The Icd Code H352 Is Used To Code Retinopathy
Retinopathy is persistent or acute damage to the retina of the eye. Ongoing inflammation and vascular remodeling may occur over periods of time where the patient is not fully aware of the extent of the disease. Frequently, retinopathy is an ocular manifestation of systemic disease as seen in diabetes or hypertension. Diabetic retinopathy is the leading cause of blindness in working-aged people.
| Specialty: |
Diabetic Retinopathy And Myocardial Infarction
During 9189 person-years of follow-up, a mean±SD follow-up of 6.6±1.8 years, there were 126 incident MIs. In bivariate analyses, those who had experienced a MI during follow-up were older, had longer diabetes duration, were more likely to be Indigenous Australians, current smokers, on insulin, have a history of severe hypoglycemia, angina, left ventricular hypertrophy, peripheral arterial disease, peripheral sensory neuropathy, higher systolic blood pressure, albuminuria, and worse kidney function . Incident MI was associated with the presence of any retinopathy , and greater DR severity .
The results of the Cox regressions for MI are shown in Table 4. In the most parsimonious model , age at diabetes diagnosis, HbA1c, current smoking, ln, angina and peripheral arterial disease were independent risk factors for MI . Retinopathy status and severity were positively, but non-significantly associated with risk of MI when added to this model . The results of the additional Cox regression that included participants with a prior MI at baseline also showed a significant association in unadjusted models but no independent association . There was insufficient power to assess the association between DR and MI in those without any prior cardiovascular or cerebrovascular history at baseline. The proportional hazards assumption was not violated in any of these Cox regressions models.
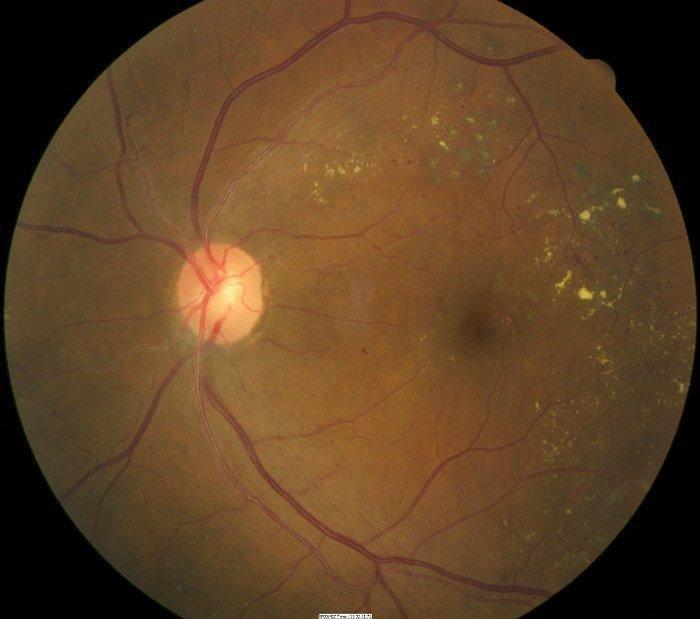
The Icd Code E113 Is Used To Code Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy , also known as diabetic eye disease, is when damage occurs to the retina due to diabetes. It can eventually lead to blindness.
| Specialty: |
- DRG Group #008 – Simultaneous pancreas or kidney transplant.
- DRG Group #010 – Pancreas transplant.
- DRG Group #124-125 – Other disorders of the eye with MCC.
- DRG Group #124-125 – Other disorders of the eye without MCC.
Read Also: How To Gain Weight With Diabetes
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus With Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy Without Macular Edema Unspecified Eye
- 2017 – New Code20182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
- E11.3599 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- Short description: Type 2 diab with prolif diab rtnop without mclr edema, unsp
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E11.3599 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of E11.3599 – other international versions of ICD-10 E11.3599 may differ.
- Applicable To annotations, or
Ascertainment Of Stroke And Myocardial Infarction
The Hospital Morbidity Data Collection and the Registry for Births, Deaths and Marriages together capture all hospitalizations and deaths within the state of Western Australia. These sources were accessed for the FDS2 participants through the Western Australian Data Linkage System . The data were used to determine the stroke and MI status and follow-up time ascertained to end-December 2016 using relevant ICD-9-CM and ICD-10-AM diagnosis and procedure codes . The admission date was considered the date of the event. Those who had had an event prior to participating in FDS2 were excluded from the relevant analysis. Causes of death, based on information provided on the death certificate or by the coroners determination of cause of death, were reviewed independently by two study physicians and classified under the system used in the UK Prospective Diabetes Study . In the case of discrepant coding, case notes were consulted and a consensus obtained. Participants assessed to have died due to a cardiac or cerebrovascular event were considered as having the respective event in analysis.
Don’t Miss: Can Diabetics Get Teeth Implants
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus With Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
ICD-10 code E11.35 for Type 2 diabetes mellitus with proliferative diabetic retinopathy
ICD-10 International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems 10th Revision
ICD-10
ICD-10 is the 10th revision of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems , a medical classification list by the World Health Organization .
It contains codes for diseases, signs and symptoms, abnormal findings, complaints, social circumstances, and external causes of injury or diseases.
ATC
The Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System is used for the classification of active ingredients of drugs according to the organ or system on which they act and their therapeutic, pharmacological and chemical properties.
It is controlled by the World Health Organization Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology .
DDD
The defined daily dose is a statistical measure of drug consumption, defined by the World Health Organization .
It is used to standardize the comparison of drug usage between different drugs or between different health care environments.
Potential Mechanisms Linking Diabetic Retinopathy And Stroke
A potential mechanism linking DR with stroke in T2D is the common soil hypothesis in which risk factors including hyperglycemia, hypertension and dyslipidemia are shared by these two complications . Adjustment for these CVD risk factors in the multivariable model did not abolish the relationship between DR and stroke. In addition, when moderate NPDR or worse was added to the most parsimonious model, HbA1c was no longer a significant predictor of stroke. A single baseline measurement of HbA1c, providing a measure of glycemia over the previous 3 months, may not adequately capture the effects of chronic glycemic exposure, which may be better represented by the presence of moderate NPDR or worse. In support of this, the weaker association between DR and stroke in our cohort compared with earlier studies could reflect more intensive contemporary long-term CVD risk factor management . The present data suggest that, if DR and especially severe DR is detected on screening, CVD risk factor management should be intensified if necessary and consideration given to other relevant investigations such as carotid ultrasound.
You May Like: What Does Insulin Shots Do
What Causes Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes may be caused by a combination of factors:
- Being overweight or having obesity
- Not being physically active
- Genetics and family history
Type 2 diabetes usually starts with insulin resistance. This is a condition in which your cells don’t respond normally to insulin. As a result, your body needs more insulin to help the glucose enter your cells. At first, your body makes more insulin to try to get cells to respond. But over time, your body can’t make enough insulin, and your blood glucose levels rise.
What Are The Treatments For Type 2 Diabetes
Treatment for type 2 diabetes involves managing your blood sugar levels. Many people are able to do this by living a healthy lifestyle. Some people may also need to take medicine.
- A healthy lifestyle includes following a healthy eating plan and getting regular physical activity. You need to learn how to balance what you eat and drink with physical activity and diabetes medicine, if you take any.
- Medicines for diabetes include oral medicines, insulin, and other injectable medicines. Over time, some people will need to take more than one type of medicine to control their diabetes.
- You will need to check your blood sugar regularly. Your health care provider will tell you how often you need to do it.
- It’s also important to keep your blood pressure and cholesterol levels close to the targets your provider sets for you. Make sure to get your screening tests regularly.
Also Check: How Much Does A Medtronic Insulin Pump Cost
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus With Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy Without Macular Edema Right Eye
- 2017 – New Code20182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
- E11.3591 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- Short description: Type 2 diab with prolif diab rtnop without mclr edema, r eye
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E11.3591 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of E11.3591 – other international versions of ICD-10 E11.3591 may differ.
- Applicable To annotations, or
The Relationship Between Diabetic Retinopathy And Myocardial Infarction
The relevant published literature linking DR and MI is inconsistent. Two other studies have similarly found no statistically significant association between DR and MI events, although the WESDR almost reached significance . The WHO MSVDD found a significant relationship between MI and DR only in type 1 diabetes . The ACCORD trial reported a significant trend between each step of DR severity at baseline and incident fatal or non-fatal MI risk but, compared to those without DR, those with severe NPDR/PDR did not have an increased MI risk . A large population-based cohort study using the UK Clinical Practice Research Datalink found that DR was associated with an increased risk of a major cardiovascular event (defined as either cardiovascular death, non-fatal MI or non-fatal ischemic stroke HR: 1.39 . Similarly, the Cardiovascular Health study also showed participants with DR had increased odds of coronary heart disease or stroke . A meta-analysis reported a significant association between DR and CVD but not specifically MI .
Read Also: How Do You Get Type 1 Diabetes
Who Is At Risk For Type 2 Diabetes
You are at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes if you
- Are over age 45. Children, teenagers, and younger adults can get type 2 diabetes, but it is more common in middle-aged and older people.
- Have prediabetes, which means that your blood sugar is higher than normal but not high enough to be called diabetes
- Had diabetes in pregnancy or gave birth to a baby weighing 9 pounds or more.
- Have a family history of diabetes
- Are overweight or have obesity
- Are Black or African American, Hispanic/Latino, American Indian, Asian American, or Pacific Islander
- Are not physically active
- Have other conditions such as high blood pressure, heart disease, stroke, polycystic ovary syndrome , or depression
- Have low HDL cholesterol and high triglycerides
- Have acanthosis nigricans – dark, thick, and velvety skin around your neck or armpits
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus With Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
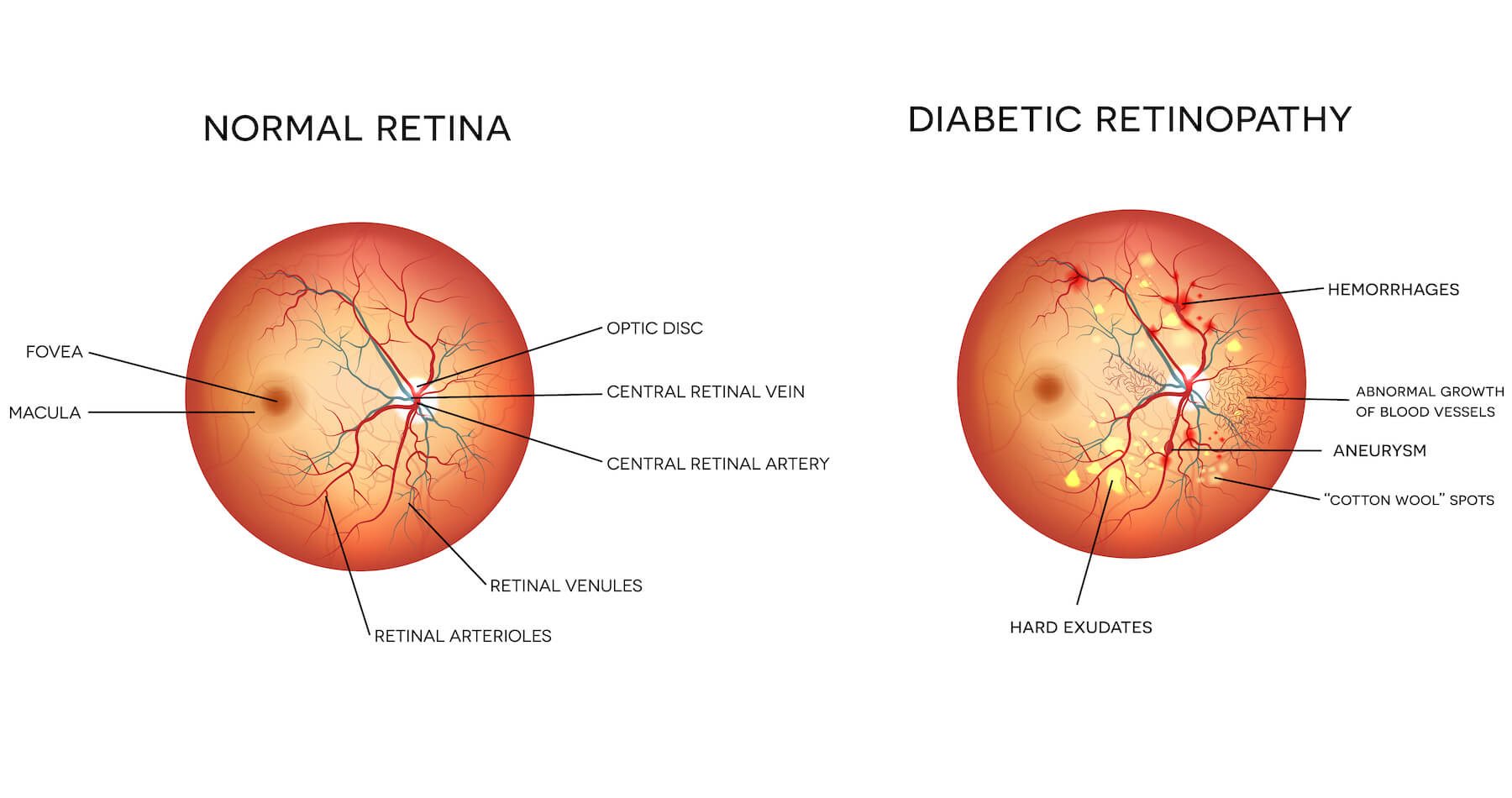
ICD-10 code E10.35 for Type 1 diabetes mellitus with proliferative diabetic retinopathy
ICD-10 International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems 10th Revision
ICD-10
ICD-10 is the 10th revision of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems , a medical classification list by the World Health Organization .
It contains codes for diseases, signs and symptoms, abnormal findings, complaints, social circumstances, and external causes of injury or diseases.
ATC
The Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System is used for the classification of active ingredients of drugs according to the organ or system on which they act and their therapeutic, pharmacological and chemical properties.
It is controlled by the World Health Organization Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology .
DDD
The defined daily dose is a statistical measure of drug consumption, defined by the World Health Organization .
It is used to standardize the comparison of drug usage between different drugs or between different health care environments.
Don’t Miss: Diabetes Injection Pen For Weight Loss
The Relationship Between Diabetic Retinopathy And Stroke
Some studies have shown that the severity of DR is associated with an increased stroke risk. The Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes trial found an increasing risk of incident fatal or non-fatal stroke during follow-up for each step of DR severity at baseline . The ACCORD participants with severe NPDR/PDR at baseline had a significantly increased risk of stroke compared to those with no DR , but this did not apply to those with mild or moderate NPDR . It should be noted, however, that this was a selected sample of patients recruited to a clinical trial. In the Wisconsin Epidemiology Study of Diabetic Retinopathy there was a positive relationship between self-reported stroke and DR severity per retinopathy severity step ) in a type 1 diabetes cohort after 20 years of follow-up . In the older-onset WESDR cohort, a significant relationship was found only between PDR and fatal stroke ) after 16 years of follow-up . The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study found a statistically significant relationship between ischemic stroke and any DR and also mild to moderate DR when compared to the participants with diabetes with no DR, but the association with severe DR was not significant . Taken together with the present results, and notwithstanding between-study differences in patient sources, type of diabetes and stroke ascertainment, there is clear evidence that severe DR is associated with an increased stroke risk.
Diabetic Retinopathy And Stroke
During 9759 person-years of follow-up, a mean±SD follow up of 6.6±1.8 years, there were 53 incident stroke events. Of these 53, there were 24 ischemic, 12 hemorrhagic, 8 intracranial hemorrhages, and 9 unclassified . In bivariate analysis, those who had a stroke during follow-up were older, had longer diabetes duration, a higher HbA1c, heart rate and supine systolic blood pressure, and were more likely to be on antihypertensive medication . They were more likely to have atrial fibrillation, poor renal function, anemia, peripheral arterial disease, to have had a MI prior to commencing the study, and to have had an eye examination in the previous year. Those who had a stroke were more likely to have moderate NPDR or worse . However, there was no statistically significant association between any DR or DR severity at baseline and incident stroke, and a power calculation showed insufficient power to avoid a type II error . Similarly, there was insufficient power to assess the association between retinopathy and the different stroke types separately . Therefore, we assessed the association between moderate NPDR or worse with any incident stroke during follow-up.
Read Also: Is Cassava Flour Good For Diabetics
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus With Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy Without Macular Edema
- 20162017 – Converted to Parent Code20182019202020212022Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code
- E11.359 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail.
- Short description: Type 2 diabetes w prolif diabetic rtnop w/o macular edema
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E11.359 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of E11.359 – other international versions of ICD-10 E11.359 may differ.
- Applicable To annotations, or
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus With Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy Without Macular Edema Left Eye
- 2017 – New Code20182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
- E11.3592 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- Short description: Type 2 diab with prolif diab rtnop without mclr edema, l eye
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E11.3592 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of E11.3592 – other international versions of ICD-10 E11.3592 may differ.
- Applicable To annotations, or
Also Check: Medipeds 8 Pair Diabetic Crew Socks With Non Binding Top
Can Type 2 Diabetes Be Prevented
You can take steps to help prevent or delay type 2 diabetes by losing weight if you are overweight, eating fewer calories, and being more physically active. If you have a condition which raises your risk for type 2 diabetes, managing that condition may lower your risk of getting type 2 diabetes.
NIH: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus With Stable Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy Right Eye
- 2017 – New Code20182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
- E11.3551 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- Short description: Type 2 diabetes with stable prolif diabetic rtnop, right eye
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E11.3551 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of E11.3551 – other international versions of ICD-10 E11.3551 may differ.
- Applicable To annotations, or
Also Check: Why Does Diabetes Affect Feet
What Is Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a disease in which your blood glucose, or blood sugar, levels are too high. Glucose is your main source of energy. It comes from the foods you eat. A hormone called insulin helps the glucose get into your cells to give them energy. If you have diabetes, your body doesn’t make enough insulin or doesn’t use insulin well. The glucose then stays in your blood and not enough goes into your cells.
Over time, having too much glucose in your blood can cause health problems. But you can take steps to manage your diabetes and try to prevent these health problems.
How Is Type 2 Diabetes Diagnosed
Your health care provider will use blood tests to diagnose type 2 diabetes. The blood tests include
- A1C test, which measures your average blood sugar level over the past 3 months
- Fasting plasma glucose test, which measures your current blood sugar level. You need to fast for at least 8 hours before the test.
- Random plasma glucose test, which measures your current blood sugar level. This test is used when you have diabetes symptoms and the provider does not want to wait for you to fast before having the test.
Read Also: Is Type 2 Diabetes Reversible With Diet And Exercise
Quality Payment Program Measures
When code E11.3513 is part of the patient’s diagnoses the following Quality Measures apply and affect reimbursement. The objective of Medicare’s Quality Measures is to improve patient care by making it more: effective, safe, efficient, patient-centered and equitable.
| Quality Measure | ||
|---|---|---|
| Percentage of patients 18-75 years of age with diabetes who had hemoglobin A1c > 9.0% during the measurement period. | Effective Clinical Care | |
| Diabetes: Eye Exam | Percentage of patients 18-75 years of age with diabetes and an active diagnosis of retinopathy overlapping the measurement period who had a retinal or dilated eye exam by an eye care professional during the measurement period or diabetics with no diagnosis of retinopathy overlapping the measurement period who had a retinal or dilated eye exam by an eye care professional during the measurement period or in the 12 months prior to the measurement period. | Effective Clinical Care |