Other Side Effects Of Insulin
Other adverse effects of insulin therapy include:
- Hypoglycemia: The most serious side effect is low blood sugar, and it occurs relatively often, especially in older people and those on intensive insulin regimens. Recurring mild episodes have negative effects on the brain and cardiovascular system. Severe cases can cause falls, seizures, loss of consciousness, and even death. The CDC reports that hypoglycemia is one of the most common adverse drug reactions seen in emergency rooms in people over age 65.
- Heart disease: Several studies have linked insulin use in type 2 diabetes with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease and death. Both insulin-related obesity and recurrent episodes of hypoglycemia are associated with a greater likelihood of hypertension, lipid abnormalities, atherosclerosis, arrhythmias, and other cardiovascular conditions.
- Cancer: Research suggests that people with type 2 diabetes have an above-average risk of several types of cancer. Insulin resistance results in high levels of insulin, and among its other functions, insulin stimulates cell growth. Obesity, another problem for most people with type 2 diabetes, also increases cancer risk. The jury is still out, but insulin injections may well add fuel to the fire.
Effects Of High Performance Inulin Supplementation On Glycemic Control And Antioxidant Status In Women With Type 2 Diabetes
1Department of Biochemistry and Diet Therapy, Nutrition Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran.
2Student Research Center, Faculty of Health and Nutrition, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran.
3Endocrine and Metabolism Section, Imam Reza Teaching Hospital, Faculty of Medicine, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran.
4Department of Statistic and Epidemiology, Faculty of Health and Nutrition, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran.
Corresponding author: Parvin Dehghan. Student Research Center, Faculty of Health and Nutrition, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Attar Nishaboori St., Golghasht St., Tabriz 51664, Iran.
Maintains Balanced Blood Sugar
People with type 2 diabetes need to get a handle on blood sugar, which can get too high after eating. Unlike other sugars, inulin doesnt raise your blood sugar. Thats because its not broken down in the stomach or small intestine. Instead, it moves right through to your colon. Research found that people with and without diabetes who ate inulin had less rise in their blood sugar. The change was likely due to the way inulin slows the absorption of carbohydrates.
Read Also: Type 2 Diabetes Support Groups Online
Myths About Insulin And Type 2 Diabetes
When you hear the word insulin, do you picture giant needles or pop culture portrayals of insulin users with low blood sugar ?Either way, most people think of insulin as a difficult, painful, or potentially scary medical treatment.The problem is that if you have type 2 diabetes, you need to know the real deal before you can make an informed choice about whether or not this potentially lifesaving therapy is right for you.Here, we take a look at the facts and fiction about insulin when it comes to treating type 2 diabetes.
Insulin: A Wonder Drug For Type 1 Diabetes
Insulin truly is a wonder drug for type 1 diabetes. Before its discovery, people with this conditionmost of them childrenrarely lived a year or two beyond diagnosis. That changed in 1922, when Canadian physicians Frederick Banting and Charles Best, who had been experimenting with diabetic dogs, were asked to treat a 12-year-old boy in the terminal stages of the disease.
After trying injections of several extracts of beef pancreas, Drs. Banting and Best hit upon one that worked. The boys blood sugar fell from 520 to 120 mg/dL, and he rapidly improved, living another 15 years until he died of pneumonia at age 27. The Nobel Prize in Medicine was awarded for this discovery, which has allowed millions of patients with type 1 diabetes to live long lives.
What about type 2? Insulin injections for type 2 diabetes are generally initiated when oral diabetes drugs fail to achieve target blood sugar levels. Some doctors advocate earlier introduction or intensive insulin therapy, which requires very close monitoring and shots several times a day, on the premise that this helps stave off diabetic complications.
I agree that insulin is an indispensable therapy when patients develop severe insulin deficiency. Yet, I know from my decades as a practicing physician treating tens of thousands of patients with type 2 diabetes, that insulin is often used prematurely, inappropriately, and in excessive dosesand when it is, it can cause tremendous harm.
Also Check: Diabetes And Lower Back Pain
How Does Inulin Work
Inulin promotes the abundance of good bacteria that keep your gut healthy and happy like Bifidobacteria, probiotic microbes that help maintain balance in the microbiome and deter invaders.
This is also true of butyrate-producing bacteria butyrate is a special short-chain fatty acid that fuels gut cells, maintains the gut lining, and combats inflammation.
Inulin is also a type of soluble fibre, which is important for general digestive health. Soluble fiber absorbs water in the gut to form a gel-like substance, which softens stool, reduces hunger, improves motility, and relieves constipation.
Higher Baseline Fasting C
In the PRIBA cohort mean HbA1c response was reduced by 1.67 mmol/mol for every 1 SD higher baseline fasting C-peptide . We observed the same direction and similar size of effect for UCPCR . Higher baseline HOMA measured insulin resistance was also associated with reduced response , but there was no evidence of an association between beta-cell function and response . Islet autoantibody prevalence was low .
DPP4 inhibitors – associations between markers of insulin resistance and HbA1c response at 6 months.
Circles denote the mean HbA1c change at 6 months per 1 standard deviation higher baseline value of each marker. Error bars denote 95% confidence intervals.
Recommended Reading: Can You Lose Weight If You Have Diabetes
Data Synthesis And Subgroup Analysis
The statistical analysis was performed using the software Review Manager 5.3. The participants were classified into four subgroups as follows: normal healthy, dyslipidemia, overweight or obesity, or T2DM. The impact of ITF in all outcomes was expressed via a mean difference , with 95% confidence interval as the continuous variable. Some articles reported outcomes in mg/dL, which required conversion to mmol/L prior to the meta-analysis to retain consistency. The methods applied for standard unit conversions are provided in the .
Allowing for heterogeneity between the studies, the data were pooled using a random-effects model to provide a more conservative estimate of the effect of ITF.
Heterogeneity between the studies was assessed using I2 statistics with a cutoff of 50% and the 2-test with a P value < 0.10 to define a significant degree of heterogeneity. Review Manager 5.3 generated forest plots of the pooled MDs for all outcomes with 95% CIs, as well as funnel plots. The potential publication bias was assessed through visual inspection of the evidence of asymmetry if there were sufficient eligible studies included in the meta-analysis and further assessed using the Beggs and Eggers tests, which were consistent with recent recommendations.
May Help Prevent Colon Cancer
Some researchers think that inulin could help protect the cells in the colon. This is because of how inulin ferments into butyrate. For this reason, several studies have looked into its effects on colon health .
One review looked at 12 animal studies and found that 88% of the groups that received inulin saw a reduction in precancerous colon growths .
In another study, inulin-fed rats showed fewer precancerous cell changes and less inflammation than the control group .
An older study on humans found that inulin caused the colon environment to be less favorable for cancer development, which is promising (
Researchers have studied the different forms of inulin extensively, and it appears to be safe for most people in small doses.
However, people who are intolerant to FODMAPs are likely to experience significant side effects.
Those who are allergic to ragweed may also experience worsened symptoms after taking chicory inulin. Additionally and very rarely people with a food allergy to inulin may experience anaphylaxis, which can be life-threatening.
When adding inulin to the diet, start with small amounts. Larger amounts are more likely to trigger side effects. Increasing intake slowly over time will help the body to adjust.
The most common side effects are:
Read Also: Free Insulin For Type 1 Diabetes
Effect Of Konjac Inulin Extracts And Ki Composition On A Blood Glucose Level Of Stz
A blood glucose level was monitored over 4 weeks after starting treatments of konjac, inulin, or KI composition at low, medium, and high doses in STZ-induced rats or their sham controls. All KI compositions showed significant reduction in the blood glucose level than the STZ group during 4-week treatment however, no difference was seen between the STZ group and the konjac or inulin group ), indicated that konjac and inulin extracts, when combined, were more efficient in decreasing the blood glucose level than a single component alone. The blood glucose level was reduced mostly in the KI-M group, showed by % of AUC increased over sham ). When changes of the blood glucose level from baseline were compared at each week, the KI-treated groups had reduction from baseline for all 4 weeks, while the konjac, inulin, and STZ groups had increased over baseline for all 4 weeks ).
Insulin Is A Treatment Of Last Resort
Although some people exhaust all possible diabetes treatments before resorting to insulin, this may not be the best strategy. By the time a person with type 2 starts insulin therapy, they likely already have diabetes-related complication because of poor blood sugar control, Dr. Crandall says. Because high blood sugar is so toxic and can up the risk of heart attack, stroke, and other problems, you shouldnt waste too much time undergoing treatments that arent getting your blood sugar under control.In fact, starting insulin sooner may avoid complications, cause oral medications to work better , or allow you to use a less-complicated insulin regimen for a longer period of time.
Also Check: Is Blindness From Diabetes Reversible
How Much Inulin To Aim For
In prehistoric times – when we were eating far more vegetables and gnawing at roots – it’s estimated that our ancestors consumed about 135 grams of inulin a day. I wouldn’t recommend aiming for those levels, given what our digestive levels are now accustomed. But we can realistically reach much lower levels that promote health benefits.
Based on research, aim for 5 grams of inulin a day to boost the growth of the probiotic Bifidobacteria in your gut. For better calcium absorption, you want to get 8 grams or more. Getting 12 grams of inulin and FOS a day has been shown to help promote regular bowel movements.
Any time you increase your fiber intake, do so gradually to give your body a chance to adjust. Be sure to drink plenty of water to help prevent constipation.
Randal Buddington, professor at the University of Tennessee Health Sciences Center, likens increasing your inulin intake to exercising more. “If a couch potato starts exercising with a very intense workout, the pain and agony may very well keep them from continuing. If they start slow, and gradually build up, the benefits will increase and the person will continue.”
The amount of inulin that’s tolerated seems to vary from person to person. Research suggests that long-chain inulin is better tolerated than FOS. Most healthy people do well with up to 10 grams of inulin and 5 grams of FOS a day.
Body Weight And Food Intake Assessment
A research assistant measured the anthropometric indices, including body weight and height, at the beginning and at the end of the trial. Weight was measured to the nearest 0.1 kg, and the height was measured, to the nearest 0.1 cm. BMI was calculated as weight in kilograms divided by the square of the height in meters. Nutrient intake data was also collected at the beginning and at the end of the trial period. Diet evaluations were performed with the use of 3-day diet record at the baseline and at the end of the study. All of the subjects attended a training meeting prior to the start of the intervention where they were instructed on how to properly use the food scale and record their food intake. Subjects were instructed to report all of the food they had consumed for 2-week days and 1-weekend day at the beginning and at the end of the study. Dietary data were analyzed using the Nutritionist 4 software .
Recommended Reading: Healthy Diet For Diabetes And High Cholesterol
Effect Of Konjac Inulin Extracts And Ki Composition On Oral Glucose Tolerance In Stz
A glucose tolerance study was performed in sham and STZ-induced rats after 24-day treatments of vehicle , konjac, inulin, or KI composition at high dose . The blood glucose levels were monitored before and at 30, 60, and 120min after oral administration of 500mg/kg D-glucose . The baseline blood glucose levels of all STZ-induced diabetic rats were significantly higher than the sham rats, and the KI-high-dose-treated group but not the konjac or inulin group had a lower blood glucose level than the STZ group ). At 120min after oral 500mg/kg D-glucose challenge, the KI-high-dose-treated group had a significant lower blood glucose level than the STZ group and all groups with STZ-induced rats had a decreased blood glucose level compared with 30min after oral D-glucose administration ). However, no significant difference in AUC was found between the groups. When changes of the blood glucose level from baseline were compared at 120min, the KI-high-dose-treated group had significant higher reduction from baseline than the STZ group ).
Keeps Your Weight Under Control
Inulin has a twin among sugar molecules called oligofructose, which does similar things in your body. Researchers have tested both kinds of sugars to see how they affect weight. Both inulin and oligofructose seem to help people eat less and lose weight. It may be that these sugars fill you up faster, or it may be that they change your digestive bacteria to help you lose weight. Yet another theory is that inulin changes the hunger hormones your body produces so you dont feel as hungry.
However it works to balance your blood sugar, cholesterol, and weight, inulin is a good addition to your diabetes diet.
While a common source of inulin is chicory root, long used as a coffee substitute, youll also find it in leeks, onions, garlic, bananas, asparagus, wheat, and Jerusalem artichokes.
Want more inulin than you get from eating onions and other veggies? You can buy it in the form of powders or supplements. Fibersure and other brands make clear-mixing inulin that can be added to foods and baked recipes supposedly leaving no taste or grittiness. And many food manufacturers add inulin to granola bars, breakfast bars, yogurt, and other foods to improve the taste and texture without adding calories. You may also notice the package mentions the food contains prebiotic, or nutrition to feed helpful bacteria in your gut. Look for inulin on the label of some Yoplait and Stonyfield Farm yogurts, Luna and PowerBar nutrition bars, and other foods.
Read Also: Type 1 Diabetes Symptoms In Adults
Inulin And Diabetes Mellitus
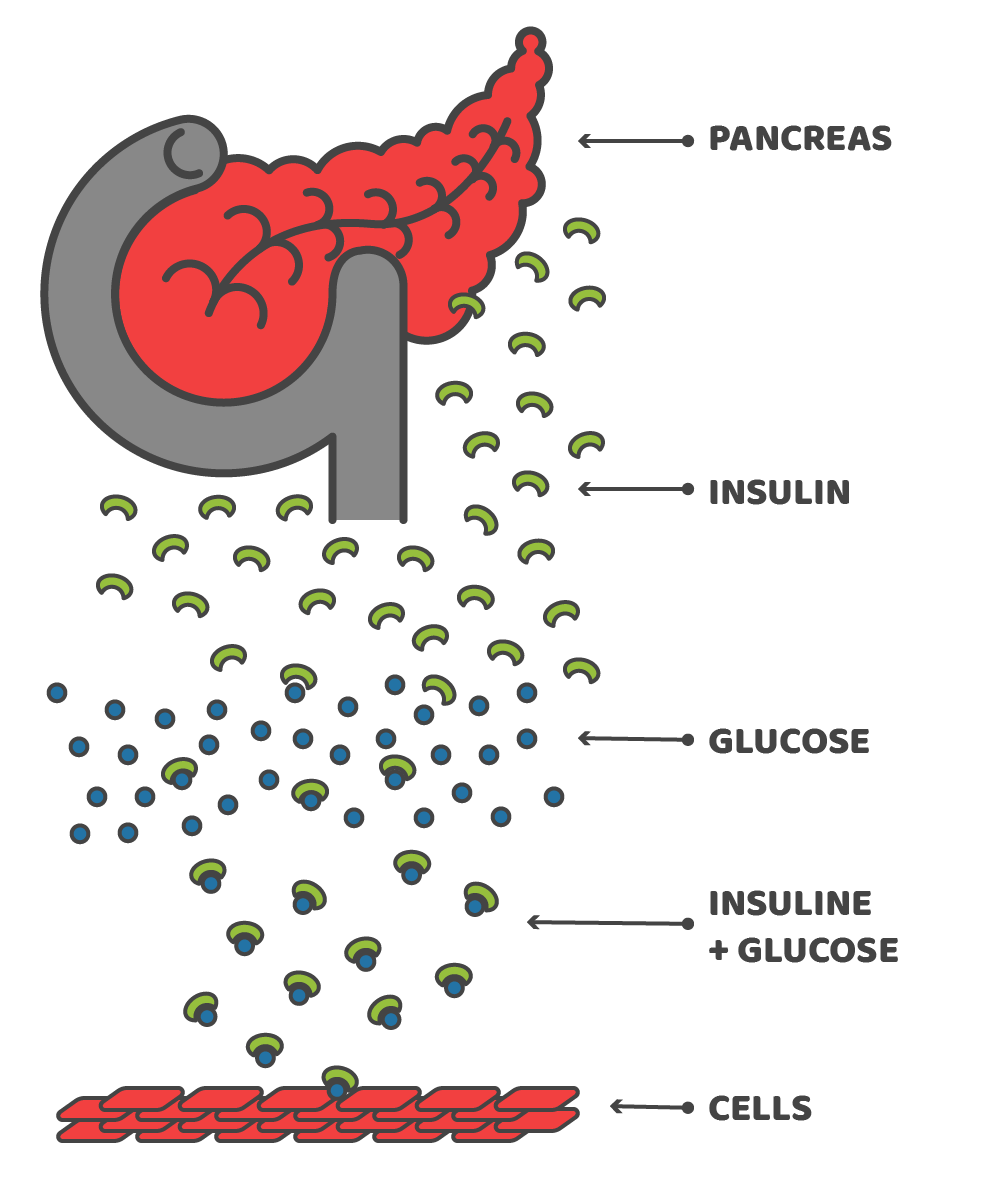
Diabetes mellitus is a disease in which blood sugar is not properly taken up into cells. Thus, the level of glucose in the blood remains high. The uptake of glucose into the body’s cells is controlled by the hormone insulin, which is produced by the pancreas. Type 1 diabetes is due to the pancreas failing to produce sufficient insulin. It is often caused by genetic factors. Non-insulin-dependent diabetes, or type 2 diabetes, occurs when the body’s cells are unable to respond very efficiently to the insulin produced. It is associated with obesity, overnutrition, excess dietary fat and sugar, and other factors. Type 2 diabetes accounts for around 90% of all diabetes. Both types of diabetes are treated by the injection of insulin, which acts to reduce the blood glucose concentration by facilitating the uptake of glucose by the cells in type 1 diabetes, and by supplementing the body’s insulin in type 2 diabetes.
Over 18 million adults in the U.S. have diabetes , and over 170 million people worldwide have the condition, while its incidence is rising dramatically. The World Health Organization estimates that there may be 300 million people with diabetes by 2025 . There is a pressing need to develop a range of approaches to tackle type 2 diabetes and also address the root causes of its increased incidence, such as obesity and poor diet. Improvements in diet are therefore an important strategy in combating type 2 diabetes.
Anthropometric And Dietary Intake Assessment
Anthropometric indices including body weight and height were measured at baseline and at the end of the trial. Dietary intakes were evaluated using a 3-day food dairy at baseline and at the end of the trial. Before the intervention, all patients were provided instructions how to use food scale and record their food intake. After recording day, each patient received a phone call for renewed recording food intake by trained person. Dietary intakes were analyzed using the nutritionist 4 software containing the database from tables of content and nutritional value of Iranian food products.
Recommended Reading: How Can Type 2 Diabetes Be Treated
Insulin Will Make You Gain Weight
Theres some truth to this one. Some people with type 2 diabetes may gain weight after starting insulin therapy. However, the insulin therapy itself does not induce weight gain. Its because if a diabetes treatment is working, the body begins to process blood glucose more normally, and the result can be weight gain. The good news is that this tends to level out as insulin therapy continues, and the weight gain may be transient, explains Dr. Crandall.
Weight And Appetite Control
Fiber is the zero-calorie indigestible part of a carbohydrate that helps to keep us full by slowing down the rate at which food empties into our stomach. Inulin, a type of fiber, may also help to control appetite by increasing feelings of fullness.
It is thought that this occurs due to short-chain fatty acids and their ability to increase appetite suppressing hormones such as glucagon-like peptide 1 .
Research has shown that supplementing with inulin may help to reduce appetite and overall calorie intake in children with overweight and obesity.
A randomized control trial published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that supplementation with 8 grams oligofructose-enriched inulin reduced appetite and overall calorie intake in children with overweight and obesity.
In another systematic review conducted on randomized control trials featuring adolescents and adults, the verdict was mixed. Some studies found that supplementation with inulin helped to reduce body weight, while others did not.
It appears that inulin supplementation may be a good way to help increase feelings of fullness, which inherently may influence weight loss.
Read Also: How To Care For Someone With Diabetes