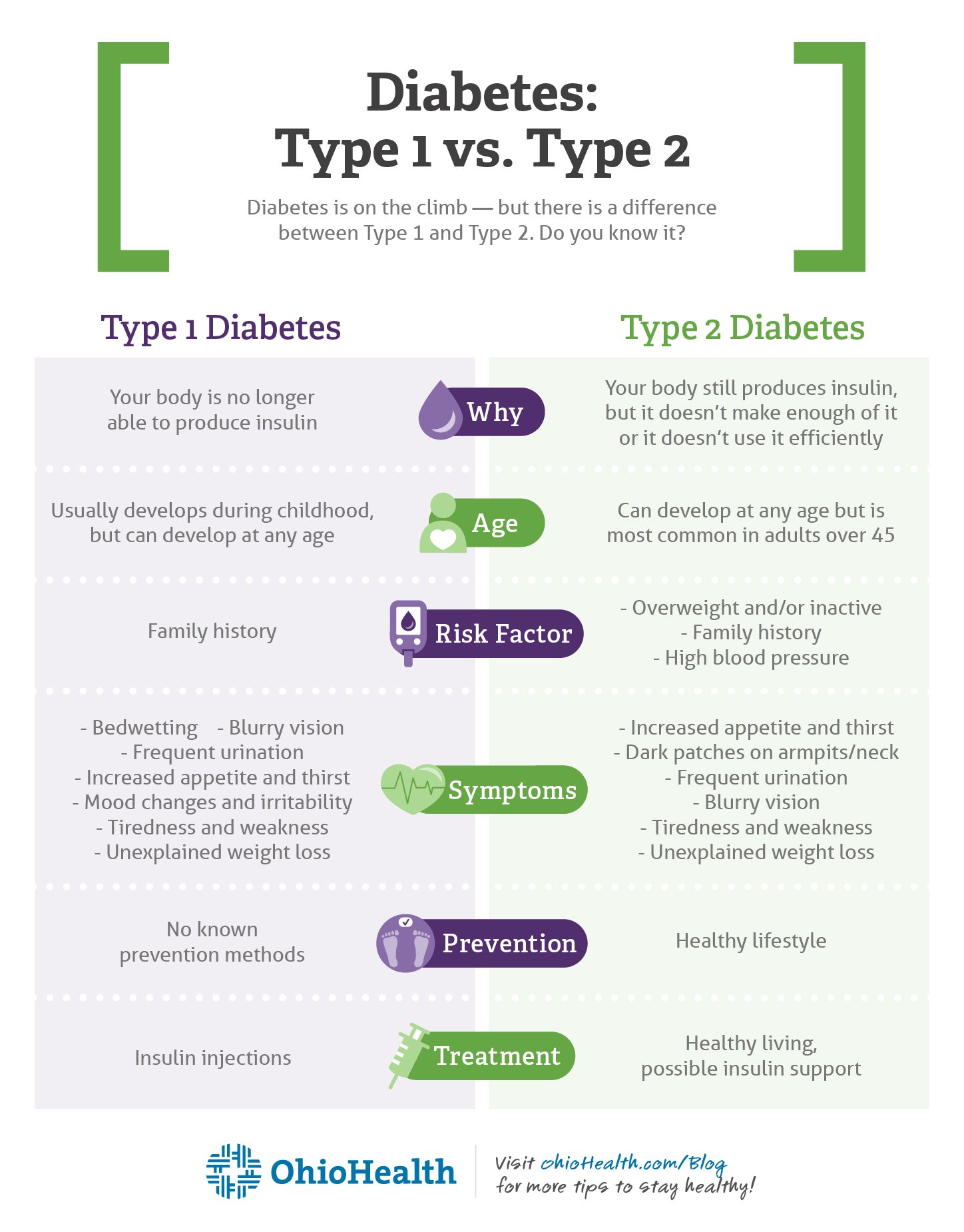
What Does Diabetes Do To The Body
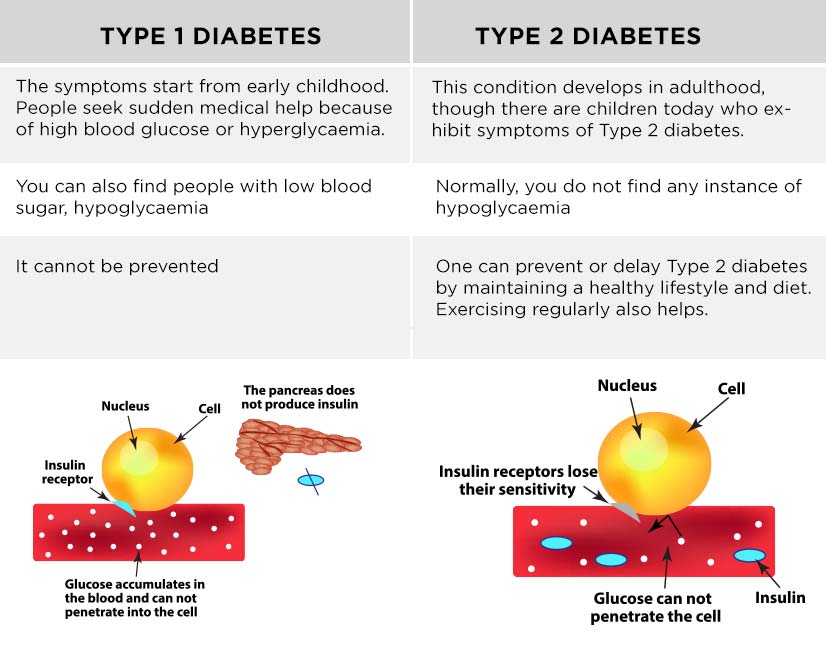
People with type 1 diabetes do not produce insulin, and as a result sugar builds up in the blood instead of going into the cells, where it’s needed for energy. In type 1 diabetes, high blood sugar causes symptoms like thirst, hunger, and fatigue and can cause devastating consequences, including damage to the nerves, blood vessels, and internal organs. The same scary complications of diabetes appear in type 2 as well. The difference is that people with type 2 diabetes still produce insulin their bodies just become less sensitive to it over time, which is what causes the complications.
Only Type 2 Diabetes Can Be Prevented
There’s no way to prevent type 1 diabetes, but you can help prevent type 2 with lifestyle modifications. We’re talking about making healthier food choices, engaging in physical activity, and taking medication, says Dr. Gonzalvo.
To get our top stories delivered to your inbox, sign up for the Healthy Living newsletter
Type 2 Diabetes Risk Factors:
Your risk of developing type 2 diabetes is higher if your diet is high in carbs and fat but low in fiber, if youre not very physically active and/or if you have high blood pressure. High alcohol consumption and age are also risk factors. Though genes do play a role in the likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes, it can be prevented with the right lifestyle choices, unlike type 1.
Also Check: Physical Symptoms Of Diabetes Type 2
Is Diabetes Treatment Different Too
A good diabetes diet and regular exercise matters for people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes, Knapp explains. “The big difference is that everybody with type 1 diabetes needs to take insulin, she says. People with type 1 diabetes need to check their blood sugar level with a device called a glucometer about four times a day to know how much insulin to take.”
Treatment for type 2 diabetes also starts with diet and exercise, and oral medication can also be used to increase the amount of insulin the pancreas makes, Knapp says. “Over time, if the pancreas stops making insulin, some people with type 2 will also need insulin.” People with type 2 diabetes also need to check their blood sugar, from one to several times a day, depending on their state of health.
How Is Type 2 Diabetes Managed
Theres no cure for Type 2 diabetes. But you can manage the condition by maintaining a healthy lifestyle and taking medication if needed. Work with your healthcare provider to manage your:
- Blood sugar: A blood glucose meter or continuous glucose monitoring can help you meet your blood sugar target. Your healthcare provider may also recommend regular A1c tests, oral medications , insulin therapy or injectable non-insulin diabetes medications.
- Blood pressure: Lower your blood pressure by not smoking, exercising regularly and eating a healthy diet. Your healthcare provider may recommend blood pressure medication such as beta blockers or ACE inhibitors.
- Cholesterol: Follow a meal plan low in saturated fats, trans fat, salt and sugar. Your healthcare provider may recommend statins, which are a type of drug to lower cholesterol.
You May Like: What Happens When You Take Insulin
Other Forms Of Diabetes
In 1% to 5% of people who have diabetes, other conditions might be the cause. These include diseases of the pancreas, certain surgeries and medications, and infections. In these cases, your doctor might want to keep an eye on your blood sugar levels.
Show Sources
American Diabetes Association: “Frequently Asked Questions about Pre-Diabetes,” “Type 2 Diabetes,” “The Dangerous Toll of Diabetes,” tion: “Gestational Diabetes,” “About Insulin and Other Drugs.”
National Library of Medicine: “Diabetes.”
National Diabetes Education Project: “About Diabetes and Pre-Diabetes.”
National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse : “National Diabetes Statistics, 2011.”
Merck Manual Consumer Version: âDiabetes Mellitus .â
CDC: âAbout Diabetes,â âPrediabetes: Your Chance to Prevent Type 2 Diabetes.â
World Journal of Diabetes: âType 2 diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents.â
Peace Of Mind With Life Line Screening
At Life Line Screening, we have years of experience helping people prevent major medical issues with vital early detection services, including A1C screenings. In fact, screenings are our specialty. We partner with community centers to help people get quick, easy access to the screenings they want to stay on top of their health. No lengthy doctors visits, no complicated insurance to deal with, just convenient screenings for health-conscious people conducted by trained professionals.
Learn more or schedule a screening today at lifelinescreening.com or give us a call at . Wed love to help.
Recommended Reading: Treatment Of Type 1 Diabetes In Child
Type 2 Diabetes And Insulin Injections
People with type 2 diabetes may need to take insulin injections, usually for one of two main reasons:
- Low sensitivity to insulin: The more excess body weight we carry, the less sensitive we are to insulin Being insensitive to insulin means insulin doesnt reduce blood glucose levels as much as it should. People with low insulin sensitivity often need to be injected with insulin to avoid hyperglycemia
- Beta cell failure: If you develop insulin resistance, you need more of it to keep your blood glucose levels stable. More insulin production means more work for the pancreas. Over time, the beta cells can become burnt out by the constant strain, and stop producing insulin altogether. Eventually, you can get to a similar situation as someone with type 1 diabetes, in which your body is incapable of producing the amount of insulin you need to keep blood glucose levels under control. Insulin injections are necessary in these situations
Causes Of Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
Diabetes is extremely common in the U.S. According to the CDCs National Diabetes Statistics Report, 1 in 10 Americans have diabetes, and 1 in 3 Americans have prediabetes, or high blood sugar.
Anyone can get type 1 diabetes, but the condition is generally diagnosed around ages 13 to 14, the CDC says. In fact, type 1 diabetes used to be referred to as Juvenile Onset Diabetes because it is often diagnosed in young children. But adults over the age of 40 can develop type 1 diabetes, too, its just typically more rare.
Type 2 diabetes, on the other hand, is often seen in individuals who are middle-aged or older. You are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes if you are age 45 or older, have a family history of the disease, or are overweight or obese. Although its generally seen in individuals aged 45 or older, more and more children and teens are developing type 2 diabetes, the CDC says.
Typically, type 1 diabetes is confirmed with antibody screening, Dr. Block says. This is a blood test that looks for islet antibodies or GAD antibodies. Both type 1 and type 2 diabetes can also be diagnosed with the A1C test, or a blood test that examines your average blood sugar levels over the course of several months. An A1C level of 6.5 or higher indicates diabetesbut more tests are typically required to determine the type of diabetes you have.
Causes of type 1 diabetes
Causes of type 2 diabetes
Recommended Reading: Gestational Diabetes Diet Meal Plan
How Are The Signs And Symptoms Similar
There isn’t a difference between the symptoms of either disease. The “classic” symptoms are the same for both diabetes type 1 and type 2:
- Increased urine output
- Unexplained weight loss
For both type 1 and type 2, early symptoms of untreated diabetes arise due to elevated blood sugar levels and the presence of glucose in the urine. High amounts of glucose in the urine can cause increased urine output and dehydration. Dehydration, in turn, causes increased thirst.
A lack of insulin or an inability of insulin to work properly affects protein, fat, and carbohydrate metabolism. Insulin normally encourages the storage of fat and protein, so when there is inadequate insulin or poorly functioning insulin, this eventually leads to weight loss despite an increase in appetite.
Some untreated diabetes patients also experience generalized symptoms like fatigue, nausea, and vomiting. People with diabetes are also at risk for infections of the bladder, skin, and vaginal areas. Changes in blood glucose levels can lead to blurred vision. When blood sugar levels are extremely high, lethargy and coma can result.
Rick Factors: Who Is Affected
Only about 5% to 10% of diagnosed diabetes cases are type 1. The disease is usually diagnosed in children and young adults, although it can technically strike at any age. Scientists do not know yet exactly what causes type 1 diabetes but suspect the disease involves a combination of genetic, environmental, and autoimmune factors.
An overweight person who does not exercise, is over 30, and/or has close relatives who have type 2 diabetes, runs a very high risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Higher-risk ethnic groups include African Americans, Latinos and Hispanics, Native Americans, Alaskan Natives, Asians, and those with Pacific Islander American heritage.
People are more likely to get diabetes if they smoke, have high blood pressure or cholesterol, or, in women, if they had gestational diabetes or gave birth to a baby who weighed more than 9 pounds. A free diabetes risk test is provided by Diabetes.org and only takes a few minutes to complete.
Recommended Reading: Type 1 Diabetes Require Insulin
What Are The Risk Factors For Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
Risk factors for type 1 diabetes include:
- Family history: People with a parent or sibling with type 1 diabetes have a higher risk of developing it themselves.
- Age: Type 1 diabetes can appear at any age, but its most common among children and adolescents.
- Geography: The prevalence of type 1 diabetes increases the farther away you are from the equator.
- Genetics: The presence of certain genes points to an increased risk of developing type 1 diabetes.
Youre at risk of developing type 2 diabetes if you:
- have prediabetes, or slightly elevated blood sugar levels
- are carrying excess weight or have obesity
- are Black, Hispanic, American Indian, or Alaska Native
- have an immediate family member with type 2 diabetes
How Are Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes Diagnosed
The primary test used to diagnose both type 1 and type 2 diabetes is known as the A1C, or glycated hemoglobin, test.
This blood test determines your average blood sugar level for the past 2 to 3 months. Your doctor may draw your blood or give you a small finger prick.
The higher your blood sugar levels have been over the past few months, the higher your A1C level will be. Test results are expressed as a percentage. An A1C level of 6.5 percent or higher indicates diabetes.
The A1C test isnt accurate for people with sickle cell anemia or the sickle cell trait. If you have this condition or trait, then your doctor will have to use a different test.
Also Check: What Happens If Diabetes Is Not Treated
Early Indications Of Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes:
- Frequent urination: When the glucose levels are high in your blood, the kidney tries to remove the excess by filtering it which results in urination.
- Increased level of thirst: While frequent urination helps in removing excess sugar from the blood it can also cause water loss.
- Increased hunger: In diabetic cases, a sufficient amount of glucose does not move to the cell. Therefore, the patient does not receive enough energy from the food that they eat.
- The feeling of fatigue: Diabetes can have an adverse effect on the patients energy level causing them to feel extremely tired after small amounts of work.
- Slow healing of wounds: Slow healing of cuts is a common symptom of diabetes. The high sugar level in blood can reduce the bodys capability to heal wounds and cuts speedily.
- Numbness or pain in arms and feet: The excess amounts of glucose in the bloodstream can damage the nerves and blood vessels which in turn affect the blood circulation.
In this article, we talked about the type 1 and type 2 diabetes differences and similarities. Diabetes may not be preventable but maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle can definitely improve the condition.
Type 1 Vs Type 2 Diabetes: Differences Center
Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic condition in which a person’s blood sugar levels are too high. Over 29.1 million children and adults in the US have diabetes. Of that, 8.1 million people have diabetes and don’t even know it. Type 1 diabetes is caused by a problem with insulin production by the pancreas. Type 2 diabetes is caused by:
Eating a lot of foods and drinking beverages with simple carbohydrates and simple sugars
- Consuming too many products withartificial sweeteners
- Lack of activity
Don’t Miss: How Can I Get Checked For Diabetes
We Know Some People Get Confused Between Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes And Were Often Asked About The Differences Between Them
Although type 1 and type 2 diabetes both have stuff in common, there are lots of differences. Like what causes them, who they affect, and how you should manage them. There are other types of diabetes like gestational and MODY. But this page is mainly about the differences between type 1 and type 2.
For a start, type 1 affects 8% of everyone with diabetes. While type 2 diabetes affects about 90%.
Lots of people get confused between type 1 and type 2 diabetes. This can mean you have to explain that what works for one type doesn’t work for the other, and that there are different causes.
The main thing to remember is that both are as serious as each other. Having high blood glucose levels can lead to serious health complications, no matter whether you have type 1 or type 2 diabetes. So if you have either condition, you need to take the right steps to manage it.
What Happens When You Have Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
If you have either type 1 or type 2 diabetes, it means you have too much glucose in your blood. This is the same for both types. But the difference between them is how this happens.
If you have type 1 diabetes, it means you have an autoimmune condition. This means your body has attacked and destroyed the cells that make a hormone called insulin. So you cant make insulin anymore.
We all need insulin as it helps take the glucose from our blood into our bodys cells. We then use this glucose for energy. Without insulin, the glucose level in your blood gets too high.
Type 2 diabetes is different. If youve got type 2, either your body doesnt make enough insulin, or your insulin doesnt work properly. This is known as insulin resistance. Like type 1, this means the level of glucose in your blood is too high.
You May Like: Mellitus Type 2 Diabetes Definition
There Are A Few Ways To Treat Type 1 Diabetes:
- Monitor your blood sugar. Living with diabetes means getting familiar with healthy blood sugar levels and checking yours regularly. Depending on your health care providers specific recommendation, you might need to check it four to ten times daily. Youll use a small blood sugar meter called a glucometer to measure glucose levels in a pin-prick of blood on a disposable test strip. Another option is to have a continuous glucose monitor, which automatically measures your blood sugar every few minutes using a sensor inserted underneath the skin.
- Take insulin. Because your body doesnt produce it on its own, youll have to get it another way. There are a few methods for taking insulin, including regular injections or a wearable insulin pump, which delivers small, steady doses of fast-acting insulin throughout the day through a thin tube. Though its certainly not the most convenient lifestyle, it often becomes second nature for people living with type 1 diabetes.
- Maintain a balanced diet. You dont have to be extremely restrictive, but carbohydrates are the foods youll want to watch, making sure to eat them consistently but not go overboard. If youre taking a fixed amount of insulin, keeping your carbohydrate intake consistent to match is important.
- Exercise. Staying active is always an important component of health, but for people with type 1 diabetes, it can help keep blood sugar levels in check and cause your body to use the insulin more efficiently.
Because Of Their Different Causes The Treatment Plans For Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes Are Also Slightly Different
“People with type 1 diabetes need multiple insulin injections a day or a continuous infusion through an insulin pump,” O’Malley says. They also need to check their blood sugar regularly, usually by pricking a finger and using a glucose monitor to test a drop of blood. “Type 1 is not yet reversible people with type 1 diabetes need to be on insulin for the rest of their lives,” O’Malley says.
In both type 1 and type 2 diabetes, regular exercise and a balanced diet are also important for keeping blood sugar levels relatively steady, according to the American Diabetes Association. People with diabetes should work with a registered dietitian to find a sustainable way of eating that balances carbohydrate intake throughout the day.
In type 2 diabetes, it’s possible for some patients to manage the condition with diet alone, O’Malley says. In fact, type 2 diabetes is sometimes reversible with proper diet and weight maintenance. But, O’Malley says this reversal can be difficult to maintain long-term. “I focus on how to control diabetes, as opposed to reversing it.”
Although some people with type 2 diabetes might use insulin injections for treatment , this isn’t common. Instead, patients are often prescribed medications meant to keep blood sugar levels low and/or improve insulin sensitivity.
Read Also: How To Reverse Ed In Diabetics