Will Supplements And Vitamins Help My Diabetes
No clear proof exists that taking dietary supplements such as vitamins, minerals, herbs, or spices can help manage diabetes.1 You may need supplements if you cannot get enough vitamins and minerals from foods. Talk with your health care provider before you take any dietary supplement since some can cause side effects or affect how your medicines work.2
Assessing A Patient’s Knowledge Of Diabetes
A patient who has just been diagnosed with diabetes will be unlikely to know much, if anything, about the disease. Also, many diabetic patients do not have the information they need to self-manage diabetes26-28 and nurses and physicians may not have an adequate knowledge base about diabetes.29-31 Research has shown that lack of knowledge negatively affects a patients self-management of diabetes.32
Assessing a patient’s knowledge level of diabetes can be accomplished using written material, classroom work, etc. There are many ways to perform this assessment. A useful assessment tool that can be used is the Diabetes Knowledge Test . The DKT has been in use for many years and is valid and reliable. Several questions from the DKT are listed in Table 3.33
|
The best way to take care of your feet is to: |
|
If you are beginning to have a low blood glucose reaction, you should: |
|
Numbness and tingling in your feet may be symptoms of: |
Teaching Daily Diabetic Care Basics
Kathy Quan RN BSN PHN
Diabetes is a serious disease. In 2015, it was the 7th leading cause of death in the U.S. with over 79,000 deaths listed as the underlying cause of death and over 250,000 death certificates listed diabetes among the causes of death. According to the Diabetes Research Institute Foundation, Diabetes is increasing at an alarming rate in the U.S. and worldwide. In the U.S. alone there are over 30.3 million people who have been diagnosed with diabetes. It is estimated that an additional 7.2 million people have diabetes but have not yet been diagnosed.
Couple these numbers with the fact that the cost of insulin in the U.S. is exorbitant and in too many cases totally unaffordable by many of the most brittle insulin-dependent diabetics. Too many people are reducing their use or unable to purchase any insulin at all and trying to manage their disease without it. Both are completely unsafe practices. The cost of Diabetes has risen almost annually. In 2017, the overall cost was calculated by the Centers for Disease and Control to exceed $327 billion. This calculates to about $17,000 per person each year, and that cost continues to rise.
Nurses Need to Understand Diabetes
What Does Insulin Do?
Common-Sense Habits for Daily Diabetic Care
Learning the Glycemic Index
Avoid Alcohol and Tobacco
4 thoughts on Teaching Daily Diabetic Care Basics
Also Check: Can You Eat After Taking Insulin
Overcoming Barriers To Effective Teaching
Many barriers prevent healthcare professionals from teaching effectively, or even at all. The first barrier is the fear of inadequate knowledge about the disease. Some dont know all the facts about diabetes and feel embarrassed to admit it in front of a patient, so they just omit the teaching. You do not have to be a certified diabetes educator to teach patients about diabetes. Healthcare professionals who teach about diabetes include lay health workers, health aids, medical assistants, nurses, pharmacists, physical therapists, social workers, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and certified diabetes educators.
Clearly knowledge is needed before you can teach, however research confirms the adage that people care more about how much you care and not just how much you know . Creating relationships of trust, non-judgment, and emotional safety are foundational for effective teaching.
Barriers to teaching also include poor communication, lack of time, low priority in acute settings, low or no reimbursement for teaching, low resources, and low interest from the patient yet making sure the information is correct and correctly understood are critical to good patient outcomes. Overcoming these barriers has been the quest of the American Association of Diabetes Educators , and the organization is a wonderful resource for content, study guides, and even lesson plans for teaching .
Clinical Scenario
Educating The Diabetic Patient
Jul 30, 2016 | Career Advice, Clinical, Nursing Articles
When patients are diagnosed with diabetes, they often can feel scared, lost, and/or confused. So when part of your job as a nurse is to educate diabetic patients about the condition and the changes they need to make in their lives, its important to know how to handle it.
Not a Death Sentence
When patients panic, they cant take in any information. That can be a problem when trying to educate them.
Vashti Johnson, RN, at BrightStar Care in Cary, North Carolina says that when she needs to educate newly diagnosed diabetics, the first thing she stresses is that its not a death sentence. If managed properly, a diabetic patient can live a long and productive life, explains Johnson. They simply need to change some habits and to focus on a healthier lifestyle.
Its important to remember that being diagnosed with any disease can be very overwhelming and almost always leaves the patient with many questions and concerns, says Brittany Dudley, RN, director of nursing at the Health Care Center at Friendship Village in Tempe, Arizona. Newly diagnosed patients are often fearful of the facts of their disease and will withdraw from engaging with education. I always assess my patients to the best of my ability on their ability to learn and what technique of teaching best fits their needs prior to initiating any education.
Timing is Everything
Using Educational Tools
Recommended Reading: How To Lower High Blood Sugar Without Insulin
What Physical Activities Should I Do If I Have Diabetes
Most kinds of physical activity can help you take care of your diabetes. Certain activities may be unsafe for some people, such as those with low vision or nerve damage to their feet. Ask your health care team what physical activities are safe for you. Many people choose walking with friends or family members for their activity.
Doing different types of physical activity each week will give you the most health benefits. Mixing it up also helps reduce boredom and lower your chance of getting hurt. Try these options for physical activity.
Patient Centered Diabetes Education
Traditional patient education models focused on disease-oriented patient education and were physician centered. Newer models are known as health-oriented patient education and include empowerment strategies that place the patient rather than the physician at the center this strategy sees the patient as a partner in decision making. Based on adult learning theory, psychodynamic motivational theories, and the Chronic Care Model, diabetes educators now focus on strategies that help patients help themselves.
The goal of diabetes education is to help patients manage their own chronic disease with the resources of a team of healthcare professionals supporting them. The role of the diabetes educator has changed from sage on stage to guide on the side. Effective diabetes education begins with a paradigm shift to a role as health coach and often cheerleader instead of professional laying down orders for the patient to follow.
Each patient should have a partnership role in making medical decisions. That means patient education must be customized to meet the individuals needs and include the patients goals and desires. Instead of a diabetes educator simply writing a patients diet and exercise plan, an effective diabetes educator needs to assess the patients goals, abilities, barriers, interests, and resources and develop a goal plan together. Adherence improves because patients are working toward their own goals and not those dictated to them.
You May Like: Does Diabetes Weaken The Immune System
The Pathological Process Of Diabetes
Patients do not need in-depth knowledge of the pathological process of diabetes, but they should have the information that is essential for successful self-management of the disease. The following points should be covered the level of detail that is provided will be situationally dependent.
What is diabetes: Diabetes is a chronic disease that affects the body’s ability to control blood sugar level. If it is not properly treated, diabetes causes high blood sugar levels and chronic high blood sugar – hyperglycemia – can cause serious complications.
The causes of diabetes: Type 1 diabetes is caused by the destruction of the pancreatic cells that produce insulin. Type 2 diabetes is caused by insufficient insulin production and an inability to use the available insulin. Type 1 diabetes is essentially genetic and inherited. Type 2 diabetes is caused by susceptibility to the disease and lifestyle factors.
What is insulin: Insulin is a naturally produced hormone that is used to carry glucose from the blood to the cells and tissues. Without insulin, glucose cannot be used by the body, and it accumulates in the blood.
Glucose: Glucose, commonly called blood sugar, is one of the primary sources of energy for the body.
A cure for diabetes: Type 1 diabetes cannot be cured, and someone who has this disease must be on life-long insulin therapy. Type 2 diabetes can be controlled but not cured, and someone who has type 2 diabetes must be on a life-long program of diabetes self-management.
When Should I Eat If I Have Diabetes
Some people with diabetes need to eat at about the same time each day. Others can be more flexible with the timing of their meals. Depending on your diabetes medicines or type of insulin, you may need to eat the same amount of carbohydrates at the same time each day. If you take mealtime insulin, your eating schedule can be more flexible.
If you use certain diabetes medicines or insulin and you skip or delay a meal, your blood glucose level can drop too low. Ask your health care team when you should eat and whether you should eat before and after physical activity.
You May Like: Healthy Diet To Lose Weight For Diabetics
General Diabetes Patient Education Handouts
General Diabetes Patient Education Handouts General Diabetes Patient Education Handouts ACU is pleased to make available eight patient education flyers on living with diabetes newly translated into Haitian Creole . The flyers are written in simple, plain language for low literacy audiences. Clinicians can download and print them on demand. The flyers are also available in English and Spanish. More than one million people living in North America speak Haitian Creole. In the US, large Haitian communities are found in New York, Boston, Miami, New Orleans, parts of New Jersey, Chicago, Philadelphia, Detroit, Washington, DC and Atlanta. Since the earthquake in Haiti in 2010, immigration from Haiti to the United States has increased. In a study published in the journal Diabetes Care , the authors found that patients with diabetes of Haitian descent had worse glycemic control than African American or non-Hispanic white patients. They recommended interventions to improve diabetes control among Haitians. Numerous ACU members have also expressed interest in low-literacy diabetes materials in Haitian Creole. Checking the Sugar in Your Blood if You Have DiabetesContinue reading > >
Diabetes Education For Your Patients
Our library of learning materials offers practical tips and expert advice.
Topics include diabetes basics, eating healthy, staying active and more
Brochures feature patient-friendly language and full-color illustrations
Spanish-language versions of select materials are available
Ready to download, print and share with your patients
Order select brochures for complimentary delivery to your office
Looking for product information? Browse library.
Recommended Reading: Can You Lose Weight If You Have Diabetes
Meats Fish Eggs Beans Pulses Nuts And Other Proteins
High in protein for building and repairing processes in the body. A source of iron. One portion of meat or fish is about the size of your palm.
- Include this food group daily.
- Eat two portions of oily fish per week to promote heart health.
- Reduce intake of processed meat choose leaner cuts of meat and try to replace meat with beans, pulses and lentils on some days. This will reduce fat and boost fibre intake.
- Whether you’re vegetarian or not, try substituting tofu for meat in stir-fries and stews.
The Identified Learning Need

Patients with diabetes have very comprhensive learning needs. The learning needs are focused on managing their glucose levels and preventing complications of diabetes.
Learning needs for the patient with diabetes are complex and include: monitoring blood glucose levels, menu planning, exercise, medications, skin care, management of co-existing disease processes, knowledge of medications, knowledge of the disease process and how to manage hypo/pyperglycemia.
Many of these patients are unaware that diabete mellitus requires lifestyle changes, especially in the areas of nutrition and physical activity. The main goal of the teaching plan is to provide the patient with the knowledge to be able to make self-directed behavioral changes to improve their overall health and manage their diabetes .
Also Check: What’s The Treatment For Type 2 Diabetes
How Is Calcium Connected To Aging Diabetes Hypoglycemia And Falls
Calcium is the most abundant mineral in your body and makes up a lot of your bones and teeth. It keeps your bones and teeth strong and supports your bodys overall structure. Calcium is also used to help your muscles move, helps with blood circulation, and your nerves to transmit messages throughout your body. The other nutrient to know when thinking about calcium is vitamin D. Vitamin D is used to absorb calcium, so without it, it can lead to not getting sufficient amounts of calcium. Also, as we get older, our bodies arent as efficient in absorbing calcium.
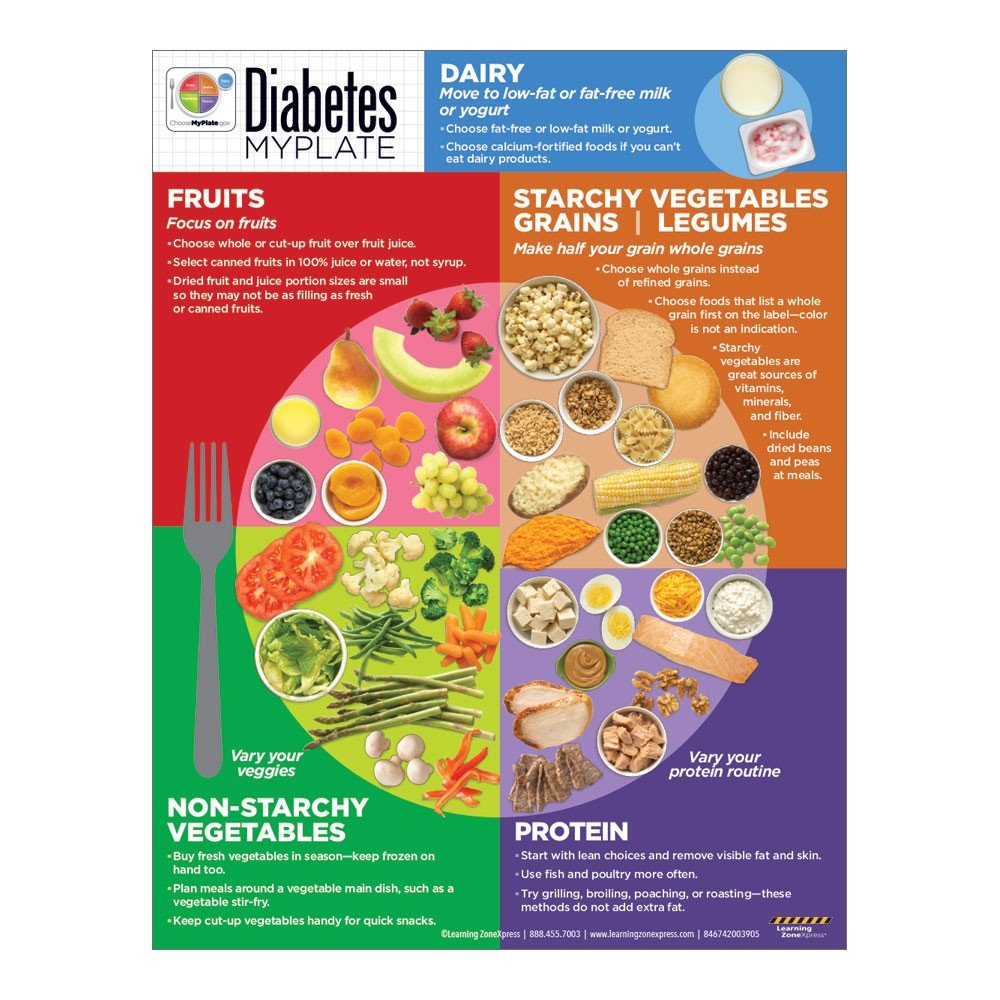
What Foods Can I Eat If I Have Diabetes
You may worry that having diabetes means going without foods you enjoy. The good news is that you can still eat your favorite foods, but you might need to eat smaller portions or enjoy them less often. Your health care team will help create a diabetes meal plan for you that meets your needs and likes.
The key to eating with diabetes is to eat a variety of healthy foods from all food groups, in the amounts your meal plan outlines.
The food groups are
- nonstarchy: includes broccoli, carrots, greens, peppers, and tomatoes
- starchy: includes potatoes, corn, and green peas
Use oils when cooking food instead of butter, cream, shortening, lard, or stick margarine.
Read Also: Herbal Medicine For Diabetes In The Philippines
How Does Type 2 Diabetes Affect Your Weight
The food you eat on a daily basis plays an important role in managing your diabetes, as well as ensuring you keep well and have enough energy for your daily activities. The same healthy-eating principles apply whether you have diabetes or not. In fact, getting the whole family to eat this sort of balanced diet if you have diabetes can benefit their health as well as yours.
Rich in fibre, vitamins and minerals. Low in calories and fat.
- Aim to eat at least five portions of fruit and vegetables per day.
- Potatoes are very high in carbohydrates, so don’t ‘count’ as a vegetable in terms of your five a day.
- Try to ‘eat a rainbow’ – combine several different vegetables or fruits of different colours to get the maximum vitamins and minerals.
- These can be fresh, frozen, canned or dried .
- Remember that on the whole, vegetables have less impact on your blood sugar than fruits.
- Limit your intake of fruit juice or smoothies to 150 ml per day, as these drinks have their fibre and carbohydrates already broken down. This means they can cause your blood sugar to rise more quickly. They are also very easy to drink so you can end up having too much, which means extra calories, carbohydrate and sugar!
- Try to avoid the more sugary tropical fruits like bananas, oranges or pineapples . Instead, eat lower glycaemic index fruits like blueberries, strawberries or raspberries.
- Instead of eating a banana, snack on an apple, which has less impact on your blood glucose.
Why Is Dsmes Important
- People who have the knowledge and support to manage their diabetes are healthier than those who do not.
- Learning how to control your diabetes will save money and time, and help you have fewer emergency and hospital visits.
- Knowing how and when to take your medication, how to monitor your blood sugar , and how to take care of yourself, helps you manage your diabetes better.
- Managing your diabetes will help you avoid or delay serious health complications.
- The skills you learn will help you take better care of yourself. Diabetes management starts with you.
Its important to go for DSMES services when you first find out you have diabetes so you can learn how to take care of yourself. However, there are three other times DSMES can help you. Read about them in the table below.
Don’t Miss: Is 6.2 A1c Diabetes
Assessing And Encouraging Compliance
Barriers to compliance should be identified, and the patient’s active participation should be used to address these barriers using specific treatments. The goals should be clear and behavior-oriented, and a follow-up schedule should be made. There is a considerable amount of information and activity that is required of diabetic patients for them to effectively self-manage the disease. The lifelong need to self-manage diabetes compounds this challenge, and patients may develop a syndrome called diabetic distress.23 Diabetic distress refers to significant negative psychological reactions related to emotional burdens and worries specific to an individual’s experience in having to manage a severe, complicated, and demanding chronic disease such as diabetes.23″ Diabetic distress is a common problem, and it can harm many aspects of self-management, e.g., adherence to the medication regimen, higher A1C levels, and poor diet and exercise habits.23 All healthcare professionals that care for diabetic patients should be aware of this syndrome, and periodic evaluation for its presence is recommended.23