What Tests Do Health Care Professionals Use To Diagnose Diabetes
Doctors use common tests to diagnose diabetes and monitor blood sugar control.
The health care professional will take a history including information about the patient’s symptoms, risk factors for diabetes, past medical problems, current medications, allergies to medications, family history of diabetes, or other medical problems , and personal habits and lifestyle.
Various laboratory tests can confirm the diagnosis of diabetes.
Fingerstick blood glucose at the point of care. This rapid test may be performed anywhere, including community-based screening programs.
- Although not as accurate as testing blood in a hospital laboratory, a fingerstick blood glucose test is easy to perform, and the adequate result is available quickly.
- The test involves sticking the patient’s finger for a tiny blood sample. The blood drop is placed on a strip to be inserted into a machine that reports the blood sugar level. These portable machines are accurate to within about 10%-20% of true laboratory values.
- Fingerstick blood glucose values tend to be most inaccurate at very high or very low levels. Abnormally low or high results should be confirmed by repeat testing. Point-of-care testing is how most people with diabetes monitor their blood sugar levels at home.
Oral glucose tolerance test. After fasting for at least six hours, the health care professional draws blood to measure plasma glucose before and at two hours after drinking a specific sweet drink .
What Exactly Is Diabetes
Mindy Sotsky, MD, FACE
Diabetes is a chronic disease in which your blood glucose, or blood sugar, levels are too high. Glucose comes from the foods you eat, and insulin is the hormone that allows glucose to enter cells to produce energy.
Over time, having too much glucose in your blood can cause serious problems. It can damage your eyes, kidneys and nerves. It can also cause heart disease and stroke, and sometimes even amputation of a limb. Pregnant women can develop a form of diabetes, called gestational diabetes.
The CDC estimates that over 30 million people in the U.S. probably have diabetes, and 25% of them do not know it. A blood test called the A1C blood test, typically done a few times a year, is the best way to determine if you have diabetes. This test identifies your blood glucose levels so adjustments can be made if theyre not where they should be.
What Is Latent Autoimmune Diabetes In Adults
Many doctors consider LADA the adult form of type 1 diabetes because its also an autoimmune condition.
As in type 1 diabetes, the islet cells in the pancreas of people with LADA are destroyed. However, this process occurs much more slowly. Once it starts, it can take several months up to several years for the pancreas to stop being able to make insulin.
Other experts consider LADA somewhere in between type 1 and type 2 and even call it type 1.5 diabetes. These researchers believe that diabetes can occur along a spectrum.
Researchers are still trying to figure out the details, but in general, LADA is known to:
- develop in adulthood
- have a slower course of onset than type 1 diabetes
- often occur in people who arent overweight
- often occur in people who dont have other metabolic issues, such as high blood pressure and high triglycerides
- result in a positive test for antibodies against the islet cells
The symptoms of LADA are similar to those of type 2 diabetes, including:
- excessive thirst
Don’t Miss: How Does Diabetes Cause Heart Disease
What Does Diabetes Do To The Body
People with type 1 diabetes do not produce insulin, and as a result sugar builds up in the blood instead of going into the cells, where it’s needed for energy. In type 1 diabetes, high blood sugar causes symptoms like thirst, hunger, and fatigue and can cause devastating consequences, including damage to the nerves, blood vessels, and internal organs. The same scary complications of diabetes appear in type 2 as well. The difference is that people with type 2 diabetes still produce insulin their bodies just become less sensitive to it over time, which is what causes the complications.
What Is Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes manifests as a result of a condition called insulin resistance, which is a buildup of fat in cells that are not meant to store fat.
In its early stages, type 2 diabetes is referred to as non-insulin-dependent, which means that your beta cells are still capable of producing insulin at levels that would be sufficient without insulin resistance.
In later stages, type 2 diabetes can become classified as insulin-dependent, in which your beta cells have become worn down from overproduction, and can no longer produce sufficient insulin.
Traditionally, this type of diabetes manifests later in life as a result of diet and lifestyle factors, and is often called adult-onset diabetes.
Unlike type 1 diabetes, which can be effectively managed, most cases of type 2 diabetes can be entirely reversed if caught early enough.
For more in-depth information on type 2 diabetes, you can explore our comprehensive article on the subject.
Don’t Miss: What Are The New Guidelines For Diabetes
The Causes Of Type 1 And Type 2 Are Different
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition, which means that your immune system mistakenly attacks your body. In the case of type 1 diabetes, immune-system cells go after the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, which causes insulin production to suddenly turn off.
No one knows exactly why your body goes on the offensive, but there are probably many contributing factors. “We don’t completely understand why this happens but there is some data that a viral infection can trigger the process if you already have a predisposition,” says Dr. Vouyiouklis Kellis. “You may already have antibodies but the second hit is a viral infection.” That predisposition could also be genetic.
With type 2 diabetes, genetics, including family history, can also play a role, but here the main risk comes from being obese or overweight, as well as other lifestyle factors, such as not being active and eating unhealthy foods, Jasmine D. Gonzalvo, PharmD, director of the Center for Health Equity and Innovation at Purdue University in West Lafayette, Indiana, tells Health. “The body still has some ability to produce insulin, but the body has a resistance to the insulin.” In type 2 diabetes, the cells may also have difficulty using the insulin effectively, called insulin resistance.
RELATED: What Causes Type 1 Diabetes? 3 Things You Need to Know, According to Doctors
What Are The Types Of Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes
The body produces little or no insulin to regulate blood glucose level.
- T1D affects about 10% of all people with diabetes in the United States.
- T1D is typically diagnosed during childhood or adolescence. In the past T1D was called juvenile-onset diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.
- Insulin deficiency can occur at any age due to destruction of the pancreas by alcohol, disease, or removal by surgery.
- T1D results from progressive destruction by the immune system of the pancreatic beta cells, the only cell type that produces significant amounts of insulin.
- People with T1D require daily insulin treatment to sustain life.
Type 2 diabetes
Although the pancreas still secretes insulin in someone with T2D, the bodyâs tissues are partially or completely incapable of responding to insulin. This is often referred to as insulin resistance. The pancreas tries to overcome this resistance by secreting more and more insulin. People with insulin resistance develop T2D when they fail to secrete enough insulin to cope with their body’s demands.
Gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a form of diabetes that occurs during the second half of pregnancy.
- Although gestational diabetes typically resolves after delivery of a baby, a woman who develops gestational diabetes is more likely than other women to develop T2D later in life.
- Women with gestational diabetes are more likely to have large babies, complicated pregnancies, and complicated deliveries.
Prediabetes
Don’t Miss: What Salad Dressing Is Good For Diabetics
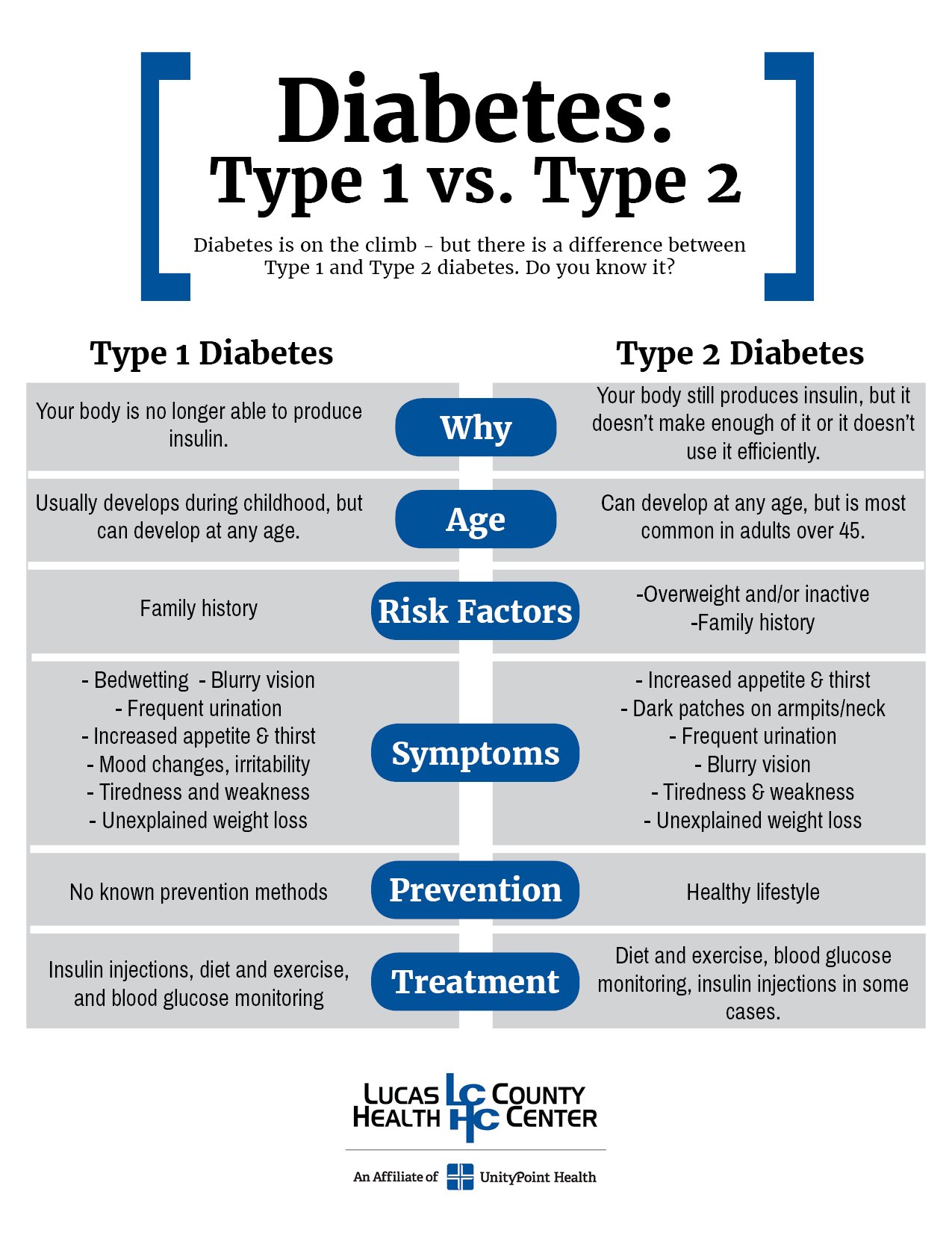
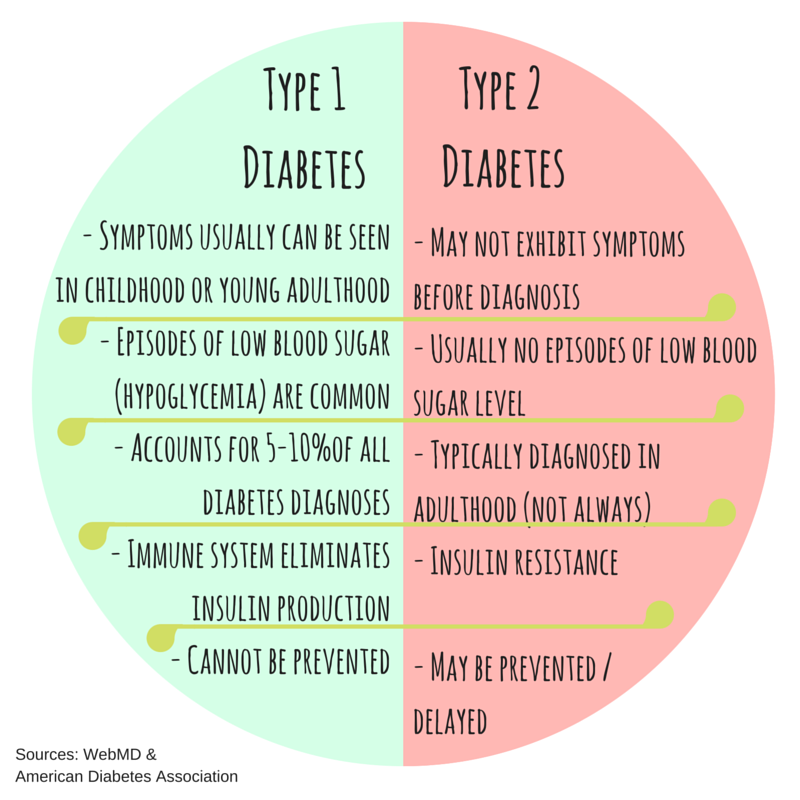
Type 1 Vs Type 2 Diabetes: Differences And Similarities
by Health Writer & Patient Advocate
Regardless of which type of diabetes you have, it can be difficult to understand what is happening to your body. Despite having very similar symptoms and medical risks, the two primary types of diabetes are actually very different when you look closely at whats going on inside the body. Learn more about the main differences and similarities between type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes Have Similar Symptoms
The symptoms for type 1 and type 2 diabetes are similar. However, how quickly symptoms develop will vary between types.
Saperstein says that indicators of type 1 diabetes develop suddenly, within days or weeks, while those of type 2 diabetes develop more gradually, usually over a period of months to years. Some people may live with type 2 diabetes for years before seeing a doctor for a diagnosis.
If you notice a combination of the following symptoms, this could be a sign of diabetes and you should schedule an appointment with a doctor:
- Frequent urination
- Frequent or chronic yeast infections
- Slow-healing cuts and sores
Recommended Reading: Number Of Grams Of Sugar Per Day For Diabetic
How Does Diabetes Affect The Body
There are two main types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2.
Both types of diabetes are chronic diseases that affect the way your body regulates blood sugar, or glucose. Glucose is the fuel that feeds your bodys cells, but to enter your cells it needs a key. Insulin is that key.
People with type 1 diabetes dont produce insulin. You can think of it as not having a key.
People with type 2 diabetes dont respond to insulin as well as they should and later in the disease often dont make enough insulin. You can think of it as having a broken key.
People with type 1 and type 2 diabetes may also experience irritability, mood changes, and unintentional weight loss.
People with type 1 and type 2 diabetes may also have numbness and tingling in their hands or feet. Good glucose management significantly reduces the risk of developing numbness and tingling in someone with type 1 diabetes, according to the American Diabetes Association .
Although many of the symptoms of type 1 and type 2 diabetes are similar, they present in very different ways.
Many people with type 2 diabetes wont have symptoms for many years, and their symptoms often develop slowly over the course of time. Some people with type 2 diabetes have no symptoms at all and dont discover they have the condition until complications arise.
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes may have similar names, but theyre different diseases with unique causes.
Is Diagnosing Diabetes Types 1 And 2 Similar
Blood tests used to diagnose type 1 and type 2 diabetes include fasting blood sugar, a hemoglobin A1C test, and a glucose tolerance test. The A1C test measures the average blood sugar level over the past few months. The glucose tolerance test measures blood sugar after a sugary drink is given.
“The blood sugar testing we do to diagnose and manage type 1 diabetes is very similar to the testing we do for type 2 diabetes,” says Drincic. “We can do a blood test that looks for antibodies. That tells us if it is type 1 or 2.” In type 1 diabetes, the immune system makes antibodies that act against the cells in the pancreas that make insulin, and these antibodies can be detected in a blood test. Your doctor may suspect type 2 diabetes based on your symptoms and risk factors, such as obesity and family history.
Recommended Reading: Normal A1c Range For Diabetics
Are There Home Remedies For Diabetes
If a person has diabetes, healthful lifestyle choices in diet, exercise, sleep, and other habits will help improve glycemic control and prevent or minimize complications from diabetes.
Diabetes diet
A healthy diet is key to controlling blood sugar levels and preventing diabetes complications.
- Patients who are obese and have had difficulty losing weight on their own should talk to a health care professional. He or she can recommend a dietitian, help set feasible goals, or supervise a weight-modification program.
- Eat a consistent, well-balanced diet high in fiber, low in saturated fat, low in concentrated sweets, and eliminate excess calories.
- A consistent diet includes roughly the same number of calories at predictably similar times of day. Such a disciplined diet helps match the correct dose of insulin or other medications.
- A healthy diet helps keep the blood sugar level relatively even. A healthy, predictable diet avoids excessively low or high blood sugar levels, which can be dangerous and even life-threatening.
Exercise
In any form, regular exercise helps reduce the risk of developing diabetes. Activity can reduce the risk of developing diabetes-related complications such as heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, blindness, and leg ulcers.
Alcohol use
Smoking
Self-monitored blood glucose
Check blood sugar levels frequently, then record the results in a logbook or digital record. At a minimum, check blood sugar before meals and at bedtime.
Type 2 Diabetes And Insulin Injections
People with type 2 diabetes may need to take insulin injections, usually for one of two main reasons:
- Low sensitivity to insulin: The more excess body weight we carry, the less sensitive we are to insulin Being insensitive to insulin means insulin doesnt reduce blood glucose levels as much as it should. People with low insulin sensitivity often need to be injected with insulin to avoid hyperglycemia
- Beta cell failure: If you develop insulin resistance, you need more of it to keep your blood glucose levels stable. More insulin production means more work for the pancreas. Over time, the beta cells can become burnt out by the constant strain, and stop producing insulin altogether. Eventually, you can get to a similar situation as someone with type 1 diabetes, in which your body is incapable of producing the amount of insulin you need to keep blood glucose levels under control. Insulin injections are necessary in these situations
Don’t Miss: Psoriasis And Diabetes Type 1
Which Type Of Diabetes Is Most Common
Type 1 diabetes is much less common and affects about 1.25 million people. It is further estimated that of the 29.1 million people affected with diabetes, about 8.1 million people are undiagnosed, meaning that they have diabetes but are not aware of it. There has been an increase in the number of Americans with prediabetes. In 2010, 79 million people were estimated to have prediabetes. In 2012, this number was 86 million.
Type 1 And Type 2 Differences
Below is a guide to some of the main differences between type 1 and type 2.
|
Your body attacks the cells in your pancreas which means it cannot make any insulin. |
Your body is unable to make enough insulin or the insulin you do make doesnt work properly. |
|
|
We dont currently know what causes type 1 diabetes. |
We know some things can put you at risk of having type 2 like weight and ethnicity. |
|
|
The symptoms for type 1 appear more quickly. |
Type 2 symptoms can be easier to miss because they appear more slowly. |
|
|
Type 1 is managed by taking insulin to control your blood sugar. |
You can manage type 2 diabetes in more ways than type 1. These include through medication, exercise and diet. People with type 2 can also be prescribed insulin. |
|
|
Currently there is no cure for type 1 but research continues. |
Type 2 cannot be cured but there is evidence to say in many cases it can be prevented and put into remission. |
Don’t Miss: Diet For Diabetics With Heart Disease
Can I Tell If I Have Diabetes How Is It Diagnosed
Most commonly, it is diagnosed with a blood test – either a high glucose level before you eat or something called a hemoglobin A1c, which is an average of your blood sugar over three months.
If your glucose level is high, you may feel symptoms like feeling thirsty all the time, urinating more than usual, weight loss, blurry vision or fatigue. Sometimes, people with Type 1 diabetes present very sick, with something called diabetic ketoacidosis, due to not having enough insulin in their body.
This can be a deadly condition that requires hospitalization to help correct the condition.
If you are on medications that can make your blood sugar go low, such as insulin, low blood sugar can result in sweating, shaking, uncharacteristic behavior, or disorientation. If it goes very low, it can even result in coma and death if not rapidly treated with glucose or a medication called glucagon.
What Is The Difference Between Type 1 And 2 Diabetes
Diabetes is a metabolic disease that is characterised by a high level of blood sugar because the body cannot process it efficiently. There are two kinds of diabetes- Type 1 and Type 2. Each is different from the other but the underlying fact is that they affect how the body processes glucose. If you are confused about which type you have, it is better to consult your doctor and undergo tests.
Both Type 1 and Type 2 are similar in the fact that they are both are chronic and cannot be cured. There are some common points of difference between the two kinds of Diabetes.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Lose A Leg To Diabetes