Can You Be Misdiagnosed With Type 2 Diabetes
Its possible for someone with type 2 diabetes to be misdiagnosed. They may have many of the symptoms of type 2 diabetes, but actually have another condition that may be more closely related to type 1 diabetes. This condition is called latent autoimmune diabetes in adults .
Researchers estimate that between 4 and 14 percent of people diagnosed with type 2 diabetes might actually have LADA. Many physicians are still unfamiliar with the condition and will assume a person has type 2 diabetes because of their age and symptoms.
In general, a misdiagnosis is possible because:
- both LADA and type 2 diabetes typically develop in adults
- the initial symptoms of LADA such as excessive thirst, blurred vision, and high blood sugar mimic those of type 2 diabetes
- doctors dont typically run tests for LADA when diagnosing diabetes
- initially, the pancreas in people with LADA still produces some insulin
- diet, exercise, and oral drugs usually used to treat type 2 diabetes work well in people with LADA at first
As of now, theres still a lot of uncertainty over how exactly to define LADA and what causes it to develop. The exact cause of LADA is unknown, but researchers have identified certain genes that may play a role.
LADA may only be suspected after your doctor realizes that youre not responding well to oral type 2 diabetes medications, diet, and exercise.
How Should A Person With Diabetes Eat
Paying close attention to your diet and exercise habits in life with type 1 and type 2 diabetes is a tremendous part of living well with diabetes.
While there is a great deal of confusion and controversy over whether people with diabetes should eat low-carb diets, low-fat diets, plant-based diets, or ketogenic diets, the one thing everyone can agree on is: mostly whole foods that you prepared yourself.
A diet full of processed crackers, cookies, breads, candy, soda, chips and other processed junk isnt good for anyone, especially for people with diabetes.
Focus on increasing the amount of whole, real food in your diet, learning to cook more meals for yourself, and reducing your consumption of processed food with long lists of ingredients that are not real food.
What Is Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus, also called diabetes, is a term for several conditions involving how your body turns food into energy.
When you eat a carbohydrate, your body turns it into a sugar called glucose and sends that to your bloodstream. Your pancreas releases insulin, a hormone that helps move glucose from your blood into your cells, which use it for energy.
When you have diabetes and donât get treatment, your body doesnât use insulin like it should. Too much glucose stays in your blood, a condition usually called high blood sugar. This can cause health problems that may be serious or even life-threatening.
Thereâs no cure for diabetes. But with treatment and lifestyle changes, you can live a long, healthy life.
Diabetes comes in different forms, depending on the cause.
Also Check: What Is The Bad Diabetes
Why Is Type 1 Worse Than Type 2 In Covid
Generally a Type 1 sufferer is likely to have had Diabetes for much longer than a person with Type 2. The longer youve had Diabetes, the more likely you would be prone to complications, including damage to the heart and kidneys.
With Type 1, the cells that make insulin are being destroyed by the immune system. This is different from Type 2, which is not a disease of the immune system. And compromised immune systems are already known to be at great risk from Covid-19.
Blood sugar levels are, on average, higher in people with Type 1 than with Type 2 Diabetes.
People with Diabetes who contract COVID-19 are clearly at a greater risk of worse outcomes, including death. In light of the vast numbers of Diabetes sufferers worldwide, they represent a worryingly large and vulnerable proportion of the COVID-19 population.
For people with Diabetes, poorer prognosis is the consequence of hyperglycaemia and comorbidities in particular, hypertension, obesity, and cardiovascular disease.
What Is The Difference Between Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
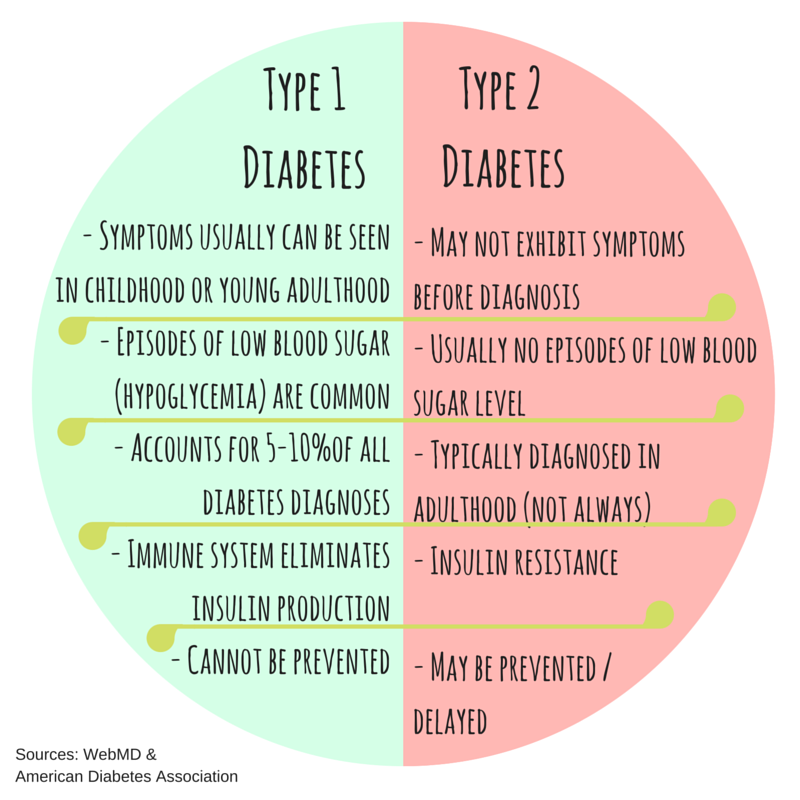
Glucose is a type of sugar. It comes from food and also is created in the liver. Glucose travels through the body in the blood. It moves from the blood to cells with the help of a hormone called insulin. Once glucose is in those cells, it can be used for energy. Diabetes mellitus is a condition that causes a buildup of glucose in the blood and makes it difficult for the bodys cells to get enough energy. There are two primary kinds of diabetes mellitus, type 1 and type 2.
In short, both types result in high levels of blood glucose. Type 1 is an autoimmune disease, caused by genetic and environmental factors, that results in too little insulin being produced by the body. Type 2 is influenced by lifestyle choices and results in the body not being able to use its insulin efficiently. According the Centers for Disease Control , Type 2 diabetes accounts for about 90% to 95% of all diagnosed cases of diabetes, and type 1 diabetes accounts for about 5%.
Read Also: Is Coffee Healthy For Diabetics
Overview Of Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
Type 1An autoimmune disease occurs when there is an abnormal immune response to a normal part of the body. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder caused by destruction of the cells that secrete insulin from the pancreas. This results in too little insulin being produced to support the bodys needs. Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in children and young adults, and was previously known as juvenile diabetes.
Without insulin, glucose from the carbohydrate foods you eat cannot enter cells. This causes glucose to build up in the blood, leaving your bodys cells and tissues starved for energy. While a variety of tissue transplantation and genetically-based treatments are being studied, at this point the only widely-available treatments for type 1 diabetes are the injection of insulin and inhaled insulin.
Image text:
Type 2Type 2 is the most common form of diabetes and can be caused by a combination of factors. One factor is that your body begins to make less insulin. A second is that your body becomes resistant to insulin. This means there is insulin in your body, but your body cannot use it effectively. Insulin resistance is often related to excess body fat. Medication, lifestyle changes, and monitoring can help control blood glucose levels in those with type 2 diabetes.
What Are The Symptoms Of Diabetes
TYPE 1 & TYPE 2: Most symptoms are the same between the two primary types of diabetes.
-
extreme thirst
-
numbness and tingling in the toes, feet, or fingers
-
difficulty with wounds healing or becoming easily infected
TYPE 1: The symptoms of type 1 diabetes usually come on very quickly compared to type 2. In children, the symptoms can become very severe over just a couple of weeks. In adults, the onset can be a bit more gradual, increasing in severity over the course of a few months.
Undiagnosed patients with type 1 diabetes can develop DKA . This condition occurs when blood sugar levels are extremely high and insulin production is at zero or extremely low. The symptoms of DKA are all of the symptoms listed above as well as vomiting and loss of consciousness. It can result in death if left untreated.
If you have diagnosed type 1 diabetes and are vomiting and unable to even keep water down, you need to visit an emergency room immediately.
TYPE 2: The symptoms of type 2 diabetes are generally very gradual, even over the course of years as the body struggles more and more to produce or properly use its own insulin.
Patients with type 2 diabetes cannot develop DKA because there is always insulin present. While they absolutely develop ketones, the severity of those ketones never reaches a level of DKA.
Don’t Miss: What Diabetic Testing Supplies Are Covered By Medicare
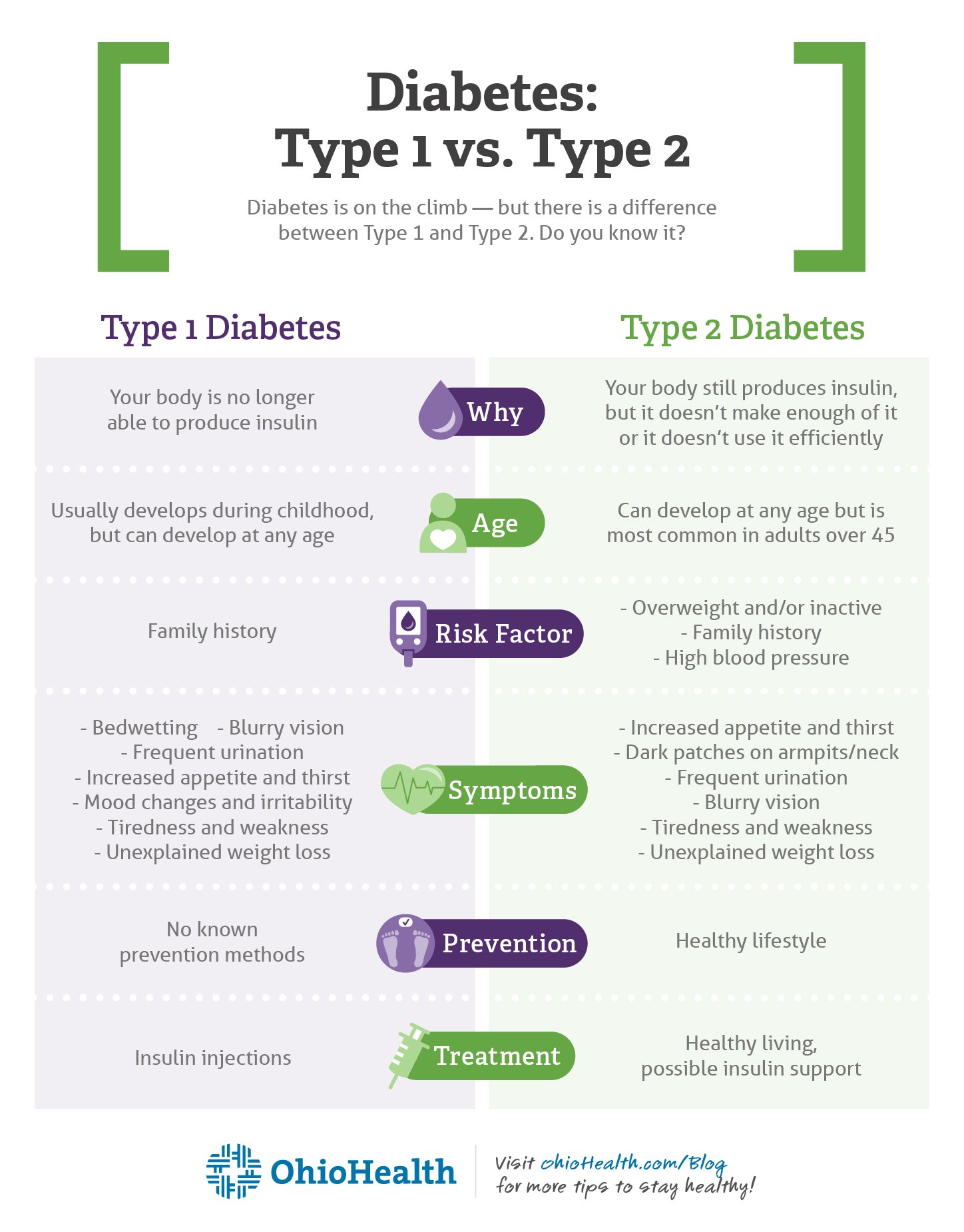
Type 1 Vs Type 2 Diabetes: Differences And Similarities
by Health Writer & Patient Advocate
Regardless of which type of diabetes you have, it can be difficult to understand what is happening to your body. Despite having very similar symptoms and medical risks, the two primary types of diabetes are actually very different when you look closely at whats going on inside the body. Learn more about the main differences and similarities between type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Are The Same Tests Used To Diagnose Both Types
A fasting blood sugar measurement can be used to diagnose any type of diabetes. This test measures the level of sugar in the bloodstream in the morning before eating breakfast. Normal fasting plasma glucose levels are less than 100 milligrams per deciliter . Fasting plasma glucose levels of more than 126 mg/dl on two or more tests on different days indicate diabetes. A random blood glucose test can also be used to diagnose diabetes. A blood glucose level of 200 mg/dl or higher indicates diabetes.
Another test that is often used is a blood test to measure levels of glycated hemoglobin . This test provides a measure of the average levels of blood glucose over the past 3 months. Other names for the A1C test are HbA1C and glycosylated hemoglobin test.
Tests to identify the abnormal antibodies produced by the immune system are used to diagnose type 1 diabetes. Some of the antibodies seen in type 1 diabetes include anti-islet cell antibodies, anti-insulin antibodies and anti-glutamic decarboxylase antibodies.
Type 1 treatment: Insulin is the treatment of choice for type 1 diabetes, because the body responds appropriately to insulin and the problem is a lack of insulin production by the pancreas.
You May Like: Urine Test For Diabetes Type 2
Mody Maturity Onset Diabetes Of The Young
MODY is a rare form of diabetes that is caused by a change in a single gene. This makes MODY a type of monogenic diabetes.
Because half of our genes come from each parent, there is a 1 in 2 chance of inheriting MODY from an affected parent, and it runs strongly in families. However, sometimes the genetic change can develop on its own, without being inherited from a parent.
The most common genes that cause MODY are HNF1A, HNF4A, HNF1B and glucokinase, and the condition behaves differently depending on which gene is affected.
A genetic test can be used to confirm MODY and work out which gene is affected. It is important to know which gene is causing MODY, as treatment varies accordingly. Some forms of MODY may require insulin injections, while others are treated using drugs to boost insulin production in the pancreas. One form of MODY requires no treatment at all.
MODY is typically diagnosed under the age of 25, often with a family history of diabetes.
What Should You Eat
If you have diabetes, you should focus on eating lean protein, high-fiber, less processed carbs, fruits, and vegetables, low-fat dairy, and healthy vegetable-based fats such as avocado, nuts, canola oil, or olive oil. You should also manage your carbohydrate intake. Have your doctor or dietitian provide you with a target carb number for meals and snacks. Generally, women should aim for about 45 grams of carb per meal while men should aim for 60. Ideally, these would come from complex carbs, fruits, and vegetables.
The American Diabetes Association offers a comprehensive list of the best foods for those with diabetes. Their recommendations include:
| Protein |
Don’t Miss: Does Diabetes Affect Your Feet
Type 1 Diabetes Arises From Insufficient Insulin Type 2 Due To Insulin Resistance
Another key difference. And it is that while type 1 diabetes is due to insufficient insulin due to the attack of the immune system on the cells of the pancreas that produce this hormone, type 2 diabetes does not It is due to insufficient insulin, but rather to the development of resistance to it.
After many years of excesses with sugar and, in general, a lifestyle that encompasses the risk factors for its onset , the body has had to produce so much insulin that the cells they have ended up becoming resistant to its effect. So that, It is not that we do not produce insulin, but that it no longer arouses the reactions it should arouse.
How Is Type 2 Diabetes Managed
Theres no cure for Type 2 diabetes. But you can manage the condition by maintaining a healthy lifestyle and taking medication if needed. Work with your healthcare provider to manage your:
- Blood sugar: A blood glucose meter or continuous glucose monitoring can help you meet your blood sugar target. Your healthcare provider may also recommend regular A1c tests, oral medications , insulin therapy or injectable non-insulin diabetes medications.
- Blood pressure: Lower your blood pressure by not smoking, exercising regularly and eating a healthy diet. Your healthcare provider may recommend blood pressure medication such as beta blockers or ACE inhibitors.
- Cholesterol: Follow a meal plan low in saturated fats, trans fat, salt and sugar. Your healthcare provider may recommend statins, which are a type of drug to lower cholesterol.
Don’t Miss: How Much Is Lantus Insulin
In Type 2 Diabetes Your Body Produces Insulin But It Doesn’t Work Properly
“In type 2 diabetes, you produce insulin, but the main issue is that the rest of your body does not listen to it,” O’Malley explains. “We call this insulin resistance.” When blood sugar is high and insulin is released, your body ignores it. Just like in type 1 diabetes, your blood sugar stays high, your liver releases even more glucose, and other cells don’t get the energy they need.
“With time, some patients with type 2 diabetes may start to produce less insulin, but not to the same extent as with type 1,” O’Malley says.
Although some people are genetically predisposed to developing type 2 diabetes, lifestyle factors also play a role. According to the NIDDK, a person is more likely to develop type 2 diabetes if they are overweight or obese, have high blood pressure, have high cholesterol or are not physically active. People over the age of 45, or with a history of heart attack or stroke, are also more likely to develop the disease.
Although people with type 2 diabetes sometimes experience the same symptoms as those with type 1 diabetes prior to diagnosis, many have no symptoms at all . Doctors routinely test for diabetes using blood glucose tests in patients over 45, or patients with two or more other risk factors, according to the NIDDK. As in type 1 diabetes, glucose levels of 126 or above for the fasting plasma glucose test, or 200 or above for the oral glucose tolerance or random plasma glucose tests, are indicative of diabetes.
Latent Autoimmune Diabetes In Adults
In two population-based studies, our Botnia study and the much larger U.K. Prospective Diabetes Study , GADAs were present in 1535% of patients diagnosed with type 2 diabetes at an age younger than 45 years, and in 79% of older patients . We called this subgroup latent autoimmune diabetes in adults and suggested a definition based on circulating GADAs, age at diagnosis of diabetes 35 years, and no treatment with insulin during the first year after diagnosis . According to this definition, excluding studies selecting for lean, young-onset, or insulin-treated patients as well as hospital-based studies, the prevalence of LADA is 4.213.2% among Caucasians of mainly Anglo-Celtic or Scandinavian ancestry and 10.2% in African-Americans , but lower in Japanese and possibly in Italians and Australians with Southern European ancestry .
Also Check: Healthy Protein Shakes For Diabetics
Differences Between Type 1 Diabetes And Type 2 Diabetes
| Type 1 diabetes | |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
When someone says that they have diabetes, its important to know specifically which type, as there are major differences. Diabetes used as a general term is a chronic disease that occurs when the body either cannot produce insulin or cannot properly use the insulin it produces. There are two main types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2. In Canada, approximately 90% people with diabetes have type 2, and 10% are living with type 1. The key differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes are discussed here.
How Is Diabetes Treated
TYPE 1: A person diagnosed with type 1 diabetes will need to begin taking insulin immediately. Depending on the severity of ketone levels, a short stay in the hospital may be necessary to get saline through an IV to flush out the ketones, rehydrate the body, and stabilize fully before heading home.
Type 1 diabetes requires constant, 24/7 attention to the balancing act of food, activity, insulin, and some non-insulin diabetes medications.
Other variables such as hormones, stress, weight-gain or weight-loss, age and growth, and menstruation all impact blood sugar levels and insulin needs. Perfection is neither expected nor reasonable to demand of any patient with type 1 diabetes, but encouraging patients to do the best they can with the medications, technology, and knowledge available today is crucial.
Thanks to many advancements in technology, people with type 1 diabetes have a variety of choices when it comes to how they take their insulin with pumps, pods, and insulin pens.
Every person living with type 1 diabetes needs their own glucose meter to check your blood sugar at least 4x per day. Many patients today are also using continuous glucose monitors .
TYPE 2:Treating type 2 diabetes comes with many more medication options than type 1 diabetes because not all type 2 patients will need to start taking insulin.
Read Also: Can You Join The Airforce With Diabetes