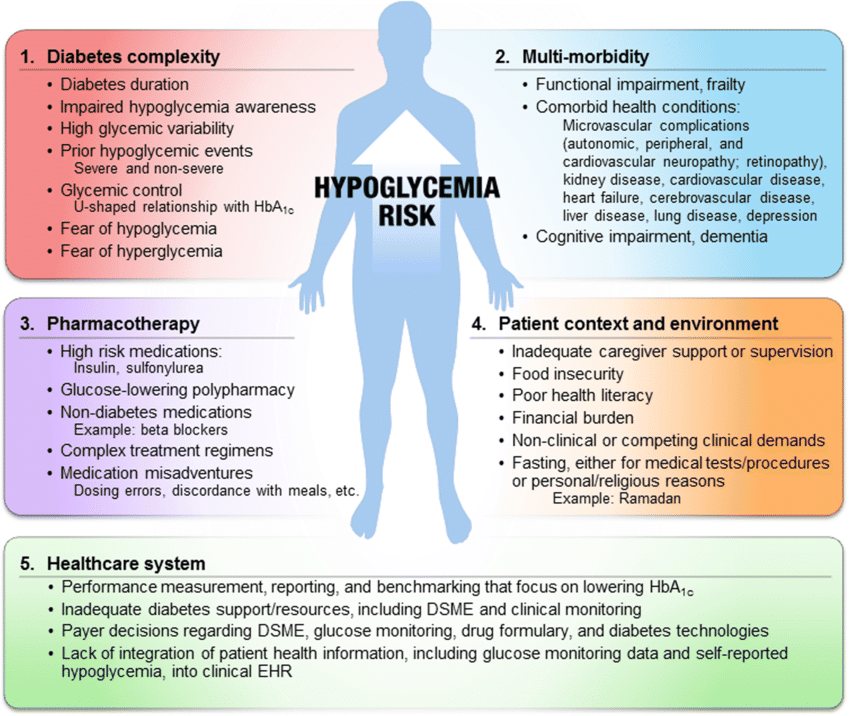
Factors Associated With Higher Risk Of Hypoglycemia In Nonpregnant Adults With T2dm Treated With Insulin
The following factors are associated with a higher risk of hypoglycemia:
-
Previous episode of severe hypoglycemia
-
Being elderly or frail
-
Long duration of diabetes
-
Autonomic neuropathy
-
Food insecurity or an erratic eating pattern
-
Low health literacy or minimal diabetes education and self-management skills
-
Insulin regimen does not mimic physiologic insulin action
-
Prandial insulin with doses not adjusted for physical activity, reduced carbohydrate intake, or skipping meals
-
Weight loss with no adjustment to glucose-lowering medications
-
Withdrawal of medications that raise blood glucose, such as corticosteroids
HbA1chemoglobin A1c, T2DMtype 2 diabetes mellitus. Data from Amiel et al and Yale et al.
Renal insufficiency. The kidneys are involved in the degradation and excretion of insulin. As glomerular filtration rate declines below 45 mL/min, there is reduced clearance of both endogenous and exogenous insulin and an increased risk of hypoglycemia., Clinically this becomes more important as eGFR approaches 30 mL/min, necessitating a reduction in the total daily dose of exogenous insulin and an adjustment of dose or injection times of individual insulins, or both, to minimize insulin stacking.
Some strategies to minimize the risk of hypoglycemia will be covered in our case discussion others include relaxing HbA1c targets, assessing insulin injection technique, and minimizing the use of oral medications associated with hypoglycemia . See CFPlus for more information.
You May Like: When Is Insulin Needed For Type 2 Diabetes
What Are The Symptoms Of Hypoglycemia
Symptoms of hypoglycemia can start quickly, with people experiencing them in different ways. The signs of hypoglycemia are unpleasant. But they provide good warnings that you should take action before blood sugar drops more. The signs include:
- Shaking or trembling.
- Tingling or numbness in the face or mouth.
During a severe hypoglycemic event, a person may:
- Be unable to eat or drink.
- Have a seizure or convulsions .
- Lose consciousness.
- Slip into a coma or die .
Talk With Your Doctor
In recent years, diabetes care has moved toward tighter control of blood glucose. Huge trials showed that complications happened less often to people who kept their blood sugars close to normal. Now, some insurers and hospitals tie physicians pay to the glucose control of their patients. Theres a lot of pressure for tight control, and lower blood sugar levels certainly have benefits.
When hypoglycemia is factored in, however, those advantages are less certain. Now, the American Diabetes Association recommends setting glucose control targets individually. Doctors and patients should decide together how tight control should be. People who are older or who have other illnesses along with diabetes might do better with less strict goals. With their doctors direction, they might shoot for an A1C of 8.0%, for example, instead of 6.5%.
What you do to lower glucose is as important as how low you go. As noted above, hypos are usually caused by insulin, sulfonylurea or meglitinide drugs. Most other medications dont cause them. Neither does eating a low-carb diet. Exercise can cause lows, but these can be easily prevented by checking sugars before, during and after a workout and treating with glucose if necessary. It might help to talk with a doctor, certified diabetes educator or support group about safer ways to lower glucose.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Get Type Ii Diabetes
When To Call 911
If someone you know falls unconscious due to a hypoglycemic event, act quickly if you are unable to provide emergency treatment yourself .
immediately if the person is unresponsive or their blood sugar stays persistently and extremely low and/or they have certain symptoms despite treatment:
- Confusion
- Irritability and changes in behavior
- Profuse sweating
- Loss of consciousness
- Seizures
As you await emergency services, the 911 staff can provide you step-by-step instructions for how to deliver a glucagon injection if an emergency kit is available.
Never try to give an unconscious person food or drink, since this can cause choking, vomiting, or asphyxiation.
In emergency situations, glucagon may be delivered intravenously to rapidly elevate blood sugar. Emergency medical personnel also commonly use intravenous dextrose, a form of sugar, until blood sugar levels are fully normalized. Once the individual is stabilized, oral glucose or sucrose is administered to help replenish glycogen stores.
Effect On Achieving Aggressive Glycemic Control
Patients with diabetes experience glucose dysregulation regardless of drug therapy. Patients with a baseline profound endogenous insulin deficiency are at greatest risk for hypoglycemia. Insulin-based therapies exert high potential maximal glucose reduction. Given the direct action of insulin to increase cellular uptake and utilization of glucose, drugs that directly increase insulin concentrations as their primary mechanism of action are associated with the highest rates of hypoglycemia.5
Several landmark clinical trials showed that hypoglycemia is the chief limitation to achieving intensive glycemic control and obtaining improved outcomes in the treatment of diabetes.6 To date, prospective clinical trials examining the benefits and safety of pinpointing lower glycemic targets using only drugs with a low hypoglycemia risk, such as metformin, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, and glucagon-like peptide-1 analoguessome of which have recently demonstrated improved cardiac outcomeshave not been completed.
Recommended Reading: Safest Sugar Substitute For Diabetics
What Causes Reactive Hypoglycemia
Reactive hypoglycemia comes from having too much insulin in your blood. It usually happens within a few hours after you eat. Other possible causes include:
- Having prediabetes or being more likely to have diabetes
Definition And Frequency Of Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia is defined by: 1) the development of autonomic or neuroglycopenic symptoms 2) a low plasma glucose level and 3) symptoms responding to the administration of carbohydrate . The severity of hypoglycemia is defined by clinical manifestations . Hypoglycemia is most frequent in people with type 1 diabetes, followed by people with type 2 diabetes managed by insulin, and people with type 2 diabetes managed by sulfonylureas.
| Table 2 |
|---|
| Mild: Autonomic symptoms are present. The individual is able to self-treat.Moderate: Autonomic and neuroglycopenic symptoms are present. The individual is able to self-treat.Severe: Individual requires assistance of another person. Unconsciousness may occur. PG is typically < 2.8mmol/L. |
You May Like: Type Of Exercise For Diabetes
Exercise Food And Alcohol
For people with type 1 diabetes, maintaining the correct blood glucose level involves balancing how much insulin you inject, the amount of food you eat, and how much energy you burn during exercise.
Hypoglycaemia may occur if you’ve taken your dose of insulin as usual, but your carbohydrate intake is lower than normal or has been used up more quickly. This may happen if you delay or miss a meal or snack, don’t eat enough carbohydrate, or exercise more than usual.
People with diabetes who’ve drunk too much alcohol, or drank alcohol on an empty stomach, can also get hypoglycaemia.
However, it’s not always possible to identify why a particular episode of hypoglycaemia has occurred, and sometimes it happens for no obvious reason.
How Can I Prevent Hypoglycemic Episodes
The key to preventing hypoglycemic events is managing diabetes:
- Follow your healthcare providers instructions about food and exercise.
- Track your blood sugar regularly, including before and after meals, before and after exercise and before bed.
- Take all your medications exactly as prescribed.
- When you do have a hypoglycemic event, write it down. Include details such as the time, what you ate recently, whether you exercised, the symptoms and your glucose level.
Recommended Reading: Patient Teaching On Diabetic Diet
Morbidity Of Hypoglycemia In Type 2 Diabetes And In The Elderly
Hypoglycemia may cause serious morbidity, provoking major vascular events such as stroke, myocardial infarction, acute cardiac failure, and ventricular arrhythmias . When the patient receives treatment, the precipitating role of hypoglycemia may not be recognized, particularly if medical attendants are unfamiliar with the age-related differences in the manifestations of hypoglycemia. In a 7-year review of 102 cases of hypoglycemic coma secondary to either insulin or glyburide , 92 patients had type 2 diabetes, 7 sustained physical injury, 5 died, 2 suffered myocardial ischemia, and 1 patient had a stroke as a consequence of severe hypoglycemia . The morbidity associated with hypoglycemia, such as impaired consciousness and convulsions, can be particularly debilitating in the elderly, who are at increased risk of injury and bone fractures because of general frailty and the presence of comorbidities, such as osteoporosis .
What Else Should I Do
- Always carry fast acting carbohydrates with you
- Wear identification that says you have diabetes
- Make a note of any hypos you have and discuss it with your doctor or Credentialled Diabetes Educator
- Make sure your family, friends, co-workers, school staff and carers know how to recognise and treat hypoglycaemia
- Look for the cause of your hypo so you can try to prevent it from occurring again
- Contact your doctor or Credentialled Diabetes Educator if you are having hypos often
- If youre taking medication called Acarbose carry pure glucose with you such as glucose tablets, glucose gel or Lucozade
- Eat carbohydrates if you are drinking alcohol
- Test your blood glucose level and ensure it is above 5mmol/L before driving a motor vehicle.
Don’t Miss: Is Insulin Used To Treat Type 2 Diabetes
Warning Signs Of Low Blood Sugar
Hypoglycemia can cause both short- and long-term complications. Know the signs so that you can treat the condition as soon as you’re aware of it.
As a person living with diabetes, you know how important it is to reduce blood sugar when it is too high, a phenomenon called hyperglycemia. But blood sugar that is too low, or hypoglycemia, is equally critical to avoid.
“Hypoglycemia happens when the amount of blood glucose drops to a level that’s too low to sustain normal functioning,” says Erin Palinski-Wade, RD, CDCES, who is based in Sparta, New Jersey. “In most people, this is defined as a blood sugar level at or below 70 milligrams per deciliter .”
Hypoglycemia is common among people with type 2 diabetes, according to a review published in June 2015 in the journal PLoS One. Individuals with the condition had an average of 19 mild or moderate episodes of hypoglycemia per year and nearly one severe episode per year on average, according to the researchers. Low blood sugar was particularly common among those taking insulin.
RELATED: What to Know Before You Use OTC Insulin
This decrease in blood sugar levels can cause both short-term complications, like confusion and dizziness, as well as more serious issues, including seizures, coma, and, rarely, death, according to the American Diabetes Association .
Hypoglycemia is usually the result of a too-high dose of insulin or a change in diet or exercise habits, according to Harvard Health Publishing.